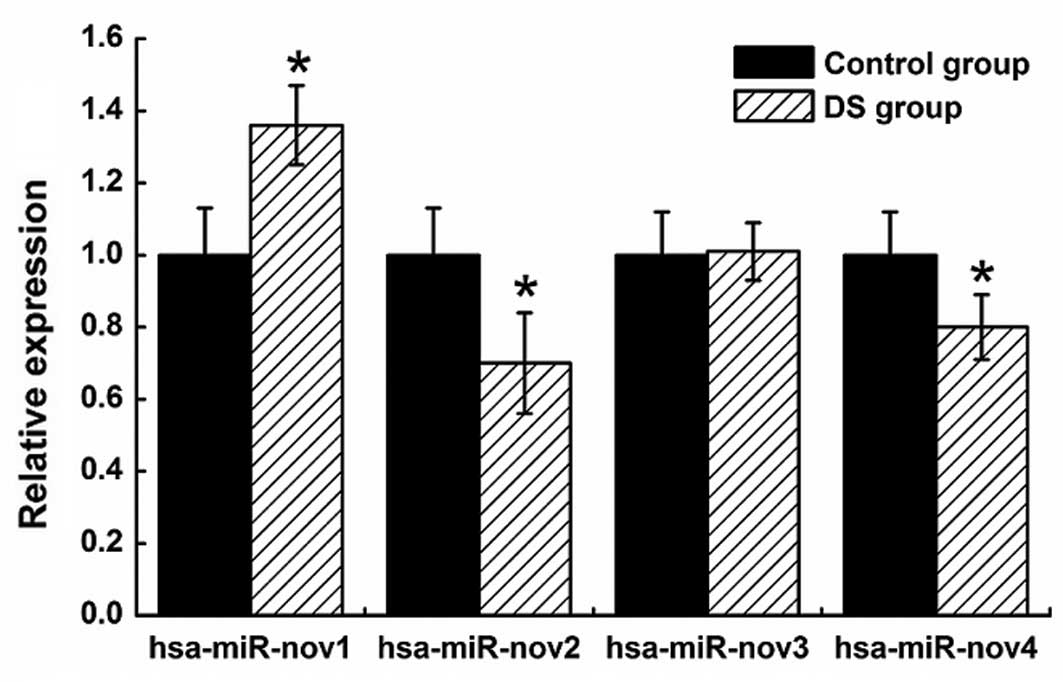
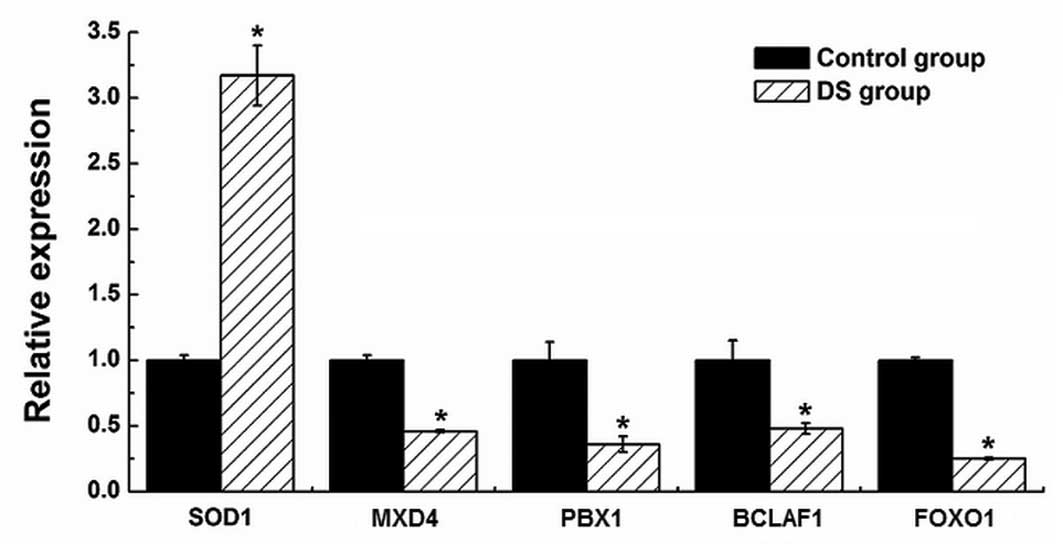
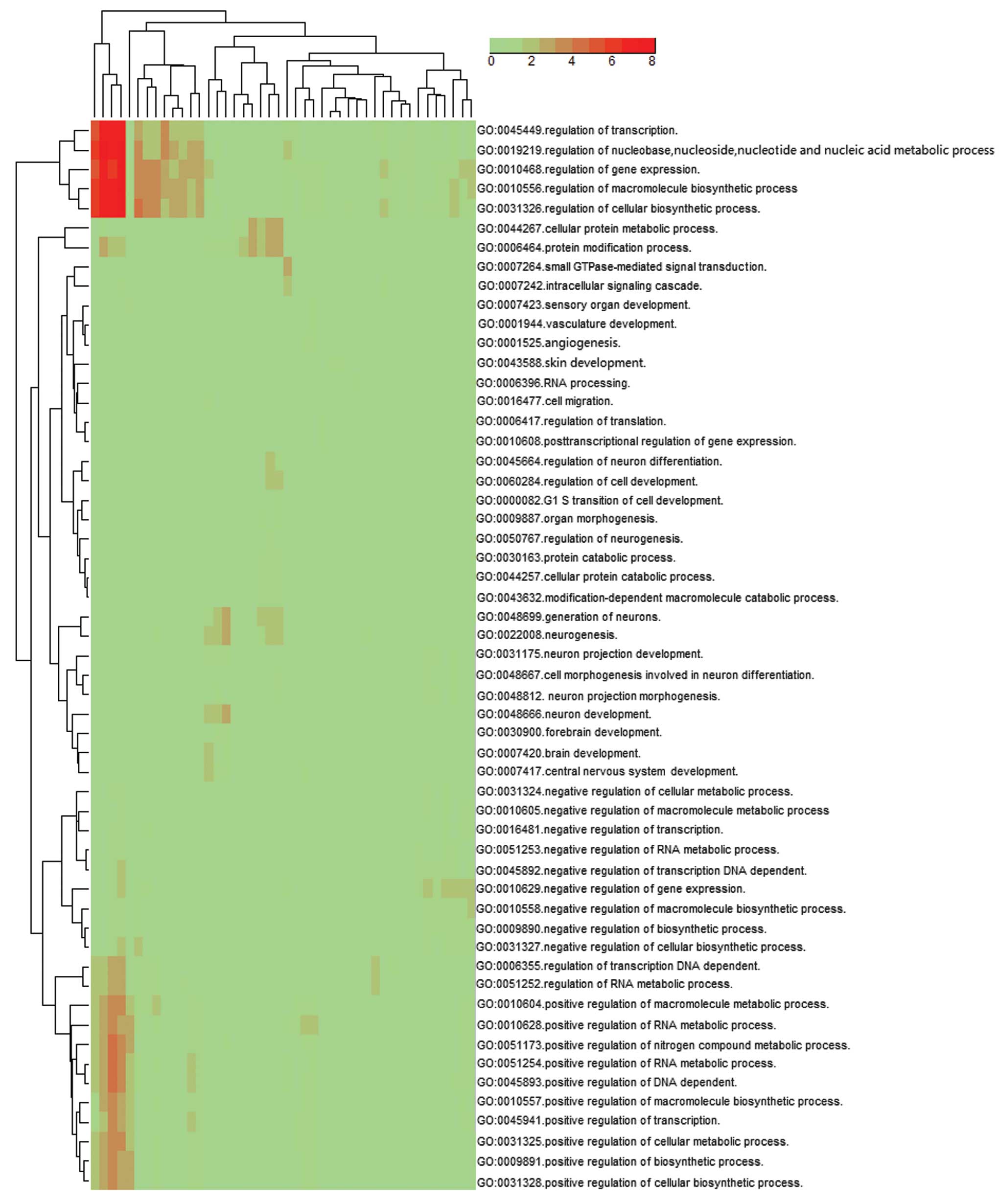
|
1
|
Elton TS, Sansom SE and Martin MM:
Trisomy-21 gene dosage over-expression of miRNAs results in the
haploinsufficiency of specific target proteins. RNA Biol.
7:540–547. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kozomara A and Griffiths-Jones S: miRBase:
integrating microRNA annotation and deep-sequencing data. Nucleic
Acids Res. 39:D152–157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kuhn DE, Nuovo GJ, Martin MM, et al: Human
chromosome 21-derived miRNAs are overexpressed in down syndrome
brains and hearts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 370:473–477. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kuhn DE, Nuovo GJ, Terry AV Jr, et al:
Chromosome 21-derived microRNAs provide an etiological basis for
aberrant protein expression in human Down syndrome brains. J Biol
Chem. 285:1529–1543. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sethupathy P, Borel C, Gagnebin M, et al:
Human microRNA-155 on chromosome 21 differentially interacts with
its polymorphic target in the AGTR1 3′ untranslated region: a
mechanism for functional single-nucleotide polymorphisms related to
phenotypes. Am J Hum Genet. 81:405–413. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cheng AM, Byrom MW, Shelton J and Ford LP:
Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an
involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids
Res. 33:1290–1297. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen CZ, Li L, Lodish HF and Bartel DP:
MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science.
303:83–86. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vaz C, Ahmad HM, Sharma P, et al: Analysis
of microRNA transcriptome by deep sequencing of small RNA libraries
of peripheral blood. BMC Genomics. 11:2882010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bandiera S, Hatem E, Lyonnet S and
Henrion-Caude A: microRNAs in diseases: from candidate to modifier
genes. Clin Genet. 77:306–313. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Havelange V and Garzon R: MicroRNAs:
emerging key regulators of hematopoiesis. Am J Hematol. 85:935–942.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Szulwach KE, Jin P and Alisch RS:
Noncoding RNAs in mental retardation. Clin Genet. 75:209–219. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
O'Connell RM, Rao DS, Chaudhuri AA, et al:
Sustained expression of microRNA-155 in hematopoietic stem cells
causes a myeloproliferative disorder. J Exp Med. 205:585–594. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Malinge S, Izraeli S and Crispino JD:
Insights into the manifestations, outcomes, and mechanisms of
leukemogenesis in Down syndrome. Blood. 113:2619–2628. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ozen M, Creighton CJ, Ozdemir M and
Ittmann M: Widespread deregulation of microRNA expression in human
prostate cancer. Oncogene. 27:1788–1793. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nagayama K, Kohno T, Sato M, Arai Y, Minna
JD and Yokota J: Homozygous deletion scanning of the lung cancer
genome at a 100-kb resolution. Genes Chromosomes Cancer.
46:1000–1010. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, et al:
Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and
genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.
101:2999–3004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Creighton CJ, Reid JG and Gunaratne PH:
Expression profiling of microRNAs by deep sequencing. Brief
Bioinform. 10:490–497. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Li R, Yu C, Li Y, et al: SOAP2: an
improved ultrafast tool for short read alignment. Bioinformatics.
25:1966–1967. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Anders S and Huber W: Differential
expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol.
11:R1062010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu G, Wu J, Zhou L, et al:
Characterization of the small RNA transcriptomes of androgen
dependent and independent prostate cancer cell line by deep
sequencing. PLoS One. 5:e155192010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen X, Li Q, Wang J, et al:
Identification and characterization of novel amphioxus microRNAs by
Solexa sequencing. Genome Biol. 10:R782009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
An J, Lai J, Lehman ML and Nelson CC:
miRDeep*: an integrated application tool for miRNA identification
from RNA sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:727–737. 2013.
|
|
25
|
Castillo-Davis CI and Hartl DL:
GeneMerge-post-genomic analysis, data mining, and hypothesis
testing. Bioinformatics. 19:891–892. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schulman BR, Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack
FJ: Reciprocal expression of lin-41 and the microRNAs let-7 and
mir-125 during mouse embryogenesis. Dev Dyn. 234:1046–1054. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wulczyn FG, Smirnova L, Rybak A, et al:
Post-transcriptional regulation of the let-7 microRNA during neural
cell specification. FASEB J. 21:415–426. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Morin RD, O'Connor MD, Griffith M, et al:
Application of massively parallel sequencing to microRNA profiling
and discovery in human embryonic stem cells. Genome Res.
18:610–621. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Patterson D: Molecular genetic analysis of
Down syndrome. Hum Genet. 126:195–214. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li CM, Guo M, Salas M, et al: Cell
type-specific over-expression of chromosome 21 genes in fibroblasts
and fetal hearts with trisomy 21. BMC Med Genet.
7:242006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Prandini P, Deutsch S, Lyle R, et al:
Natural gene-expression variation in Down syndrome modulates the
outcome of gene-dosage imbalance. Am J Hum Genet. 81:252–263. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Velu CS, Baktula AM and Grimes HL: Gfi1
regulates miR-21 and miR-196b to control myelopoiesis. Blood.
113:4720–4728. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gracias DT and Katsikis PD: MicroRNAs: key
components of immune regulation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 780:15–26. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lu LF and Liston A: MicroRNA in the immune
system, microRNA as an immune system. Immunology. 127:291–298.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rodriguez A, Vigorito E, Clare S, et al:
Requirement of bic/microRNA-155 for normal immune function.
Science. 316:608–611. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fernando TR, Rodriguez-Malave NI and Rao
DS: MicroRNAs in B cell development and malignancy. J Hematol
Oncol. 5:72012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gururajan M, Haga CL, Das S, et al:
MicroRNA 125b inhibition of B cell differentiation in germinal
centers. Int Immunol. 22:583–592. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Banerjee R, Mosley RL, Reynolds AD, et al:
Adaptive immune neuroprotection in G93A-SOD1 amyotrophic lateral
sclerosis mice. PLoS One. 3:e27402008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Vasilevsky NA, Ruby CE, Hurlin PJ and
Weinberg AD: OX40 engagement stabilizes Mxd4 and Mnt protein levels
in antigen-stimulated T cells leading to an increase in cell
survival. Eur J Immunol. 41:1024–1034. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ficara F, Murphy MJ, Lin M and Cleary ML:
Pbx1 regulates self-renewal of long-term hematopoietic stem cells
by maintaining their quiescence. Cell Stem Cell. 2:484–496. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
McPherson JP, Sarras H, Lemmers B, et al:
Essential role for Bclaf1 in lung development and immune system
function. Cell Death Differ. 16:331–339. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sarras H, Alizadeh Azami S and McPherson
JP: In search of a function for BCLAF1. Scientific World Journal.
10:1450–1461. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Dejean AS, Hedrick SM and Kerdiles YM:
Highly specialized role of Forkhead box O transcription factors in
the immune system. Antioxid Redox Signal. 14:663–674. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ouyang W, Beckett O, Flavell RA and Li MO:
An essential role of the Forkhead-box transcription factor Foxo1 in
control of T cell homeostasis and tolerance. Immunity. 30:358–371.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dengler HS, Baracho GV, Omori SA, et al:
Distinct functions for the transcription factor Foxo1 at various
stages of B cell differentiation. Nat Immunol. 9:1388–1398. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
de Hingh YC, van der Vossen PW, Gemen EF,
et al: Intrinsic abnormalities of lymphocyte counts in children
with Down syndrome. J Pediat. 147:744–747. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ram G and Chinen J: Infections and
immunodeficiency in Down syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol. 164:9–16.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lee J, Duan W and Mattson MP: Evidence
that brain-derived neurotrophic factor is required for basal
neurogenesis and mediates, in part, the enhancement of neurogenesis
by dietary restriction in the hippocampus of adult mice. J
Neurochem. 82:1367–1375. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zuccotti P, Barbieri A, Colombrita C, et
al: Identification of post-transcriptional regulatory elements in
CDK5R1 3′UTR gene involved in CNS development and functioning. Eur
J Hum Genet. 19:3542011.
|
|
50
|
Holler CJ, Webb RL, Laux AL, et al: BACE2
expression increases in human neurodegenerative disease. Am J
Pathol. 180:337–350. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Webb RL and Murphy MP: β-Secretases,
Alzheimer's disease, and Down syndrome. Curr Gerontol Geriatr Res.
2012:3628392012.
|