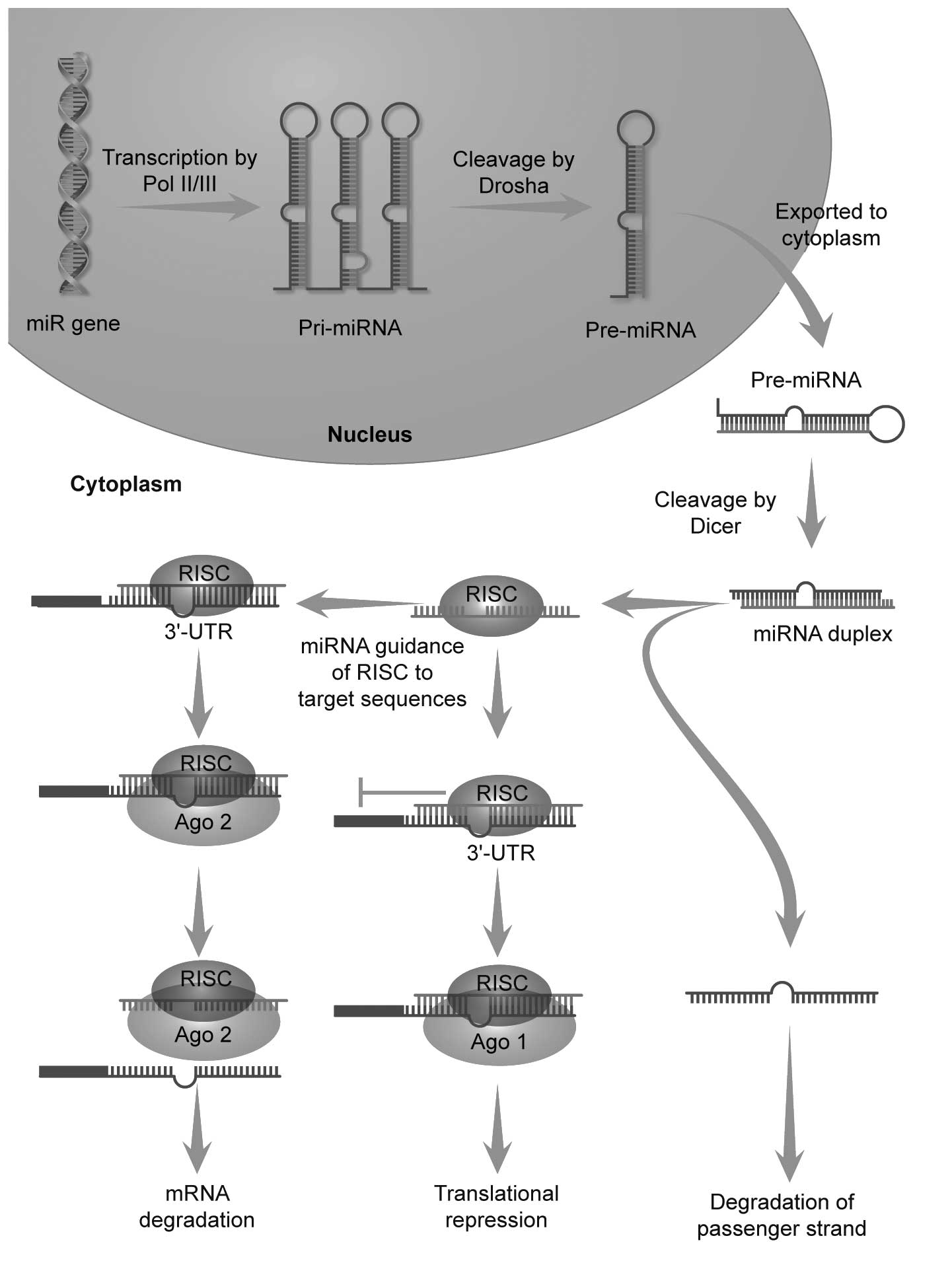
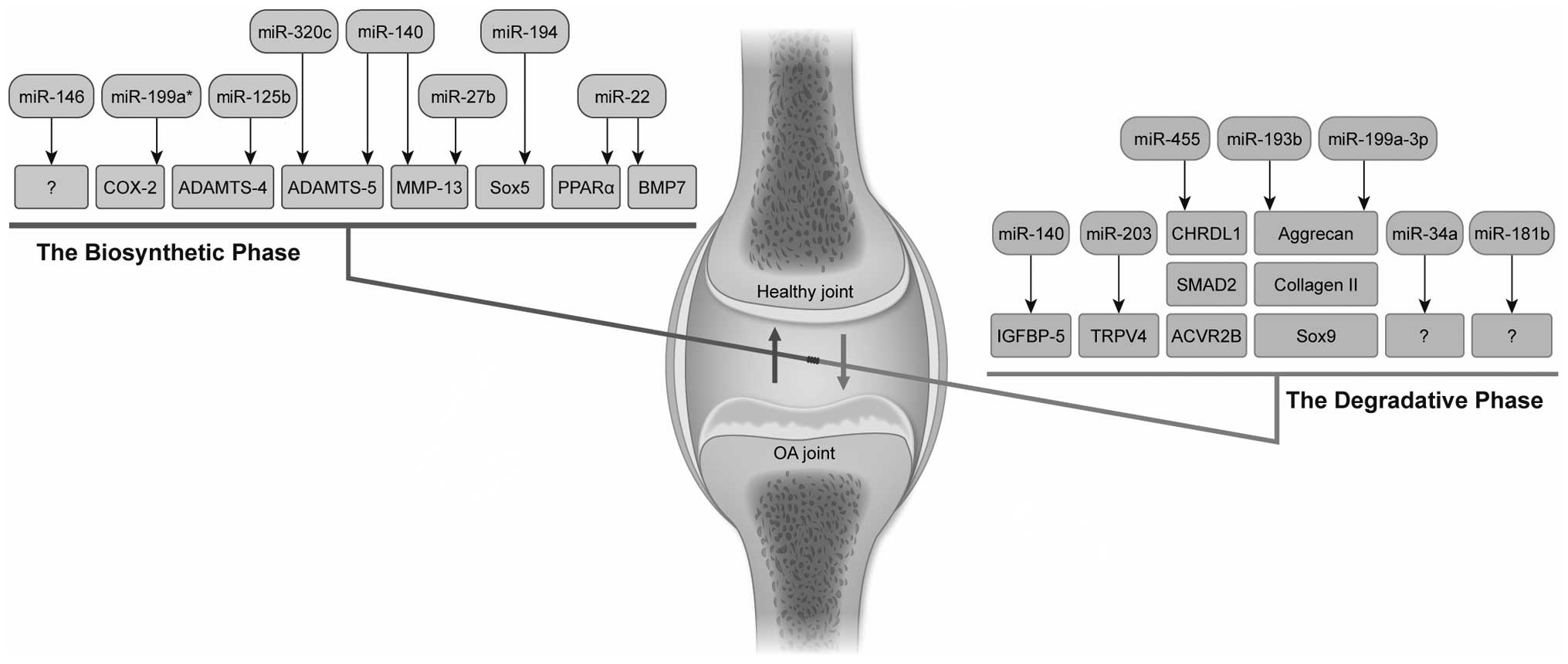
|
1
|
Iannone F and Lapadula G: The
pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Aging Clin Exp Res. 15:364–372.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mortellaro CM: Pathophysiology of
osteoarthritis. Vet Res Commun. 27(Suppl 1): S75–S78. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Martel-Pelletier J: Pathophysiology of
osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 12(Suppl A): S31–S33.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Mandelbaum B and Waddell D: Etiology and
pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Orthopedics. 28(Suppl 2):
s207–s214. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Felson DT, Lawrence RC, Dieppe PA, et al:
Osteoarthritis: new insights. Part 1: the disease and its risk
factors. Ann Intern Med. 133:635–646. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lawrence RC, Felson DT, Helmick CG, et al:
Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic
conditions in the United States. Part II. Arthritis Rheum.
58:26–35. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Naumann A, Dennis JE, Awadallah A, et al:
Immunochemical and mechanical characterization of cartilage
subtypes in rabbit. J Histochem Cytochem. 50:1049–1058. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wong M and Carter DR: Articular cartilage
functional histomorphology and mechanobiology: a research
perspective. Bone. 33:1–13. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Burgeson RE, Hebda PA, Morris NP and
Hollister DW: Human cartilage collagens. Comparison of cartilage
collagens with human type V collagen. J Biol Chem. 257:7852–7856.
1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Eyre D: Collagen of articular cartilage.
Arthritis Res. 4:30–35. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Poole AR, Kojima T, Yasuda T, Mwale F,
Kobayashi M and Laverty S: Composition and structure of articular
cartilage: a template for tissue repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
391:S26–S33. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Knudson CB and Knudson W: Cartilage
proteoglycans. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 12:69–78. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cawston TE and Wilson AJ: Understanding
the role of tissue degrading enzymes and their inhibitors in
development and disease. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol.
20:983–1002. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Plaas A, Osborn B, Yoshihara Y, et al:
Aggrecanolysis in human osteoarthritis: confocal localization and
biochemical characterization of ADAMTS5-hyaluronan complexes in
articular cartilages. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 15:719–734. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wu W, Billinghurst RC, Pidoux I, et al:
Sites of collagenase cleavage and denaturation of type II collagen
in aging and osteoarthritic articular cartilage and their
relationship to the distribution of matrix metalloproteinase 1 and
matrix metalloproteinase 13. Arthritis Rheum. 46:2087–2094. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cordes KR and Srivastava D: MicroRNA
regulation of cardiovascular development. Circ Res. 104:724–732.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N and Filipowicz W:
Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev
Biochem. 79:351–379. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu N and Olson EN: MicroRNA regulatory
networks in cardiovascular development. Dev Cell. 18:510–525. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang DZ: MicroRNAs in cardiac development
and remodeling. Pediatr Cardiol. 31:357–362. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao Y and Srivastava D: A developmental
view of microRNA function. Trends Biochem Sci. 32:189–197. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Farh KK, Grimson A, Jan C, et al: The
widespread impact of mammalian MicroRNAs on mRNA repression and
evolution. Science. 310:1817–1821. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chendrimada TP, Gregory RI, Kumaraswamy E,
et al: TRBP recruits the Dicer complex to Ago2 for microRNA
processing and gene silencing. Nature. 436:740–744. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee Y, Ahn C, Han J, et al: The nuclear
RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature.
425:415–419. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gregory RI, Yan KP, Amuthan G, et al: The
Microprocessor complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs. Nature.
432:235–240. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Denli AM, Tops BB, Plasterk RH, Ketting RF
and Hannon GJ: Processing of primary microRNAs by the
Microprocessor complex. Nature. 432:231–235. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Small EM and Olson EN: Pervasive roles of
microRNAs in cardiovascular biology. Nature. 469:336–342. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ghayor C, Chadjichristos C, Herrouin JF,
et al: Sp3 represses the Sp1-mediated transactivation of the human
COL2A1 gene in primary and de-differentiated chondrocytes. J Biol
Chem. 276:36881–36895. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang Z, Kang Y, Zhang H, et al:
Expression of microRNAs during chondrogenesis of human
adipose-derived stem cells. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 20:1638–1646.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cancedda R, Descalzi Cancedda F and
Castagnola P: Chondrocyte differentiation. Int Rev Cytol.
159:265–358. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang B, Guo H, Zhang Y, Chen L, Ying D and
Dong S: MicroRNA-145 regulates chondrogenic differentiation of
mesenchymal stem cells by targeting Sox9. PLoS One. 6:e216792011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Martinez-Sanchez A, Dudek KA and Murphy
CL: Regulation of human chondrocyte function through direct
inhibition of cartilage master regulator SOX9 by microRNA-145
(miRNA-145). J Biol Chem. 287:916–924. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ning G, Liu X, Dai M, Meng A and Wang Q:
MicroRNA-92a upholds Bmp signaling by targeting noggin3 during
pharyngeal cartilage formation. Dev Cell. 24:283–295. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ohgawara T, Kubota S, Kawaki H, et al:
Regulation of chondrocytic phenotype by micro RNA 18a: involvement
of Ccn2/Ctgf as a major target gene. FEBS Lett. 583:1006–1010.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Soullier S, Jay P, Poulat F, Vanacker JM,
Berta P and Laudet V: Diversification pattern of the HMG and SOX
family members during evolution. J Mol Evol. 48:517–527. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wright E, Hargrave MR, Christiansen J, et
al: The Sry-related gene Sox9 is expressed during chondrogenesis in
mouse embryos. Nat Genet. 9:15–20. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bi W, Deng JM, Zhang Z, Behringer RR and
de Crombrugghe B: Sox9 is required for cartilage formation. Nat
Genet. 22:85–89. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ikeda T, Kawaguchi H, Kamekura S, et al:
Distinct roles of Sox5, Sox6, and Sox9 in different stages of
chondrogenic differentiation. J Bone Miner Metab. 23:337–340. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bell DM, Leung KK, Wheatley SC, et al:
SOX9 directly regulates the type-II collagen gene. Nat Genet.
16:174–178. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang P, Jimenez SA and Stokes DG:
Regulation of human COL9A1 gene expression. Activation of the
proximal promoter region by SOX9. J Biol Chem. 278:117–123. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu Y, Li H, Tanaka K, Tsumaki N and
Yamada Y: Identification of an enhancer sequence within the first
intron required for cartilage-specific transcription of the
alpha2(XI) collagen gene. J Biol Chem. 275:12712–12718. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sekiya I, Tsuji K, Koopman P, et al: SOX9
enhances aggrecan gene promoter/enhancer activity and is
up-regulated by retinoic acid in a cartilage-derived cell line,
TC6. J Biol Chem. 275:10738–10744. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tew SR, Li Y, Pothacharoen P, Tweats LM,
Hawkins RE and Hardingham TE: Retroviral transduction with SOX9
enhances re-expression of the chondrocyte phenotype in passaged
osteoarthritic human articular chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 13:80–89. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cucchiarini M, Thurn T, Weimer A, Kohn D,
Terwilliger EF and Madry H: Restoration of the extracellular matrix
in human osteoarthritic articular cartilage by overexpression of
the transcription factor SOX9. Arthritis Rheum. 56:158–167. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Dai L, Zhang X, Hu X, Zhou C and Ao Y:
Silencing of microRNA-101 prevents IL-1beta-induced extracellular
matrix degradation in chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther.
14:R2682012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Xu J, Kang Y, Liao WM and Yu L: MiR-194
regulates chondrogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived
stem cells by targeting Sox5. PLoS One. 7:e318612012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Parvizi J, Zmistowski B, Berbari EF, et
al: New definition for periprosthetic joint infection: from the
Workgroup of the Musculoskeletal Infection Society. Clin Orthop
Relat Res. 469:2992–2994. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hatakeyama Y, Nguyen J, Wang X, Nuckolls
GH and Shum L: Smad signaling in mesenchymal and chondroprogenitor
cells. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 85-A(Suppl 3): S13–S18.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pan Q, Yu Y, Chen Q, et al: Sox9, a key
transcription factor of bone morphogenetic protein-2-induced
chondrogenesis, is activated through BMP pathway and a CCAAT box in
the proximal promoter. J Cell Physiol. 217:228–241. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Denker AE, Nicoll SB and Tuan RS:
Formation of cartilage-like spheroids by micromass cultures of
murine C3H10T1/2 cells upon treatment with transforming growth
factor-beta 1. Differentiation. 59:25–34. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lin EA, Kong L, Bai XH, Luan Y and Liu CJ:
miR-199a, a bone morphogenic protein 2-responsive MicroRNA,
regulates chondrogenesis via direct targeting to Smad1. J Biol
Chem. 284:11326–11335. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liang ZJ, Zhuang H, Wang GX, et al:
MiRNA-140 is a negative feedback regulator of MMP-13 in
IL-1beta-stimulated human articular chondrocyte C28/I2 cells.
Inflamm Res. 61:503–509. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Buechli ME, Lamarre J and Koch TG:
MicroRNA-140 expression during chondrogenic differentiation of
equine cord blood-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cells
Dev. 22:1288–1296. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Miyaki S, Nakasa T, Otsuki S, et al:
MicroRNA-140 is expressed in differentiated human articular
chondrocytes and modulates interleukin-1 responses. Arthritis
Rheum. 60:2723–2730. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Nicolas FE, Pais H, Schwach F, et al: mRNA
expression profiling reveals conserved and non-conserved miR-140
targets. RNA Biol. 8:607–615. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Pais H, Nicolas FE, Soond SM, et al:
Analyzing mRNA expression identifies Smad3 as a microRNA-140 target
regulated only at protein level. RNA. 16:489–494. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Nakamura Y, Inloes JB, Katagiri T and
Kobayashi T: Chondrocyte-specific microRNA-140 regulates
endochondral bone development and targets Dnpep to modulate bone
morphogenetic protein signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 31:3019–3028. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Song J, Kim D and Jin EJ: MicroRNA-488
suppresses cell migration through modulation of the focal adhesion
activity during chondrogenic differentiation of chick limb
mesenchymal cells. Cell Biol Int. 35:179–185. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Kim D, Song J, Kim S, Chun CH and Jin EJ:
MicroRNA-34a regulates migration of chondroblast and
IL-1beta-induced degeneration of chondrocytes by targeting EphA5.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 415:551–557. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Abouheif MM, Nakasa T, Shibuya H, Niimoto
T, Kongcharoensombat W and Ochi M: Silencing microRNA-34a inhibits
chondrocyte apoptosis in a rat osteoarthritis model in vitro.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 49:2054–2060. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kim D, Song J and Jin EJ: MicroRNA-221
regulates chondrogenic differentiation through promoting
proteosomal degradation of slug by targeting Mdm2. J Biol Chem.
285:26900–26907. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Dunn W, DuRaine G and Reddi AH: Profiling
microRNA expression in bovine articular cartilage and implications
for mechanotransduction. Arthritis Rheum. 60:2333–2339. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Magee C, Nurminskaya M, Faverman L, Galera
P and Linsenmayer TF: SP3/SP1 transcription activity regulates
specific expression of collagen type X in hypertrophic
chondrocytes. J Biol Chem. 280:25331–25338. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Kavurma MM and Khachigian LM: Sp1 inhibits
proliferation and induces apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells
by repressing p21WAF1/Cip1 transcription and cyclin
D1-Cdk4-p21WAF1/Cip1 complex formation. J Biol Chem.
278:32537–32543. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Deniaud E, Baguet J, Chalard R, et al:
Overexpression of transcription factor Sp1 leads to gene expression
perturbations and cell cycle inhibition. PLoS One. 4:e70352009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Yang J, Qin S, Yi C, et al: MiR-140 is
co-expressed with Wwp2-C transcript and activated by Sox9 to target
Sp1 in maintaining the chondrocyte proliferation. FEBS Lett.
585:2992–2997. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Sumiyoshi K, Kubota S, Ohgawara T, et al:
Identification of miR-1 as a micro RNA that supports late-stage
differentiation of growth cartilage cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 402:286–290. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Guan YJ, Yang X, Wei L and Chen Q:
MiR-365: a mechanosensitive microRNA stimulates chondrocyte
differentiation through targeting histone deacetylase 4. FASEB J.
25:4457–4466. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Vega RB, Matsuda K, Oh J, et al: Histone
deacetylase 4 controls chondrocyte hypertrophy during
skeletogenesis. Cell. 119:555–566. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Tuddenham L, Wheeler G, Ntounia-Fousara S,
et al: The cartilage specific microRNA-140 targets histone
deacetylase 4 in mouse cells. FEBS Lett. 580:4214–4217. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Nicolas FE, Pais H, Schwach F, et al:
Experimental identification of microRNA-140 targets by silencing
and overexpressing miR-140. RNA. 14:2513–2520. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhong N, Sun J, Min Z, et al: MicroRNA-337
is associated with chondrogenesis through regulating TGFBR2
expression. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 20:593–602. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Ham O, Song BW, Lee SY, et al: The role of
microRNA-23b in the differentiation of MSC into chondrocyte by
targeting protein kinase A signaling. Biomaterials. 33:4500–4507.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Iliopoulos D, Malizos KN, Oikonomou P and
Tsezou A: Integrative microRNA and proteomic approaches identify
novel osteoarthritis genes and their collaborative metabolic and
inflammatory networks. PLoS One. 3:e37402008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Glasson SS, Askew R, Sheppard B, et al:
Deletion of active ADAMTS5 prevents cartilage degradation in a
murine model of osteoarthritis. Nature. 434:644–648. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Stanton H, Rogerson FM, East CJ, et al:
ADAMTS5 is the major aggrecanase in mouse cartilage in vivo and in
vitro. Nature. 434:648–652. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Miyaki S, Sato T, Inoue A, et al:
MicroRNA-140 plays dual roles in both cartilage development and
homeostasis. Genes Dev. 24:1173–1185. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Zhang M, Liu L, Xiao T and Guo W:
Detection of the expression level of miR-140 using realtime
fluorescent quantitative PCR in knee synovial fluid of
osteoarthritis patients. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.
37:1210–1214. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
80
|
Tardif G, Hum D, Pelletier JP, Duval N and
Martel-Pelletier J: Regulation of the IGFBP-5 and MMP-13 genes by
the microRNAs miR-140 and miR-27a in human osteoarthritic
chondrocytes. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 10:1482009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Ukai T, Sato M, Akutsu H, Umezawa A and
Mochida J: MicroRNA-199a-3p, microRNA-193b, and microRNA-320c are
correlated to aging and regulate human cartilage metabolism. J
Orthop Res. 30:1915–1922. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Matsukawa T, Sakai T, Yonezawa T, et al:
MicroRNA-125b regulates the expression of aggrecanase-1 (ADAMTS-4)
in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther.
15:R282013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Xu N, Zhang L, Meisgen F, et al:
MicroRNA-125b down-regulates matrix metallopeptidase 13 and
inhibits cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation,
migration, and invasion. J Biol Chem. 287:29899–29908. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Muramatsu F, Kidoya H, Naito H, Sakimoto S
and Takakura N: microRNA-125b inhibits tube formation of blood
vessels through translational suppression of VE-cadherin. Oncogene.
32:414–421. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Little CB, Barai A, Burkhardt D, et al:
Matrix metalloproteinase 13-deficient mice are resistant to
osteoarthritic cartilage erosion but not chondrocyte hypertrophy or
osteophyte development. Arthritis Rheum. 60:3723–3733. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Mapp PI and Walsh DA: Mechanisms and
targets of angiogenesis and nerve growth in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev
Rheumatol. 8:390–398. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Akhtar N, Rasheed Z, Ramamurthy S,
Anbazhagan AN, Voss FR and Haqqi TM: MicroRNA-27b regulates the
expression of matrix metalloproteinase 13 in human osteoarthritis
chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 62:1361–1371. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Akhtar N and Haqqi TM:
MicroRNA-199a* regulates the expression of
cyclooxygenase-2 in human chondrocytes. Ann Rheum Dis.
71:1073–1080. 2012.
|
|
89
|
He L, He X, Lim LP, et al: A microRNA
component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature.
447:1130–1134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Chang TC, Wentzel EA, Kent OA, et al:
Transactivation of miR-34a by p53 broadly influences gene
expression and promotes apoptosis. Mol Cell. 26:745–752. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Jones SW, Watkins G, Le Good N, et al: The
identification of differentially expressed microRNA in
osteoarthritic tissue that modulate the production of TNF-alpha and
MMP13. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 17:464–472. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Yamasaki K, Nakasa T, Miyaki S, et al:
Expression of MicroRNA-146a in osteoarthritis cartilage. Arthritis
Rheum. 60:1035–1041. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Li X, Gibson G, Kim JS, et al:
MicroRNA-146a is linked to pain-related pathophysiology of
osteoarthritis. Gene. 480:34–41. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Song J, Lee M, Kim D, Han J, Chun CH and
Jin EJ: MicroRNA-181b regulates articular chondrocytes
differentiation and cartilage integrity. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 431:210–214. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Swingler TE, Wheeler G, Carmont V, et al:
The expression and function of microRNAs in chondrogenesis and
osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 64:1909–1919. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Dudek KA, Lafont JE, Martinez-Sanchez A
and Murphy CL: Type II collagen expression is regulated by
tissue-specific miR-675 in human articular chondrocytes. J Biol
Chem. 285:24381–24387. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Steck E, Boeuf S, Gabler J, et al:
Regulation of H19 and its encoded microRNA-675 in osteoarthritis
and under anabolic and catabolic in vitro conditions. J Mol Med
(Berl). 90:1185–1195. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Hu F, Zhu W and Wang L: MicroRNA-203
up-regulates nitric oxide expression in temporomandibular joint
chondrocytes via targeting TRPV4. Arch Oral Biol. Nov 16–2012.(Epub
ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|