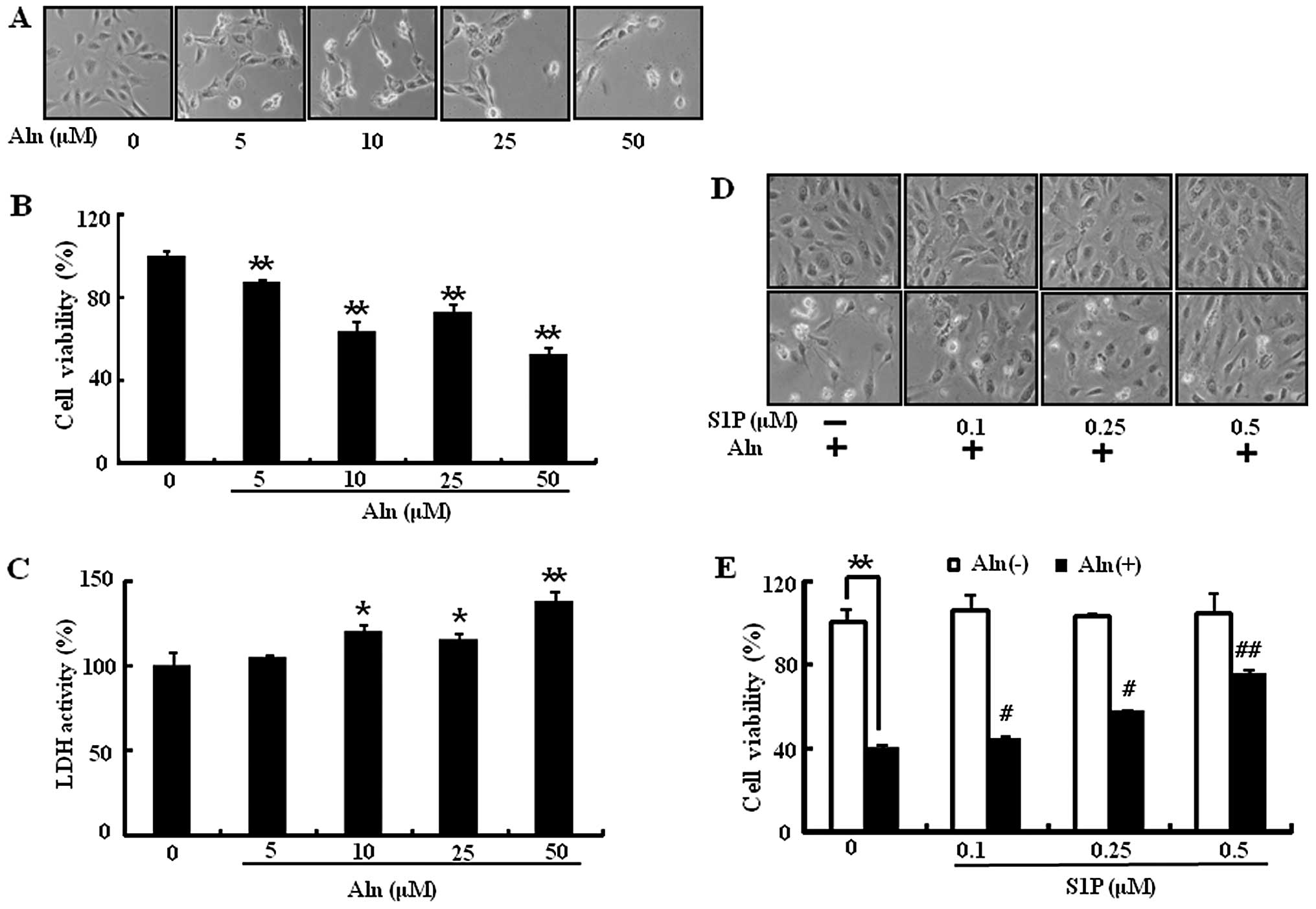
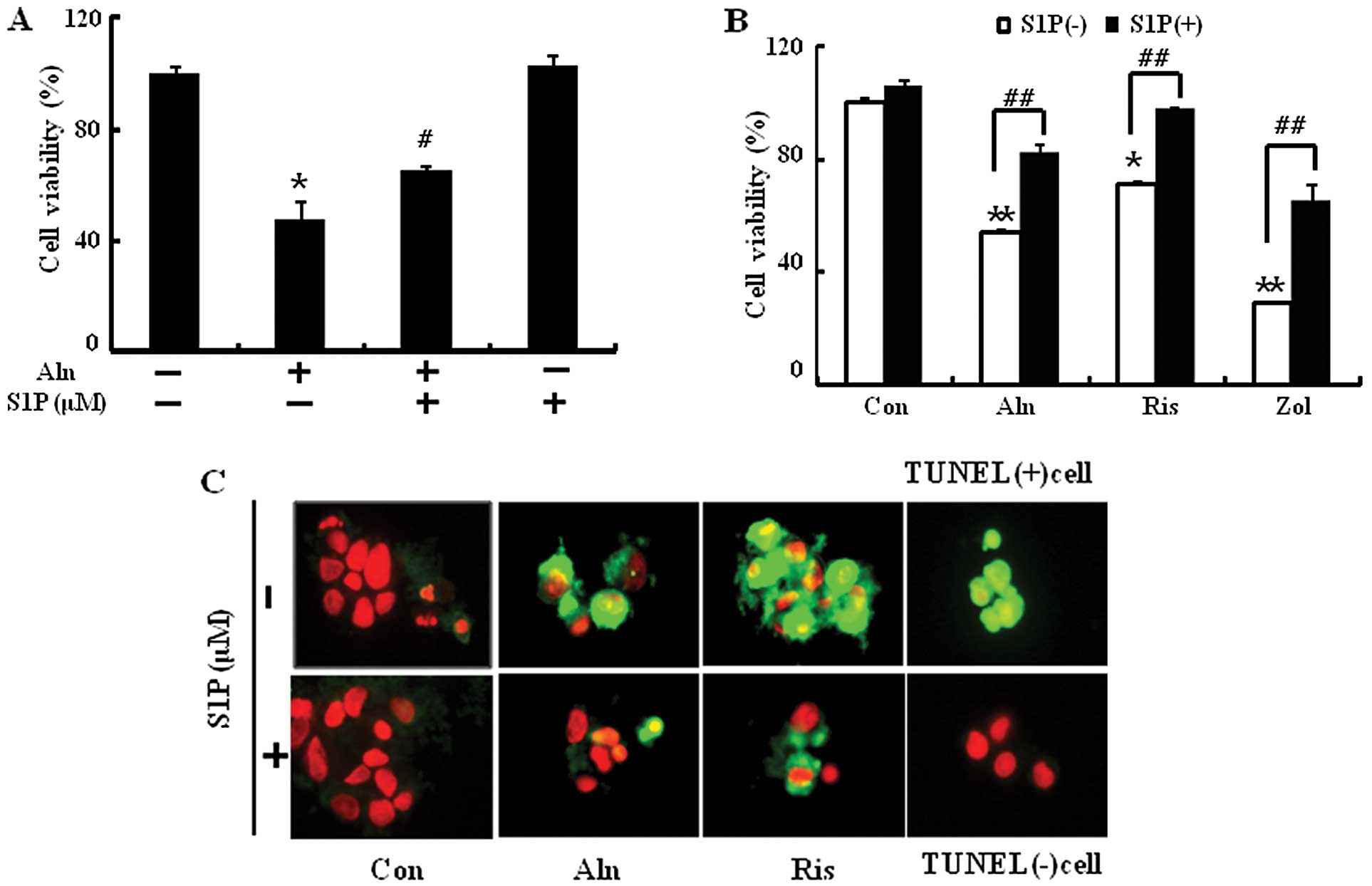
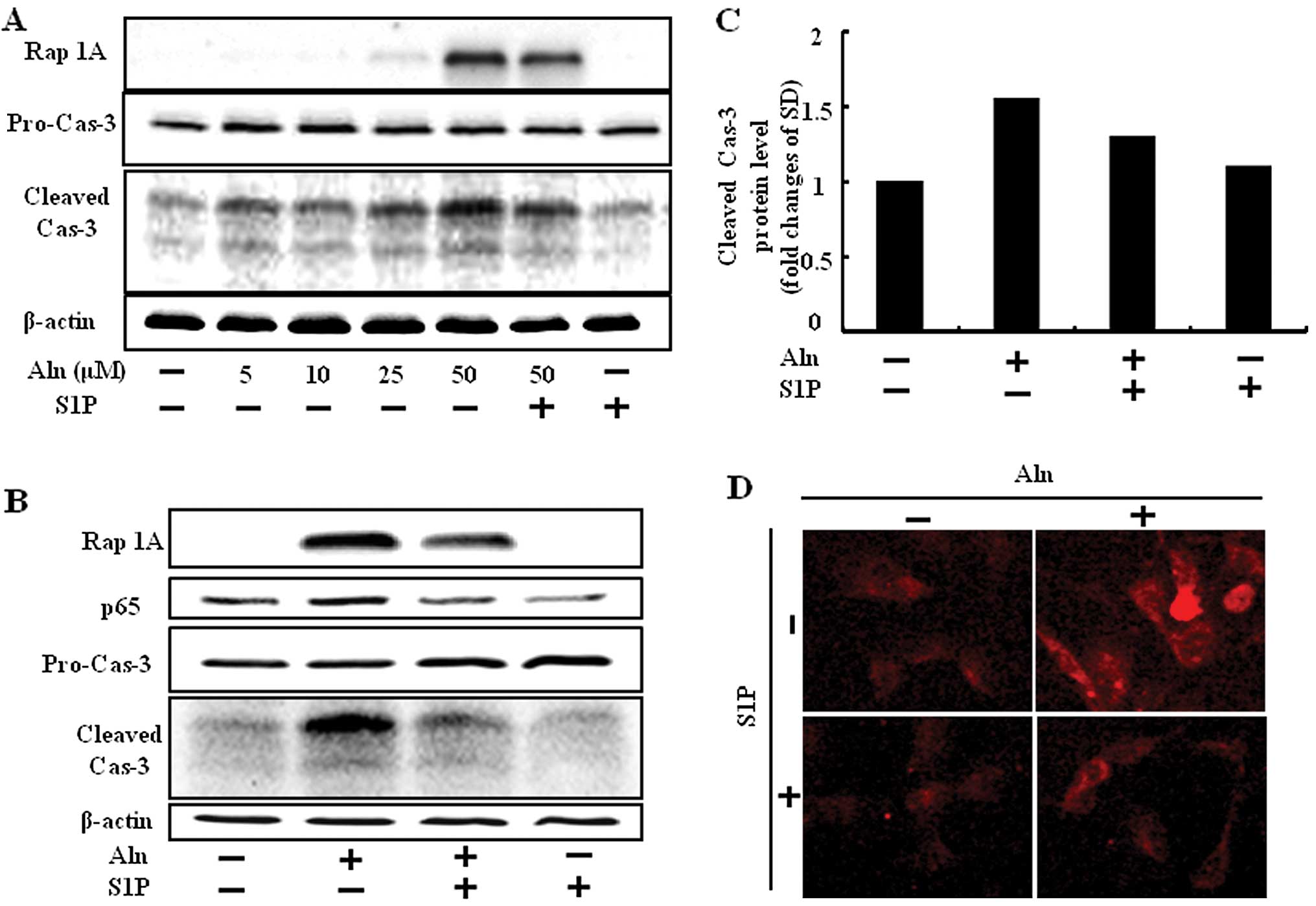
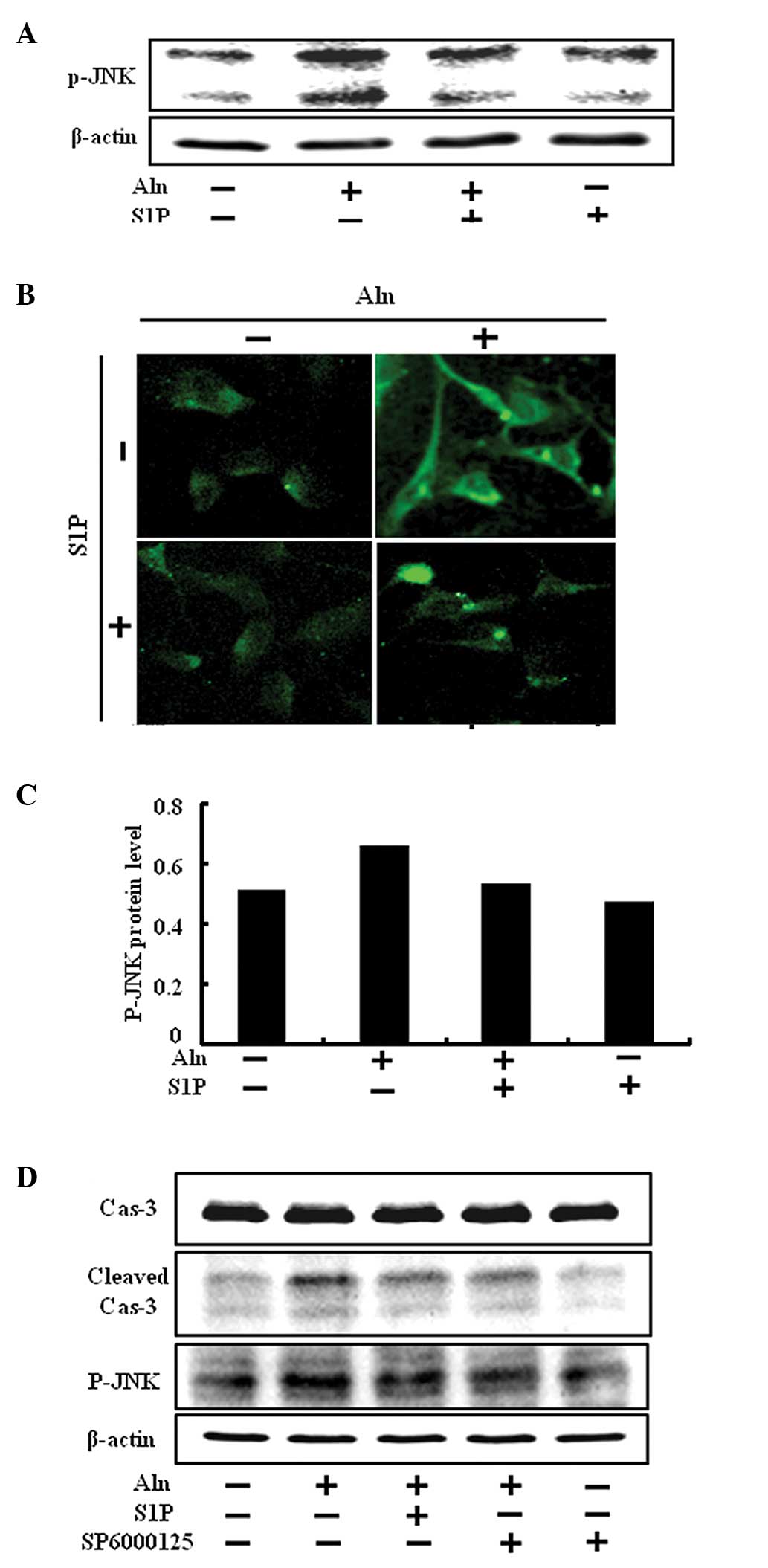
|
1
|
Roelofs AJ, Thompson K, Gordon S and
Rogers MJ: Molecular mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates:
current status. Clin Cancer Res. 12:6222s–6230s. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Allegra A, Alonci A, Penna G, et al:
Bisphosphonates induce apoptosis of circulating endothelial cells
in multiple myeloma patients and in subjects with
bisphosphonate-induced osteonecrosis of the jaws. Acta Haematol.
124:79–85. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Tassone P, Tagliaferri P, Viscomi C, et
al: Zoledronic acid induces antiproliferative and apoptotic effects
in human pancreatic cancer cells in vitro. Br J Cancer.
88:1971–1978. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hashimoto K, Morishige K, Sawada K, et al:
Alendronate suppresses tumor angiogenesis by inhibiting Rho
activation of endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
354:478–484. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fu L, Tang T, Miao Y, Zhang S, Qu Z and
Dai K: Stimulation of osteogenic differentiation and inhibition of
adipogenic differentiation in bone marrow stromal cells by
alendronate via ERK and JNK activation. Bone. 43:40–47. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Inoue R, Matsuki NA, Jing G, Kanematsu T,
Abe K and Hirata M: The inhibitory effect of alendronate, a
nitrogen-containing bisphosphonate on the PI3K-Akt-NFkappaB pathway
in osteosarcoma cells. Br J Pharmacol. 146:633–641. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hasmim M, Bieler G and Ruegg C:
Zoledronate inhibits endothelial cell adhesion, migration and
survival through the suppression of multiple, prenylation-dependent
signaling pathways. J Thromb Haemost. 5:166–173. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tsai SH, Huang PH, Chang WC, et al:
Zoledronate inhibits ischemia-induced neovascularization by
impairing the mobilization and function of endothelial progenitor
cells. PLoS One. 7:e410652012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Maceyka M, Harikumar KB, Milstien S and
Spiegel S: Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling and its role in
disease. Trends Cell Biol. 22:50–60. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Morales-Ruiz M, Lee MJ, Zollner S, et al:
Sphingosine 1-phosphate activates Akt, nitric oxide production, and
chemotaxis through a Gi protein/phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway
in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 276:19672–19677. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ishii M and Kikuta J:
Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling controlling osteoclasts and bone
homeostasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1831:223–227. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kimura T, Sato K, Kuwabara A, et al:
Sphingosine 1-phosphate may be a major component of plasma
lipoproteins responsible for the cytoprotective actions in human
umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 276:31780–31785.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Seol JW, Lee YJ, Jackson CJ, Sambrook PN
and Park SY: Activated protein C inhibits bisphosphonate-induced
endothelial cell death via the endothelial protein C receptor and
nuclear factor-κB pathways. Int J Mol Med. 27:835–840.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wolf AM, Rumpold H, Tilg H, Gastl G,
Gunsilius E and Wolf D: The effect of zoledronic acid on the
function and differentiation of myeloid cells. Haematologica.
91:1165–1171. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Russell RG, Watts NB, Ebetino FH and
Rogers MJ: Mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates: similarities
and differences and their potential influence on clinical efficacy.
Osteoporos Int. 19:733–759. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rogers MJ, Russell RG, Blackburn GM,
Williamson MP and Watts DJ: Metabolism of halogenated
bisphosphonates by the cellular slime mould Dictyostelium
discoideum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 189:414–423. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Luckman SP, Hughes DE, Coxon FP, Graham R,
Russell G and Rogers MJ: Nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates
inhibit the mevalonate pathway and prevent post-translational
prenylation of GTP-binding proteins, including Ras. J Bone Miner
Res. 13:581–589. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Luckman SP, Coxon FP, Ebetino FH, Russell
RG and Rogers MJ: Heterocycle-containing bisphosphonates cause
apoptosis and inhibit bone resorption by preventing protein
prenylation: evidence from structure-activity relationships in J774
macrophages. J Bone Miner Res. 13:1668–1678. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Perez-Sala D and Mollinedo F: Inhibition
of isoprenoid biosynthesis induces apoptosis in human promyelocytic
HL-60 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 199:1209–1215. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yatomi Y, Igarashi Y, Yang L, et al:
Sphingosine 1-phosphate, a bioactive sphingolipid abundantly stored
in platelets, is a normal constituent of human plasma and serum. J
Biochem. 121:969–973. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Limaye V, Li X, Hahn C, et al: Sphingosine
kinase-1 enhances endothelial cell survival through a
PECAM-1-dependent activation of PI-3K/Akt and regulation of Bcl-2
family members. Blood. 105:3169–3177. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kumar A, Byun HS, Bittman R and Saba JD:
The sphingolipid degradation product trans-2-hexadecenal
induces cytoskeletal reorganization and apoptosis in a
JNK-dependent manner. Cell Signal. 23:1144–1152. 2011.
|
|
23
|
Dunford JE, Rogers MJ, Ebetino FH, Phipps
RJ and Coxon FP: Inhibition of protein prenylation by
bisphosphonates causes sustained activation of Rac, Cdc42, and Rho
GTPases. J Bone Miner Res. 21:684–694. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|