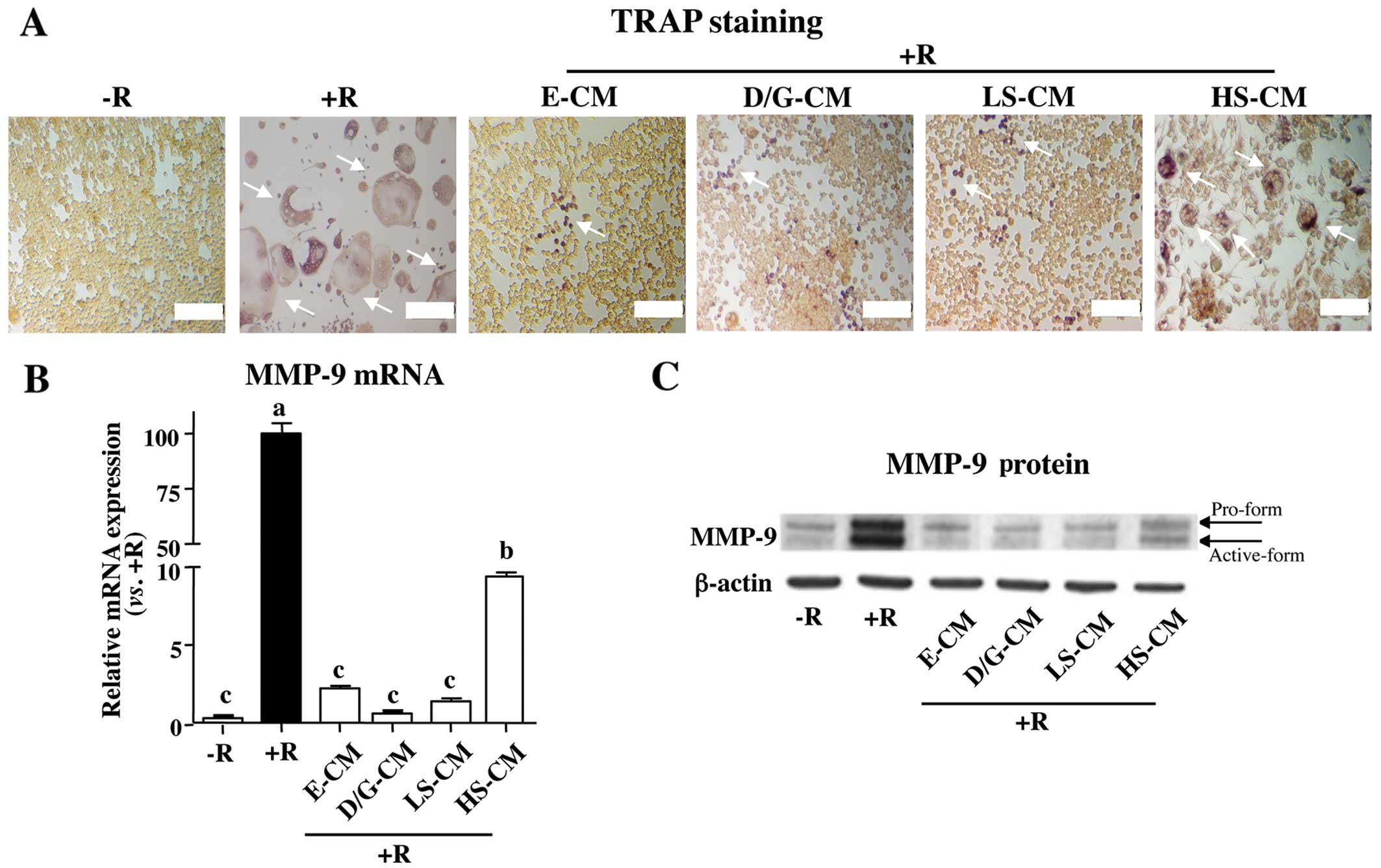
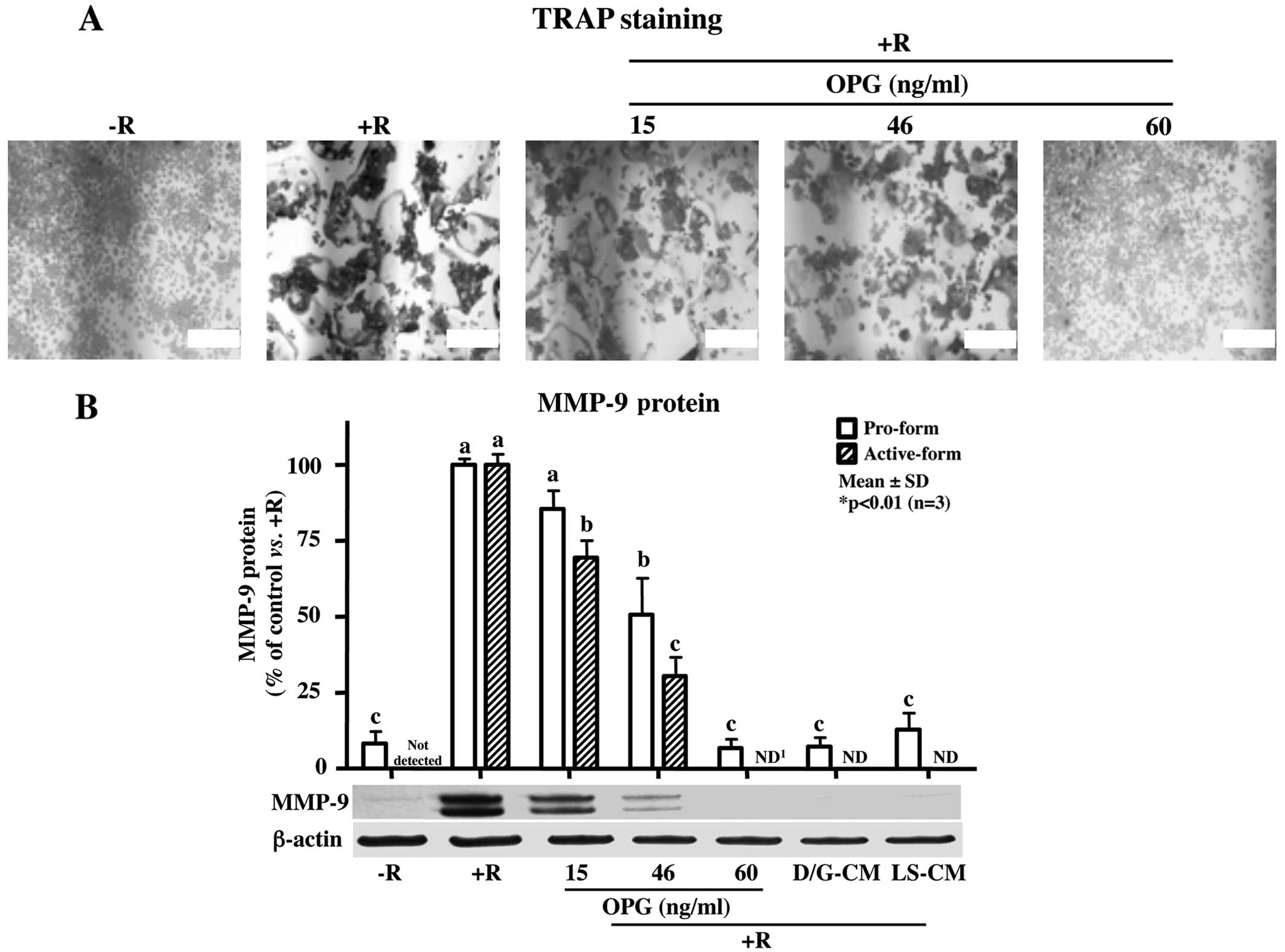
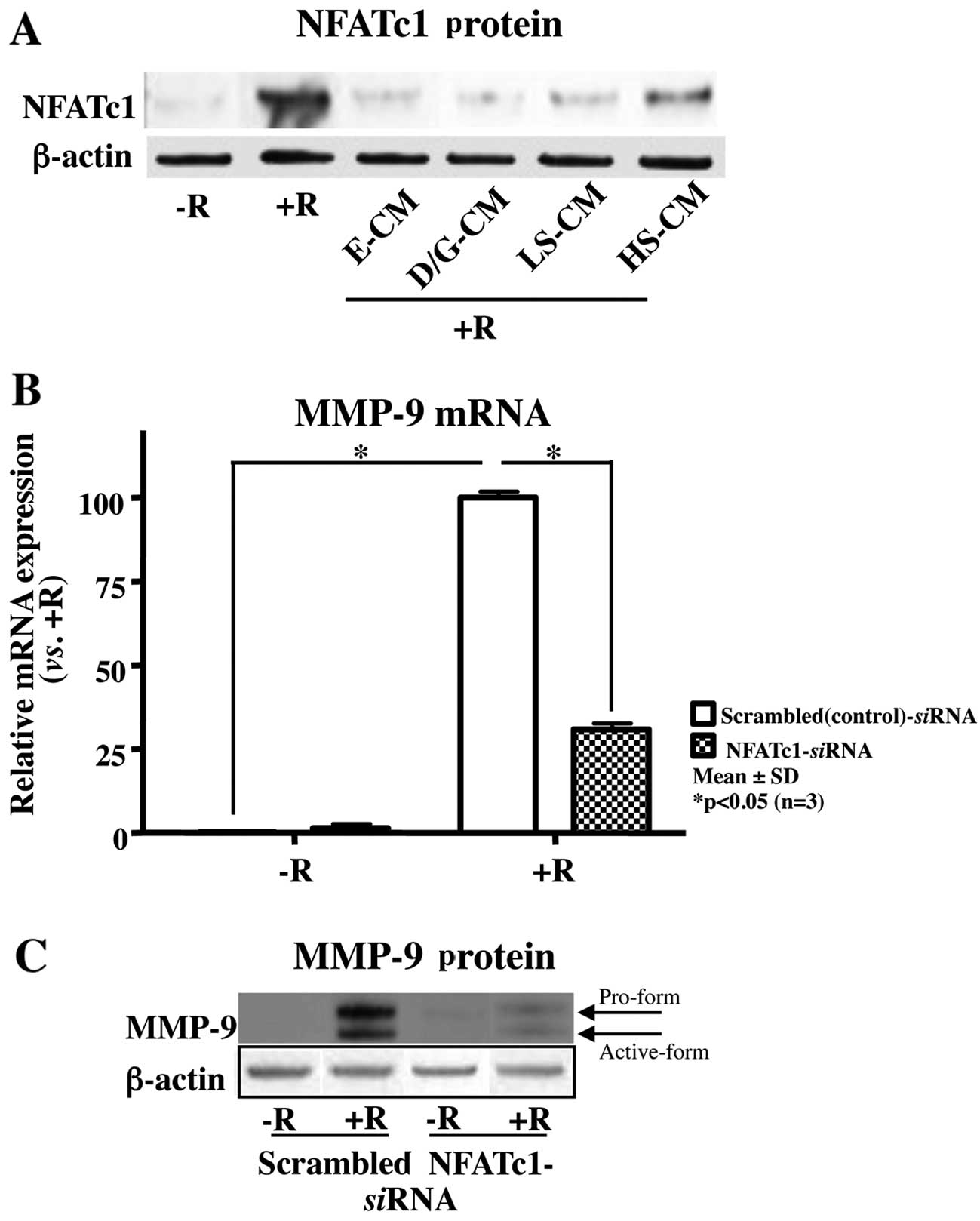
|
1
|
Spelsberg TC, Subramaniam M, Riggs BL and
Khosla S: The actions and interactions of sex steroids and growth
factor/cytokines on the skeleton. Mol Endocrinol. 13:819–828. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Barton M and Shapiro D: Transient
administration of estradiol-17 beta establishes an autoregulatory
loop permanently inducing estrogen receptor mRNA. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 85:7119–7123. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Babiker FA, De Windt LJ, van Eickels M,
Grohe C, Meyer R and Doevendans PA: Estrogenic hormone action in
the heart: regulatory network and function. Cardiovasc Res.
53:709–719. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kang KS, Morita I, Cruz A, Jeon YJ, Trosko
JE and Chang CC: Expression of estrogen receptors in a normal human
breast epithelial cell type with luminal and stem cell
characteristics and its neoplastically transformed cell lines.
Carcinogenesis. 18:251–257. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lindgren PR, Cajander S, Bäckström T,
Gustafsson JA, Mäkelä S and Olofsson JI: Estrogen and progesterone
receptors in ovarian epithelial tumors. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
221:97–104. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Couse JF, Lindzey J, Grandien K,
Gustafsson JA and Korach KS: Tissue distribution and quantitative
analysis of estrogen receptor-alpha (ERalpha) and estrogen
receptor-beta (ERbeta) messenger ribonucleic acid in the wild-type
and ERalpha-knockout mouse. Endocrinology. 138:4613–4621. 1997.
|
|
7
|
Ernst M, Schmid C and Froesch ER: Enhanced
osteoblast proliferation and collagen gene expression by estradiol.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 85:2307–2310. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Okazaki R, Inoue D, Shibata M, Saika M,
Kido S, Ooka H, Tomiyama H, Sakamoto Y and Matsumoto T: Estrogen
promotes early osteoblast differentiation and inhibits adipocyte
differentiation in mouse bone marrow stromal cell lines that
express estrogen receptor (ER) alpha or beta. Endocrinology.
143:2349–2356. 2002.
|
|
9
|
Balica M, Boström K, Shin V, Tillisch K
and Demer LL: Calcifying subpopulation of bovine aortic smooth
muscle cells is responsive to 17 beta-estradiol. Circulation.
95:1954–1960. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bord S, Ireland DC, Beavan SR and Compston
JE: The effects of estrogen on osteoprotegerin, RANKL, and estrogen
receptor expression in human osteoblasts. Bone. 32:136–141. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kameda T, Mano H, Yuasa T, Mori Y,
Miyazawa K, Shiokawa M, Nakamaru Y, Hiroi E, Hiura K, Kameda A,
Yang NN, Hakeda Y and Kumegawa M: Estrogen inhibits bone resorption
by directly inducing apoptosis of the bone-resorbing osteoclasts. J
Exp Med. 186:489–495. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Collier FM, Huang WH, Holloway WR, Hodge
JM, Gillespie MT, Daniels LL, Zheng MH and Nicholson GC:
Osteoclasts from human giant cell tumors of bone lack estrogen
receptors. Endocrinology. 139:1258–1267. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Grodstein F, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA,
Willett WC, Manson JE, Joffe M, Rosner B, Fuchs C, Hankinson SE,
Hunter DJ, Hennekens CH and Speizer FE: Postmenopausal hormone
therapy and mortality. N Engl J Med. 336:1769–1775. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Compston JE: Sex steroids and bone.
Physiol Rev. 81:419–447. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Keinan-Boker L, van Der Schouw YT, Grobbee
DE and Peeters PH: Dietary phytoestrogens and breast cancer risk.
Am J Clin Nutr. 79:282–288. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Setchell KD and Lydeking-Olsen E: Dietary
phytoestrogens and their effect on bone: evidence from in vitro and
in vivo, human observational, and dietary intervention studies. Am
J Clin Nutr. 78(Suppl 3): 593S–609S. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim J, Um SJ, Woo J, Kim JY, Kim HA, Jang
KH, Kang SA, Lim BO, Kang I, Choue RW and Cho Y: Comparative effect
of seeds of Rhynchosia volubilis and soybean on MG-63 human
osteoblastic cell proliferation and estrogenicity. Life Sci.
78:30–40. 2005.
|
|
18
|
Qu Q, Härkönen PL, Mönkkönen J and
Väänänen HK: Conditioned medium of estrogen-treated osteoblasts
inhibits osteoclast maturation and function in vitro. Bone.
25:211–215. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wong BR, Josien R, Lee SY, Vologodskaia M,
Steinman RM and Choi Y: The TRAF family of signal transducers
mediates NF-kappaB activation by the TRANCE receptor. J Biol Chem.
273:28355–28359. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ishida N, Hayashi K, Hoshijima M, Ogawa T,
Koga S, Miyatake Y, Kumegawa M, Kimura T and Takeya T: Large scale
gene expression analysis of osteoclastogenesis in vitro and
elucidation of NFAT2 as a key regulator. J Biol Chem.
277:41147–41156. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park K, Elias PM, Oda Y, Mackenzie D,
Mauro T, Holleran WM and Uchida Y: Regulation of cathelicidin
antimicrobial peptide expression by an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
stress signaling, vitamin D receptor-independent pathway. J Biol
Chem. 286:34121–34130. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Kelley
M, Chang MS, Lüthy R, Nguyen HQ, Wooden S, Bennett L, Boone T,
Shimamoto G, DeRose M, Elliott R, Colombero A, Tan HL, Trail G,
Sullivan J, Davy E, Bucay N, Renshaw-Gegg L, Hughes TM, Hill D,
Pattison W, Campbell P, Sander S, Van G, Tarpley J, Derby P, Lee R
and Boyle WJ: Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in
the regulation of bone density. Cell. 89:309–319. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Santanam N, Shern-Brewer R, McClatchey R,
Castellano PZ, Murphy AA, Voelkel S and Parthasarathy S: Estradiol
as an antioxidant: incompatible with its physiological
concentrations and function. J Lipid Res. 39:2111–2118.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Khosla S: Minireview: the OPG/RANKL/RANK
system. Endocrinology. 142:5050–5055. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sundaram K, Nishimura R, Senn J, Youssef
RF, London SD and Reddy SV: RANK ligand signaling modulates the
matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene expression during osteoclast
differentiation. Exp Cell Res. 313:168–178. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Karieb S and Fox SW: Phytoestrogens
directly inhibit TNF-α-induced bone resorption in RAW264.7 cells by
suppressing c-fos-induced NFATc1 expression. J Cell Biochem.
112:476–487. 2011.
|
|
27
|
Tyagi AM, Srivastava K, Sharan K, Yadav D,
Maurya R and Singh D: Daidzein prevents the increase in
CD4+CD28null T cells and B lymphopoesis in
ovariectomized mice: a key mechanism for anti-osteoclastogenic
effect. PLoS One. 6:e212162011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
García Palacios V, Robinson LJ, Borysenko
CW, Lehmann T, Kalla SE and Blair HC: Negative regulation of
RANKL-induced osteoclastic differentiation in RAW264.7 cells by
estrogen and phytoestrogens. J Biol Chem. 280:13720–13727.
2005.
|
|
29
|
Lorget F, Kamel S, Mentaverri R, Wattel A,
Naassila M, Maamer M and Brazier M: High extracellular calcium
concentrations directly stimulate osteoclast apoptosis. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 268:899–903. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gao YH and Yamaguchi M: Suppressive effect
of genistein on rat bone osteoclasts: Involvement of protein kinase
inhibition and protein tyrosine phosphatase activation. Int J Mol
Med. 5:261–267. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fu YX, Gu JH, Zhang YR, Tong XS, Zhao HY,
Yuan Y, Liu XZ, Bian JC and Liu ZP: Osteoprotegerin influences the
bone resorption activity of osteoclasts. Int J Mol Med.
31:1411–1417. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Takayanagi H, Kim S, Koga T, Nishina H,
Isshiki M, Yoshida H, Saiura A, Isobe M, Yokochi T, Inoue J, Wagner
EF, Mak TW, Kodama T and Taniguchi T: Induction and activation of
the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2) integrate RANKL signaling
in terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 3:889–901.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|