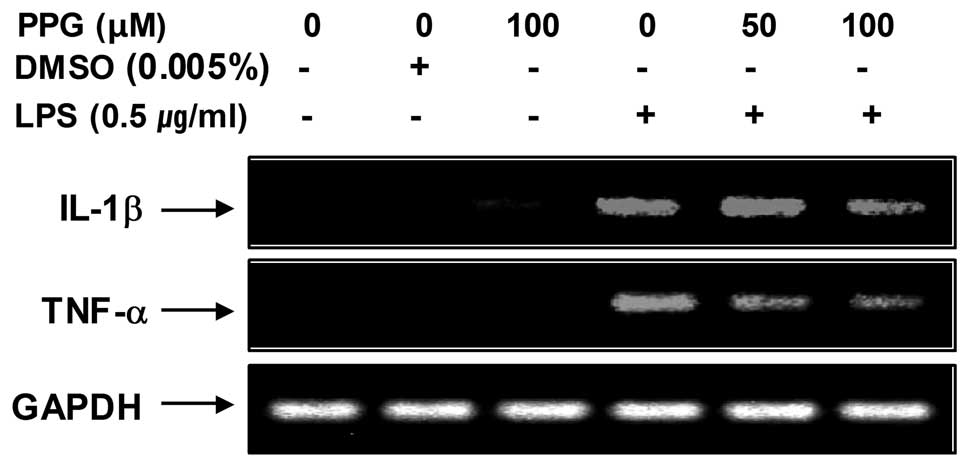
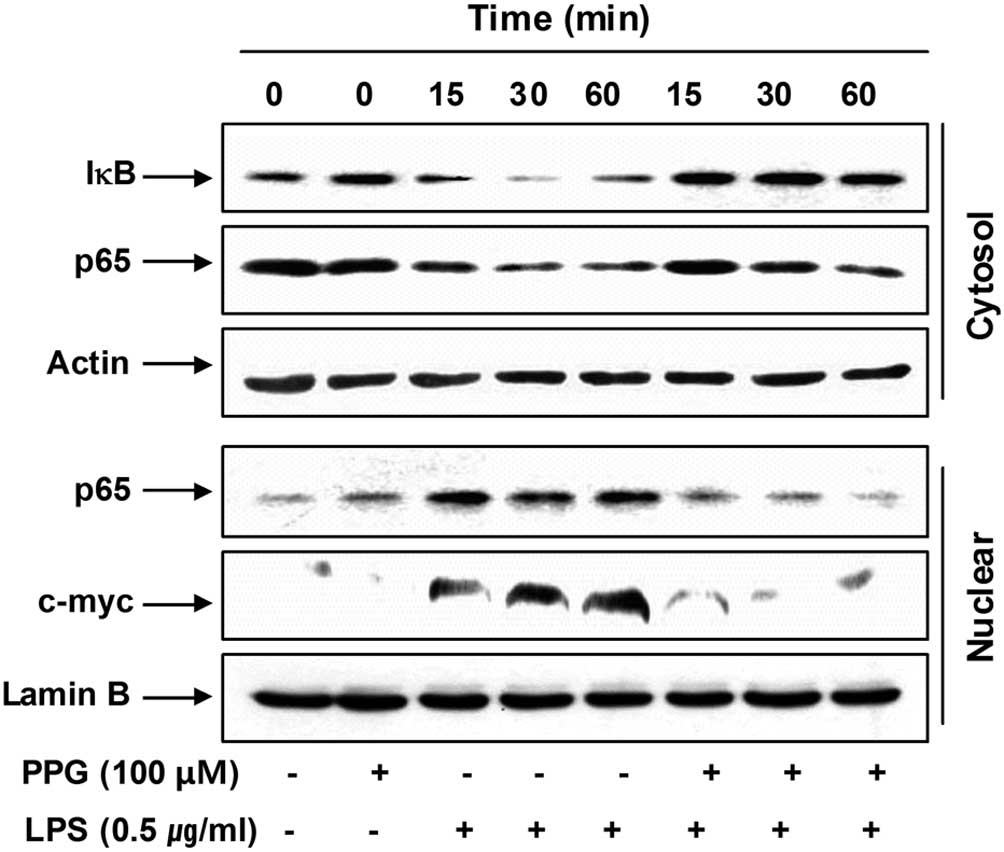
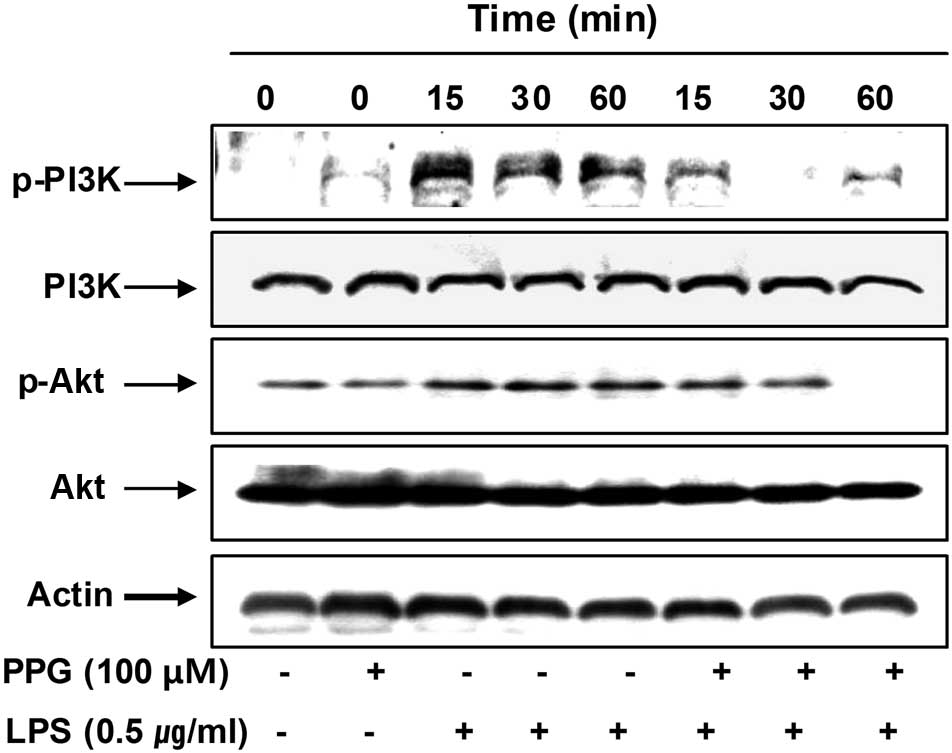
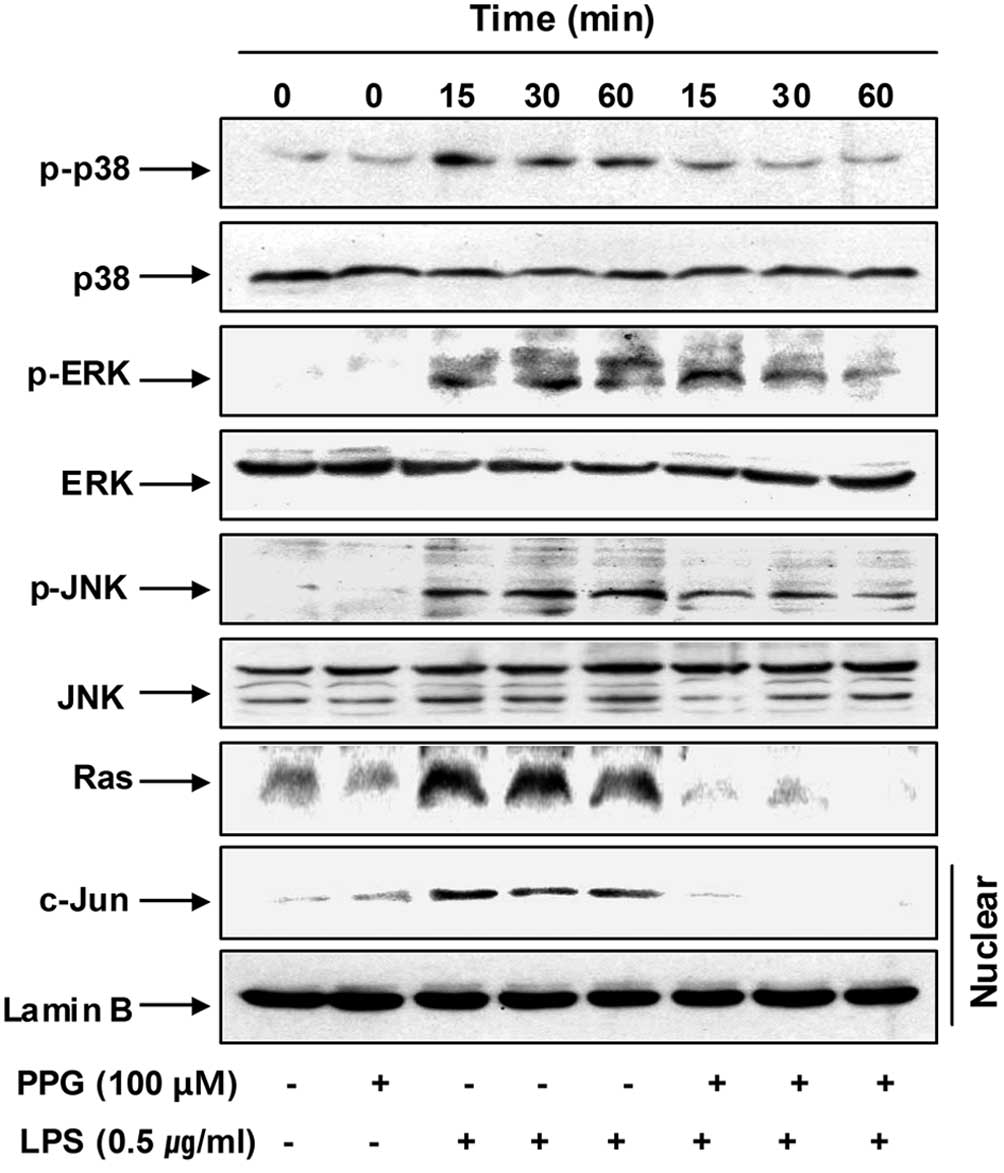
|
1
|
Mosley RL, Benner EJ, Kadiu I, Thomas M,
Boska MD, Hasan K, Laurie C and Gendelman HE: Neuroinflammation,
oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Clin
Neurosci Res. 6:261–281. 2006.
|
|
2
|
Reynolds A, Laurie C, Mosley RL and
Gendelman HE: Oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of
neurodegenerative disorders. Int Rev Neurobiol. 82:297–325. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Perry VH, Nicoll JA and Holmes C:
Microglia in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 6:193–201.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Rivest S: Molecular insights on the
cerebral innate immune system. Brain Behav Immun. 17:13–19. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Das S and Basu A: Inflammation: a new
candidate in modulating adult neurogenesis. J Neurosci Res.
86:1199–1208. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stadelmann C: Multiple sclerosis as a
neurodegenerative disease: pathology, mechanisms and therapeutic
implications. Curr Opin Neurol. 24:224–229. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lull ME and Block ML: Microglial
activation and chronic neurodegeneration. Neurotherapeutics.
7:354–365. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Long-Smith CM, Sullivan AM and Nolan YM:
The influence of microglia on the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s
disease. Prog Neurobiol. 89:277–287. 2009.
|
|
9
|
Dixon RA and Steele CL: Flavonoids and
isoflavonoids - a gold mine for metabolic engineering. Trends Plant
Sci. 4:394–400. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Le Marchand L, Murphy SP, Hankin JH,
Wilkens LR and Kolonel LN: Intake of flavonoids and lung cancer. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 92:154–160. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Szejtli J and Szente L: Elimination of
bitter, disgusting tastes of drugs and foods by cyclodextrins. Eur
J Pharm Biopharm. 61:115–125. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen D, Chen MS, Cui QC, Yang H and Dou
QP: Structure-proteasome-inhibitory activity relationships of
dietary flavonoids in human cancer cells. Front Biosci.
12:1935–1945. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Abou-Karam M and Shier WT: Inhibition of
oncogene product enzyme activity as an approach to cancer
chemoprevention. Tyrosine-specific protein kinase inhibition by
purpurogallin from Quercus sp nutgall. Phytother Res.
13:337–340. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wu TW, Zeng LH, Wu J, Fung KP, Weisel RD,
Hempel A and Camerman N: Molecular structure and antioxidant
specificity of purpurogallin in three types of human cardiovascular
cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 52:1073–1080. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Prasad K and Laxdal VA: Evaluation of
hydroxyl radical-scavenging property of purpurogallin using high
pressure liquid chromatography. Mol Cell Biochem. 135:153–158.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sugiyama H, Fung KP and Wu TW:
Purpurogallin as an antioxidant protector of human erythrocytes
against lysis by peroxyl radicals. Life Sci. 53:PL39–PL43. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Inamori Y, Muro C, Sajima E, Katagiri M,
Okamoto Y, Tanaka H, Sakagami Y and Tsujibo H: Biological activity
of purpurogallin. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 61:890–892. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Farnet CM, Wang B, Hansen M, Lipford JR,
Zalkow L, Robinson WE Jr, Siegel J and Bushman F: Human
immunodeficiency virus type 1 cDNA integration: new aromatic
hydroxylated inhibitors and studies of the inhibition mechanism.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 42:2245–2253. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lambert JD, Chen D, Wang CY, Ai N, Sang S,
Ho CT, Welsh WJ and Yang CS: Benzotropolone inhibitors of estradiol
methylation: kinetics and in silico modeling studies. Bioorg Med
Chem. 13:2501–2507. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fung KP, Wu TW and Lui CP: Purpurogallin
inhibits DNA synthesis of murine fibrosarcoma L-929 and human U-87
MG glioblastoma cells in vitro. Chemotherapy. 42:199–205. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kitada S, Leone M, Sareth S, Zhai D, Reed
JC and Pellecchia M: Discovery, characterization, and
structure-activity relationships studies of proapoptotic
polyphenols targeting B-cell lymphocyte/leukemia-2 proteins. J Med
Chem. 46:4259–4264. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Tang G, Yang CY, Nikolovska-Coleska Z, Guo
J, Qiu S, Wang R, Gao W, Wang G, Stuckey J, Krajewski K, Jiang S,
Roller PP and Wang S: Pyrogallol-based molecules as potent
inhibitors of the antiapoptotic Bcl-2 proteins. J Med Chem.
50:1723–1726. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Doulias PT, Nousis L, Zhu BZ, Frei B and
Galaris D: Protection by tropolones against
H2O2-induced DNA damage and apoptosis in
cultured Jurkat cells. Free Radic Res. 39:125–135. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Méchin V, Baumberger S, Pollet B and
Lapierre C: Peroxidase activity can dictate the in vitro lignin
dehydrogenative polymer structure. Phytochemistry. 68:571–579.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Moniruzzaman M, Kamiya N and Goto M:
Biocatalysis in water-in-ionic liquid microemulsions: a case study
with horseradish peroxidase. Langmuir. 25:977–982. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cheong MH, Lee SR, Yoo HS, Jeong JW, Kim
GY, Kim WJ, Jung IC and Choi YH: Anti-inflammatory effects of
Polygala tenuifolia root through inhibition of NF-κB
activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV2 microglial cells. J
Ethnopharmacol. 137:1402–1408. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim TH, Ku SK, Lee IC and Bae JS:
Anti-inflammatory functions of purpurogallin in LPS-activated human
endothelial cells. BMB Rep. 45:200–205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee YA, Choi HM, Lee SH, Yang HI, Yoo MC,
Hong SJ and Kim KS: Synergy between adiponectin and interleukin-1β
on the expression of interleukin-6, interleukin-8, and
cyclooxygenase-2 in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Exp Mol Med.
44:440–447. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee SH, Kim DW, Eom SA, Jun SY, Park M,
Kim DS, Kwon HJ, Kwon HY, Han KH, Park J, Hwang HS, Eum WS and Choi
SY: Suppression of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate
(TPA)-induced skin inflammation in mice by transduced Tat-Annexin
protein. BMB Rep. 45:354–359. 2012.
|
|
30
|
Atreya I, Atreya R and Neurath MF:
NF-kappaB in inflammatory bowel disease. J Intern Med. 263:591–596.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wright JG and Christman JW: The role of
nuclear factor kappa B in the pathogenesis of pulmonary diseases:
implications for therapy. Am J Respir Med. 2:211–219. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sebban H and Courtois G: NF-kappaB and
inflammation in genetic disease. Biochem Pharmacol. 72:1153–1160.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Duyao MP, Buckler AJ and Sonenshein GE:
Interaction of an NF-kappa B-like factor with a site upstream of
the c-myc promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 87:4727–4731. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Turjanski AG, Vaqué JP and Gutkind JS: MAP
kinases and the control of nuclear events. Oncogene. 26:3240–3253.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Montagut C and Settleman J: Targeting the
RAF-MEK-ERK pathway in cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 283:125–134.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Garden GA and Möller T: Microglia biology
in health and disease. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 1:127–137. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sugama S, Takenouchi T, Fujita M, Conti B
and Hashimoto M: Differential microglial activation between acute
stress and lipopolysaccharide treatment. J Neuroimmunol. 207:24–31.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schwartz M and Shechter R: Systemic
inflammatory cells fight off neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev
Neurol. 6:405–410. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gebicke-Haerter PJ: Microglia in
neurodegeneration: molecular aspects. Micros Res Tech. 54:47–58.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Inoue K: The function of microglia through
purinergic receptors: neuropathic pain and cytokine release.
Pharmacol Ther. 109:210–226. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Merson TD, Binder MD and Kilpatrick TJ:
Role of cytokines as mediators and regulators of microglial
activity in inflammatory demyelination of the CNS. Neuromolecular
Med. 12:99–132. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Madrid LV, Wang CY, Guttridge DC,
Schottelius AJ, Baldwin AS Jr and Mayo MW: Akt suppresses apoptosis
by stimulating the transactivation potential of the RelA/p65
subunit of NF-kappaB. Mol Cell Biol. 20:1626–1638. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lee JY, Jhun BS, Oh YT, Lee JH, Choe W,
Baik HH, Ha J, Yoon KS, Kim SS and Kang I: Activation of adenosine
A3 receptor suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-alpha
production through inhibition of PI 3-kinase/Akt and NF-kappaB
activation in murine BV2 microglial cells. Neurosci Lett. 396:1–6.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Shin WS, Szuba A and Rockson SG: The role
of chemokines in human cardiovascular pathology: enhanced
biological insights. Atherosclerosis. 160:91–102. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Nam NH: Naturally occurring NF-kappaB
inhibitors. Mini Rev Med Chem. 6:945–951. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Luqman S and Pezzuto JM: NFkappaB: a
promising target for natural products in cancer chemoprevention.
Phytother Res. 24:949–963. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kaminska B: MAPK signalling pathways as
molecular targets for anti-inflammatory therapy - from molecular
mechanisms to therapeutic benefits. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1754:253–262. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kaminska B, Gozdz A, Zawadzka M,
Ellert-Miklaszewska A and Lipko M: MAPK signal transduction
underlying brain inflammation and gliosis as therapeutic target.
Anat Rec (Hoboken). 292:1902–1913. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wei J and Feng J: Signaling pathways
associated with inflammatory bowel disease. Recent Pat Inflamm
Allergy Drug Discov. 4:105–117. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pyo H, Jou I, Jung S, Hong S and Joe EH:
Mitogen-activated protein kinases activated by lipopolysaccharide
and beta-amyloid in cultured rat microglia. Neuroreport. 9:871–874.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|