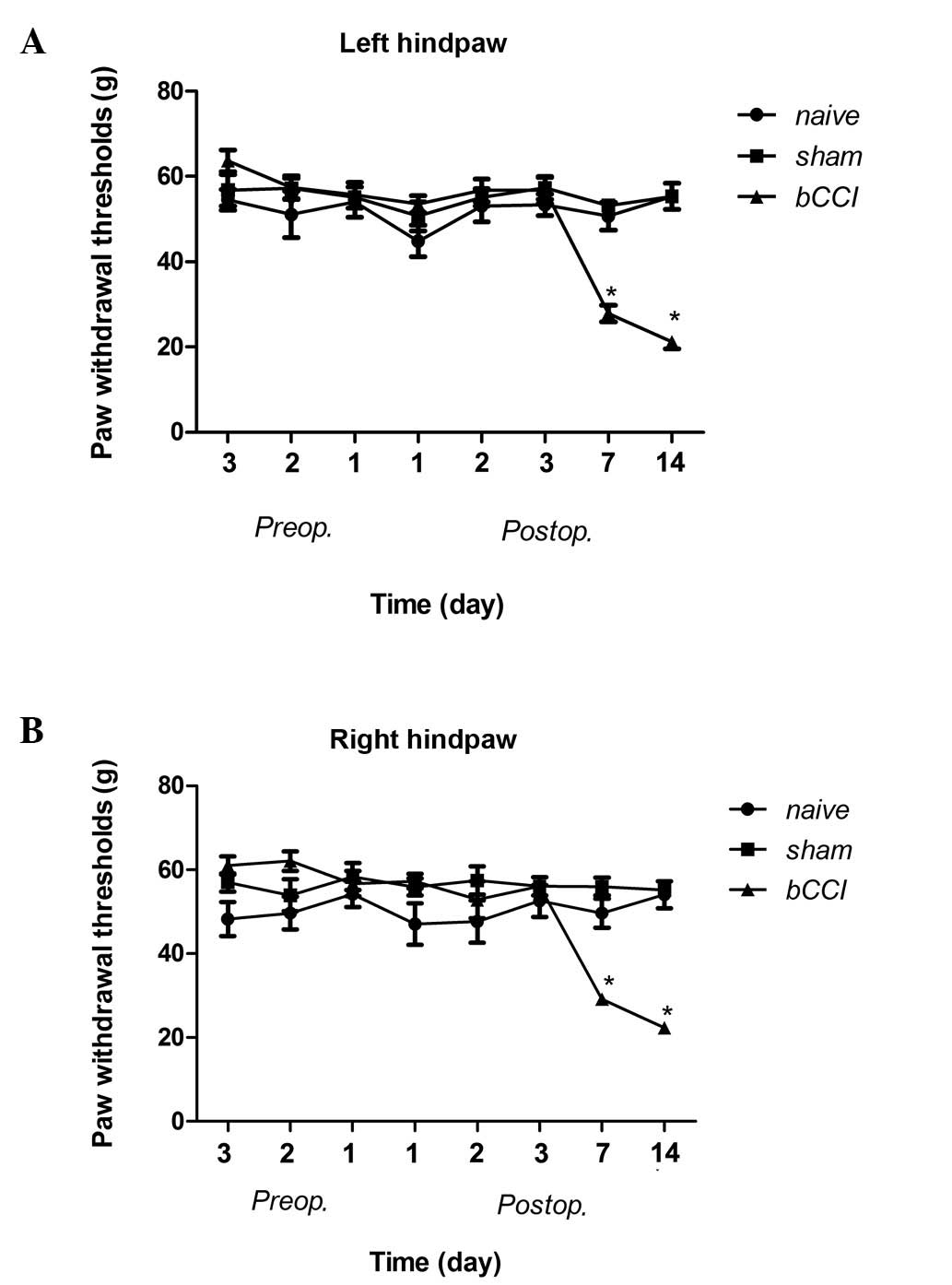
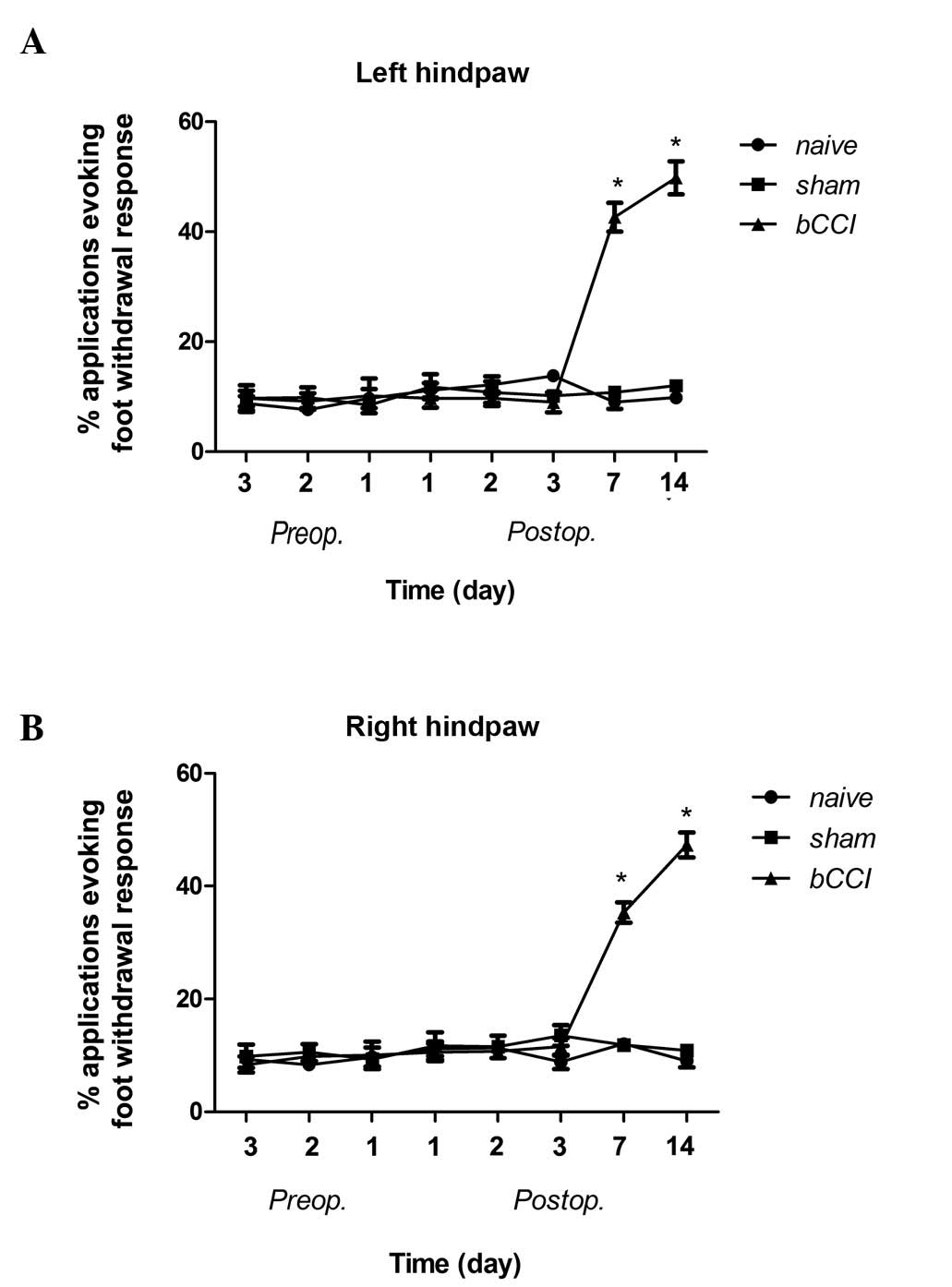
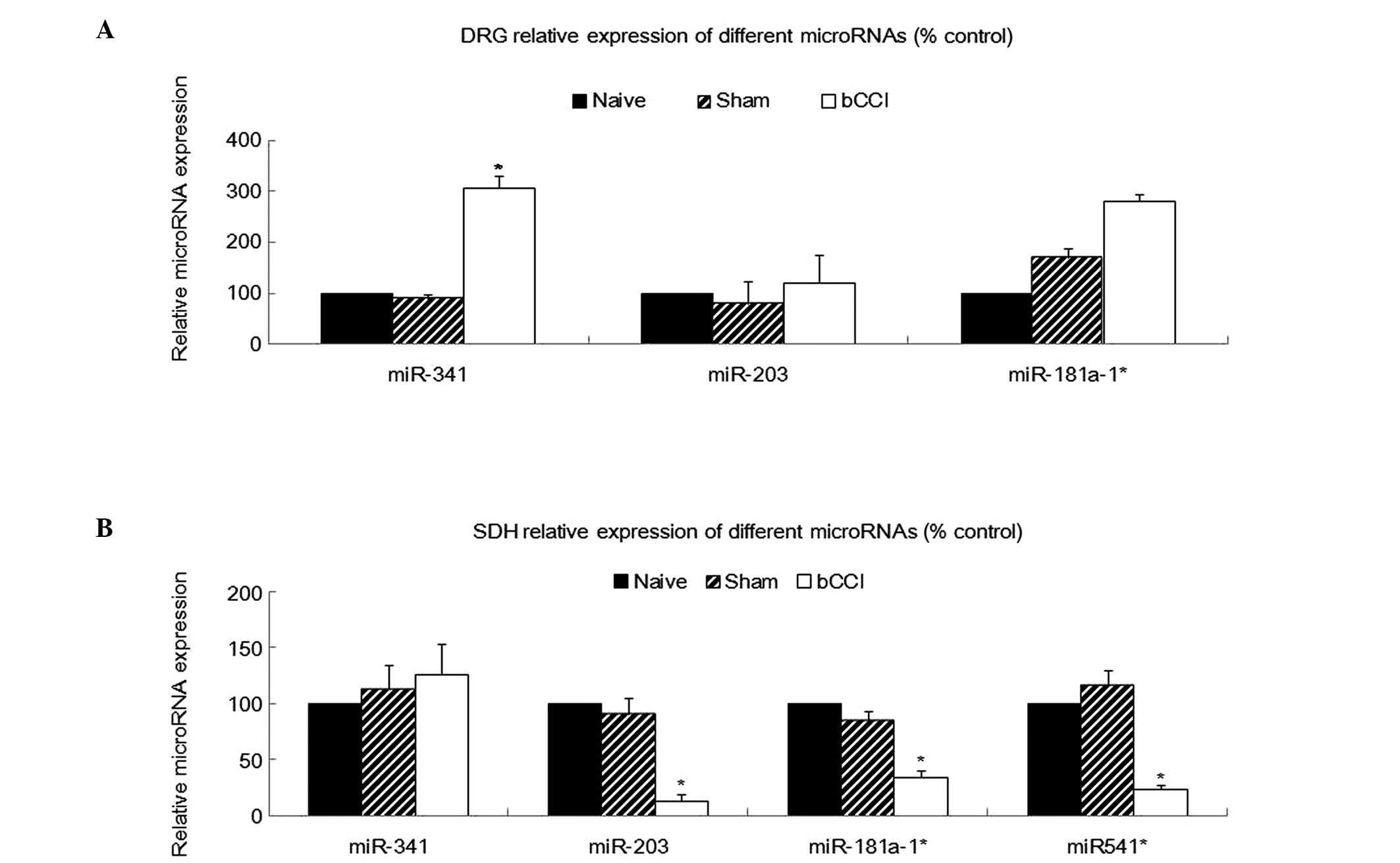
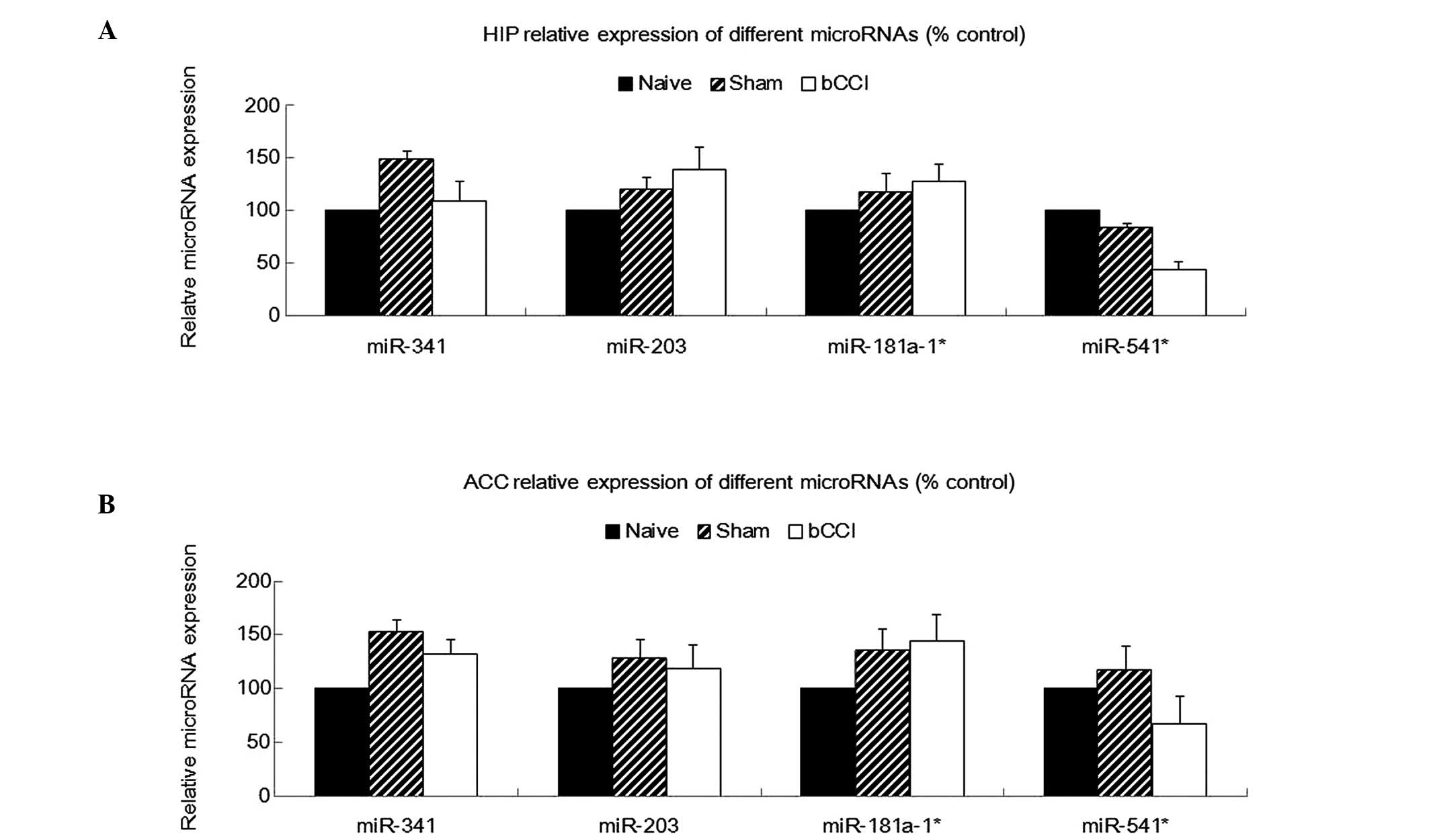
|
1.
|
Treede RD, Jensen TS, Campbell JN, et al:
Neuropathic pain: redefinition and a grading system for clinical
and research purposes. Neurology. 70:1630–1635. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Haanpää M, Attal N, Backonja M, et al:
NeuPSIG guidelines on neuropathic pain assessment. Pain. 152:14–27.
2011.
|
|
3.
|
Green L and McGhie J: Assessment of acute
and chronic pain. Anaesth Intensive Care Med. 12:9–11. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Bie B, Brown DL and Naguib M: Increased
synaptic GluR1 subunits in the anterior cingulate cortex of rats
with peripheral inflammation. Eur J Pharmacol. 653:26–31. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Boroujerdi A, Zeng J, Sharp K, Kim D,
Steward O and Luo ZD: Calcium channel alpha-2-delta-1 protein
upregulation in dorsal spinal cord mediates spinal cord
injury-induced neuropathic pain states. Pain. 152:649–655. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Chou CW, Wong GT, Lim G, et al: Peripheral
nerve injury alters the expression of NF-kappaB in the rat’s
hippocampus. Brain Res. 1378:66–71. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Emery EC, Young GT, Berrocoso EM, Chen L
and McNaughton PA: HCN2 ion channels play a central role in
inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Science. 333:1462–1466. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Jaggi AS and Singh N: Role of different
brain areas in peripheral nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain.
Brain Res. 1381:187–201. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Vogt BA: Pain and emotion interactions in
subregions of the cingulate gyrus. Nat Rev Neurosci. 6:533–544.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Hodgdon KE, Hingtgen CM and Nicol GD:
Dorsal root ganglia isolated from Nf1+/− mice exhibit
increased levels of mRNA expression of voltage-dependent sodium
channels. Neuroscience. 206:237–244. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Kim DS, Figueroa KW, Li KW, Boroujerdi A,
Yolo T and Luo ZD: Profiling of dynamically changed gene expression
in dorsal root ganglia post peripheral nerve injury and a critical
role of injury-induced glial fibrillary acetic protein in
maintenance of pain behaviors. Pain. 143:114–122. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Cady RJ, Glenn JR, Smith KM and Durham PL:
Calcitonin gene-related peptide promotes cellular changes in
trigeminal neurons and glia implicated in peripheral and central
sensitization. Mol Pain. 7:942011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Uchida H, Ma L and Ueda H: Epigenetic gene
silencing underlies C-fiber dysfunctions in neuropathic pain. J
Neurosci. 30:4806–4814. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Aldrich BT, Frakes EP, Kasuya J, Hammond
DL and Kitamoto T: Changes in expression of sensory organ-specific
microRNAs in rat dorsal root ganglia in association with mechanical
hyper-sensitivity induced by spinal nerve ligation. Neuroscience.
164:711–723. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Bak M, Silahtaroglu A, Moller M, et al:
MicroRNA expression in the adult mouse central nervous system. RNA.
14:432–444. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Bastian I, Tam Tam S, Zhou X-F, et al:
Differential expression of microRNA-1 in dorsal root ganglion
neurons. Histochem Cell Biol. 135:37–45. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
von Schack D, Agostino MJ, Murray BS, et
al: Dynamic changes in the microRNA expression profile reveal
multiple regulatory mechanisms in the spinal nerve ligation model
of neuropathic pain. PLoS One. 6:e176702011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Chiang HR, Schoenfeld LW, Ruby JG, et al:
Mammalian microRNAs: experimental evaluation of novel and
previously annotated genes. Genes Dev. 24:992–1009. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Hua YJ, Tang ZY, Tu K, et al:
Identification and target prediction of miRNAs specifically
expressed in rat neural tissue. BMC Genomics. 10:2142009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Kosik KS: The neuronal microRNA system.
Nat Rev Neurosci. 7:911–920. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Wheeler G, Ntounia-Fousara S, Granda B,
Rathjen T and Dalmay T: Identification of new central nervous
system specific mouse microRNAs. FEBS Lett. 580:2195–2200. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Kusuda R, Cadetti F, Ravanelli MI, et al:
Differential expression of microRNAs in mouse pain models. Mol
Pain. 7:172011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Harraz MM, Dawson TM and Dawson VL:
MicroRNAs in Parkinson’s disease. J Chem Neuroanat. 42:127–130.
2011.
|
|
24.
|
Zhang HY, Zheng SJ, Zhao JH, et al:
MicroRNAs 144, 145, and 214 are down-regulated in primary neurons
responding to sciatic nerve transection. Brain Res. 1383:62–70.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Datta S, Chatterjee K, Kline RH and Wiley
RG: Behavioral and anatomical characterization of the bilateral
sciatic nerve chronic constriction (bCCI) injury: correlation of
anatomic changes and responses to cold stimuli. Mol Pain. 6:72010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
Vierck CJ, Acosta-Rua AJ and Johnson RD:
Bilateral chronic constriction of the sciatic nerve: a model of
long-term cold hyper-algesia. J Pain. 6:507–517. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM
and Yaksh TL: Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the
rat paw. J Neurosci Methods. 53:55–63. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Krichevsky AM, King KS, Donahue CP,
Khrapko K and Kosik KS: A microRNA array reveals extensive
regulation of microRNAs during brain development. RNA. 9:1274–1281.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Schratt GM, Tuebing F, Nigh EA, et al: A
brain-specific microRNA regulates dendritic spine development.
Nature. 439:283–289. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Mercader JM, Gonzalez JR, Lozano JJ, et
al: Aberrant brain microRNA target and miRISC gene expression in
the anx/anx anorexia mouse model. Gene. 497:181–190. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Wei L, Wang M, Qu X, et al: Differential
expression of microRNAs during allograft rejection. Am J
Transplant. 12:1113–1123. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Liu PT, Wheelwright M, Teles R, et al:
MicroRNA-21 targets the vitamin D-dependent antimicrobial pathway
in leprosy. Nat Med. 18:267–273. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Kocerha J, Faghihi MA, Lopez-Toledano MA,
et al: MicroRNA-219 modulates NMDA receptor-mediated
neurobehavioral dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:3507–3512.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Zhao J, Lee MC, Momin A, et al: Small RNAs
control sodium channel expression, nociceptor excitability, and
pain thresholds. J Neurosci. 30:10860–10871. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Kuner R: Central mechanisms of
pathological pain. Nature Med. 16:1258–1266. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Gold MS and Gebhart GF: Nociceptor
sensitization in pain pathogenesis. Nature Med. 16:1248–1257. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Ruangsri S, Lin A, Mulpuri Y, Lee K,
Spigelman I and Nishimura I: Relationship of axonal voltage-gated
sodium channel 1.8 (NaV1.8) mRNA accumulation to sciatic nerve
injury-induced painful neuropathy in rats. J Biol Chem.
286:39836–39847. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Huang B, Zhao X, Zheng LB, Zhang L, Ni B
and Wang YW: Different expression of tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinase family members in rat dorsal root ganglia and
their changes after peripheral nerve injury. Neuroscience.
193:421–428. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41.
|
Koturbash I, Zemp F, Kolb B and Kovalchuk
O: Sex-specific radiation-induced microRNAome responses in the
hippocampus, cerebellum and frontal cortex in a mouse model. Mutat
Res. 722:114–118. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Rao MK, Pham J, Imam JS, et al:
Tissue-specific RNAi reveals that WT1 expression in nurse cells
controls germ cell survival and spermatogenesis. Genes Dev.
20:147–152. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Bo J, Yang G, Huo K, et al: microRNA-203
suppresses bladder cancer development by repressing bcl-w
expression. FEBS J. 278:786–792. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Elmén J, Lindow M, Schütz S, et al:
LNA-mediated microRNA silencing in non-human primates. Nature.
452:896–899. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Broderick JA and Zamore PD: MicroRNA
therapeutics. Gene Ther. 18:1104–1110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|