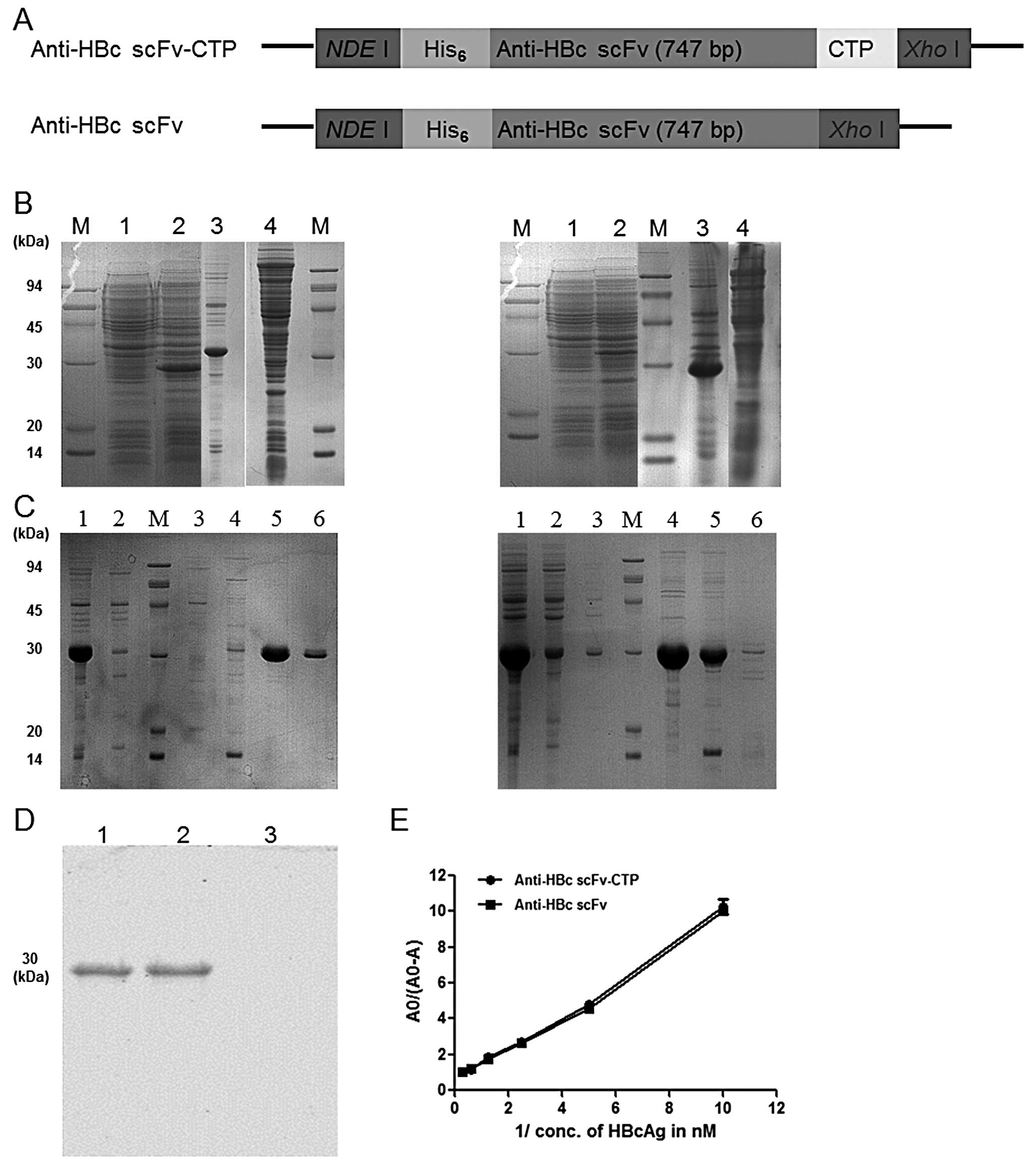
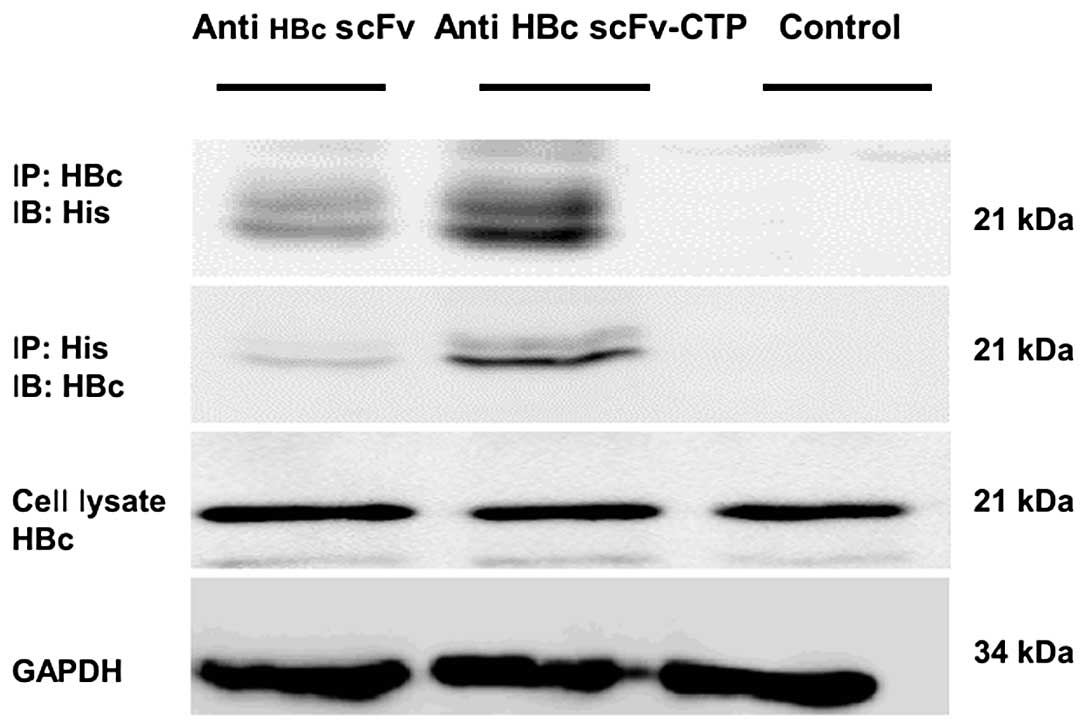
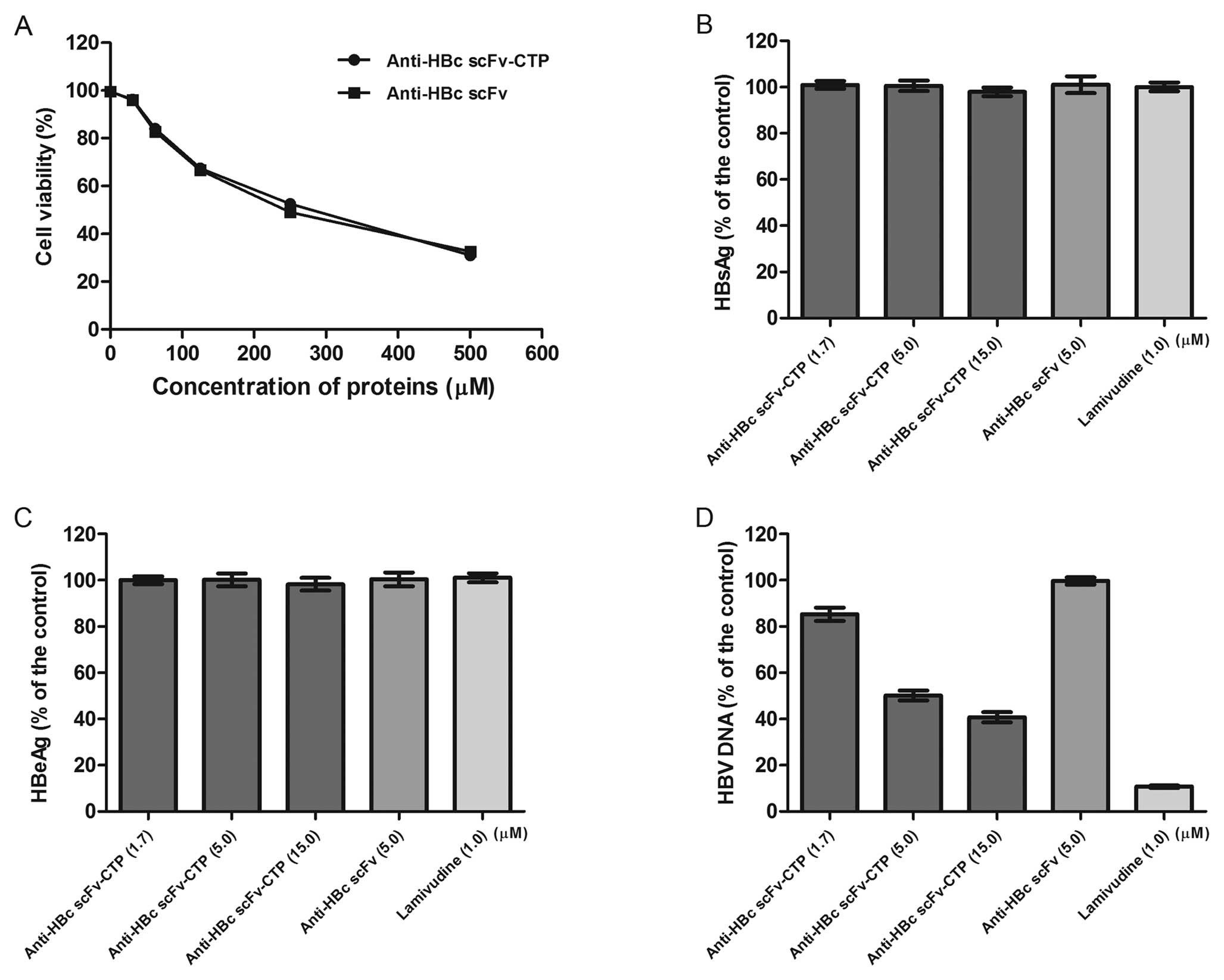
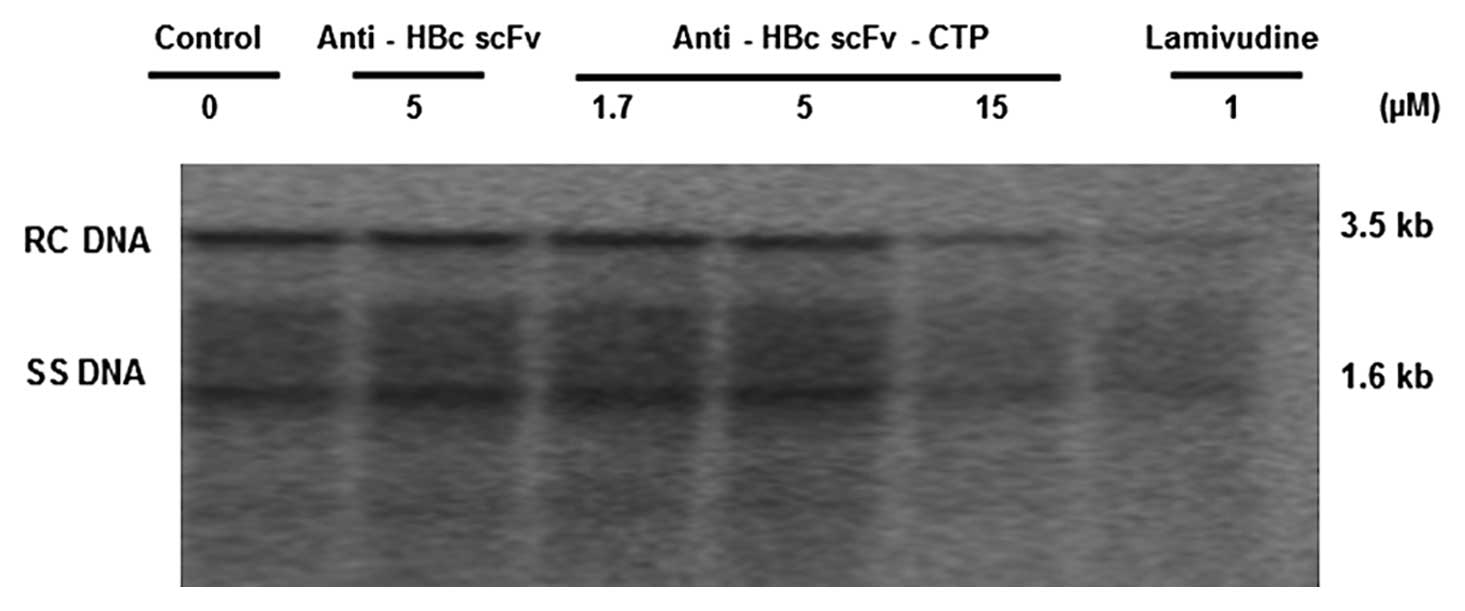
|
1.
|
Zanetti AR, Van Damme P and Shouval D: The
global impact of vaccination against hepatitis B: a historical
overview. Vaccine. 26:6266–6273. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Perrillo R: Benefits and risks of
interferon therapy for hepatitis B. Hepatology. 49(Suppl 5):
S103–S111. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Dienstag JL: Benefits and risks of
nucleoside analog therapy for hepatitis B. Hepatology. 49(Suppl 5):
S112–S121. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Snow-Lampart A, Chappell B, Curtis M, et
al: No resistance to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate detected after
up to 144 weeks of therapy in patients monoinfected with chronic
hepatitis B virus. Hepatology. 53:763–773. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Bingfa X, Qinglin F, Hui H, Canjun W, Wei
W and Lihua S: Anti-hepatitis B virus activity and mechanisms of
recombinant human serum albumin-interferon-alpha-2b fusion protein
in vitro and in vivo. Pharmacology. 83:323–332. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Carey I and Harrison PM: Monotherapy
versus combination therapy for the treatment of chronic hepatitis
B. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 18:1655–1666. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Urban S, Schulze A, Dandri M and Petersen
J: The replication cycle of hepatitis B virus. J Hepatol.
52:282–284. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Stein LL and Loomba R: Drug targets in
hepatitis B virus infection. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 9:105–116.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Grimm D, Thimme R and Blum HE: HBV life
cycle and novel drug targets. Hepatol Int. 5:644–653. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Levrero M, Pollicino T, Petersen J,
Belloni L, Raimondo G and Dandri M: Control of cccDNA function in
hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 51:581–592. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Katen SP, Chirapu SR, Finn MG and Zlotnick
A: Trapping of hepatitis B virus capsid assembly intermediates by
phenylpropenamide assembly accelerators. ACS Chem Biol.
5:1125–1136. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Deres K, Schroder CH, Paessens A, et al:
Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication by drug-induced
depletion of nucleocapsids. Science. 299:893–896. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Shi C, Wu CQ, Cao AM, Sheng HZ, Yan XZ and
Liao MY: NMR-spectroscopy-based metabonomic approach to the
analysis of Bay41-4109, a novel anti-HBV compound, induced
hepatotoxicity in rats. Toxicol Lett. 173:161–167. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Han J, Pan X, Gao Y and Weil L: Inhibition
of hepatitis B virus replication by the internal fragment of
hepatitis B core protein. Virus Res. 150:129–134. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Yamamoto M, Hayashi N, Takehara T, et al:
Intracellular single-chain antibody against hepatitis B virus core
protein inhibits the replication of hepatitis B virus in cultured
cells. Hepatology. 30:300–307. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Jin YH, Hong SH, Kim K, Shin HJ and Park
S: Intracellular antibody fragment against hepatitis B virus X
protein does not inhibit viral replication. Yonsei Med J.
47:721–728. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Heng BC and Cao T: Making cell-permeable
recombinant telomerase (trans-telomerase) through fusion of its
catalytic subunit (hTERT) with protein transduction domains (PTD):
a possible strategy to overcome replicative senescence during ex
vivo culture of primary explanted cells. Med Hypotheses.
65:199–200. 2005.
|
|
18.
|
Gump JM and Dowdy SF: TAT transduction:
the molecular mechanism and therapeutic prospects. Trends Mol Med.
13:443–448. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Zorko M and Langel U: Cell-penetrating
peptides: mechanism and kinetics of cargo delivery. Adv Drug Deliv
Rev. 57:529–545. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Doorbar J and Griffin H: Intrabody
strategies for the treatment of human papillomavirus-associated
disease. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 7:677–689. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Fonseca SB, Pereira MP and Kelley SO:
Recent advances in the use of cell-penetrating peptides for medical
and biological applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 61:953–964. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Chames P, Van Regenmortel M, Weiss E and
Baty D: Therapeutic antibodies: successes, limitations and hopes
for the future. Br J Pharmacol. 157:220–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Pan XB, Wei L, Han JC, Ma H, Deng K and
Cong X: Artificial recombinant cell-penetrating peptides interfere
with envelopment of hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid and viral
production. Antiviral Res. 89:109–114. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Tang ZH, Ma HH, Chen WS, Gu L, Li G and
Yao JL: Screening, identifying and sequencing of human single-chain
variable fragment specific to hepatitis B virus core protein.
Zhongguo Binglishengli Zazhi. 19:329–333. 2003.(In Chinese).
|
|
25.
|
Kim D, Jeon C, Kim JH, et al: Cytoplasmic
transduction peptide (CTP): new approach for the delivery of
biomolecules into cytoplasm in vitro and in vivo. Exp Cell Res.
312:1277–1288. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Friguet B, Chaffotte AF, Djavadi-Ohaniance
L and Goldberg ME: Measurements of the true affinity constant in
solution of antigen-antibody complexes by enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay. J Immunol Methods. 77:305–319. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Butz K, Denk C, Fitscher B, et al: Peptide
aptamers targeting the hepatitis B virus core protein: a new class
of molecules with antiviral activity. Oncogene. 20:6579–6586. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|