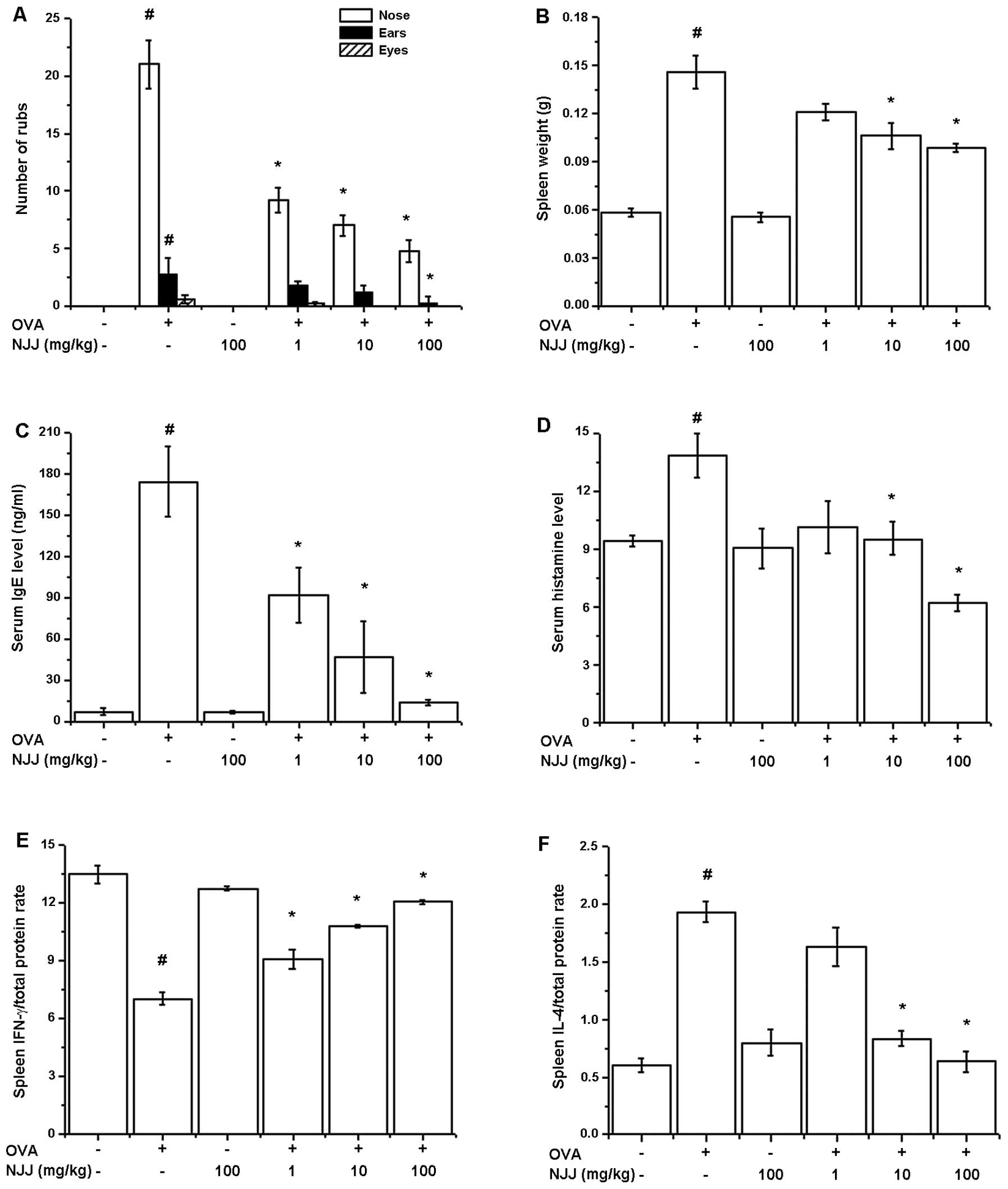
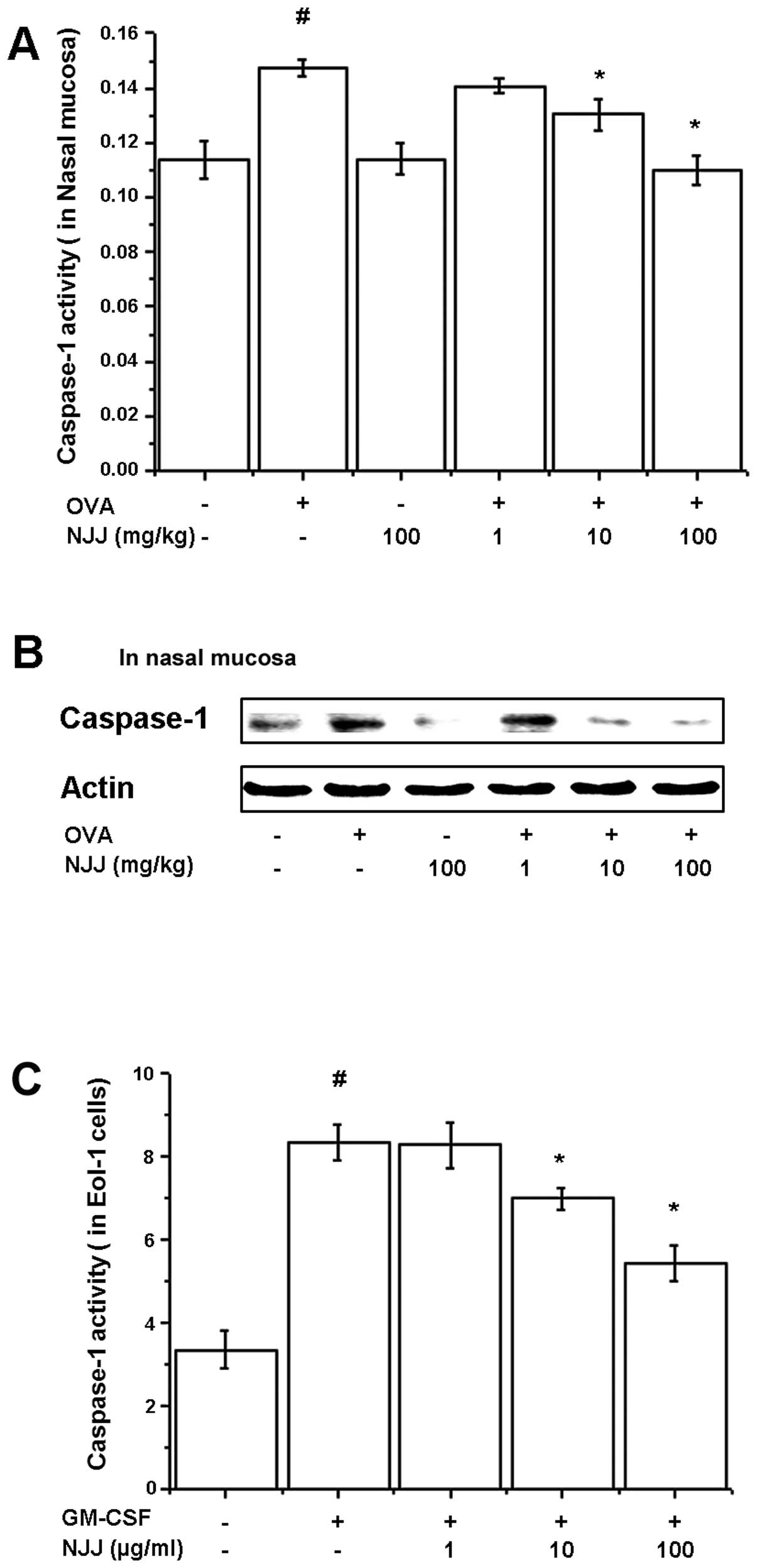
|
1
|
Varney VA, Jacobson MR, Suddarick RM, et
al: Immunohistology of nasal mucosa following allergen induced
rhinitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 146:170–175. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sim TC, Grant JA, Hilsmeier KA, Fukuda Y
and Alam R: Pro-inflammatory cytokines in nasal secretions of
allergic subjects after antigen challenge. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 149:339–344. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gupta S, Feng L, Yoshimura T, Redick J, Fu
SM and Rose CE Jr: Intra-alveolar macrophage-inflammation peptide 2
induces rapid neutrophil localization in the lung. Am J Respir Cell
Mol Biol. 15:656–663. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Durham SR, Ying S, Varney VA, et al:
Cytokine messenger RNA expression for IL-3, IL-4, IL-5 and
granulocyte/macrophase colony stimulating factors in the nasal
mucosa after local allergen provocation. J ImmunoI. 148:2390–2394.
1992.
|
|
5
|
Bacon AS, McGill JI, Anderson DF, Baddeley
S, Lightman SL and Holgate ST: Adhesion molecules and relationship
to leukocyte levels in allergic eye disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis
Sci. 39:322–330. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tai PC and Spry CJ: The effects of
recombinant granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor
(GM-CSF) and interleukin-3 on the secretory capacity of human blood
eosinophils. Clin Exp Immunol. 80:426–434. 1990.
|
|
7
|
Jeong HJ, Shin SY, Oh HA, Kim MH, Cho JS
and Kim HM: IL-32 up-regulation is associated with inflammatory
cytokine production in allergic rhinitis. J Path. 224:553–563.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Marcondes AM, Mhyre AJ, Stirewalt DL, Kim
SH, Dinarello CA and Deeg HJ: Dysregulation of IL-32 in
myelodysplastic syndrome and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia
modulates apoptosis and impairs NK function. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:2865–2870. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bae S, Kang D, Hong J, et al:
Characterizing antiviral mechanism of interleukin-32 and a
circulating soluble isoform in viral infection. Cytokine. 58:79–86.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Heinhuis B, Koenders MI, van Riel PL, et
al: Tumour necrosis factor alpha-driven IL-32 expression in
rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue amplifies an inflammatory
cascade. Ann Rheum Dis. 70:660–667. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim SH, Han SY, Azam T, Yoon DY and
Dinarello CA: Interleukin-32: a cytokine and inducer of TNF alpha.
Immunity. 22:131–142. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Netea MG, Azam T, Ferwerda G, et al: IL-32
synergizes with nucleotide oligomerization domain (NOD) 1 and NOD2
ligands for IL-1beta and IL-6production through a caspase
1-dependent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:16309–16314.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nishida A, Andoh A, Shioya M,
Kim-Mitsuyama S, Takayanagi A and Fujiyama Y: Phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt signaling mediates interleukin-32alpha induction in
human pancreatic periacinar myofibroblasts. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 294:G831–G838. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Heinhuis B, Koenders MI, van den Berg WB,
Netea MG, Dinarello CA and Joosten LA: IL-32 contains a typical
alpha-helix bundle structure that resembles the focal adhesion
targeting region of focal adhesion kinase-1. J Biol Chem.
287:5733–5743. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ying S, O’Connor B, Ratoff J, et al:
Expression and cellular provenance of thymic stromal lymphopoietin
and chemokines in patients with severe asthma and chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. J Immunol. 181:2790–2798. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Soumelis V, Reche PA, Kanzler H, et al:
Human epithelial cells trigger dendritic cell mediated allergic
inflammation by producing TSLP. Nat Immunol. 3:673–680.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bunyavanich S, Melen E, Wilk JB, et al:
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) is associated with allergic
rhinitis in children with asthma. Clin Mol Allergy. 9:12011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moon PD and Kim HM: Thymic stromal
lymphopoietin is expressed and produced by caspase-1/NF-κB pathway
in mast cells. Cytokine. 54:239–243. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Song YH, Nam SY, Choi Y, Kim JH, Kim YS
and Jeong HJ: Socioeconomic impact of traditional Korean medicine,
Pyeongwee-San (KMP6) as an anti-allergic inflammatory drug. TANG.
2:52–60. 2012.
|
|
20
|
Jeong HJ, Nam SY, Oh HA, et al:
Interleukin-32-induced thymic stromal lymphopoietin plays a
critical role in macrophage differentiation through the activation
of caspase-1 in vitro. Arthritis Res Ther. 14:R2592012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Iwaki K, Satomi KM, Kohno K, Ushio S and
Fukuda S: Antimicrobial activity of Polygonum tinctorium
Lour: extract against oral pathogenic bacteria. J Nat Med.
60:121–125. 2006.
|
|
22
|
Satomi KM, Kimoto T, Micallef MJ, et al:
Prevention of azoxymethane-induced intestinal tumors by a crude
ethyl acetate-extract and tryptanthrin extracted from Polygonum
tinctorium Lour. Anticancer Res. 21:3295–3300. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kataoka M, Hirata K, Kunikata T, et al:
Antibacterial action of tryptanthrin and kaempferol, isolated from
the indigo plant (Polygonum tinctorium Lour.), against
Helicobacter pylori-infected Mongolian gerbils. J
Gastroenterol. 36:5–9. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim HM, Hong DR and Lee EH: Inhibition of
mast cell-dependent anaphylactic reactions by the pigment of
Polygonum tinctorium (Chung-Dae) in rats. Gen Pharmacol.
31:361–365. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Miyata M, Hatsushika K, Ando T, et al:
Mast cell regulation of epithelial TSLP expression plays an
important role in the development of allergic rhinitis. Eur J
Immunol. 38:1487–1492. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Han NR, Kim HM and Jeong HJ: Thymic
stromal lymphopoietin is regulated by the intracellular calcium.
Cytokine. 59:215–217. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Spada CS, Nieves AL, Krauss AH and
Woodward DF: Comparison of leukotriene B4 and D4 effects on human
eosinophil and neutrophil motility in vitro. J Leukoc Biol.
55:183–191. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sugimoto H, Shichijo M, Iino T, et al: An
orally bioavailable small molecule antagonist of CRTH2, ramatroban
(BAY u3405), inhibits prostaglandin D2-induced eosinophil migration
in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 305:347–352. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Melvin TA and Ramanathan M Jr: Role of
innate immunity in the pathogenesis of allergic rhinitis. Curr Opin
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 20:194–198. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Isobe Y, Kato T and Arita M: Emerging
roles of eosinophils and eosinophil-derived lipid mediators in the
resolution of inflammation. Front Immunol. 3:2702012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Moshkovits I, Shik D, Itan M, et al:
CMRF35-like molecule 1 (CLM-1) regulates eosinophil homeostasis by
suppressing cellular chemotaxis. Mucosal Immunol. Jul 3–2013.(Epub
ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bystrom J, Patel SY, Amin K and
Bishop-Bailey D: Dissecting the role of eodinophil cationic protein
in upper airway disease. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 12:18–23.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Soyka MB, Treis A, Eiwegger T, et al:
Regulation and expression of IL-32 in chronic rhinosinusitis.
Allergy. 67:790–798. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nomura K, Kojima T, Fuchimoto J, Obata K,
Keira T, Himi T and Sawada N: Regulation of interleukin-33 and
thymic stromal lymphopoietin in human nasal fibroblasts by
proinflammatory cytokines. Laryngoscope. 122:1185–1192. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Oh HA, Kim HM and Jeong HJ: Alleviation of
allergic rhinitis symptoms with Pyeongwee-San extract (KMP6).
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 34:135–142. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vashisht P and Casale T: Omalizumab for
treatment of allergic rhinitis. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 13:933–945.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sollberger G, Strittmatter GE,
Garstkiewicz M, Sand J and Beer HD: Caspase-1: the inflammasome and
beyond. Innate Immun. May 15–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
38
|
Grzegorczyk J, Kowalski ML, Pilat A and
Iwaszkiewicz J: Increased apoptosis of peripheral blood mononuclear
cells in patients with perennial allergic asthma/rhinitis: relation
to serum markers of apoptosis. Mediators Inflamm. 11:225–233. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Han NR, Kim HM and Jeong HJ: Kanamycin
activates caspase-1 in NC/Nga mice. Exp Dermatol. 20:659–663. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cunha TM, Talbot J, Pinto LG, et al:
Caspase-1 is involved in the genesis of inflammatory
hypernociception by contributing to peripheral IL-1β maturation.
Mol Pain. 6:632010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee EJ, Ji GE and Sung MK: Quercetin and
kaempferol suppress immunoglobulin E-mediated allergic inflammation
in RBL-2H3 and Caco-2 cells. Inflamm Res. 59:847–854. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gong JH, Shin D, Han SY, Kim JL and Kang
YH: Kaempferol suppresses eosionphil infiltration and airway
inflammation in airway epithelial cells and in mice with allergic
asthma. J Nutr. 142:47–56. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kunikata T, Tatefuji T, Aga H, Iwaki K,
Ikeda M and Kurimoto M: Indirubin inhibits inflammatory reactions
in delayed-type hypersensitivity. Eur J Pharmacol. 410:93–100.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kim MH, Choi YY, Yang G, Cho IH, Nam D and
Yang WM: Indirubin, a purple 3,2-bisindole, inhibited allergic
contact dermatitis via regulating Thelper(Th)-mediated immune
system in DNCB-induced model. J Ethnopharmacol. 145:214–219. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|