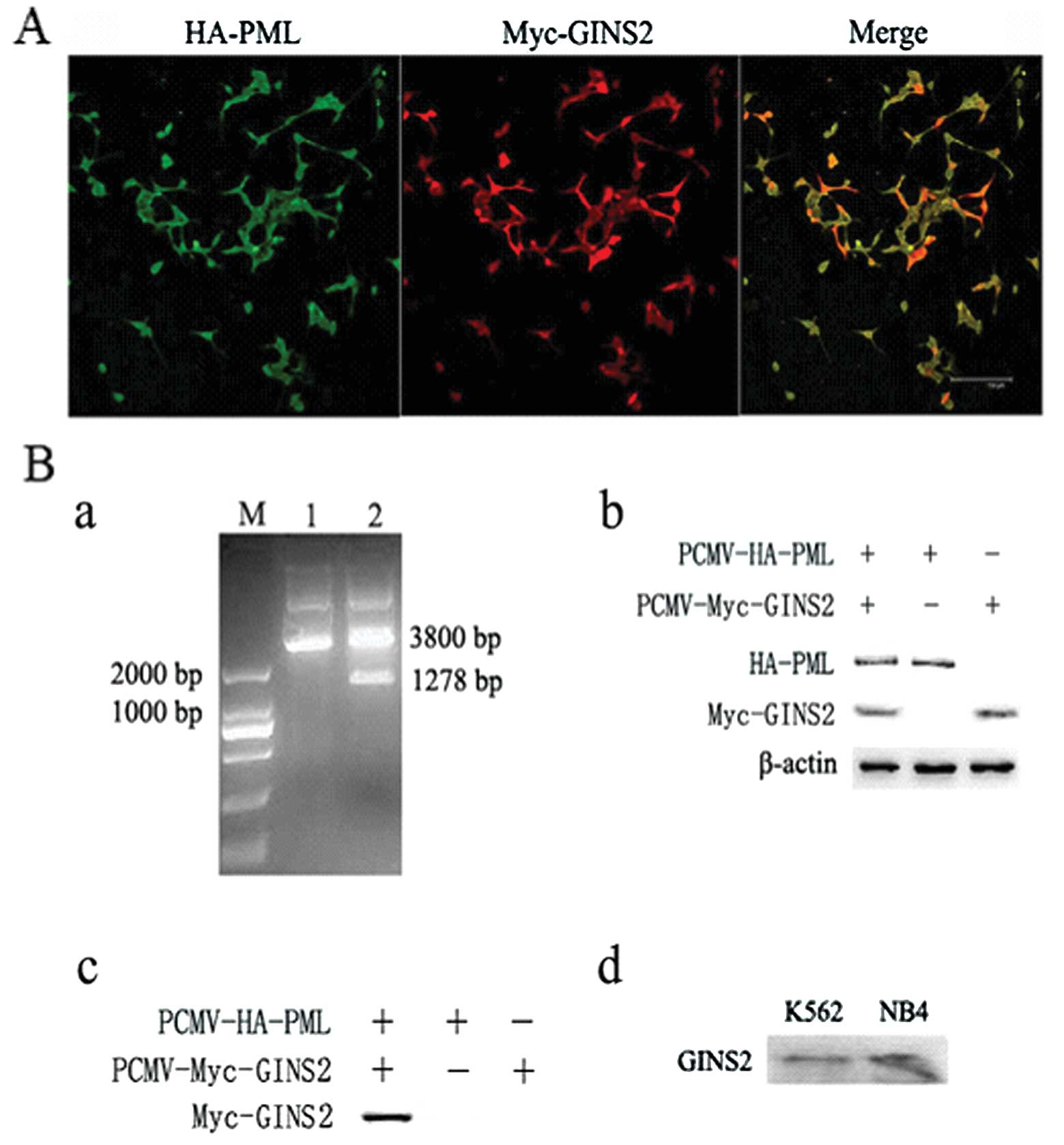
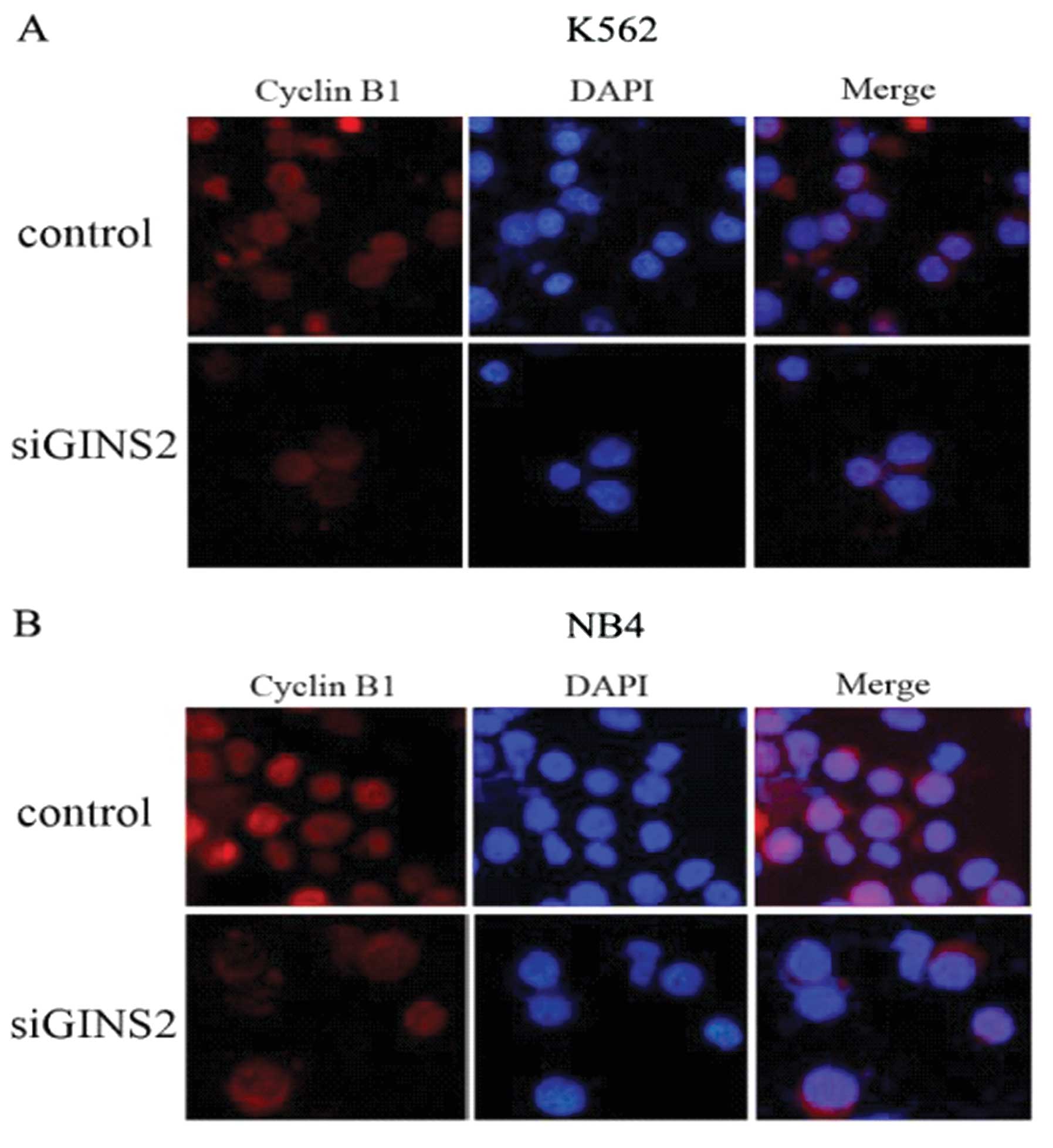
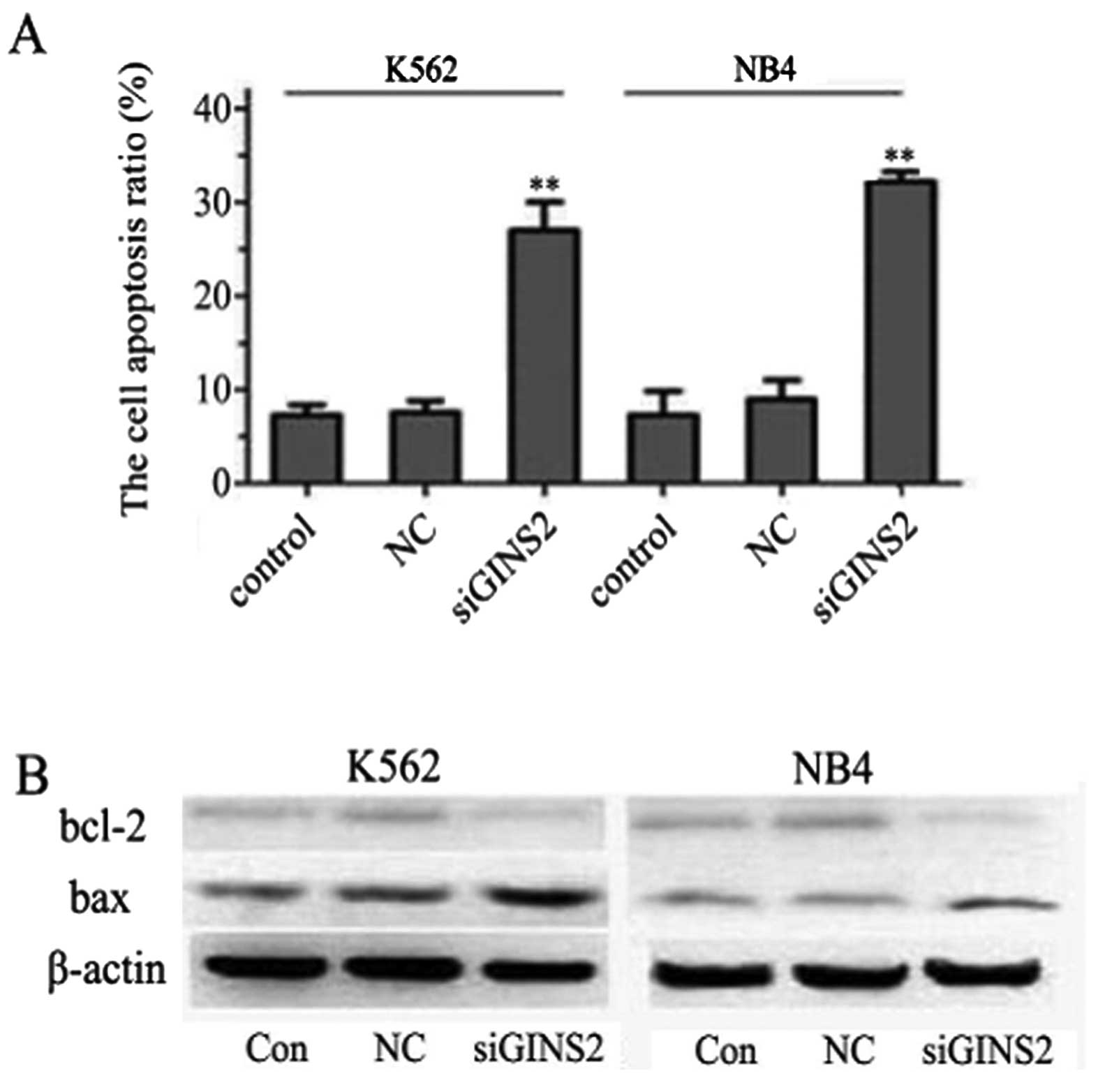
|
1
|
de Thé H, Lavau C, Marchio A, Chomienne C,
Degos L and Dejean A: The PML-RAR alpha fusion mRNA generated by
the t(15;17) translocation in acute promyelocytic leukemia encodes
a functionally altered RAR. Cell. 66:675–684. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hayakawa F and Privalsky ML:
Phosphorylation of PML by mitogen-activated protein kinases plays a
key role in arsenic trioxide-mediated apoptosis. Cancer Cell.
5:389–401. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shima Y, Shima T, Chiba T, Irimura T,
Pandolfi PP and Kitabayashi I: PML activates transcription by
protecting HIPK2 and p300 from SCFFbx3-mediated degradation. Mol
Cell Biol. 28:7126–7138. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Scaglioni PP, Yung TM, Cai LF, et al: A
CK2-dependent mechanism for degradation of the PML tumor
suppressor. Cell. 126:269–283. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
So CW, Dong S, So CK, et al: The impact of
differential binding of wild-type RARalpha, PML-, PLZF- and
NPM-RARalpha fusion proteins towards transcriptional co-activator,
RIP-140, on retinoic acid responses in acute promyelocytic
leukemia. Leukemia. 14:77–83. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lane AA and Ley TJ: Neutrophil elastase is
important for PML-retinoic acid receptor alpha activities in early
myeloid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 25:23–33. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lane AA and Ley TJ: Neutrophil elastase
cleaves PML-RARα and is important for the development of acute
promyelocytic leukemia in mice. Cell. 115:305–318. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhu D, Wang C, Liu B, Zhong L, Wang C and
Wu Y: Screening and identification of target proteins interacting
with structural domain of PML-C by yeast two-hybrid system
techniques. Yi Xue Fen Zi Sheng Wu Xue Za Zhi. 7:242–246. 2010.(In
Chinese).
|
|
9
|
Walther A, Houlston R and Tomlinson I:
Association between chromosomal instability and prognosis in
colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. Gut. 57:941–950. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
MacNeill SA: Structure and function of the
GINS complex, a key component of the eukaryotic replisome. Biochem
J. 425:489–500. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Takayama Y, Kamimura Y, Okawa M, Muramatsu
S, Sugino A and Araki H: GINS, a novel multiprotein complex
required for chromosomal DNA replication in budding yeast. Genes
Dev. 17:1153–1165. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kanemaki M, Sanchez-Diaz A, Gambus A and
Labib K: Functional proteomic identification of DNA replication
proteins by induced proteolysis in vivo. Nature. 423:720–724. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Moyer SE, Lewis PW and Botchan MR:
Isolation of the Cdc45/Mcm2–7/GINS (CMG) complex, a candidate for
the eukaryotic DNA replication fork helicase. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 103:10236–10241. 2006.
|
|
14
|
Pacek M, Tutter AV, Kubota Y, Takisawa H
and Walter JC: Localization of MCM2–7, Cdc45, and GINS to the site
of DNA unwinding during eukaryotic DNA replication. Mol Cell.
21:581–587. 2006.
|
|
15
|
Chang YP, Wang G, Bermudez V, Hurwitz J
and Chen XS: Crystal structure of the GINS complex and functional
insights into its role in DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:12685–12690. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
De Falco M, Ferrari E, De Felice M,
Hübscher U and Pisani FM: The human GINS complex binds to and
specifically stimulates human DNA polymerase alpha-primase. EMBO
Rep. 8:99–103. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Boskovic J, Coloma J, Aparicio T, et al:
Molecular architecture of the human GINS complex. EMBO Rep.
8:678–684. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Barkley LR, Song IY, Zou Y and Vaziri C:
Reduced expression of GINS complex members induces hallmarks of
pre-malignancy in primary untransformed human cells. Cell Cycle.
8:1577–1588. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Matsuoka S, Ballif BA, Smogorzewska A, et
al: ATM and ATR substrate analysis reveals extensive protein
networks responsive to DNA damage. Science. 316:1160–1166. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hayashi R, Arauchi T, Tategu M, Goto Y and
Yoshida K: A combined computational and experimental study on the
structure-regulation relationships of putative mammalian DNA
replication initiator GINS. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics.
4:156–164. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rantala JK, Edgren H, Lehtinen L, et al:
Integrative functional genomics analysis of sustained polyploidy
phenotypes in breast cancer cells identifies an oncogenic profile
for GINS2. Neoplasia. 12:877–888. 2010.
|
|
22
|
Ryu B, Kim DS, Deluca AM and Alani RM:
Comprehensive expression profiling of tumor cell lines identifies
molecular signatures of melanoma progression. PLoS One. 2:e5942007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nakahara I, Miyamoto M, Shibata T, et al:
Up-regulation of PSF1 promotes the growth of breast cancer cells.
Genes Cells. 15:1015–1024. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Singh SV, Herman-Antosiewicz A, Singh AV,
et al: Sulforaphane-induced G2/M phase cell cycle arrest involves
checkpoint kinase 2-mediated phosphorylation of cell division cycle
25C. J Biol Chem. 279:25813–25822. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Morgan DO: Principles of CDK regulation.
Nature. 374:131–134. 1995. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Toyoshima F, Moriguchi T, Wada A, Fukuda M
and Nishida E: Nuclear export of cyclin B1 and its possible role in
the DNA damage-induced G2 checkpoint. EMBO J. 17:2728–2735. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tang D, Wu D, Hirao A, et al: ERK
activation mediates cell cycle arrest and apoptosis after DNA
damage independently of p53. J Biol Chem. 277:12710–12717. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Goulet AC, Chigbrow M, Frisk P and Nelson
MA: Selenomethionine induces sustained ERK phosphofylation leading
to cell-cycle arrest in human colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis.
26:109–117. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bulavin DV, Amundson SA and Fornace AJ:
p38 and Chk l kinases: different conductors for the
G(2)/M checkpoint symphony. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
12:92–97. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bulavin DV, Higashimoto Y, Popoff IJ, et
al: Initiation of G2/M checkpoint after ultraviolet radiation
requires p38 kinase. Nature. 411:102–107. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|