|
1
|
Gustafsson JA: Novel aspects of estrogen
action. J Soc Gynecol Investig. 7(Suppl 1): S8–S9. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Moggs JG and Orphanides G: Estrogen
receptors: orchestrators of pleiotropic cellular responses. EMBO
Rep. 2:775–781. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cos S, González A, Martínez-Campa C,
Mediavilla MD, Alonso-González C and Sánchez-Barceló EJ:
Estrogen-signaling pathway: a link between breast cancer and
melatonin oncostatic actions. Cancer Detect Prev. 30:118–128. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fornari FA, Randolph JK, Yalowich JC,
Ritke MK and Gewirtz DA: Interference by doxorubicin with DNA
unwinding in MCF-7 breast tumor cells. Mol Pharmacol. 45:649–656.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Akar U, Chaves-Reyez A, Barria M, Tari A,
Sanguino A, Kondo Y, Kondo S, Arun B, Lopez-Berestein G and Ozpolat
B: Silencing of Bcl-2 expression by small interfering RNA induces
autophagic cell death in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Autophagy.
4:669–679. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Deroo BJ and Korach KS: Estrogen receptors
and human disease. J Clin Invest. 116:561–570. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shang Y, Hu X, DiRenzo J, Lazar MA and
Brown M: Cofactor dynamics and sufficiency in estrogen
receptor-regulated transcription. Cell. 103:843–852. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bursch W, Ellinger A, Kienzl H, Török L,
Pandey S, Sikorska M, Walker R and Hermann RS: Active cell death
induced by the anti-estrogens tamoxifen and ICI 164 384 in human
mammary carcinoma cells (MCF-7) in culture: the role of autophagy.
Carcinogenesis. 17:1595–1607. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Paglin S, Hollister T, Delohery T, Hackett
N, McMahill M, Sphicas E, Domingo D and Yahalom J: A novel response
of cancer cells to radiation involves autophagy and formation of
acidic vesicles. Cancer Res. 61:439–444. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Charafe-Jauffret E, Ginestier C and
Birnbaum D: Breast cancer stem cells: tools and models to rely on.
BMC Cancer. 9:2022009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Y, Yang J, Zheng H, Tomasek GJ, Zhang
P, McKeever PE, Lee EY and Zhu Y: Expression of mutant p53 proteins
implicates a lineage relationship between neural stem cells and
malignant astrocytic glioma in a murine model. Cancer Cell.
15:514–526. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Santisteban M, Reiman JM, Asiedu MK,
Behrens MD, Nassar A, Kalli KR, Haluska P, Ingle JN, Hartmann LC,
Manjili MH, Radisky DC, Ferrone S and Knutson KL: Immune-induced
epithelial to mesenchymal transition in vivo generates breast
cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 69:2887–2895. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Charafe-Jauffret E, Monville F, Ginestier
C, Dontu G, Birnbaum D and Wicha MS: Cancer stem cells in breast:
current opinion and future challenges. Pathobiology. 75:75–84.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dean M, Fojo T and Bates S: Tumour stem
cells and drug resistance. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:275–284. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhou S, Schuetz JD, Bunting KD, Colapietro
AM, Sampath J, Morris JJ, Lagutina I, Grosveld GC, Osawa M,
Nakauchi H and Sorrentino BP: The ABC transporter Bcrp1/ABCG2 is
expressed in a wide variety of stem cells and is a molecular
determinant of the side-population phenotype. Nat Med. 7:1028–1034.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hait WN and Yang JM: Clinical management
of recurrent breast cancer: development of multidrug resistance
(MDR) and strategies to circumvent it. Semin Oncol. 32(Suppl 7):
S16–S21. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wolman SR, Heppner GH and Wolman E: New
directions in breast cancer research. FASEB J. 11:535–543.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ponti D, Costa A, Zaffaroni N, Pratesi G,
Petrangolini G, Coradini D, Pilotti S, Pierotti MA and Daidone MG:
Isolation and in vitro propagation of tumorigenic breast cancer
cells with stem/progenitor cell properties. Cancer Res.
65:5506–5511. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,
Morrison SJ and Clarke MF: Prospective identification of
tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:3983–3988. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yorimitsu T and Klionsky DJ: Autophagy:
molecular machinery for self-eating. Cell Death Differ. 12(Supp 2):
S1542–S1552. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shintani T and Klionsky DJ: Autophagy in
health and disease: a double-edged sword. Science. 306:990–995.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ravikumar B, Moreau K, Jahreiss L, Puri C
and Rubinsztein DC: Plasma membrane contributes to the formation of
pre-autophagosomal structures. Nat Cell Biol. 12:747–757. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
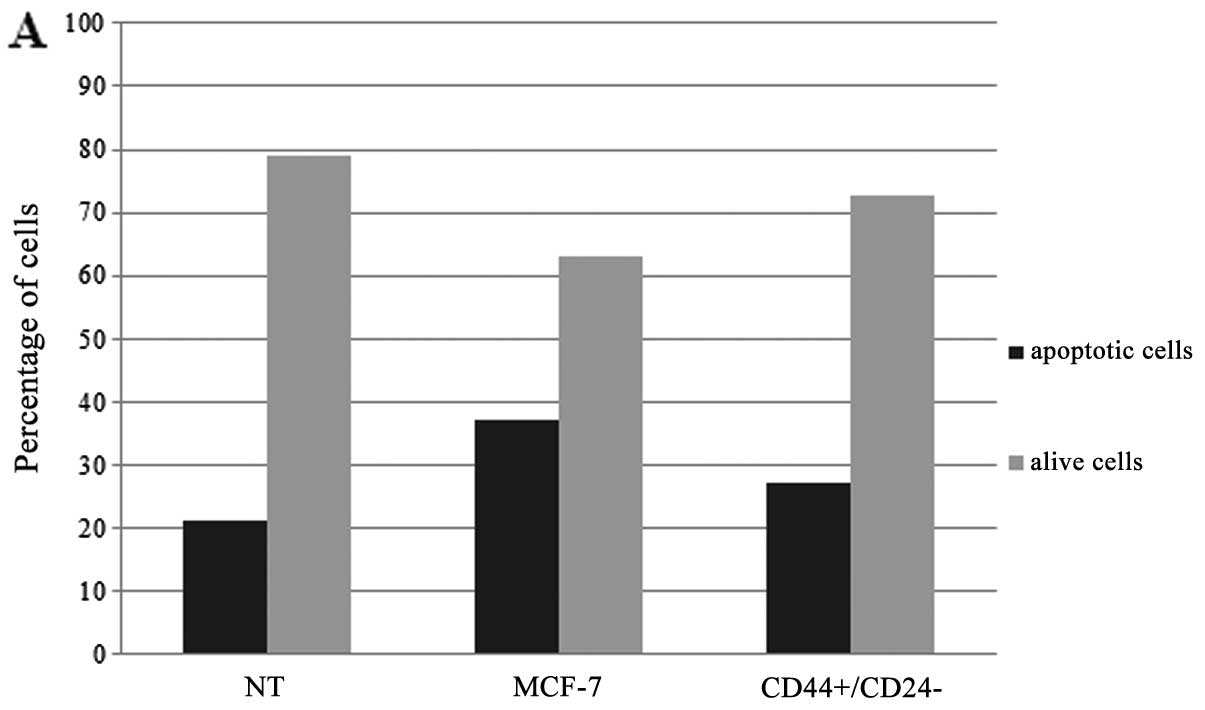
Abedin MJ, Wang D, McDonnell MA, Lehmann U
and Kelekar A: Autophagy delays apoptotic death in breast cancer
cells following DNA damage. Cell Death Differ. 14:500–510. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Codogno P and Meijer AJ: Autophagy and
signaling: their role in cell survival and cell death. Cell Death
Differ. 12:1509–1518. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lum JJ, Bauer DE, Kong M, Harris MH, Li C,
Lindsten T and Thompson CB: Growth factor regulation of autophagy
and cell survival in the absence of apoptosis. Cell. 120:237–248.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Beau I, Mehrpour M and Codogno P:
Autophagosomes and human diseases. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
43:460–464. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schneider L and Zhang J: Lysosomal
function in macromolecular homeostasis and bioenergetics in
Parkinson’s disease. Mol Neurodegener. Apr 13–2010.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Weissman IL, Anderson DJ and Gage F: Stem
and progenitor cells: origins, phenotypes, lineage commitments, and
transdifferentiations. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 17:387–403. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wright MH, Calcagno AM, Salcido CD,
Carlson MD, Ambudkar SV and Varticovski L: Brca1 breast tumors
contain distinct CD44+/CD24− and
CD133+ cells with cancer stem cell characteristics.
Breast Cancer Res. 10:R102008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fillmore CM and Kuperwasser C: Human
breast cancer cell lines contain stem-like cells that self-renew,
give rise to phenotypically diverse progeny and survive
chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res. 10:R252008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim HJ, Kim JB, Lee KM, Shin I, Han W, Ko
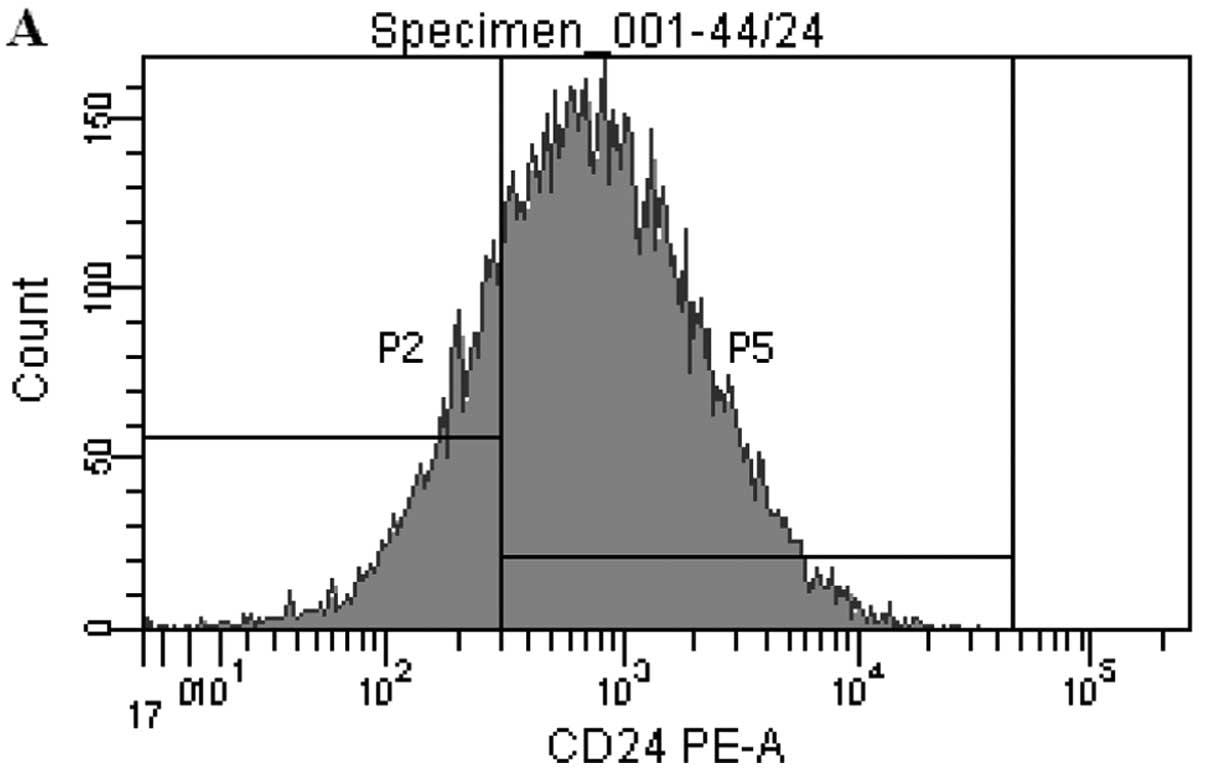
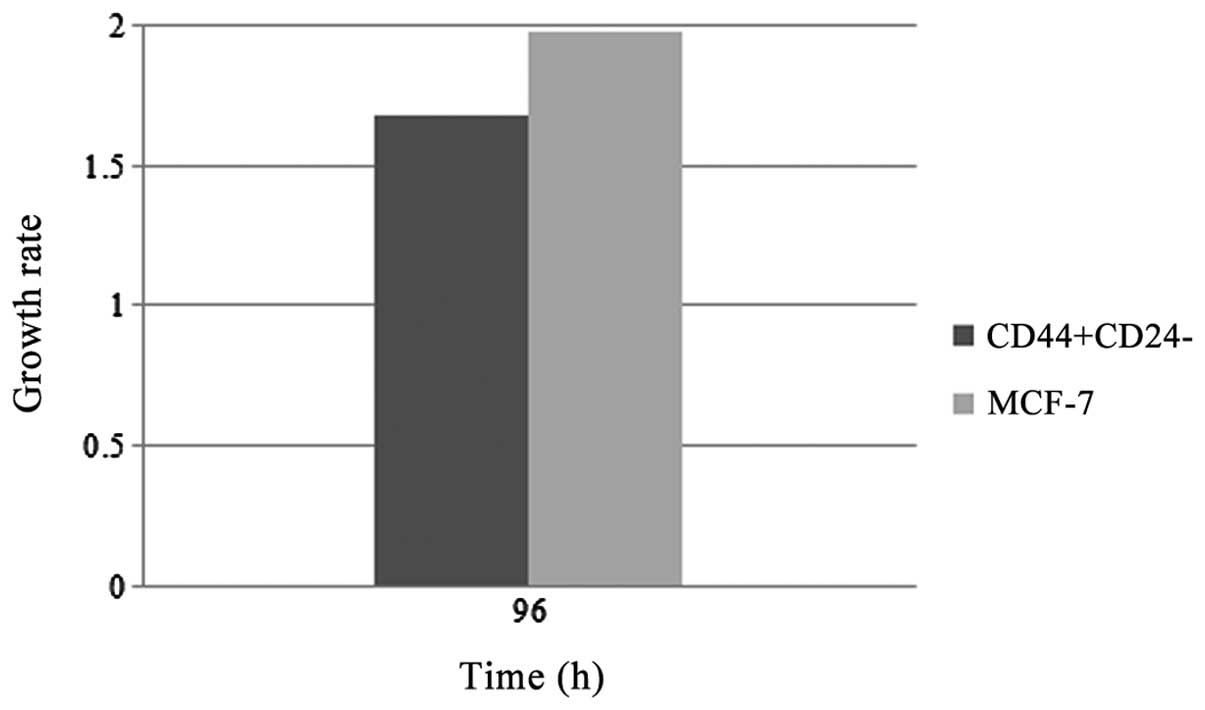
E, Bae JY and Noh DY: Isolation of CD24high and
CD24low/− cells from MCF-7: CD24 expression is
positively related with proliferation, adhesion and invasion in
MCF-7. Cancer Lett. 258:98–108. 2007.
|
|
32
|
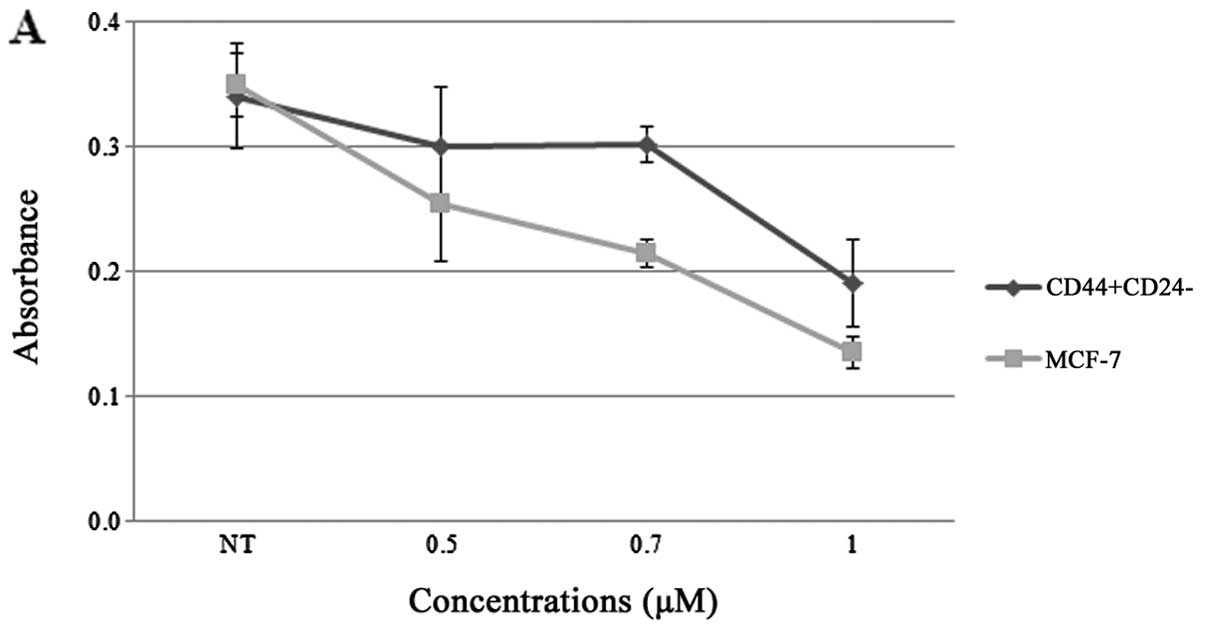
Li X, Lewis MT, Huang J, Gutierrez C,
Osborne CK, Wu MF, Hilsenbeck SG, Pavlick A, Zhang X, Chamness GC,
Wong H, Rosen J and Chang JC: Intrinsic resistance of tumorigenic
breast cancer cells to chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst.
100:672–679. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|