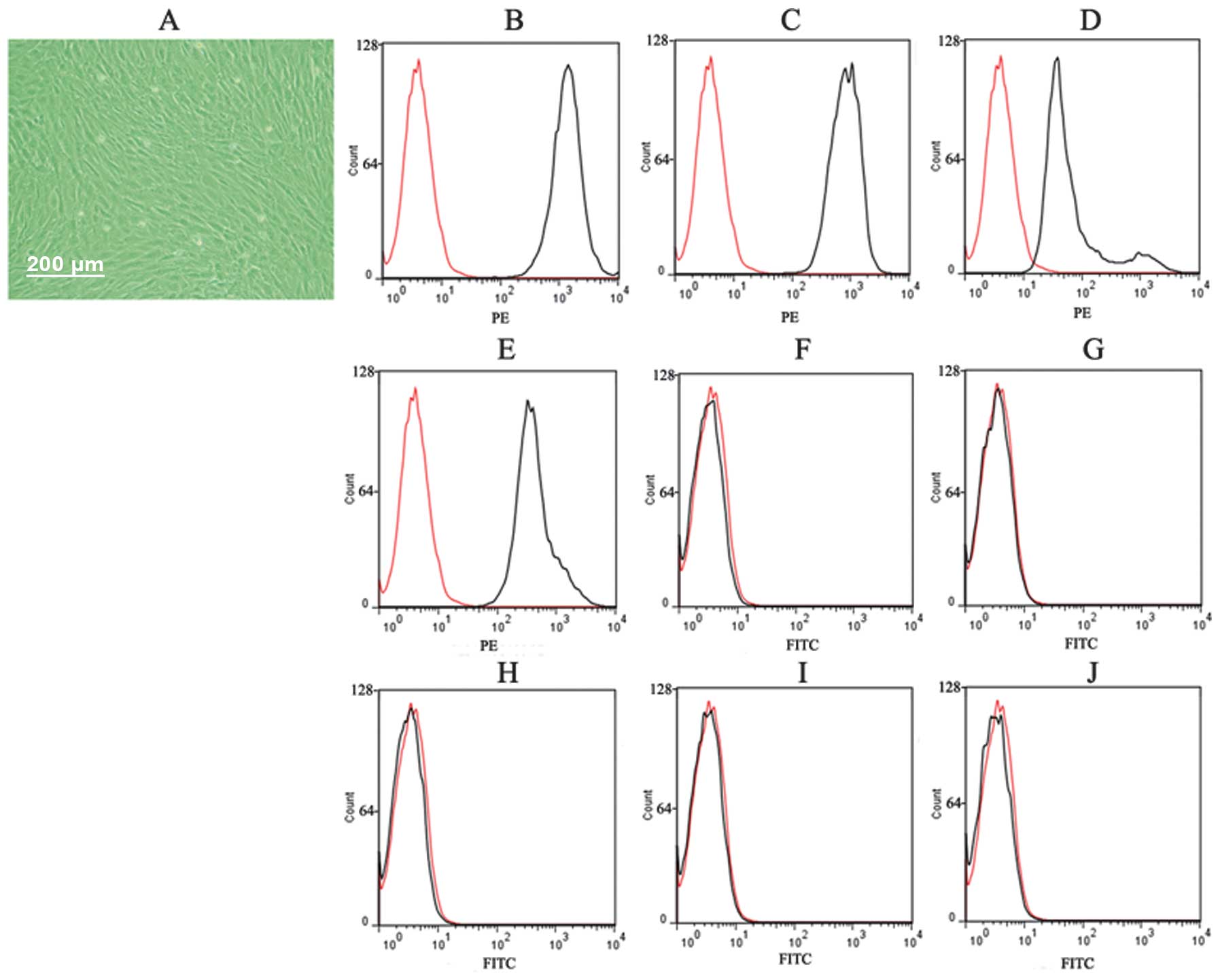
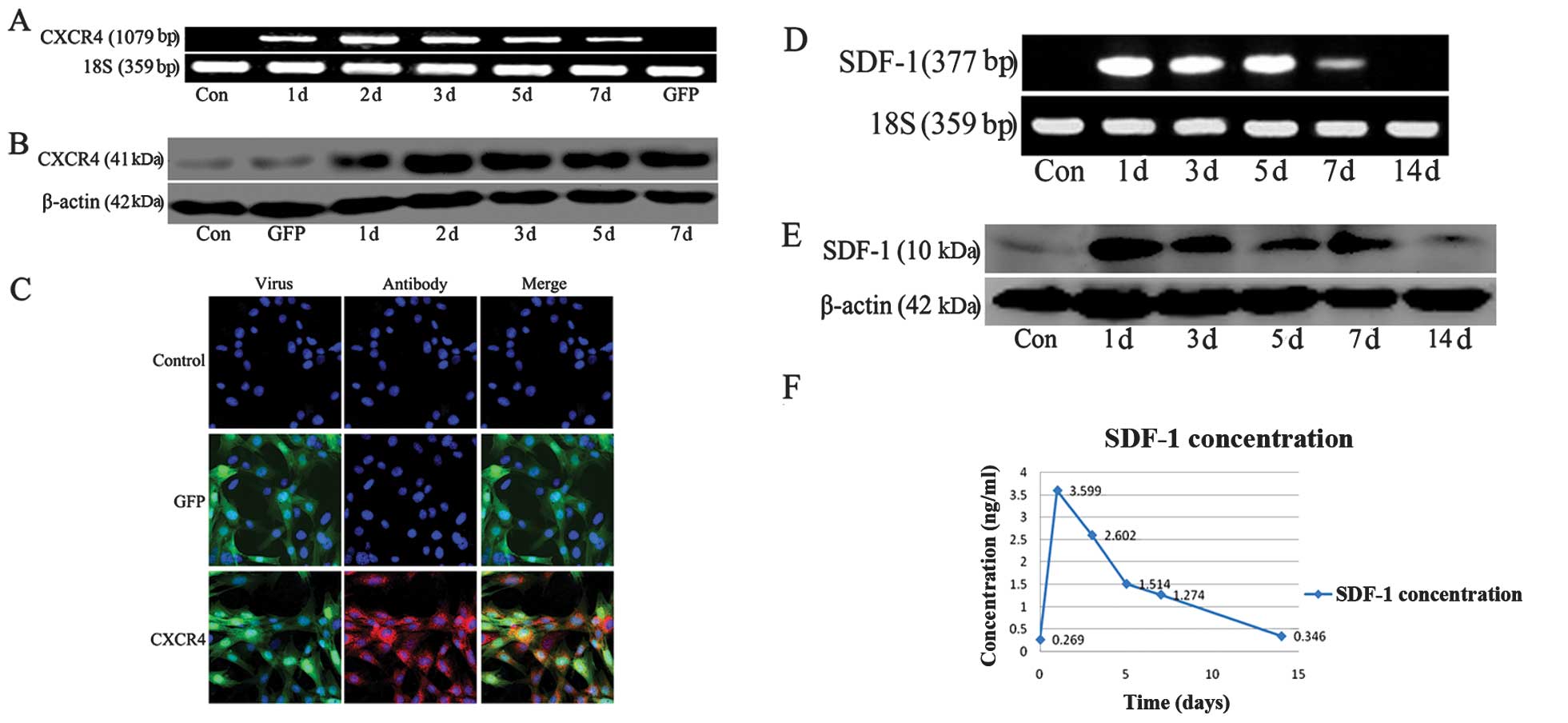
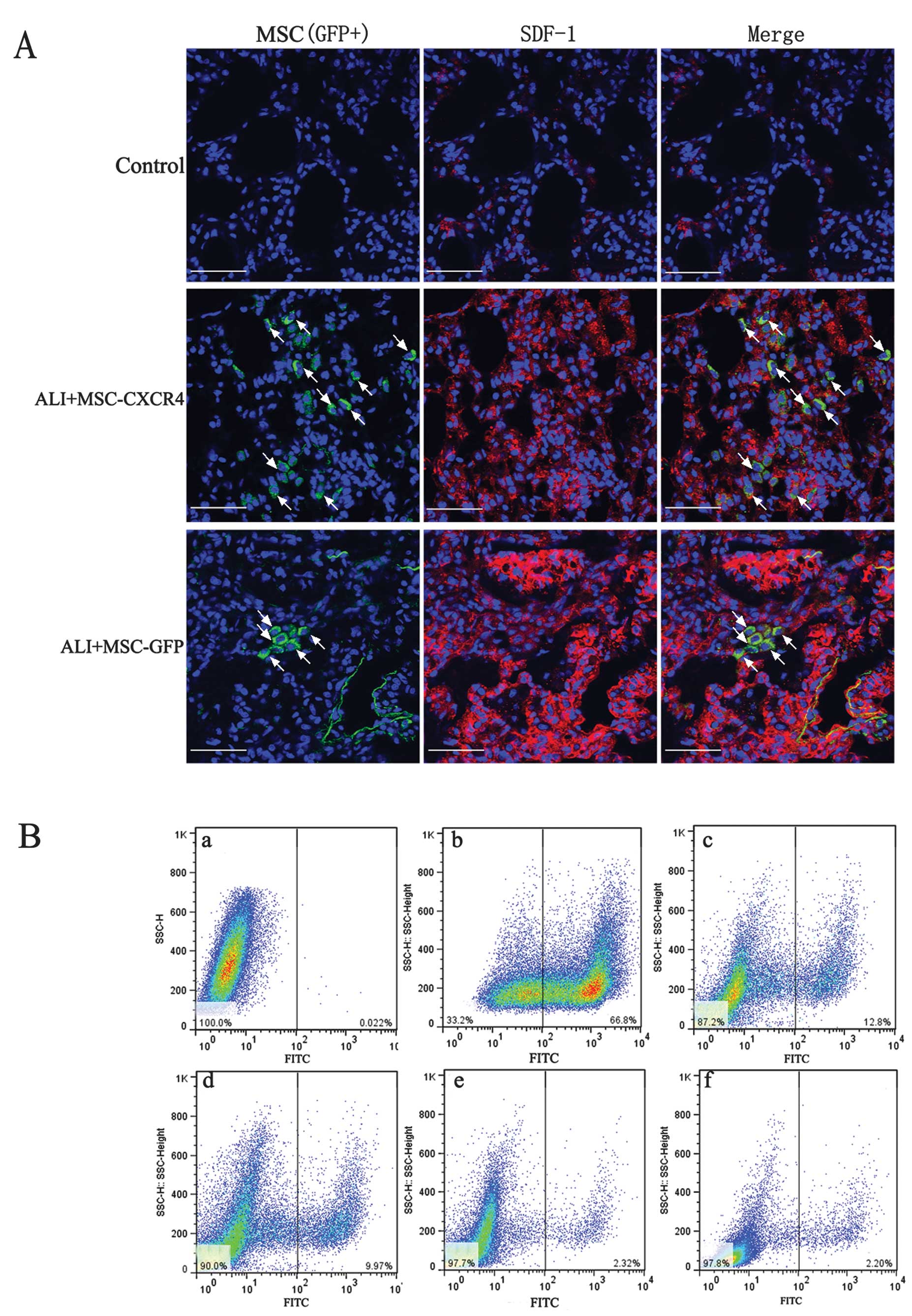
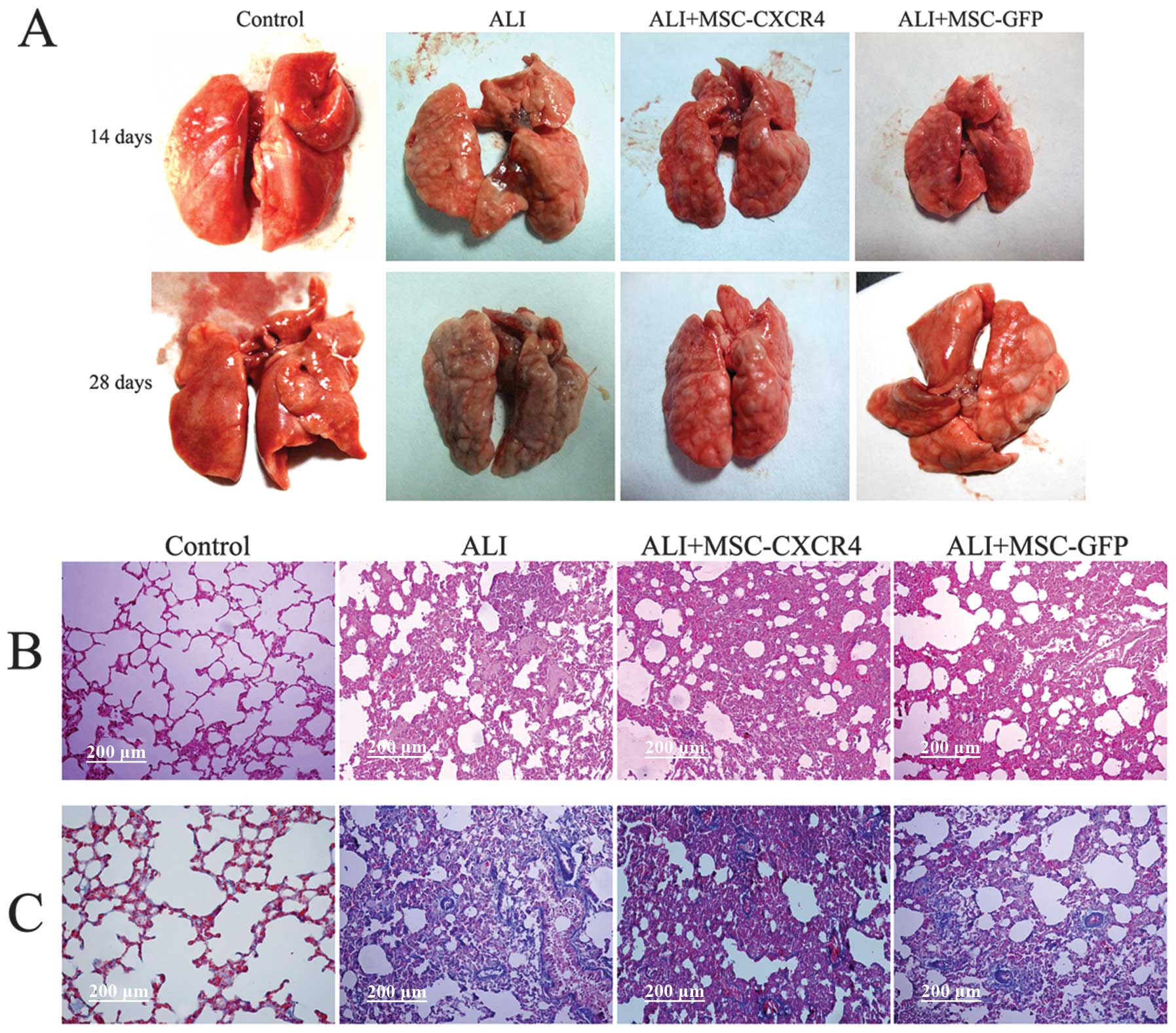
|
1
|
Ware LB and Matthay MA: The acute
respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 342:1334–1349. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Matute-Bello G, Frevert CW and Martin TR:
Animal models of acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 295:L379–L399. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Meduri GU: The role of the host defence
response in the progression and outcome of ARDS: pathophysiological
correlations and response to glucocorticoid treatment. Eur Respir
J. 9:2650–2670. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Prockop DJ: Marrow stromal cells as stem
cells for continual renewal of nonhematopoietic tissues and as
potential vectors for gene therapy. J Cell Biochem Suppl.
30–31:284–285. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Okamoto R, Yajima T, Yamazaki M, et al:
Damaged epithelia regenerated by bone marrow-derived cells in the
human gastrointestinal tract. Nat Med. 8:1011–1017. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Matsumoto T, Okamoto R, Yajima T, et al:
Increase of bone marrow-derived secretory lineage epithelial cells
during regeneration in the human intestine. Gastroenterology.
128:1851–1867. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Krause DS: Plasticity of marrow-derived
stem cells. Gene Ther. 9:754–758. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A, et al:
Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for
angiogenesis. Science. 275:964–967. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lapidot T, Dar A and Kollet O: How do stem
cells find their way home? Blood. 106:1901–1910. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Son BR, Marquez-Curtis LA, Kucia M, et al:
Migration of bone marrow and cord blood mesenchymal stem cells in
vitro is regulated by stromal-derived factor-1-CXCR4 and hepatocyte
growth factor-c-met axes and involves matrix metalloproteinases.
Stem Cells. 24:1254–1264. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liebler JM, Lutzko C, Banfalvi A, et al:
Retention of human bone marrow-derived cells in murine lungs
following bleomycin-induced lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 295:L285–L292. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lapidot T: Mechanism of human stem cell
migration and repopulation of NOD/SCID and B2mnull NOD/SCID mice.
The role of SDF-1/CXCR4 interactions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 938:83–95.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Askari AT, Unzek S, Popovic ZB, et al:
Effect of stromal-cell-derived factor 1 on stem-cell homing and
tissue regeneration in ischaemic cardiomyopathy. Lancet.
362:697–703. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ji JF, He BP, Dheen ST and Tay SS:
Interactions of chemokines and chemokine receptors mediate the
migration of mesenchymal stem cells to the impaired site in the
brain after hypoglossal nerve injury. Stem Cells. 22:415–427. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kollet O, Shivtiel S, Chen YQ, et al: HGF,
SDF-1, and MMP-9 are involved in stress-induced human
CD34+stem cell recruitment to the liver. J Clin Invest.
112:160–169. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hashimoto N, Jin H, Liu T, Chensue SW and
Phan SH: Bone marrow-derived progenitor cells in pulmonary
fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 113:243–252. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rojas M, Xu J, Woods CR, et al: Bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in repair of the injured
lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 33:145–152. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xu J, Mora A, Shim H, Stecenko A, Brigham
KL and Rojas M: Role of the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis in the pathogenesis of
lung injury and fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 37:291–299.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cheon SS, Nadesan P, Poon R and Alman BA:
Growth factors regulate β-catenin-mediated TCF-dependent
transcriptional activation in fibroblasts during the proliferative
phase of wound healing. Exp Cell Res. 293:267–274. 2004.
|
|
20
|
Chilosi M, Poletti V, Zamò A, et al:
Aberrant Wnt/β-catenin pathway activation in idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 162:1495–1502. 2003.
|
|
21
|
Pongracz JE and Stockley RA: Wnt
signalling in lung development and diseases. Respir Res. 7:152006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Königshoff M, Balsara N, Pfaff EM, et al:
Functional Wnt signaling is increased in idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. PLoS One. 3:e21422008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Uematsu K, He B, You L, Xu Z, McCormick F
and Jablons DM: Activation of the Wnt pathway in non small cell
lung cancer: evidence of dishevelled overexpression. Oncogene.
22:7218–7221. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang Y, Sun Z, Qiu X, Li Y, Qin J and Han
X: Roles of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in epithelial differentiation
of mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
390:1309–1314. 2009.
|
|
25
|
Sun Z, Wang Y, Gong X, Su H and Han X:
Secretion of rat tracheal epithelial cells induces mesenchymal stem
cells to differentiate into epithelial cells. Cell Biol Int.
36:169–175. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
White ES, Atrasz RG, Hu B, et al: Negative
regulation of myofibroblast differentiation by PTEN (Phosphatase
and Tensin Homolog Deleted on chromosome 10). Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 173:112–121. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Qiu X, Lin H, Wang Y, et al:
Intracavernous transplantation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal
stem cells restores erectile function of streptozocin-induced
diabetic rats. J Sex Med. 8:427–436. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cargnoni A, Gibelli L, Tosini A, et al:
Transplantation of allogeneic and xenogeneic placenta-derived cells
reduces bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Cell Transplant.
18:405–422. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chang YS, Oh W, Choi SJ, et al: Human
umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate
hyperoxia-induced lung injury in neonatal rats. Cell Transplant.
18:869–886. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Galvez BG, Sampaolesi M, Brunelli S, et
al: Complete repair of dystrophic skeletal muscle by
mesoangioblasts with enhanced migration ability. J Cell Biol.
174:231–243. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Romagnani P, Lasagni L, Mazzinghi B,
Lazzeri E and Romagnani S: Pharmacological modulation of stem cell
function. Curr Med Chem. 14:1129–1139. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ratajczak MZ, Zuba-Surma E, Kucia M, Reca
R, Wojakowski W and Ratajczak J: The pleiotropic effects of the
SDF-1-CXCR4 axis in organogenesis, regeneration and tumorigenesis.
Leukemia. 20:1915–1924. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Song JS, Kang CM, Kang HH, Yoon HK, Kim
YK, Kim KH, Moon HS and Park SH: Inhibitory effect of CXC chemokine
receptor 4 antagonist AMD3100 on bleomycin induced murine pulmonary
fibrosis. Exp Mol Med. 42:465–476. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mehrad B, Burdick MD and Strieter RM:
Fibrocyte CXCR4 regulation as a therapeutic target in pulmonary
fibrosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 41:1708–1718. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Phillips RJ, Burdick MD, Hong K, et al:
Circulating fibrocytes traffic to the lungs in response to CXCL12
and mediate fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 114:438–446. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Antoniou KM, Papadaki HA, Soufla G, et al:
Investigation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BM MSCs)
involvement in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF). Respir Med.
104:1535–1542. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ortiz LA, Gambelli F, McBride C, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cell engraftment in lung is enhanced in response
to bleomycin exposure and ameliorates its fibrotic effects. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:8407–8411. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fine A: Marrow cells as progenitors of
lung tissue. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 32:95–96. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kotton DN, Summer R and Fine A: Lung stem
cells: new paradigms. Exp Hematol. 32:340–343. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ling L, Nurcombe V and Cool SM: Wnt
signaling controls the fate of mesenchymal stem cells. Gene.
433:1–7. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Pinto D and Clevers H: Wnt control of stem
cells and differentiation in the intestinal epithelium. Exp Cell
Res. 306:357–363. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Logan CY and Nusse R: The Wnt signaling
pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
20:781–810. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Van Amerongen R and Berns A: Knockout
mouse models to study Wnt signal transduction. Trends Genet.
22:678–689. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Scotton CJ and Chambers RC: Molecular
targets in pulmonary fibrosis: the myofibroblast in focus. Chest.
132:1311–1321. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|