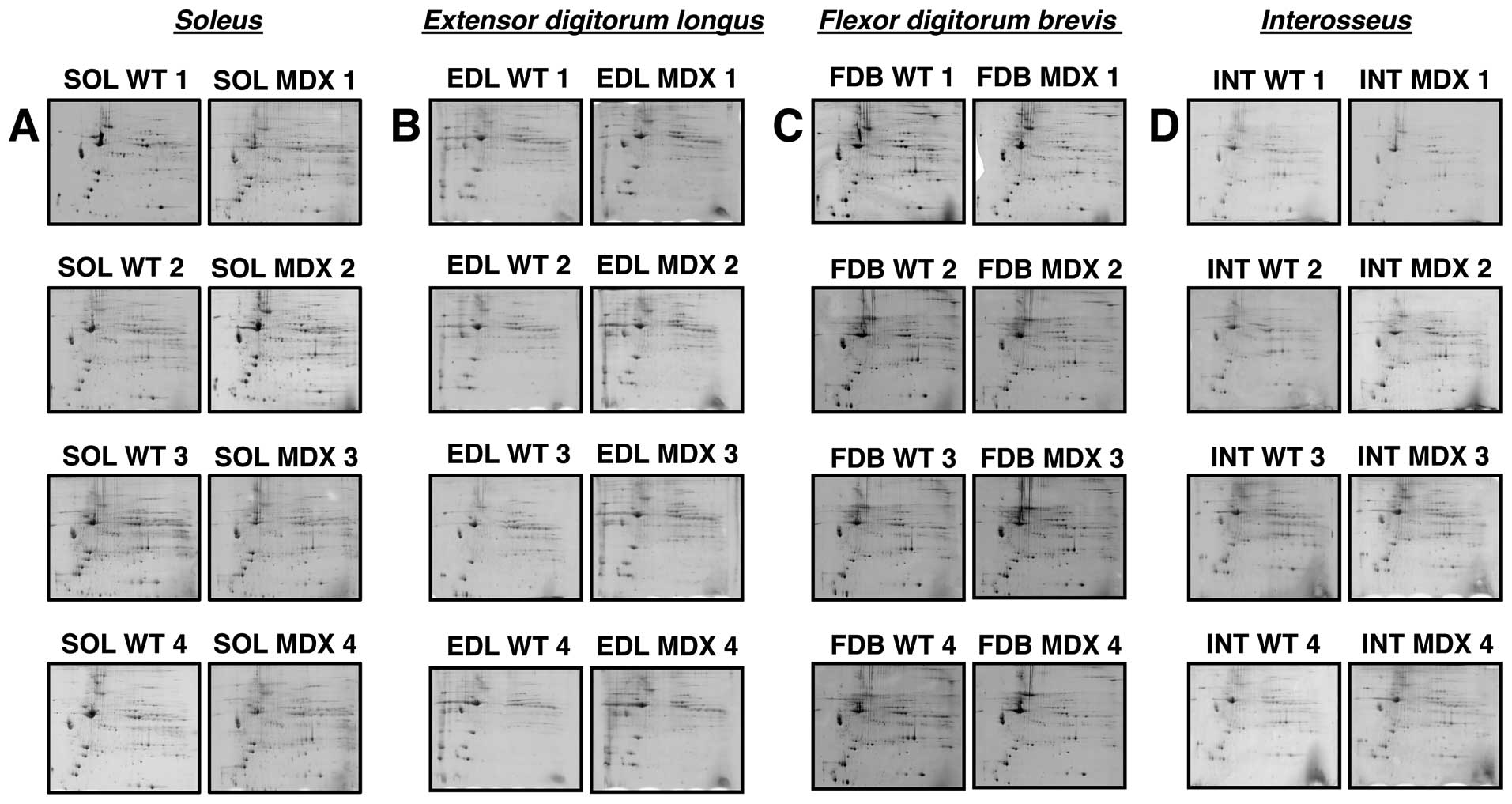
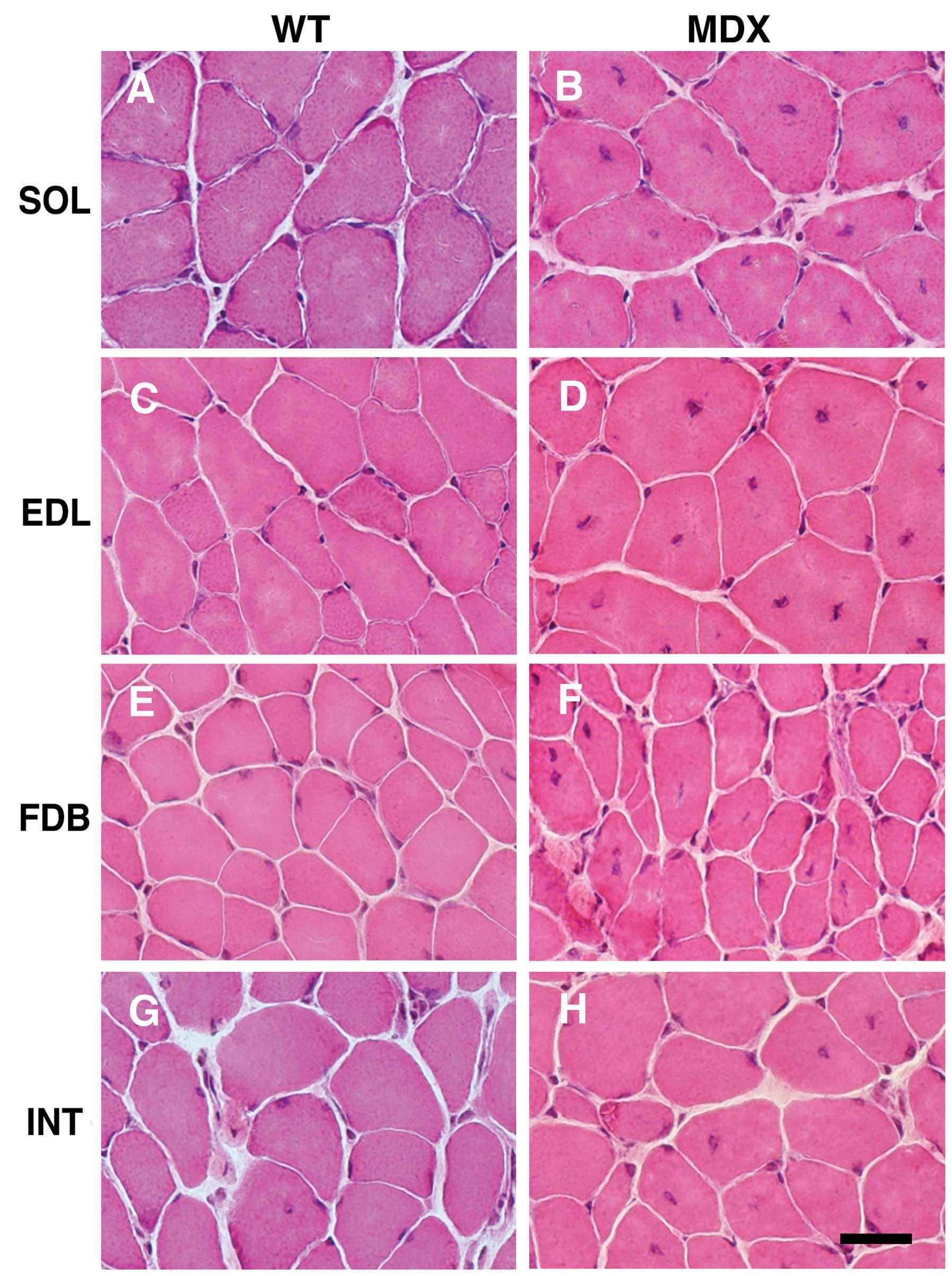
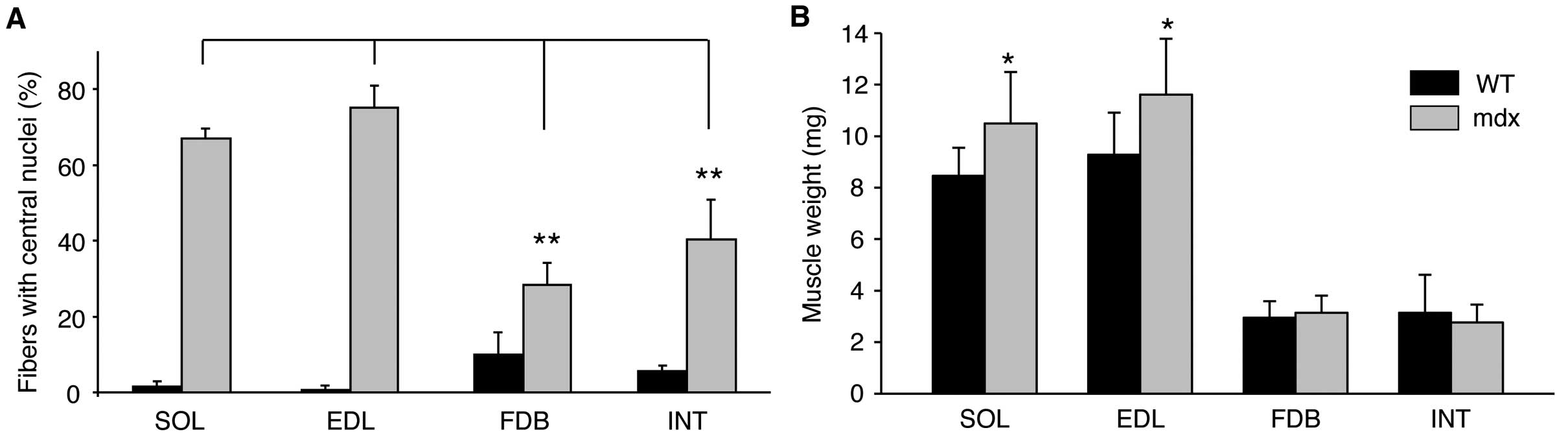
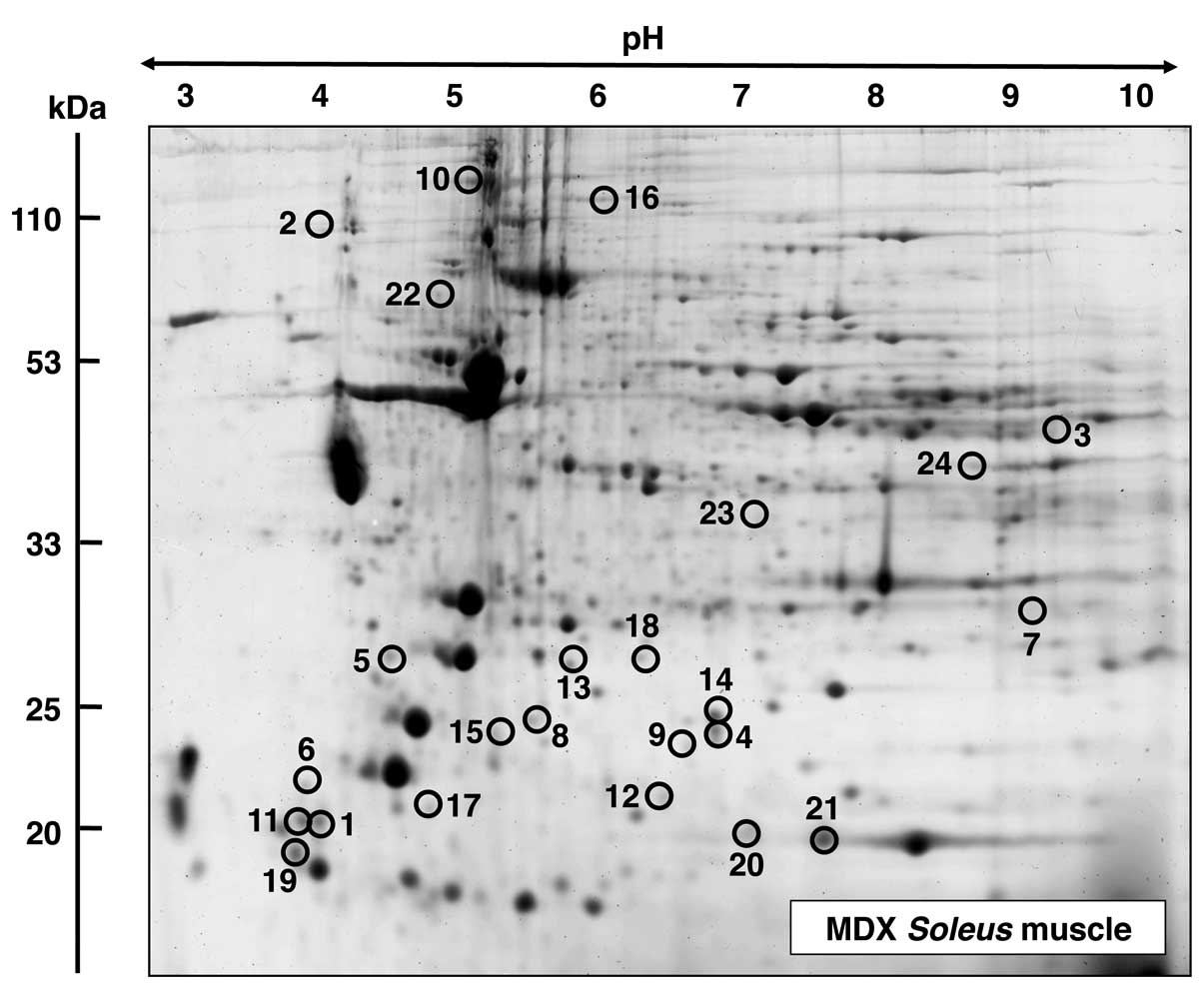
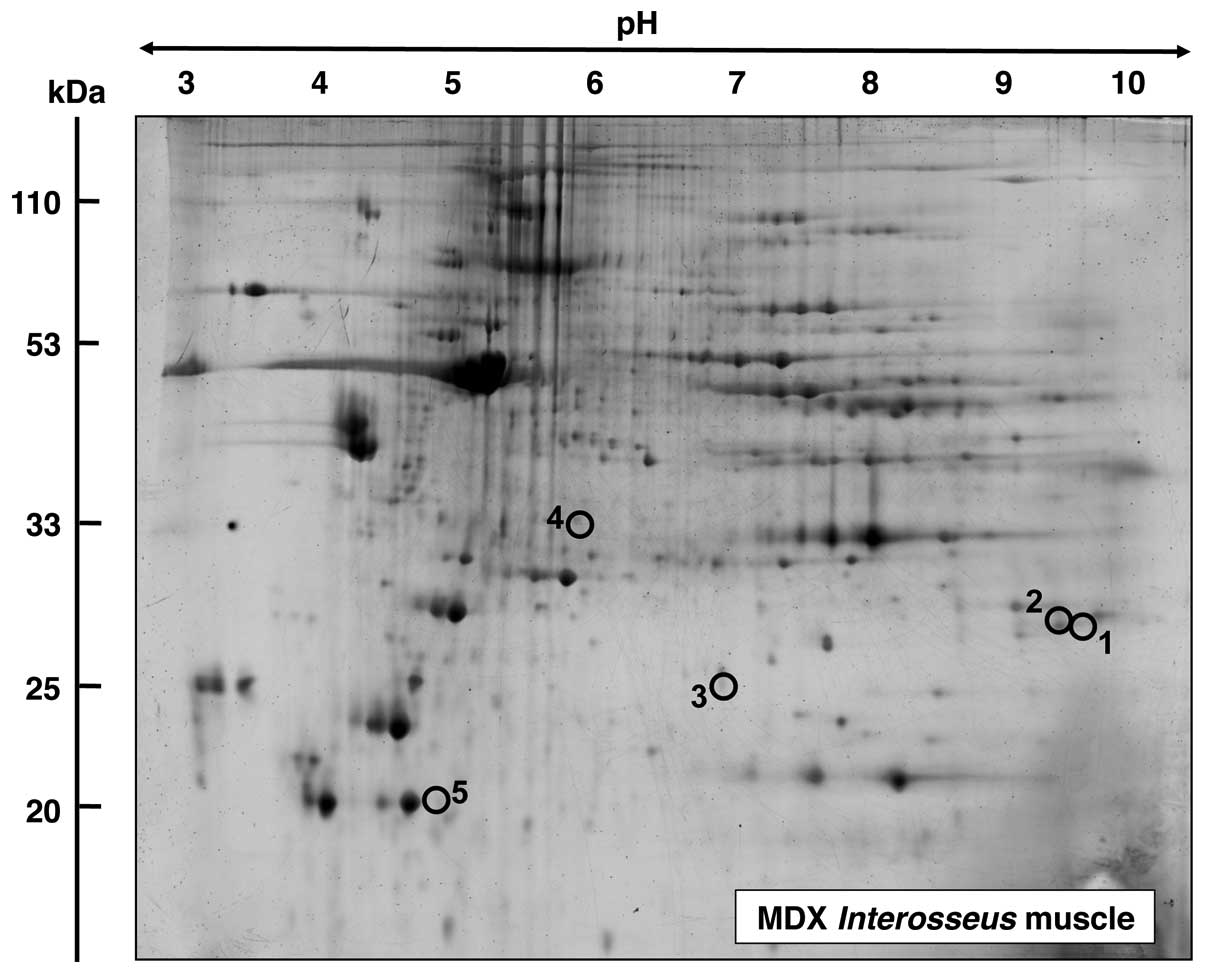
|
1
|
Bushby K, Finkel R, Birnkrant DJ, Case LE,
Clemens PR, Cripe L, Kaul A, Kinnett K, McDonald C, Pandya S,
Poysky J, Shapiro F, Tomezsko J and Constantin C: Diagnosis and
management of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, part 1: diagnosis, and
pharmacological and psychosocial management. Lancet Neurol.
9:77–93. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dalkilic I and Kunkel LM: Muscular
dystrophies: genes to pathogenesis. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
13:231–238. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Guglieri M and Bushby K: Molecular
treatments in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Curr Opin Pharmacol.
10:331–337. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mosqueira M, Zeiger U, Förderer M,
Brinkmeier H and Fink RH: Cardiac and respiratory dysfunction in
Duchenne muscular dystrophy and the role of second messengers. Med
Res Rev. April 30–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
5
|
Partridge TA: Impending therapies for
Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Curr Opin Neurol. 24:415–422. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Spurney CF, Gordish-Dressman H, Guerron
AD, Sali A, Pandey GS, Rawat R, Van Der Meulen JH, Cha HJ, Pistilli
EE, Partridge TA, Hoffman EP and Nagaraju K: Preclinical drug
trials in the mdx mouse: assessment of reliable and sensitive
outcome measures. Muscle Nerve. 39:591–602. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Banks GB and Chamberlain JS: The value of
mammalian models for duchenne muscular dystrophy in developing
therapeutic strategies. Curr Top Dev Biol. 84:431–453. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Durbeej M and Campbell KP: Muscular
dystrophies involving the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex: an
overview of current mouse models. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 12:349–361.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tutdibi O, Brinkmeier H, Rüdel R and Föhr
KJ: Increased calcium entry into dystrophin-deficient muscle fibres
of MDX and ADR-MDX mice is reduced by ion channel blockers. J
Physiol. 515:859–868. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wells DJ and Wells KE: What do animal
models have to tell us regarding Duchenne muscular dystrophy? Acta
Myol. 24:172–180. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sicinski P, Geng Y, Ryder-Cook AS, Barnard
EA, Darlison MG and Barnard PJ: The molecular basis of muscular
dystrophy in the mdx mouse: a point mutation. Science.
244:1578–1580. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dowling P, Lohan J and Ohlendieck K:
Comparative analysis of Dp427-deficient mdx tissues shows that the
milder dystrophic phenotype of extraocular and toe muscle fibres is
associated with a persistent expression of beta-dystroglycan. Eur J
Cell Biol. 82:222–230. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Marques MJ, Ferretti R, Vomero VU, Minatel
E and Neto HS: Intrinsic laryngeal muscles are spared from
myonecrosis in the mdx mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Muscle Nerve. 35:349–353. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Porter JD, Merriam AP, Khanna S, Andrade
FH, Richmonds CR, Leahy P, Cheng G, Karathanasis P, Zhou X, Kusner
LL, Adams ME, Willem M, Mayer U and Kaminski HJ: Constitutive
properties, not molecular adaptations, mediate extraocular muscle
sparing in dystrophic mdx mice. FASEB J. 17:893–895.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Carnwath JW and Shotton DM: Muscular
dystrophy in the mdx mouse: histopathology of the soleus and
extensor digitorum longus muscles. J Neurol Sci. 80:39–54. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Coulton GR, Morgan JE, Partridge TA and
Sloper JC: The mdx mouse skeletal muscle myopathy: I. A
histological, morphometric and biochemical investigation.
Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 14:53–70. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Torres LF and Duchen LW: The mutant mdx:
inherited myopathy in the mouse. Morphological studies of nerves,
muscles and end-plates. Brain. 110:269–299. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Stedman HH, Sweeney HL, Shrager JB,
Maguire HC, Panettieri RA, Petrof B, Narusawa M, Leferovich JM,
Sladky JT and Kelly AM: The mdx mouse diaphragm reproduces the
degenerative changes of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nature.
352:536–539. 1991. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dupont-Versteegden EE and McCarter RJ:
Differential expression of muscular dystrophy in diaphragm versus
hindlimb muscles of mdx mice. Muscle Nerve. 15:1105–1110. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lynch GS, Rafael JA, Hinkle RT, Cole NM,
Chamberlain JS and Faulkner JA: Contractile properties of diaphragm
muscle segments from old mdx and old transgenic mdx mice. Am J
Physiol. 272:C2063–C2068. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ohlendieck K: Proteomics of skeletal
muscle differentiation, neuromuscular disorders and fiber aging.
Expert Rev Proteomics. 7:283–296. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gelfi C, Vasso M and Cerretelli P:
Diversity of human skeletal muscle in health and disease:
contribution of proteomics. J Proteomics. 74:774–795. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ohlendieck K: Skeletal muscle proteomics:
current approaches, technical challenges and emerging techniques.
Skelet Muscle. 1:62011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ohlendieck K: Proteomic identification of
biomarkers of skeletal muscle disorders. Biomark Med. 7:169–186.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lewis C, Carberry S and Ohlendieck K:
Proteomic profiling of x-linked muscular dystrophy. J Muscle Res
Cell Motil. 30:267–269. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ge Y, Molloy MP, Chamberlain JS and
Andrews PC: Proteomic analysis of mdx skeletal muscle: great
reduction of adenylate kinase 1 expression and enzymatic activity.
Proteomics. 3:1895–1903. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ge Y, Molloy MP, Chamberlain JS and
Andrews PC: Differential expression of the skeletal muscle proteome
in mdx mice at different ages. Electrophoresis. 25:2576–2585. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Doran P, Dowling P, Lohan J, McDonnell K,
Poetsch S and Ohlendieck K: Subproteomics analysis of
Ca+-binding proteins demonstrates decreased
calsequestrin expression in dystrophic mouse skeletal muscle. Eur J
Biochem. 271:3943–3952. 2004.
|
|
29
|
Doran P, Dowling P, Donoghue P, Buffini M
and Ohlendieck K: Reduced expression of regucalcin in young and
aged mdx diaphragm indicates abnormal cytosolic calcium handling in
dystrophin-deficient muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1764:773–785.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Doran P, Martin G, Dowling P, Jockusch H
and Ohlendieck K: Proteome analysis of the dystrophin-deficient MDX
diaphragm reveals a drastic increase in the heat shock protein
cvHSP. Proteomics. 6:4610–4621. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Doran P, Wilton SD, Fletcher S and
Ohlendieck K: Proteomic profiling of antisense-induced exon
skipping reveals reversal of pathobiochemical abnormalities in
dystrophic mdx diaphragm. Proteomics. 9:671–685. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gardan-Salmon D, Dixon JM, Lonergan SM and
Selsby JT: Proteomic assessment of the acute phase of dystrophin
deficiency in mdx mice. Eur J Appl Physiol. 111:2763–2773. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Carberry S, Zweyer M, Swandulla D and
Ohlendieck K: Proteomics reveals drastic increase of extracellular
matrix proteins collagen and dermatopontin in the aged mdx
diaphragm model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Int J Mol Med.
30:229–234. 2012.
|
|
34
|
Carberry S, Zweyer M, Swandulla D and
Ohlendieck K: Profiling of age-related changes in the tibialis
anterior muscle proteome of the mdx mouse model of
dystrophinopathy. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012:6916412012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lewis C and Ohlendieck K: Proteomic
profiling of naturally protected extraocular muscles from the
dystrophin-deficient mdx mouse. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
396:1024–1029. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rayavarapu S, Coley W, Cakir E, Jahnke V,
Takeda S, Aoki Y, Gordish-Dressman H, Jaiswal JK, Hoffman EP, Brown
KJ, Hathout Y and Nagaraju K: Identification of disease specific
pathways using in vivo SILAC proteomics in dystrophin deficient mdx
mouse. Mol Cell Proteomics. 12:1061–1073. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Alagaratnam S, Mertens BJ, Dalebout JC,
Deelder AM, van Ommen GJ, den Dunnen JT and ‘t Hoen PA: Serum
protein profiling in mice: identification of Factor XIIIa as a
potential biomarker for muscular dystrophy. Proteomics.
8:1552–1563. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Colussi C, Banfi C, Brioschi M, Tremoli E,
Straino S, Spallotta F, Mai A, Rotili D, Capogrossi MC and Gaetano
C: Proteomic profile of differentially expressed plasma proteins
from dystrophic mice and following suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid
treatment. Proteomics Clin Appl. 4:71–83. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Gulston MK, Rubtsov DV, Atherton HJ,
Clarke K, Davies KE, Lilley KS and Griffin JL: A combined
metabolomic and proteomic investigation of the effects of a failure
to express dystrophin in the mouse heart. J Proteome Res.
7:2069–2077. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Johnson EK, Zhang L, Adams ME, Phillips A,
Freitas MA, Froehner SC, Green-Church KB and Montanaro F: Proteomic
analysis reveals new cardiac-specific dystrophin-associated
proteins. PLoS One. 7:e435152012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lewis C, Jockusch H and Ohlendieck K:
Proteomic profiling of the Dystrophin-deficient MDX heart reveals
drastically altered levels of key metabolic and contractile
proteins. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010:6485012010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Holland A, Dowling P, Zweyer M, Swandulla
D, Henry M, Clynes M and Ohlendieck K: Proteomic profiling of
cardiomyopathic tissue from the aged mdx model of Duchenne muscular
dystrophy reveals a drastic decrease in laminin, nidogen and
annexin. Proteomics. May 23–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
43
|
Jarmey C: The Atlas of Musculo-skeletal
Anatomy. Lotus Publishing; Chichester: 2004
|
|
44
|
Lieber RL: Skeletal muscle Structure,
Function, and Plasticity. 3rd edition. Lippincott Williams &
Wilkins; Baltimore, MD: 2009
|
|
45
|
Stal P, Eriksson PO, Eriksson A and
Thornell LE: Enzyme-histochemical differences in fibre-type between
the human major and minor zygomatic and the first dorsal
interosseus muscles. Arch Oral Biol. 32:833–841. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Staron RS: Human skeletal muscle fiber
types: delineation, development, and distribution. Can J Appl
Physiol. 22:307–327. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mallouk N, Jacquemond V and Allard B:
Elevated subsarcolemmal Ca2+in mdx mouse skeletal muscle
fibers detected with Ca2+-activated
K+channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:4950–4955.
2000.
|
|
48
|
Pritschow BW, Lange T, Kasch J,
Kunert-Keil C, Liedtke W and Brinkmeier H: Functional TRPV4
channels are expressed in mouse skeletal muscle and can modulate
resting Ca2+influx and muscle fatigue. Pflügers Arch.
461:115–122. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Boittin FX, Shapovalov G, Hirn C and Rüegg
UT: Phospholipase A2-derived lysophosphatidylcholine triggers
Ca2+entry in dystrophic skeletal muscle fibers. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 391:401–406. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Teichmann MD, Wegner FV, Fink RH,
Chamberlain JS, Launikonis BS, Martinac B and Friedrich O:
Inhibitory control over Ca2+ sparks via mechanosensitive
channels is disrupted in dystrophin deficient muscle but restored
by mini-dystrophin expression. PLoS One. 3:e36442008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ohlendieck K and Campbell KP:
Dystrophin-associated proteins are greatly reduced in skeletal
muscle from mdx mice. J Cell Biol. 115:1685–1694. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Krüger J, Kunert-Keil C, Bisping F and
Brinkmeier H: Transient receptor potential cation channels in
normal and dystrophic mdx muscle. Neuromuscul Disord. 18:501–513.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gannon J, Staunton L, O’Connell K, Doran P
and Ohlendieck K: Phosphoproteomic analysis of aged skeletal
muscle. Int J Mol Med. 22:33–42. 2008.
|
|
55
|
Rabilloud T, Strub JM, Luche S, van
Dorsselaer A and Lunardi J: A comparison between Sypro Ruby and
ruthenium II tris (bathophenanthroline disulfonate) as fluorescent
stains for protein detection in gels. Proteomics. 1:699–704. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lewis C and Ohlendieck K: Mass
spectrometric identification of dystrophin isoform Dp427 by
on-membrane digestion of sarcolemma from skeletal muscle. Anal
Biochem. 404:197–203. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Donoghue P, Doran P, Wynne K, Pedersen K,
Dunn MJ and Ohlendieck K: Proteomic profiling of chronic
low-frequency stimulated fast muscle. Proteomics. 7:3417–3430.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Staunton L, Jockusch H, Wiegand C,
Albrecht T and Ohlendieck K: Identification of secondary effects of
hyperexcitability by proteomic profiling of myotonic mouse muscle.
Mol Biosyst. 7:2480–2489. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kornegay JN, Childers MK, Bogan DJ, Bogan
JR, Nghiem P, Wang J, Fan Z, Howard JF Jr, Schatzberg SJ, Dow JL,
Grange RW, Styner MA, Hoffman EP and Wagner KR: The paradox of
muscle hypertrophy in muscular dystrophy. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N
Am. 23:149–172. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Andres-Mateos E, Brinkmeier H, Burks TN,
Mejias R, Files DC, Steinberger M, Soleimani A, Marx R, Simmers JL,
Lin B, Finanger Hedderick E, Marr TG, Lin BM, Hourde C, Leinwand
LA, Kuhl D, Foller M, Vogelsang S, Hernandez-Diaz I, Vaughan DK,
Alvarez de la Rosa D, Lang F and Cohn RD: Activation of
serum/glucocorticoid-induced kinase 1 (SGK1) is important to
maintain skeletal muscle homeostasis and prevent atrophy. EMBO Mol
Med. 5:80–91. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Gundersen K: Excitation-transcription
coupling in skeletal muscle: the molecular pathways of exercise.
Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 86:564–600. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zeiger U, Mitchell CH and Khurana TS:
Superior calcium homeostasis of extraocular muscles. Exp Eye Res.
91:613–622. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Swartz DR, Yang Z, Sen A, Tikunova SB and
Davis JP: Myofibrillar troponin exists in three states and there is
signal transduction along skeletal myofibrillar thin filaments. J
Mol Biol. 361:420–435. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Gordon AM, Homsher E and Regnier M:
Regulation of contraction in striated muscle. Physiol Rev.
80:853–924. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Gonzalez B, Negredo P, Hernando R and
Manso R: Protein variants of skeletal muscle regulatory myosin
light chain isoforms: prevalence in mammals, generation and
transitions during muscle remodelling. Pflügers Arch. 443:377–386.
2002.
|
|
66
|
Bozzo C, Spolaore B, Toniolo L, Stevens L,
Bastide B, Cieniewski-Bernard C, Fontana A, Mounier Y and Reggiani
C: Nerve influence on myosin light chain phosphorylation in slow
and fast skeletal muscles. FEBS J. 272:5771–5785. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Clark KA, McElhinny AS, Beckerle MC and
Gregorio CC: Striated muscle cytoarchitecture: an intricate web of
form and function. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 18:637–706. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Pette D and Staron RS: Myosin isoforms,
muscle fiber types, and transitions. Microsc Res Tech. 50:500–509.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Holland A and Ohlendieck K: Proteomic
profiling of the contractile apparatus from skeletal muscle. Expert
Rev Proteomics. (In press).
|
|
70
|
Donoghue P, Doran P, Dowling P and
Ohlendieck K: Differential expression of the fast skeletal muscle
proteome following chronic low-frequency stimulation. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1752:166–176. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Philippova M, Banfi A, Ivanov D,
Gianni-Barrera R, Allenspach R, Erne P and Resink T: Atypical
GPI-anchored T-cadherin stimulates angiogenesis in vitro and in
vivo. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 26:2222–2230. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Steinacker P, Aitken A and Otto M: 14-3-3
proteins in neurodegeneration. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 22:696–704.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Ohlendieck K: Proteomics of skeletal
muscle glycolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1804:2089–2101. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Gelfi C, Vigano A, De Palma S, Ripamonti
M, Begum S, Cerretelli P and Wait R: 2-D protein maps of rat
gastrocnemius and soleus muscles: a tool for muscle plasticity
assessment. Proteomics. 6:321–340. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Wells GD, Selvadurai H and Tein I:
Bioenergetic provision of energy for muscular activity. Paediatr
Respir Rev. 10:83–90. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Rakus D, Pasek M, Krotkiewski H and Dzugaj
A: Interaction between muscle aldolase and muscle fructose
1,6-bisphosphatase results in the substrate channeling.
Biochemistry. 43:14948149572004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Kim JW and Dang CV: Multifaceted roles of
glycolytic enzymes. Trends Biochem Sci. 30:142–150. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|