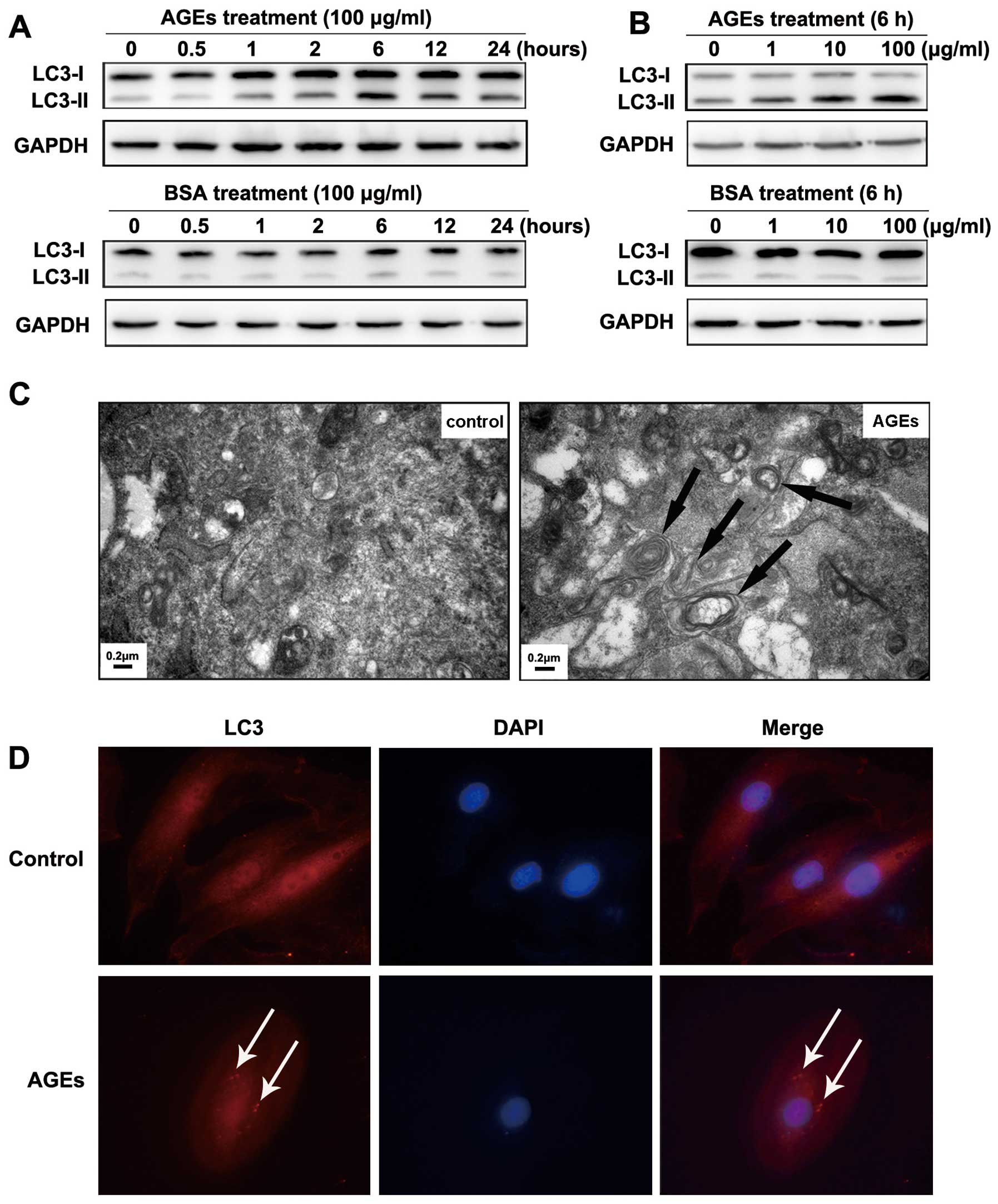
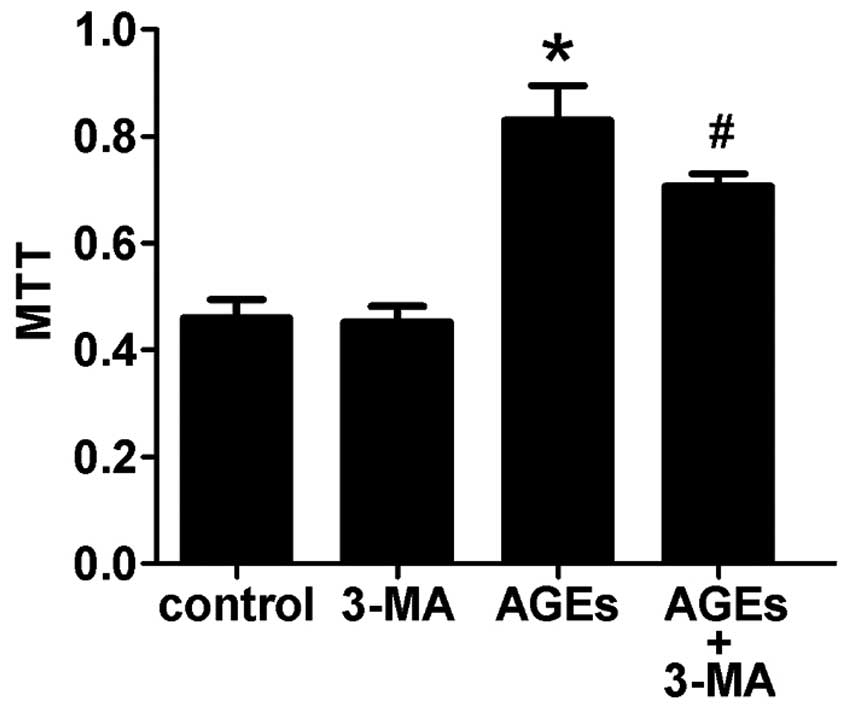
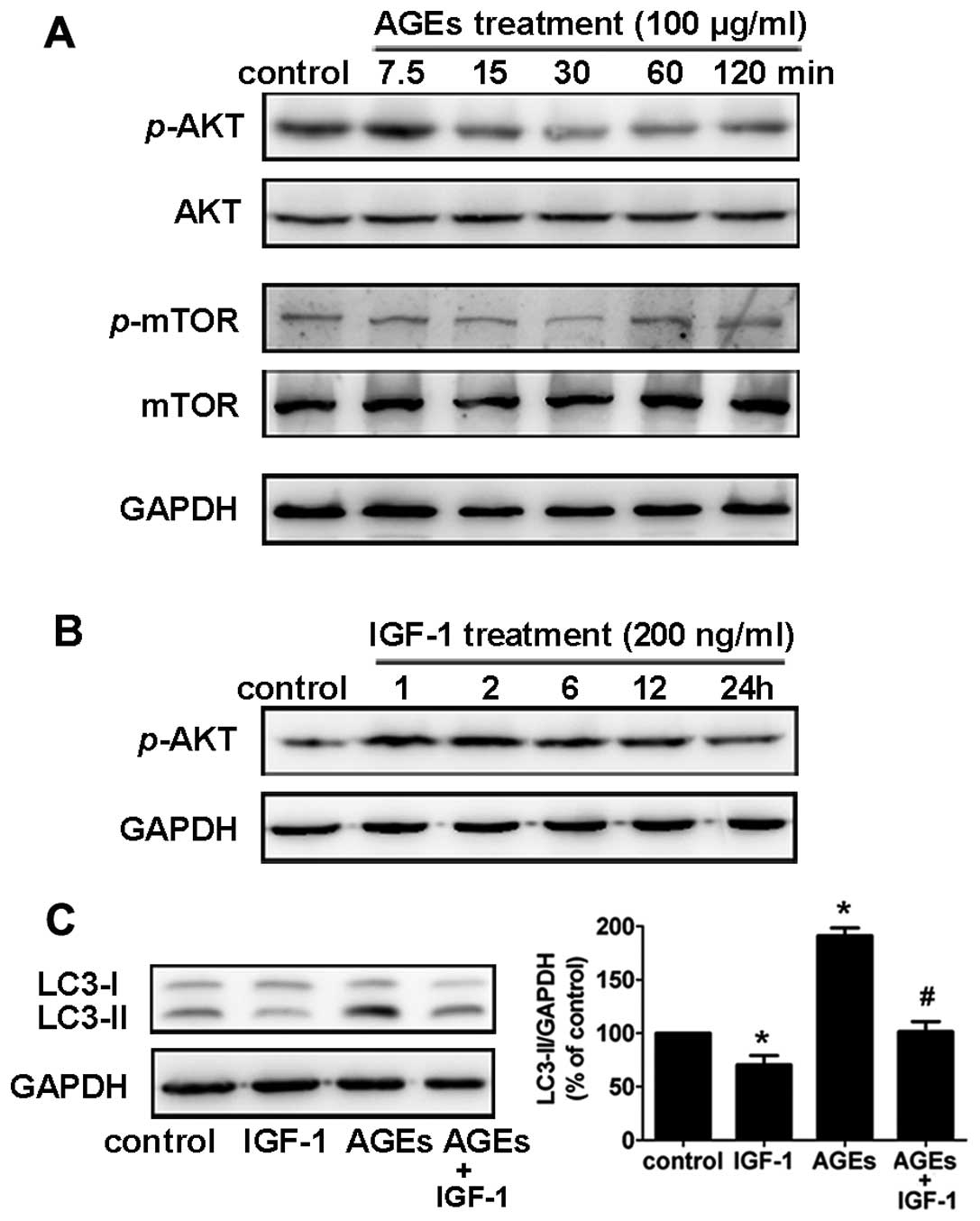
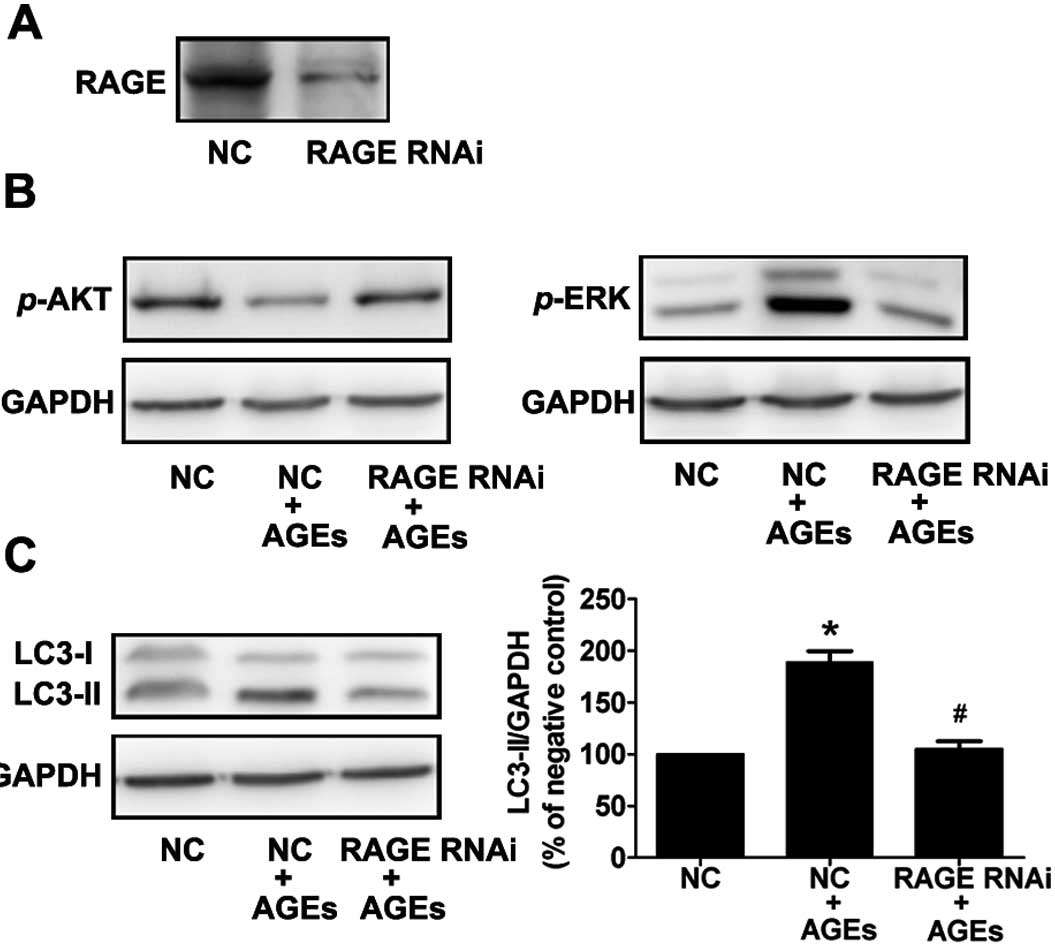
|
1
|
S YamagishiM TakeuchiY InagakiK NakamuraT
ImaizumiRole of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and their
receptor (RAGE) in the pathogenesis of diabetic microangiopathyInt
J Clin Pharmacol Res23129134200315224502
|
|
2
|
BK KilhovdTJ BergKI BirkelandP ThorsbyKF
HanssenSerum levels of advanced glycation end products are
increased in patients with type 2 diabetes and coronary heart
diseaseDiabetes
Care2215431548199910.2337/diacare.22.9.154310480523
|
|
3
|
DP BarlovicA Soro-PaavonenKA
Jandeleit-DahmRAGE biology, atherosclerosis and diabetesClin Sci
(Lond)1214355201110.1042/CS2010050121457145
|
|
4
|
VJ DzauRC Braun-DullaeusDG SeddingVascular
proliferation and atherosclerosis: New perspectives and therapeutic
strategiesNat Med812491256200210.1038/nm1102-124912411952
|
|
5
|
N SakataJ MengS TakebayashiEffects of
advanced glycation end products on the proliferation and
fibronectin production of smooth muscle cellsJ Atheroscler
Thromb7169176200010.5551/jat1994.7.16911480459
|
|
6
|
LG BucciarelliT WendtW QuRAGE blockade
stabilizes established atherosclerosis in diabetic apolipoprotein
E-null
miceCirculation10628272835200210.1161/01.CIR.0000039325.03698.3612451010
|
|
7
|
DX BuV RaiX ShenActivation of the ROCK1
branch of the transforming growth factor-beta pathway contributes
to RAGE-dependent acceleration of atherosclerosis in diabetic
ApoE-null miceCirc
Res10610401051201010.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.20110320133903
|
|
8
|
DJ KlionskyAutophagy: from phenomenology
to molecular understanding in less than a decadeNat Rev Mol Cell
Biol8931937200710.1038/nrm224517712358
|
|
9
|
T YorimitsuDJ KlionskyAutophagy: molecular
machinery for self-eatingCell Death Differ12Suppl
215421552200510.1038/sj.cdd.4401765
|
|
10
|
N MizushimaT YoshimoriHow to interpret LC3
immunoblottingAutophagy3542545200710.4161/auto.460017611390
|
|
11
|
W MartinetDM SchrijversJP TimmermansH
BultInteractions between cell death induced by statins and
7-ketocholesterol in rabbit aorta smooth muscle cellsBr J
Pharmacol15412361246200810.1038/bjp.2008.18118469840
|
|
12
|
R KiffinU BandyopadhyayAM CuervoOxidative
stress and autophagyAntioxid Redox
Signal8152162200610.1089/ars.2006.8.152
|
|
13
|
D HeymannAutophagy: A protective mechanism
in response to stress and inflammationCurr Opin Investig
Drugs7443450200616729721
|
|
14
|
P CodognoS PattingreC BauvyAmino acids
interfere with the ERK1/2-dependent control of macroautophagy by
controlling the activation of Raf-1 in human colon cancer HT-29
cellsJ Biol Chem2781666716674200310.1074/jbc.M21099820012609989
|
|
15
|
HW ChiuSY HoHR GuoYJ WangCombination
treatment with arsenic trioxide and irradiation enhances autophagic
effects in U118-MG cells through increased mitotic arrest and
regulation of PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signaling
pathwaysAutophagy5472483200910.4161/auto.5.4.7759
|
|
16
|
FF HouGM ChertowJ KayInteraction between
beta 2-microglobulin and advanced glycation end products in the
development of dialysis related-amyloidosisKidney
Int5115141519199710.1038/ki.1997.2089150467
|
|
17
|
CS MitsiadesN MitsiadesV PoulakiActivation
of NF-kappaB and upregulation of intracellular anti-apoptotic
proteins via the IGF-1/Akt signaling in human multiple myeloma
cells: therapeutic
implicationsOncogene2156735683200210.1038/sj.onc.1205664
|
|
18
|
MA CreagerA GoldinJA BeckmanAM
SchmidtAdvanced glycation end products - Sparking the development
of diabetic vascular
injuryCirculation114597605200610.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.62185416894049
|
|
19
|
YW YoonTS KangBK LeePathobiological role
of advanced glycation endproducts via mitogen-activated protein
kinase dependent pathway in the diabetic vasculopathyExp Mol
Med40398406200810.3858/emm.2008.40.4.39818779652
|
|
20
|
M KawanoT KoshikawaT KanzakiN MorisakiY
SaitoS YoshidaDiabetes mellitus induces accelerated growth of
aortic smooth muscle cells: association with overexpression of PDGF
beta-receptorsEur J Clin
Invest238490199310.1111/j.1365-2362.1993.tb00745.x8462625
|
|
21
|
N TaniguchiH KanetoM AsahiInvolvement of
glycation and oxidative stress in diabetic
macroangiopathyDiabetes45Suppl
38183199610.2337/diab.45.3.S818674900
|
|
22
|
G BastaG LazzeriniS Del TurcoGM RattoAM
SchmidtR De CaterinaAt least 2 distinct pathways generating
reactive oxygen species mediate vascular cell adhesion molecule-1
induction by advanced glycation end productsArterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol2514011407200510.1161/01.ATV.0000167522.48370.5e
|
|
23
|
B XuR ChibberD RuggieroE KohnerJ RitterA
FerroImpairment of vascular endothelial nitric oxide synthase
activity by advanced glycation end productsFASEB
J1712891291200312738813
|
|
24
|
T MiyataO HoriJ ZhangThe receptor for
advanced glycation end products (RAGE) is a central mediator of the
interaction of AGE-beta2microglobulin with human mononuclear
phagocytes via an oxidant-sensitive pathway. Implications for the
pathogenesis of dialysis-related amyloidosisJ Clin
Invest9810881094199610.1172/JCI118889
|
|
25
|
Y YamamotoS YamagishiCC HsuH
YamamotoAdvanced glycation endproducts-receptor interactions
stimulate the growth of human pancreatic cancer cells through the
induction of platelet-derived growth factor-BBiochem Biophys Res
Commun222700705199610.1006/bbrc.1996.0807
|
|
26
|
T ShintaniDJ KlionskyAutophagy in health
and disease: a double-edged
swordScience306990995200410.1126/science.109999315528435
|
|
27
|
MM KockxGR De MeyerN BuyssensMW KnaapenH
BultAG HermanCell composition, replication, and apoptosis in
atherosclerotic plaques after 6 months of cholesterol
withdrawalCirc Res83378387199810.1161/01.RES.83.4.3789721694
|
|
28
|
HM LanderJM TaurasJS OgisteO HoriRA MossAM
SchmidtActivation of the receptor for advanced glycation end
products triggers a p21(ras)-dependent mitogen-activated protein
kinase pathway regulated by oxidant stressJ Biol
Chem2721781017814199710.1074/jbc.272.28.178109211935
|
|
29
|
HJ HuttunenC FagesH RauvalaReceptor for
advanced glycation end products (RAGE)-mediated neurite outgrowth
and activation of NF-kappa B require the cytoplasmic domain of the
receptor but different downstream signaling pathwaysJ Biol
Chem2741991919924199910.1074/jbc.274.28.1991910391939
|