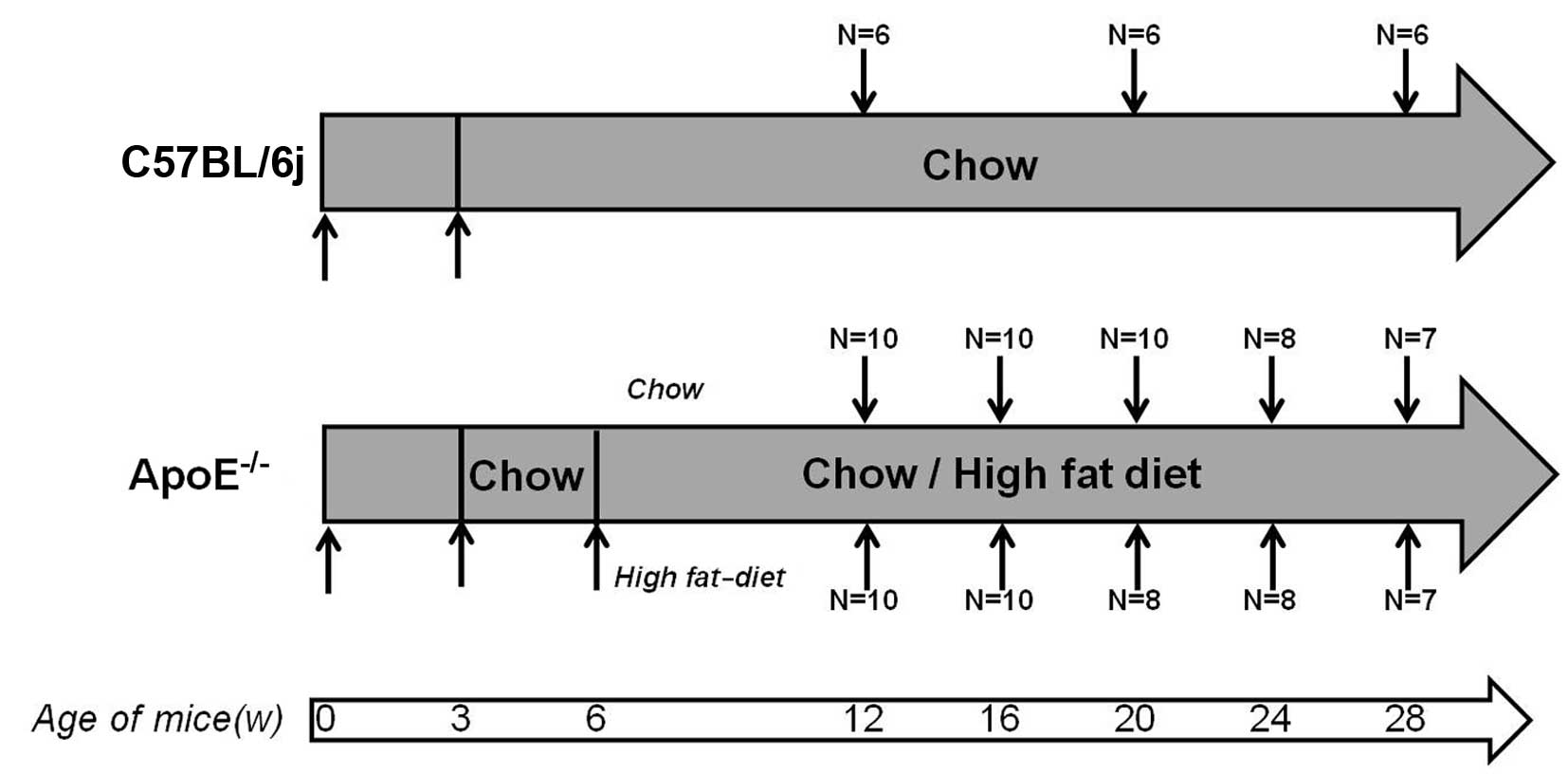
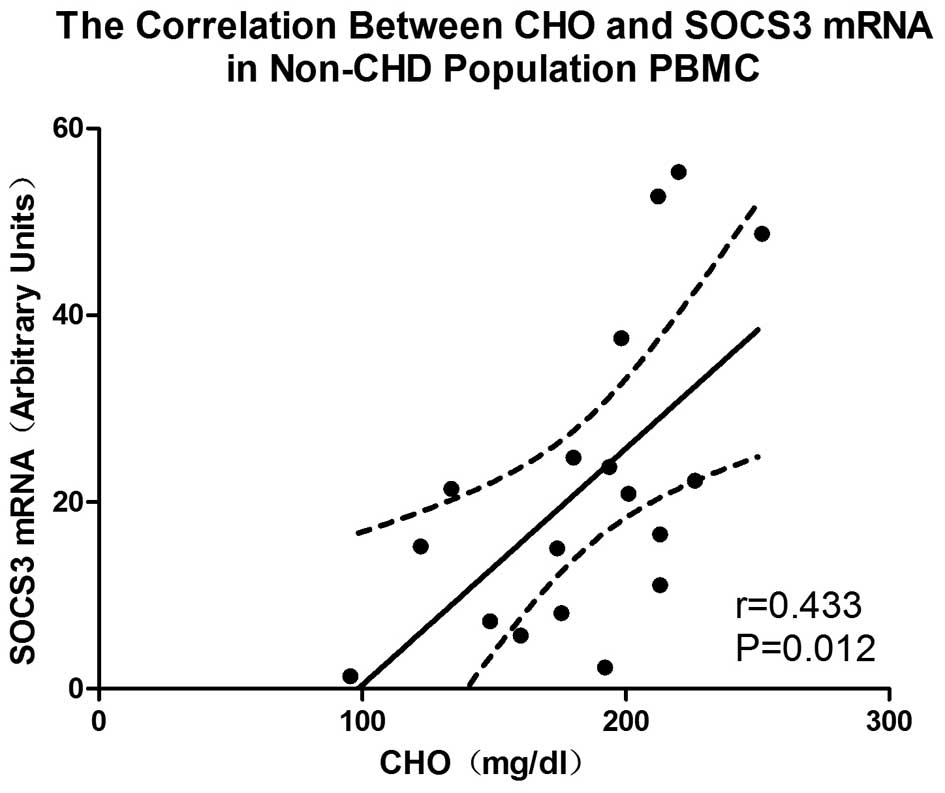
|
1
|
Ross R: Atherosclerosis - an inflammatory
disease. N Engl J Med. 340:115–126. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tedgui A and Mallat Z: Cytokines in
atherosclerosis: pathogenic and regulatory pathways. Physiol Rev.
86:515–581. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ortiz-Munoz G, Martin-Ventura JL,
Hernandez-Vargas P, et al: Suppressors of cytokine signaling
modulate JAK/STAT-mediated cell responses during atherosclerosis.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:525–531. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yan C, Cao J, Wu M, et al: Suppressor of
cytokine signaling 3 inhibits LPS-induced IL-6 expression in
osteoblasts by suppressing CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein {beta}
activity. J Biol Chem. 285:37227–37239. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Albanesi C, Fairchild HR, Madonna S, et
al: IL-4 and IL-13 negatively regulate TNF-alpha- and
IFN-gamma-induced beta-defensin expression through STAT-6,
suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)-1, and SOCS-3. J Immunol.
179:984–992. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Alexander WS and Hilton DJ: The role of
suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins in regulation of
the immune response. Annu Rev Immunol. 22:503–529. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yoshimura A, Naka T and Kubo M: SOCS
proteins, cytokine signalling and immune regulation. Nat Rev
Immunol. 7:454–465. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Davey GM, Heath WR and Starr R: SOCS1: a
potent and multifaceted regulator of cytokines and cell-mediated
inflammation. Tissue Antigens. 67:1–9. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Egan PJ, Lawlor KE, Alexander WS and Wicks
IP: Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 regulates acute inflammatory
arthritis and T cell activation. J Clin Invest. 111:915–924. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Metcalf D, Di Rago L, Mifsud S, et al: The
development of fatal myocarditis and polymyositis in mice
heterozygous for IFN-gamma and lacking the SOCS-1 gene. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 97:9174–9179. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ilangumaran S, Ramanathan S and Rottapel
R: Regulation of the immune system by SOCS family adaptor proteins.
Semin Immunol. 16:351–365. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jo D, Liu D, Yao S, et al: Intracellular
protein therapy with SOCS3 inhibits inflammation and apoptosis. Nat
Med. 11:892–898. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li Y, Chu N, Rostami A and Zhang GX:
Dendritic cells transduced with SOCS-3 exhibit a tolerogenic/DC2
phenotype that directs type 2 Th cell differentiation in vitro and
in vivo. J Immunol. 177:1679–1688. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Matsumura Y, Kobayashi T, Ichiyama K, et
al: Selective expansion of foxp3-positive regulatory T cells and
immunosuppression by suppressors of cytokine signaling 3-deficient
dendritic cells. J Immunol. 179:2170–2179. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu Y, Stewart KN, Bishop E, et al: Unique
expression of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 is essential for
classical macrophage activation in rodents in vitro and in vivo. J
Immunol. 180:6270–6278. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
O’Keefe GM, Nguyen VT, Ping Tang LL and
Benveniste EN: IFN-gamma regulation of class II transactivator
promoter IV in macrophages and microglia: involvement of the
suppressors of cytokine signaling-1 protein. J Immunol.
166:2260–2269. 2001.
|
|
17
|
Croker BA, Krebs DL, Zhang JG, et al:
SOCS3 negatively regulates IL-6 signaling in vivo. Nat Immunol.
4:540–545. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yoshimura A, Suzuki M, Sakaguchi R, et al:
SOCS, inflammation, and autoimmunity. Front Immunol. 3:202012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wormald S and Hilton DJ: Inhibitors of
cytokine signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 279:821–824. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Brown MS and Goldstein JL: Lipoprotein
metabolism in the macrophage: implications for cholesterol
deposition in atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 52:223–261. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gower RM, Wu H, Foster GA, et al:
CD11c/CD18 expression is upregulated on blood monocytes during
hypertriglyceridemia and enhances adhesion to vascular cell
adhesion molecule-1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 31:160–166.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Gokalp D, Tuzcu A, Bahceci M, et al:
Levels of proinflammatory cytokines and hs-CRP in patients with
homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia. Acta Cardiol.
64:603–609. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sima AV, Stancu CS and Simionescu M:
Vascular endothelium in atherosclerosis. Cell Tissue Res.
335:191–203. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Steinberg D: Atherogenesis in perspective:
hypercholesterolemia and inflammation as partners in crime. Nat
Med. 8:1211–1217. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tian Y, Yuan Z, Liu Y, et al: Pioglitazone
modulates the balance of effector and regulatory T cells in
apolipoprotein E deficient mice. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis.
21:25–32. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Anderson JL, Adams CD, Antman EM, et al:
ACC/AHA 2007 guidelines for the management of patients with
unstable angina/non-ST-Elevation myocardial infarction: a report of
the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task
Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the 2002
Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Unstable
Angina/Non-ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction) developed in
collaboration with the American College of Emergency Physicians,
the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and
the Society of Thoracic Surgeons endorsed by the American
Association of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation and the
Society for Academic Emergency Medicine. J Am Coll Cardiol.
50:e1–e157. 2007.
|
|
27
|
Zhao Y, Yuan Z, Liu Y, et al: Activation
of cannabinoid CB2 receptor ameliorates atherosclerosis associated
with suppression of adhesion molecules. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol.
55:292–298. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xue JH, Yuan Z, Wu Y, et al: High glucose
promotes intracellular lipid accumulation in vascular smooth muscle
cells by impairing cholesterol influx and efflux balance.
Cardiovasc Res. 86:141–150. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
He L, He M, Lv X, et al: NF-kappaB binding
activity and pro-inflammatory cytokines expression correlate with
body mass index but not glycosylated hemoglobin in Chinese
population. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 90:73–80. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Tang J, Kozaki K, Farr AG, et al: The
absence of platelet-derived growth factor-B in circulating cells
promotes immune and inflammatory responses in atherosclerosis-prone
ApoE−/− mice. Am J Pathol. 167:901–912. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Endo TA, Masuhara M, Yokouchi M, et al: A
new protein containing an SH2 domain that inhibits JAK kinases.
Nature. 387:921–924. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Park SJ, Oh EJ, Yoo MA and Lee SH:
Involvement of DNA-dependent protein kinase in regulation of
stress-induced JNK activation. DNA Cell Biol. 20:637–645. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kinjyo I, Hanada T, Inagaki-Ohara K, et
al: SOCS1/JAB is a negative regulator of LPS-induced macrophage
activation. Immunity. 17:583–591. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Libby P, Ridker PM and Hansson GK:
Inflammation in atherosclerosis: from pathophysiology to practice.
J Am Coll Cardiol. 54:2129–2138. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li Y, Schwabe RF, DeVries-Seimon T, et al:
Free cholesterol-loaded macrophages are an abundant source of tumor
necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6: model of NF-kappaB- and
map kinase-dependent inflammation in advanced atherosclerosis. J
Biol Chem. 280:21763–21772. 2005.
|
|
36
|
Frisdal E, Lesnik P, Olivier M, et al:
Interleukin-6 protects human macrophages from cellular cholesterol
accumulation and attenuates the proinflammatory response. J Biol
Chem. 286:30926–30936. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|