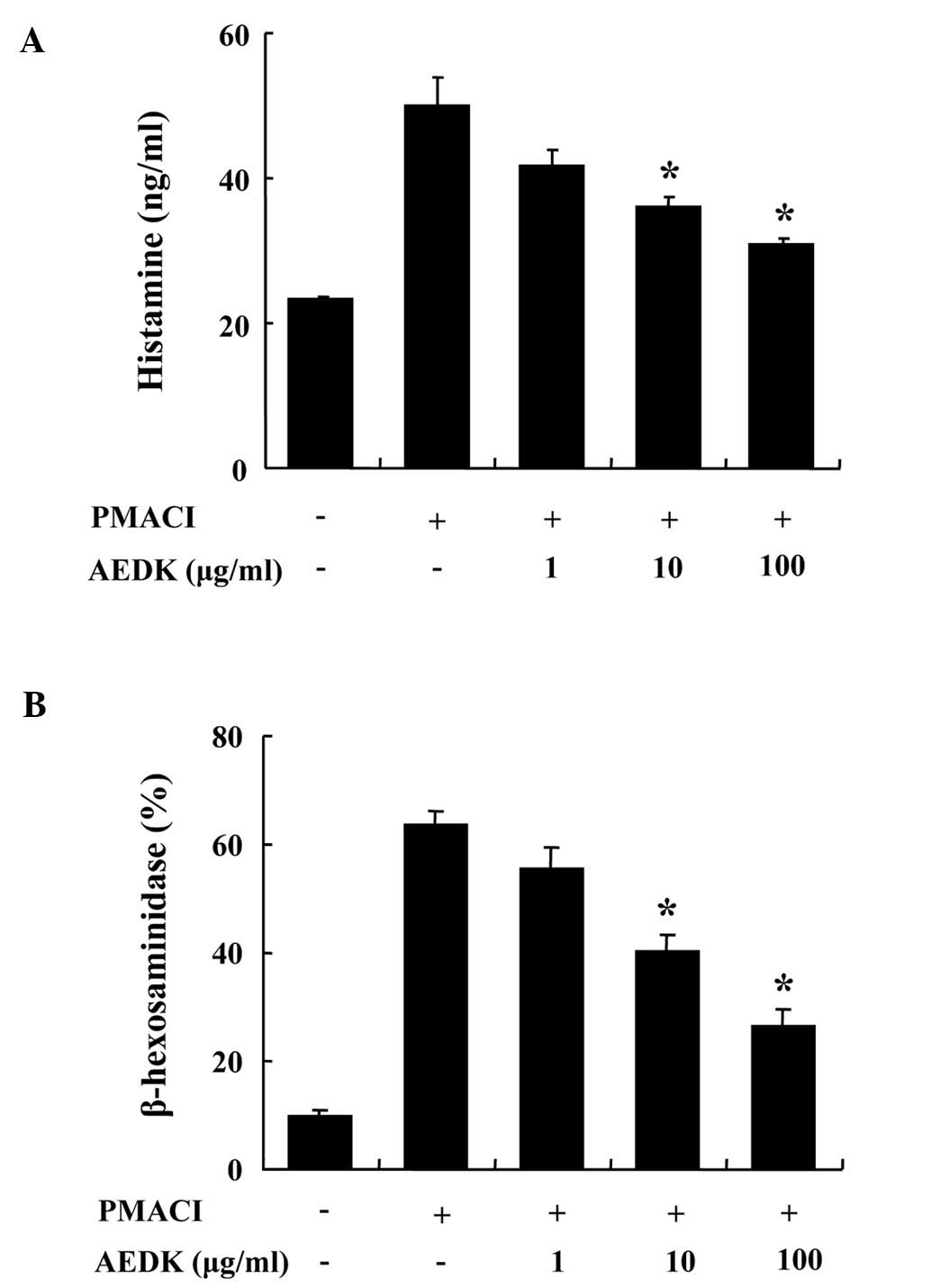
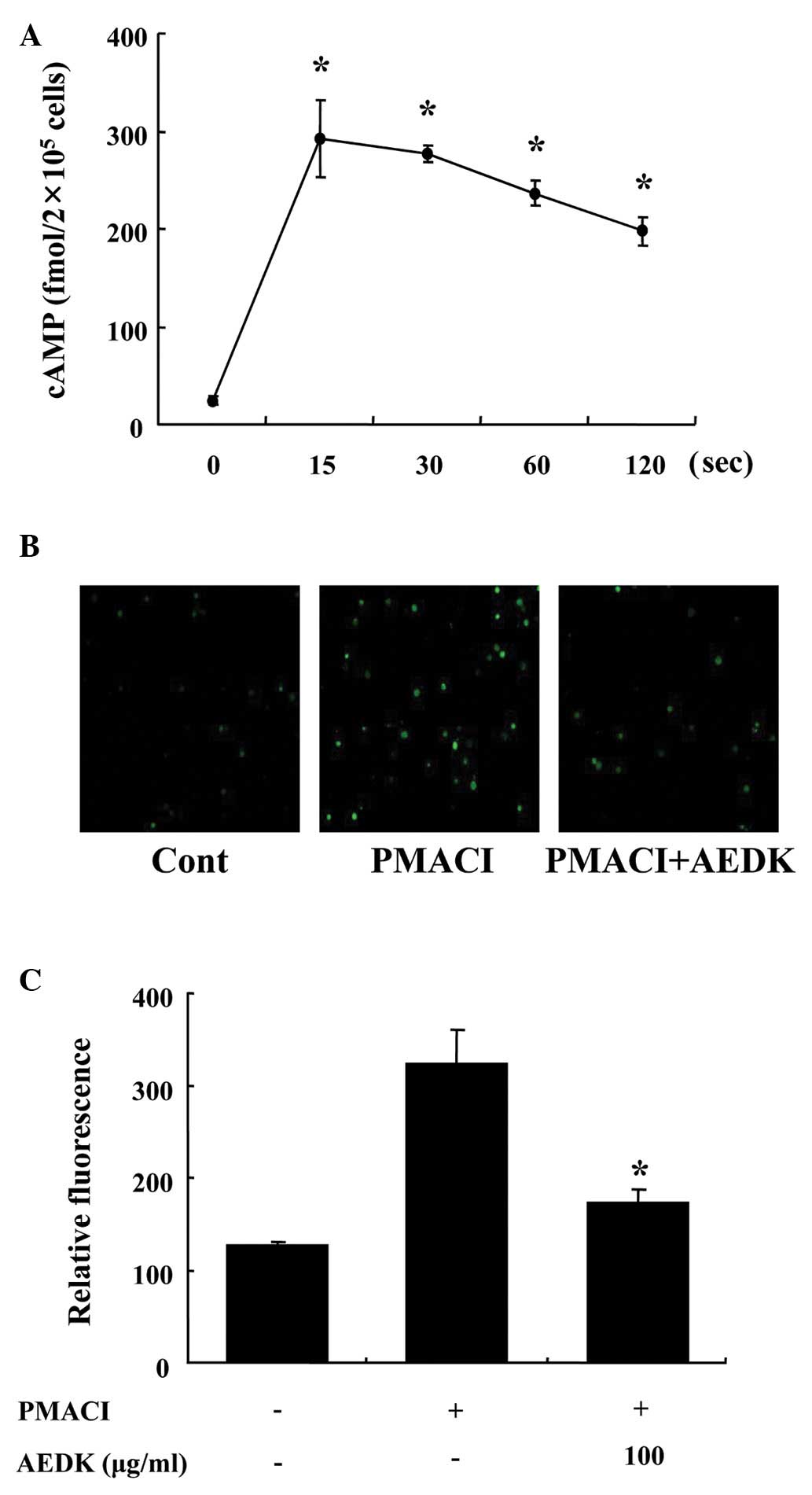
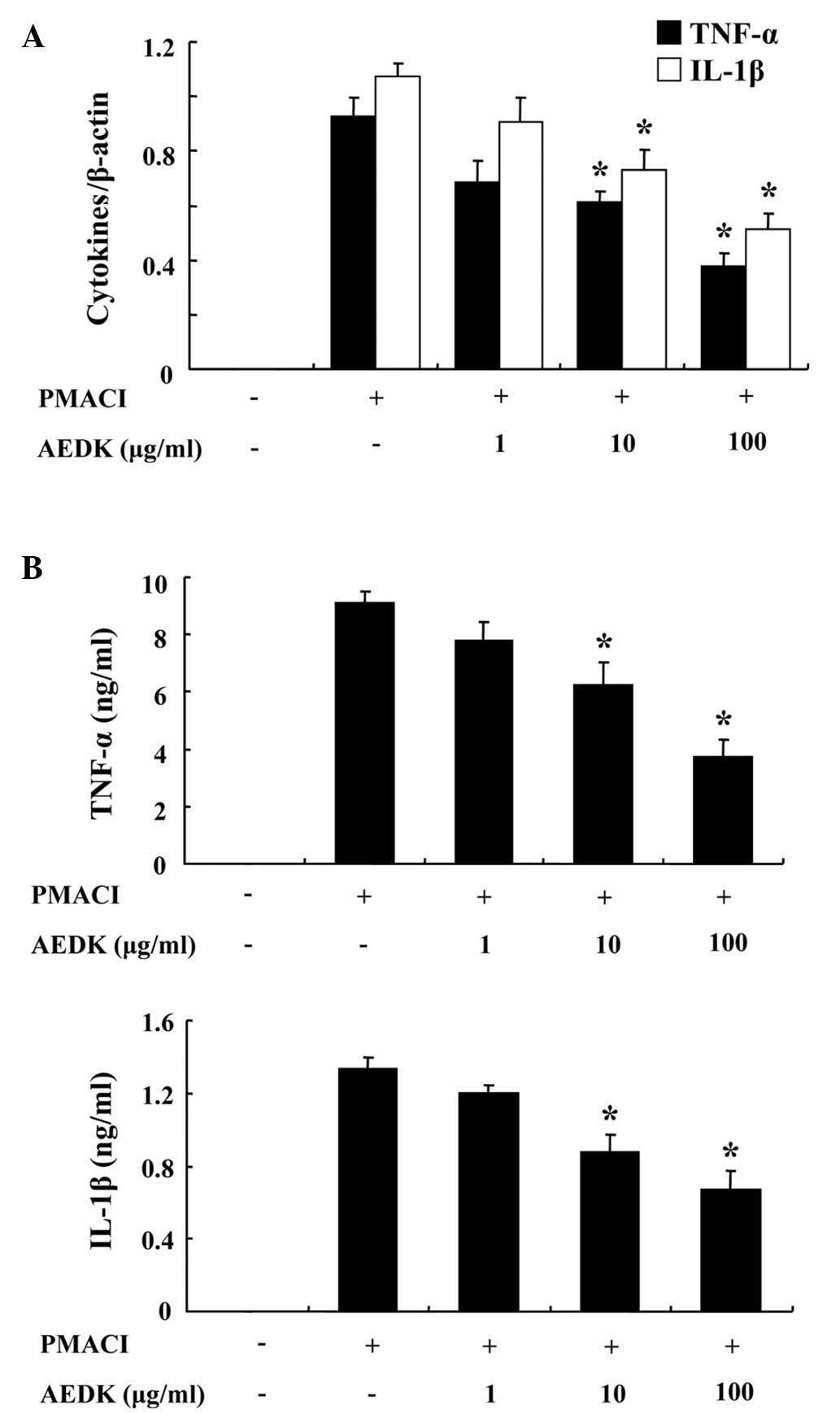
|
1
|
Caughey GH: Mast cell proteases as
protective and inflammatory mediators. Adv Exp Med Biol.
716:212–234. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Galli SJ, Tsai M and Piliponsky AM: The
development of allergic inflammation. Nature. 454:445–454. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Galli SJ, Kalesnikoff J, Grimbaldeston MA,
Piliponsky AM, Williams CM and Tsai M: Mast cells as ‘tunable’
effector and immunoregulatory cells: recent advances. Annu Rev
Immunol. 23:749–786. 2005.
|
|
4
|
Kim SH, Jun CD, Suk K, et al: Gallic acid
inhibits histamine release and pro-inflammatory cytokine production
in mast cells. Toxicol Sci. 91:123–131. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Amin K: The role of mast cells in allergic
inflammation. Respir Med. 106:9–14. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee DH, Kim SH, Eun JS and Shin TY:
Mosla dianthera inhibits mast cell-mediated allergic
reactions through the inhibition of histamine release and
inflammatory cytokine production. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
216:479–484. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tagen M, Elorza A, Kempuraj D, et al:
Mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2 inhibits mast cell activation
and reduces histamine content. J Immunol. 183:6313–6319. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gwack Y, Feske S, Srikanth S, Hogan PG and
Rao A: Signalling to transcription: store-operated Ca2+
entry and NFAT activation in lymphocytes. Cell Calcium. 42:145–156.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sismanopoulos N, Delivanis DA,
Alysandratos KD, et al: Mast cells in allergic and inflammatory
diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 18:2261–2277. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mallavadhani UV, Panda AK and Rao YR:
Pharmacology and chemotaxonomy of Diospyros. Phytochemistry.
49:901–951. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Duan J, Zheng Y, Dong Q and Fang J:
Structural analysis of a pectic polysaccharide from the leaves of
Diospyros kaki. Phytochemistry. 65:609–615. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Matsumoto N, Okushio K and Hara Y: Effect
of black tea polyphenols on plasma lipids in cholesterol-fed rats.
J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 44:337–342. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kotani M, Matsumoto M, Fujita A, et al:
Persimmon leaf extract and astragalin inhibit development of
dermatitis and IgE elevation in NC/Nga mice. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 106:159–166. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kameda K, Takaku T, Okuda H, et al:
Inhibitory effects of various flavonoids isolated from leaves of
persimmon on angiotensin-converting enzyme activity. J Nat Prod.
50:680–683. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Funayama S and Hikino H: Hypotensive
principles of Diospyros kaki leaves. Chem Pharm Bull
(Tokyo). 27:2865–2868. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sun L, Zhang J, Lu X, Zhang L and Zhang Y:
Evaluation to the antioxidant activity of total flavonoids extract
from persimmon (Diospyros kaki L.) leaves. Food Chem
Toxicol. 49:2689–2696. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Steinmetz KA and Potter JD: Vegetables,
fruit, and cancer prevention: a review. J Am Diet Assoc.
96:1027–1039. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rattmann YD, Cipriani TR, Sassaki GL, et
al: Nitric oxide-dependent vasorelaxation induced by extractive
solutions and fractions of Maytenus ilicifolia Mart ex
Reissek (Celastraceae) leaves. J Ethnopharmacol. 104:328–335. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ali K, Maltese F, Toepfer R, Choi YH and
Verpoorte R: Metabolic characterization of Palatinate German white
wines according to sensory attributes, varieties, and vintages
using NMR spectroscopy and multivariate data analyses. J Biomol
NMR. 49:255–266. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kim SH, Lee S, Kim IK, et al: Suppression
of mast cell-mediated allergic reaction by Amomum
xanthioides. Food Chem Toxicol. 45:2138–2144. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim HH, Yoo JS, Lee HS, Kwon TK, Shin TY
and Kim SH: Elsholtzia ciliata inhibits mast cell-mediated
allergic inflammation: role of calcium, p38 mitogen-activated
protein kinase and nuclear factor-{kappa}B. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
236:1070–1077. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Itoh T, Tsukane M, Koike M, et al:
Inhibitory effects of whisky congeners on IgE-mediated
degranulation in rat basophilic leukemia RBL-2H3 cells and passive
cutaneous anaphylaxis reaction in mice. J Agric Food Chem.
58:7149–7157. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bae Y, Lee S and Kim SH: Chrysin
suppresses mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation: involvement of
calcium, caspase-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 254:56–64. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee S, Yun HS and Kim SH: The comparative
effects of mesoporous silica nanoparticles and colloidal silica on
inflammation and apoptosis. Biomaterials. 32:9434–9443. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Eisenhut M and Wallace H: Ion channels in
inflammation. Pflugers Arch. 461:401–421. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Park HH, Lee S, Oh JM, et al:
Anti-inflammatory activity of fisetin in human mast cells (HMC-1).
Pharmacol Res. 55:31–37. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Boden SR and Wesley Burks A: Anaphylaxis:
a history with emphasis on food allergy. Immunol Rev. 242:247–257.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Beaven MA, Rogers J, Moore JP, Hesketh TR,
Smith GA and Metcalfe JC: The mechanism of the calcium signal and
correlation with histamine release in 2H3 cells. J Biol Chem.
259:7129–7136. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Alfonso A, Cabado AG, Vieytes MR and
Botana LM: Functional compartments in rat mast cells for cAMP and
calcium on histamine release. Cell Signal. 12:343–350. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Makino H, Saijo T, Ashida Y, Kuriki H and
Maki Y: Mechanism of action of an antiallergic agent, amlexanox
(AA-673), in inhibiting histamine release from mast cells.
Acceleration of cAMP generation and inhibition of
phosphodiesterase. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 82:66–71. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Walsh LJ, Trinchieri G, Waldorf HA,
Whitaker D and Murphy GF: Human dermal mast cells contain and
release tumor necrosis factor alpha, which induces endothelial
leukocyte adhesion molecule 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
88:4220–4224. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Karin M: NF-kappaB as a critical link
between inflammation and cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
1:a0001412009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bani D, Giannini L, Ciampa A, et al:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate reduces allergen-induced asthma-like
reaction in sensitized guinea pigs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
317:1002–1011. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|