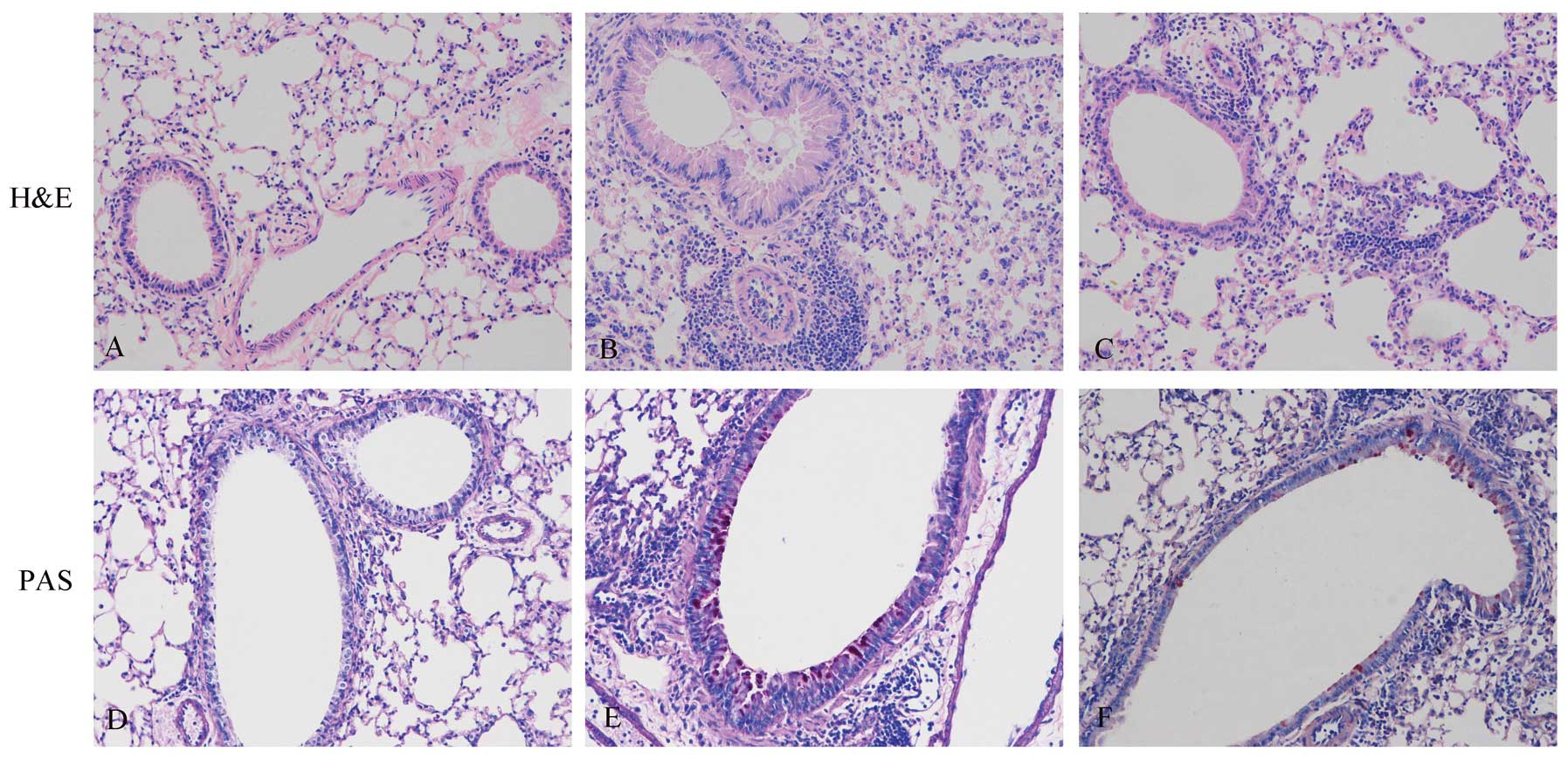
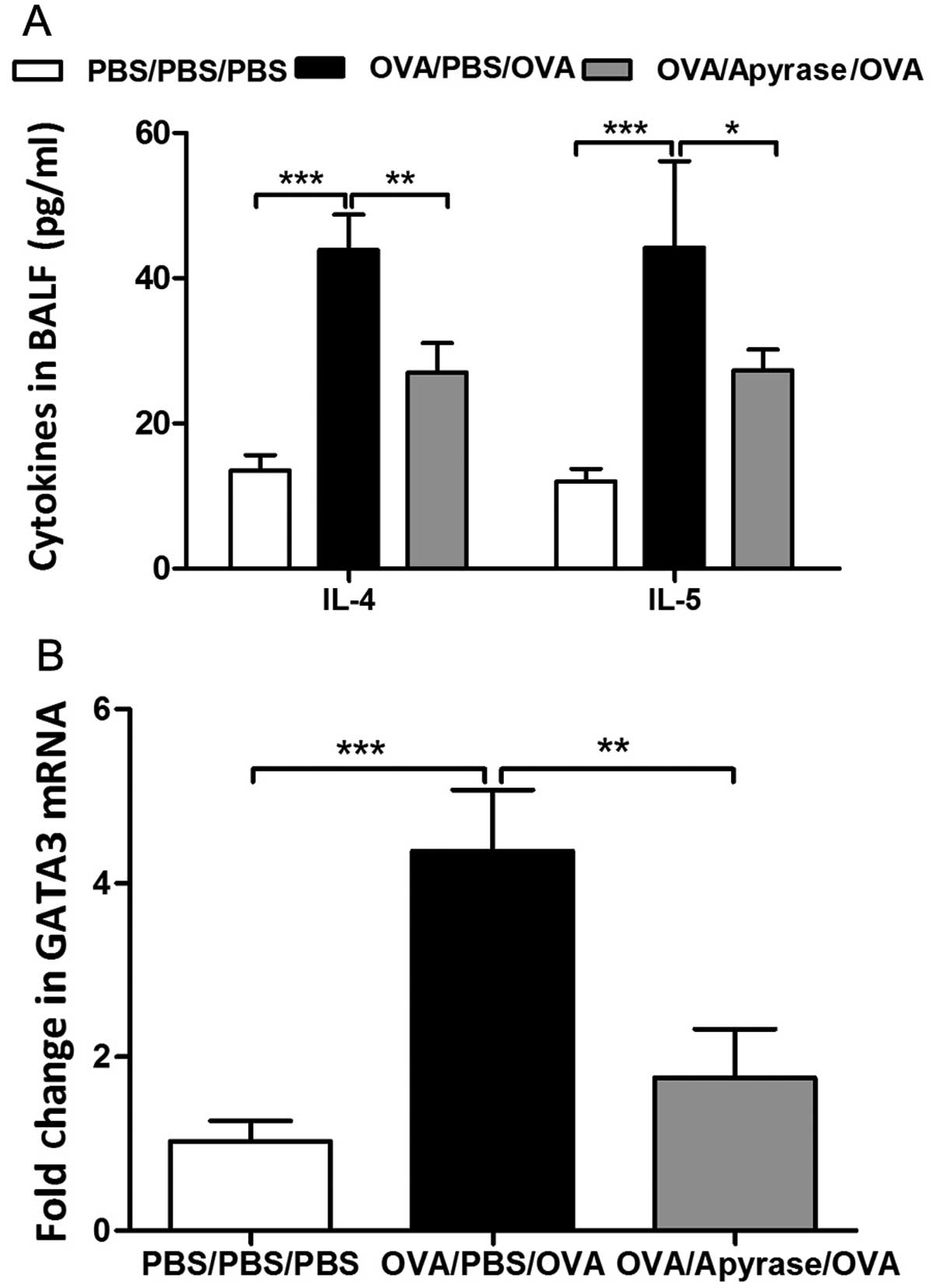
|
1
|
Lloyd CM and Hessel EM: Functions of T
cells in asthma: more than just T(H)2 cells. Nat Rev Immun.
10:838–848. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Adcock IM, Caramori G and Chung KF: New
targets for drug development in asthma. Lancet. 372:1073–1087.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Holgate ST and Polosa R: Treatment
strategies for allergy and asthma. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:218–230.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lambrecht BN and Hammad H: Biology of lung
dendritic cells at the origin of asthma. Immunity. 31:412–424.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim HY, DeKruyff RH and Umetsu DT: The
many paths to asthma: phenotype shaped by innate and adaptive
immunity. Nat Immunol. 11:577–584. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Trautmann A: Extracellular ATP in the
immune system: more than just a ‘danger signal’. Sci signal.
2:pe62009.
|
|
7
|
Robson SC, Wu Y, Sun X, Knosalla C, Dwyer
K and Enjyoji K: Ectonucleotidases of CD39 family modulate vascular
inflammation and thrombosis in transplantation. Semin Thromb
Hemost. 31:217–233. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Idzko M, Hammad H, van Nimwegen M, et al:
Extracellular ATP triggers and maintains asthmatic airway
inflammation by activating dendritic cells. Nat Med. 13:913–919.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Müller T, Robaye B, Vieira RP, et al: The
purinergic receptor P2Y2 receptor mediates chemotaxis of dendritic
cells and eosinophils in allergic lung inflammation. Allergy.
65:1545–1553. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Müller T, Vieira RP, Grimm M, et al: A
potential role for P2X7R in allergic airway inflammation in mice
and humans. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 44:456–464. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Manthei DM, Jackson DJ, Evans MD, et al:
Protection from asthma in a high-risk birth cohort by attenuated
P2X(7) function. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 130:496–502. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Crikis S, Lu B, Murray-Segal LM, et al:
Transgenic overexpression of CD39 protects against renal
ischemia-reperfusion and transplant vascular injury. Am J
Transplant. 10:2586–2595. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Künzli BM, Berberat PO, Dwyer K, et al:
Variable impact of CD39 in experimental murine colitis. Dig Dis
Sci. 56:1393–1403. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Künzli BM, Nuhn P, Enjyoji K, et al:
Disordered pancreatic inflammatory responses and inhibition of
fibrosis in CD39-null mice. Gastroenterology. 134:292–305.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dwyer KM, Deaglio S, Gao W, Friedman D,
Strom TB and Robson SC: CD39 and control of cellular immune
responses. Purinergic Signal. 3:171–180. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Deaglio S and Robson SC: Ectonucleotidases
as regulators of purinergic signaling in thrombosis, inflammation,
and immunity. Adv Pharmacol. 61:301–332. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Antonioli L, Pacher P, Vizi ES and Haskó
G: CD39 and CD73 in immunity and inflammation. Trends Mol Med.
19:355–367. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kwak YG, Song CH, Yi HK, et al:
Involvement of PTEN in airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation
in bronchial asthma. J Clin Invest. 111:1083–1092. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Idzko M, Dichmann S, Ferrari D, et al:
Nucleotides induce chemotaxis and actin polymerization in immature
but not mature human dendritic cells via activation of pertussis
toxin-sensitive P2y receptors. Blood. 100:925–932. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Enjyoji K, Sévigny J, Lin Y, et al:
Targeted disruption of cd39/ATP diphosphohydrolase results in
disordered hemostasis and thromboregulation. Nat Med. 5:1010–1017.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kapojos JJ, van den Berg A, Borghuis T, et
al: Enhanced ecto-apyrase activity of stimulated endothelial or
mesangial cells is downregulated by glucocorticoids in vitro. Eur J
Pharmacol. 501:191–198. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Heine P, Braun N, Sévigny J, Robson SC,
Servos J and Zimmermann H: The C-terminal cysteine-rich region
dictates specific catalytic properties in chimeras of the
ectonucleotidases NTPDase1 and NTPDase2. Eur J Biochem.
268:364–373. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Paletta-Silva R and Meyer-Fernandes JR:
Adenosine and immune imbalance in visceral leishmaniasis: the
possible role of ectonucleotidases. J Trop Med. 2012:6508742012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Souza Vdo C, Schlemmer KB, Noal CB, et al:
E-NTPDase and E-ADA activities are altered in lymphocytes of
patients with indeterminate form of Chagas’ disease. Parasitol Int.
61:690–696. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fan J, Zhang Y, Chuang-Smith ON, et al:
Ecto-5′-nucleotidase: a candidate virulence factor in
Streptococcus sanguinis experimental endocarditis. PloS One.
7:e380592012.
|
|
26
|
Théâtre E, Frederix K, Guilmain W, et al:
Overexpression of CD39 in mouse airways promotes bacteria-induced
inflammation. J Immunol. 189:1966–1974. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fletcher JM, Lonergan R, Costelloe L, et
al: CD39+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells suppress
pathogenic Th17 cells and are impaired in multiple sclerosis. J
Immunol. 183:7602–7610. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Moncrieffe H, Nistala K, Kamhieh Y, et al:
High expression of the ectonucleotidase CD39 on T cells from the
inflamed site identifies two distinct populations, one regulatory
and one memory T cell population. J Immunol. 185:134–143. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Peelen E, Damoiseaux J, Smolders J, et al:
Th17 expansion in MS patients is counterbalanced by an expanded
CD39+ regulatory T cell population during remission but not during
relapse. J Neuroimmunol. 240–241:97–103. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hart ML, Gorzolla IC, Schittenhelm J,
Robson SC and Eltzschig HK: SP1-dependent induction of CD39
facilitates hepatic ischemic preconditioning. J Immunol.
184:4017–4024. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Bönner F, Borg N, Burghoff S and Schrader
J: Resident cardiac immune cells and expression of the
ectonucleotidase enzymes CD39 and CD73 after ischemic injury. PloS
One. 7:e347302012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Friedman DJ, Künzli BM, A-Rahim YI, et al:
CD39 deletion exacerbates experimental murine colitis and human
polymorphisms increase susceptibility to inflammatory bowel
disease. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA. 106:16788–16793. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Chen X, Gao YD and Yang J: Elevated
interferon regulatory factor 4 levels in patients with allergic
asthma. J Asthma. 49:441–449. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Stellato C, Gubin MM, Magee JD, et al:
Coordinate regulation of GATA-3 and Th2 cytokine gene expression by
the RNA-binding protein HuR. J Immunol. 187:441–449. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|