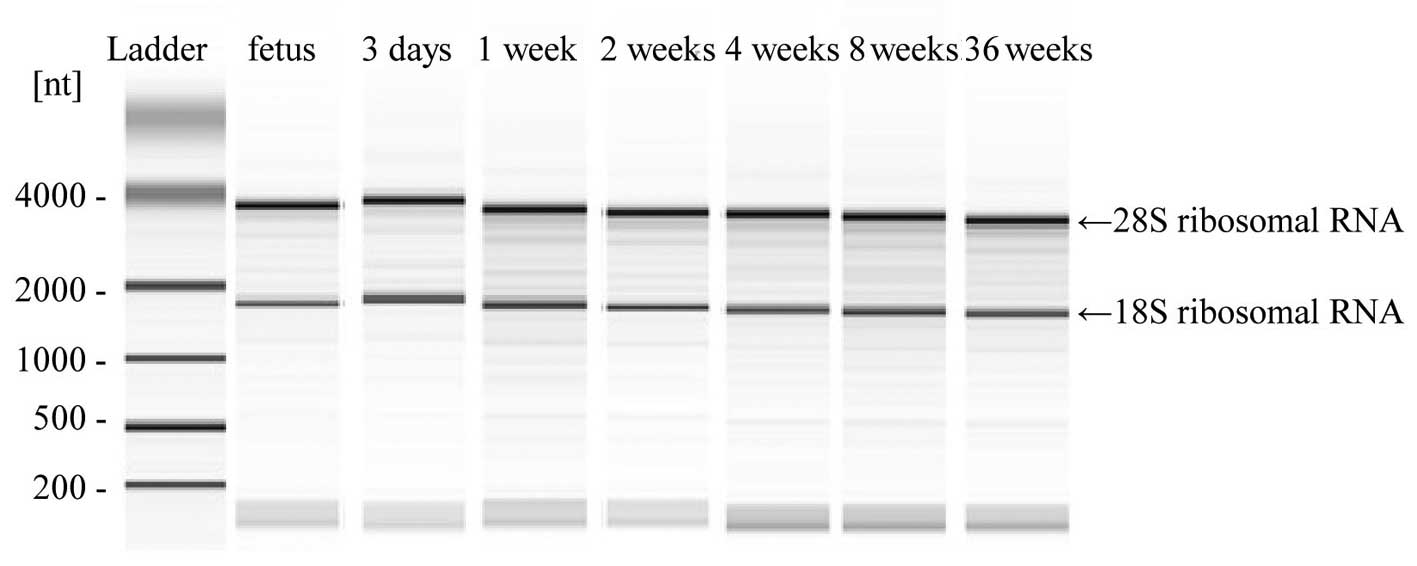
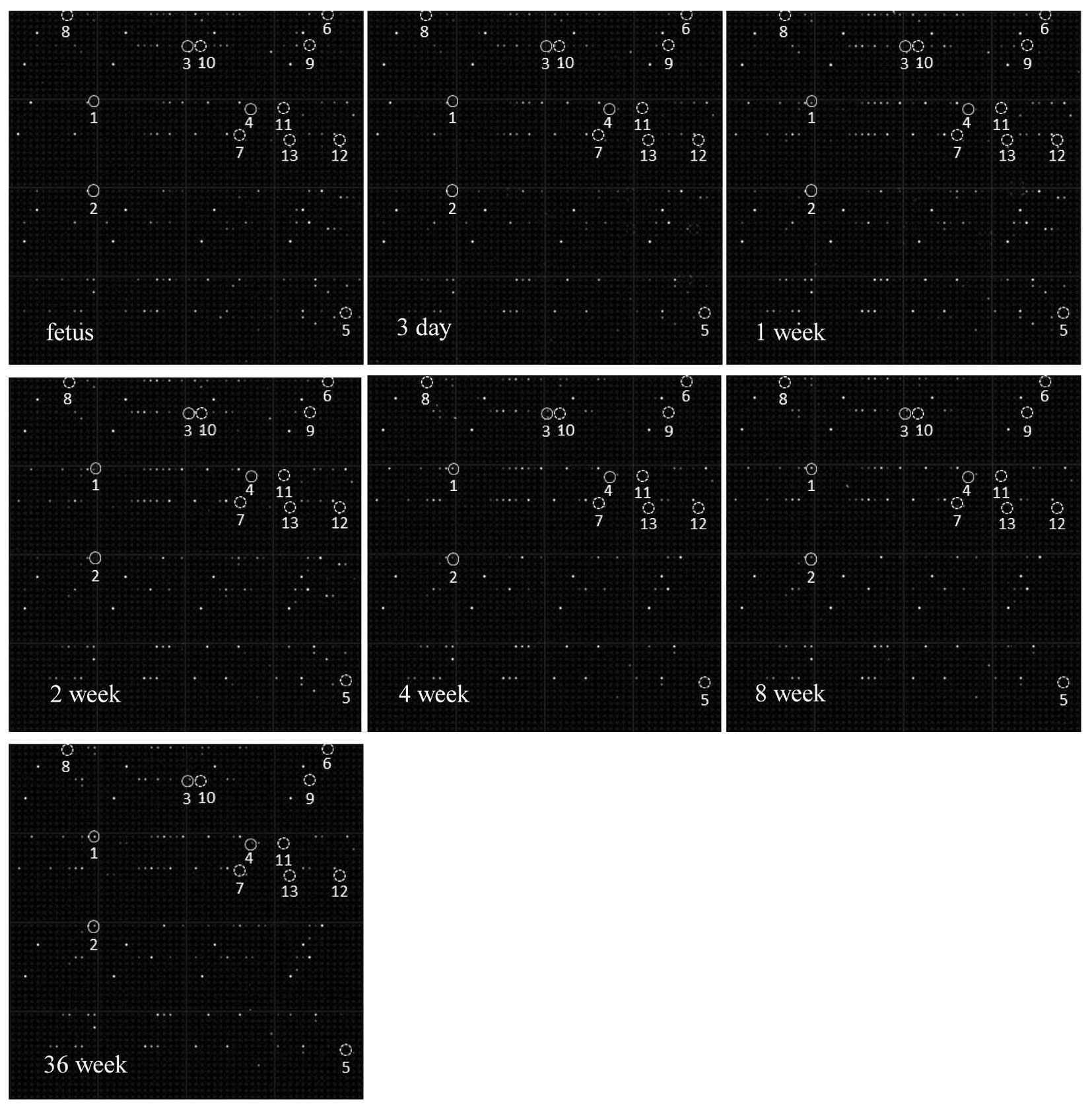
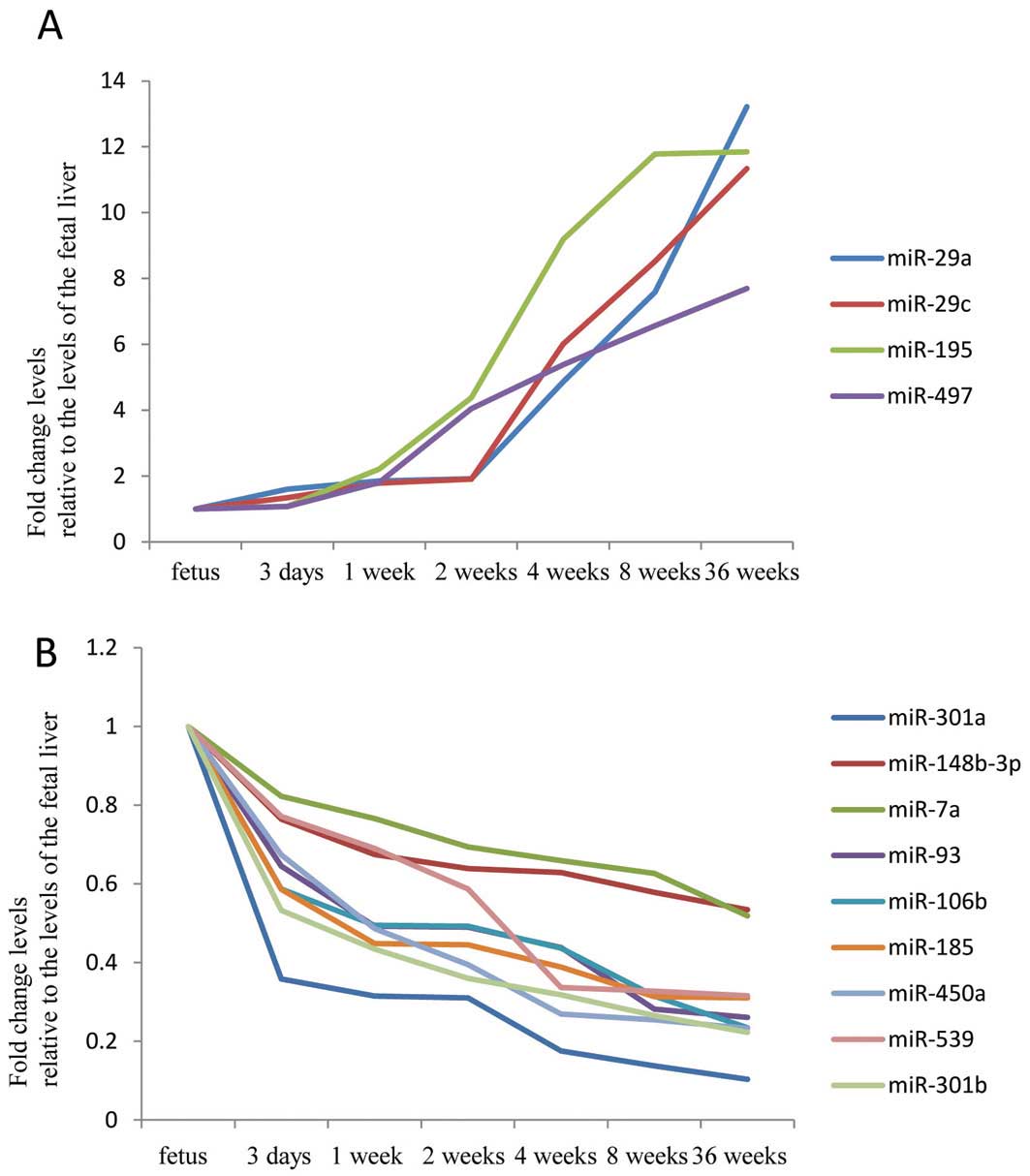
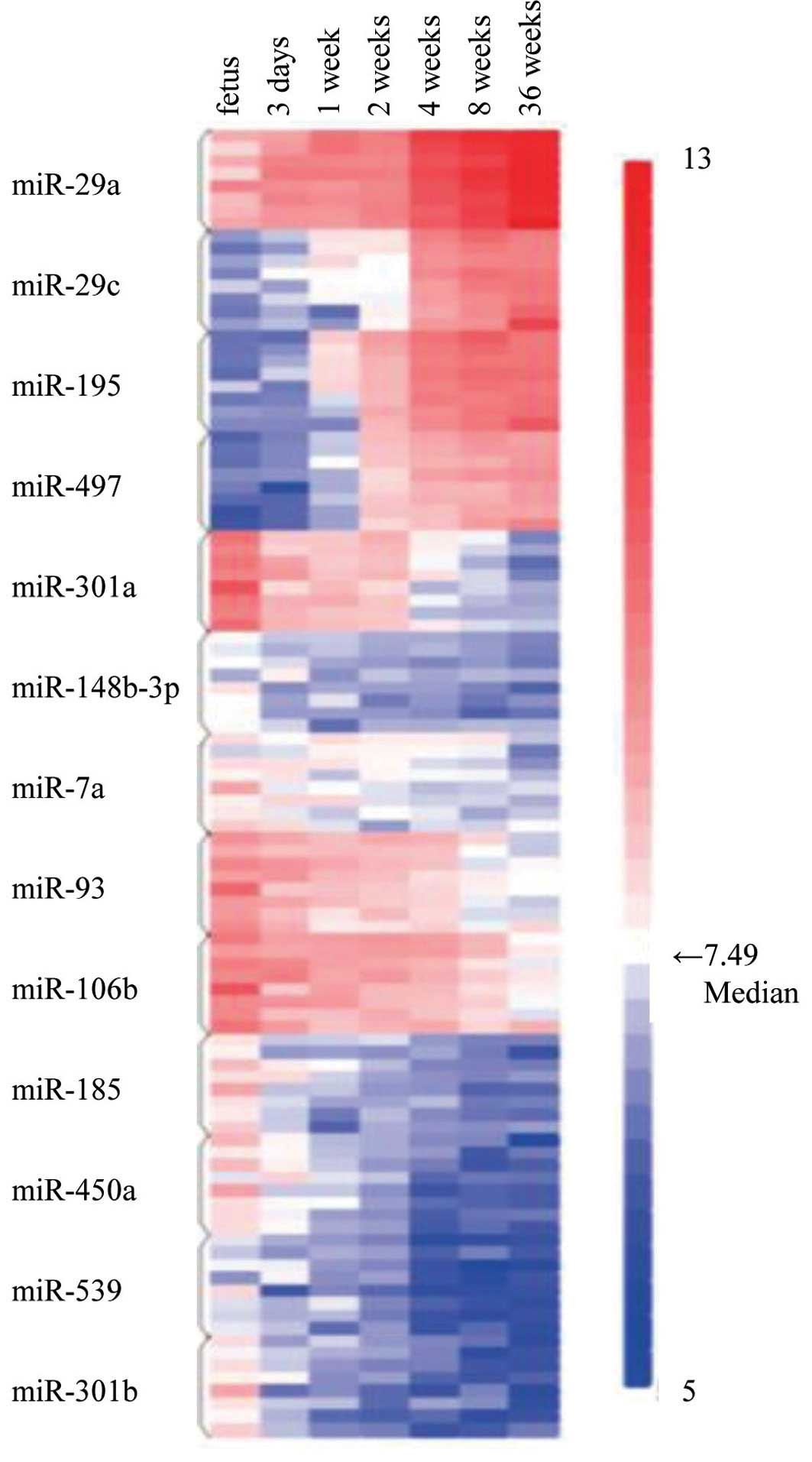
|
1
|
Lakner AM, Bonkovsky HL and Schrum LW:
MicroRNAs: Fad or future of liver disease. World J Gastroenterol.
17:2536–2542. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pogribny IP, Tryndyak VP, Boyko A, et al:
Induction of microRNAome deregulation in rat liver by long-term
tamoxifen exposure. Mutat Res. 619:30–37. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Eda A, Takahashi M, Fukushima T and Hohjoh
H: Alteration of microRNA expression in the process of mouse brain
growth. Gene. 485:46–52. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Yalcin A, et
al: Identification of tissue-specific microRNAs from mouse. Curr
Biol. 12:735–739. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W
and Tuschl T: Identification of novel genes coding for small
expressed RNAs. Science. 294:853–858. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tzur G, Israel A, Levy A, et al:
Comprehensive gene and microRNA expression profiling reveals a role
for microRNAs in human liver development. PLoS One. 4:75112009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li N, Bates DJ, An J, et al: Up-regulation
of key microRNAs, and inverse down-regulation of their predicted
oxidative phosphorylation target genes, during aging in mouse
brain. Neurobiol Aging. 32:944–955. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li N, Muthusamy S, Liang R, et al:
Increased expression of miR-34a and miR-93 in rat liver during
aging, and their impact on the expression of Mgst1 and Sirt1. Mech
Ageing Dev. 132:75–85. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bates DJ, Li N, Liang R, et al: MicroRNA
regulation in Ames dwarf mouse liver may contribute to delayed
aging. Aging Cell. 9:1–18. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Maes OC, An J, Sarojini H and Wang E:
Murine microRNAs implicated in liver functions and aging process.
Mech Ageing Dev. 129:534–541. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ugalde AP, Ramsay AJ, de la Rosa J, et al:
Aging and chronic DNA damage response activate a regulatory pathway
involving miR-29 and p53. EMBO J. 30:2219–2232. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bradford M: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgramof protein utilizing the principle
of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural
proteins during the assembly of the head of bactriophage T4.
Nature. 227:680–685. 1970. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Towbin H, Staehelin T and Gordon J:
Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to
nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 76:4350–4354. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Aw S and Cohen SM: Time is of the essence:
microRNAs and age-associated neurodegeneration. Cell Res.
22:1218–1220. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Inukai S, de Lencastre A, Turner M and
Slack F: Novel microRNAs differentially expressed during aging in
the mouse brain. PLoS One. 7:e400282012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ungvari Z, Tucsek Z, Sosnowska D, et al:
Aging-induced dysregulation of dicer1-dependent microRNA expression
impairs angiogenic capacity of rat cerebromicrovascular endothelial
cells. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 68:877–891. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Rao YS, Mott NN, Wang Y and Chung WC:
MicroRNAs in the aging female brain: a putative mechanism for
age-specific estrogen effects. Endocrinology. 154:2795–2806. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ma L and Qu L: The function of microRNAs
in renal development and pathophysiology. J Genet Genomics.
40:143–152. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dumortier O and Van Obberghen E: MicroRNAs
in pancreas development. Diabetes Obes Metab. 14(Suppl 3): 22–28.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ugalde AP, Español Y and López-Otín C:
Micromanaging aging with miRNAs: new messages from the nuclear
envelope. Nucleus. 2:549–555. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Roderburg C, Urban GW, Bettermann K, et
al: Micro-RNA profiling reveals a role for miR-29 in human and
murine liver fibrosis. Hepatology. 53:209–218. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Boon RA, Seeger T, Heydt S, et al:
MicroRNA-29 in aortic dilation: implications for aneurysm
formation. Circ Res. 109:1115–1119. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Milewicz DM: MicroRNAs, fibrotic
remodeling, and aortic aneurysms. J Clin Invest. 122:490–493. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Williams AE, Perry MM, Moschos SA and
Lindsay MA: MicroRNA expression in the aging mouse lung. BMC
Genomics. 8:1722007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang Y, Scheiber MN, Neumann C, et al:
MicroRNA regulation of ionizing radiation-induced premature
senescence. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 81:839–848. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schneider EL, Sternberg H, Tice RR, et al:
Cellular replication and aging. Mech Ageing Dev. 9:313–324. 1979.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kuhn HG, Dickinson-Anson H and Gage FH:
Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat: age-related
decrease of neuronal progenitor proliferation. J Neurosci.
16:2027–2033. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Timchenko NA: Aging and liver
regeneration. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 20:171–176. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Salminen A, Ojala J and Kaarniranta K:
Apoptosis and aging: increased resistance to apoptosis enhances the
aging process. Cell Mol Life Sci. 68:1021–1031. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kwiecinski M, Noetel A, Elfimova N, et al:
Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) inhibits collagen I and IV synthesis
in hepatic stellate cells by miRNA-29 induction. PLoS One.
6:e245682011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xiong Y, Fang JH, Yun JP, et al: Effects
of microRNA-29 on apoptosis, tumorigenicity, and prognosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 51:836–845. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ma W, Xie S, Ni M, et al: MicroRNA-29a
inhibited epididymal epithelial cell proliferation by targeting
nuclear autoantigenic sperm protein (NASP). J Biol Chem.
287:10189–10199. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang B, Komers R, Carew R, et al:
Suppression of microRNA-29 expression by TGF-β1 promotes collagen
expression and renal fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 23:252–265.
2012.
|
|
35
|
Cui Y, Su WY, Xing J, et al: MiR-29a
inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest through
the downregulation of p42.3 in human gastric cancer. PLoS One.
6:e258722011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lippi G, Steinert JR, Marczylo EL, et al:
Targeting of the Arpc3 actin nucleation factor by miR-29a/b
regulates dendritic spine morphology. J Cell Biol. 194:889–904.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pullen TJ, da Silva Xavier G, Kelsey G and
Rutter GA: miR-29a and miR-29b contribute to pancreatic
beta-cell-specific silencing of monocarboxylate transporter 1
(Mct1). Mol Cell Biol. 31:3182–3194. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Braconi C, Kogure T, Valeri N, et al:
microRNA-29 can regulate expression of the long non-coding RNA gene
MEG3 in hepatocellular cancer. Oncogene. 30:4750–4756. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pekarsky Y, Santanam U, Cimmino A, et al:
Tcl1 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia is regulated by
miR-29 and miR-181. Cancer Res. 66:11590–11593. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fabbri M, Garzon R, Cimmino A, et al:
MicroRNA-29 family reverts aberrant methylation in lung cancer by
targeting DNA methyltransferases 3A and 3B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:15805–15810. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kong G, Zhang J, Zhang S, et al:
Upregulated microRNA-29a by hepatitis B virus X protein enhances
hepatoma cell migration by targeting PTEN in cell culture model.
PLoS One. 6:e195182011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang CM, Wang Y, Fan CG, et al: miR-29c
targets TNFAIP3, inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis
in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 411:586–592. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zong Y, Wang H, Dong W, et al: miR-29c
regulates BACE1 protein expression. Brain Res. 1395:108–115. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ding DP, Chen ZL, Zhao XH, et al: miR-29c
induces cell cycle arrest in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by
modulating cyclin E expression. Carcinogenesis. 32:1025–1032. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lin Y, Wu J, Chen H, et al:
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 is a novel target in micoRNA-195-mediated
cell cycle arrest in bladder cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 586:442–447.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen YQ, Wang XX, Yao XM, et al:
MicroRNA-195 promotes apoptosis in mouse podocytes via enhanced
caspase activity driven by BCL2 insufficiency. Am J Nephrol.
34:549–559. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhu H, Yang Y, Wang Y, et al: MicroRNA-195
promotes palmitate-induced apoptosis in cardiomyocytes by
down-regulating Sirt1. Cardiovasc Res. 92:75–84. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liu L, Chen L, Xu Y, et al: microRNA-195
promotes apoptosis and suppresses tumorigenicity of human
colorectal cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 400:236–240.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sekiya Y, Ogawa T, Iizuka M, et al:
Down-regulation of cyclin E1 expression by microRNA-195 accounts
for interferon-β-induced inhibition of hepatic stellate cell
proliferation. J Cell Physiol. 226:2535–2542. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Xu T, Zhu Y, Xiong Y, et al: MicroRNA-195
suppresses tumorigenicity and regulates G1/S transition of human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology. 50:113–21. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li D, Zhao Y, Liu C, et al: Analysis of
MiR-195 and MiR-497 expression, regulation and role in breast
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 17:1722–1730. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang QQ, Xu H, Huang MB, et al:
MicroRNA-195 plays a tumor-suppressor role in human glioblastoma
cells by targeting signaling pathways involved in cellular
proliferation and invasion. Neuro Oncol. 14:278–287. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhu W, Zhu D, Lu S, et al: miR-497
modulates multidrug resistance of human cancer cell lines by
targeting BCL2. Med Oncol. 29:384–391. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yadav S, Pandey A, Shukla A, et al:
miR-497 and miR-302b regulate ethanol-induced neuronal cell death
through BCL2 protein and cyclin D2. J Biol Chem. 286:37347–37357.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Patel N, Tahara SM, Malik P and Kalra VK:
Involvement of miR-30c and miR-301a in immediate induction of
plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 by placental growth factor in
human pulmonary endothelial cells. Biochem J. 434:473–482. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhao G, Zhang JG, Liu Y, et al: miR-148b
functions as a tumor suppressor in pancreatic cancer by targeting
AMPKα1. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:83–93. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Cimino D, De Pittà C, Orso F, et al:
miR148b is a major coordinator of breast cancer progression in a
relapse-associated microRNA signature by targeting ITGA5, ROCK1,
PIK3CA, NRAS, and CSF1. FASEB J. 27:1223–1235. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kim BM, Woo J, Kanellopoulou C and
Shivdasani RA: Regulation of mouse stomach development and Barx1
expression by specific microRNAs. Development. 138:1081–1086. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Fang L, Deng Z, Shatseva T, et al:
MicroRNA miR-93 promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis by targeting
integrin-β8. Oncogene. 30:806–821. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Du L, Schageman JJ, Subauste MC, et al:
miR-93, miR-98, and miR-197 regulate expression of tumor suppressor
gene FUS1. Mol Cancer Res. 7:1234–1243. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kim YK, Yu J, Han TS, et al: Functional
links between clustered microRNAs: suppression of cell-cycle
inhibitors by microRNA clusters in gastric cancer. Nucleic Acids
Res. 37:1672–1681. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ivanovska I, Ball AS, Diaz RL, et al:
MicroRNAs in the miR-106b family regulate p21/CDKN1A and promote
cell cycle progression. Mol Cell Biol. 28:2167–2174. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Li B, Shi XB, Nori D, et al:
Down-regulation of microRNA 106b is involved in p21-mediated cell
cycle arrest in response to radiation in prostate cancer cells.
Prostate. 71:567–574. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Hu S, Dong TS, Dalal SR, et al: The
microbe-derived short chain fatty acid butyrate targets
miRNA-dependent p21 gene expression in human colon cancer. PLoS
One. 6:e162212011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Cai K, Wang Y and Bao X: MiR-106b promotes
cell proliferation via targeting RB in laryngeal carcinoma. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 30:732011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Zhang Z, Tang H, Wang Z, et al: MiR-185
targets the DNA methyltransferases 1 and regulates global DNA
methylation in human glioma. Mol Cancer. 10:1242011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Liu M, Lang N, Chen X, et al: miR-185
targets RhoA and Cdc42 expression and inhibits the proliferation
potential of human colorectal cells. Cancer Lett. 301:151–160.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Imam JS, Buddavarapu K, Lee-Chang JS, et
al: MicroRNA-185 suppresses tumor growth and progression by
targeting the Six1 oncogene in human cancers. Oncogene.
29:4971–4979. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Weng Z, Wang D, Zhao W, et al:
microRNA-450a targets DNA methyltransferase 3a in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Exp Ther Med. 2:951–955. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Bao B, Rodriguez-Melendez R, Wijeratne SS
and Zempleni J: Biotin regulates the expression of holocarboxylase
synthetase in the miR-539 pathway in HEK-293 cells. J Nutr.
140:1546–1551. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Bao B, Rodriguez-Melendez R and Zempleni
J: Cytosine methylation in miR-153 gene promoters increases the
expression of holocarboxylase synthetase, thereby increasing the
abundance of histone H4 biotinylation marks in HEK-293 human kidney
cells. J Nutr Biochem. 23:635–39. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Funamizu N, Lacy CR, Parpart ST, et al:
MicroRNA-301b promotes cell invasiveness through targeting TP63 in
pancreatic carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 44:725–734.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|