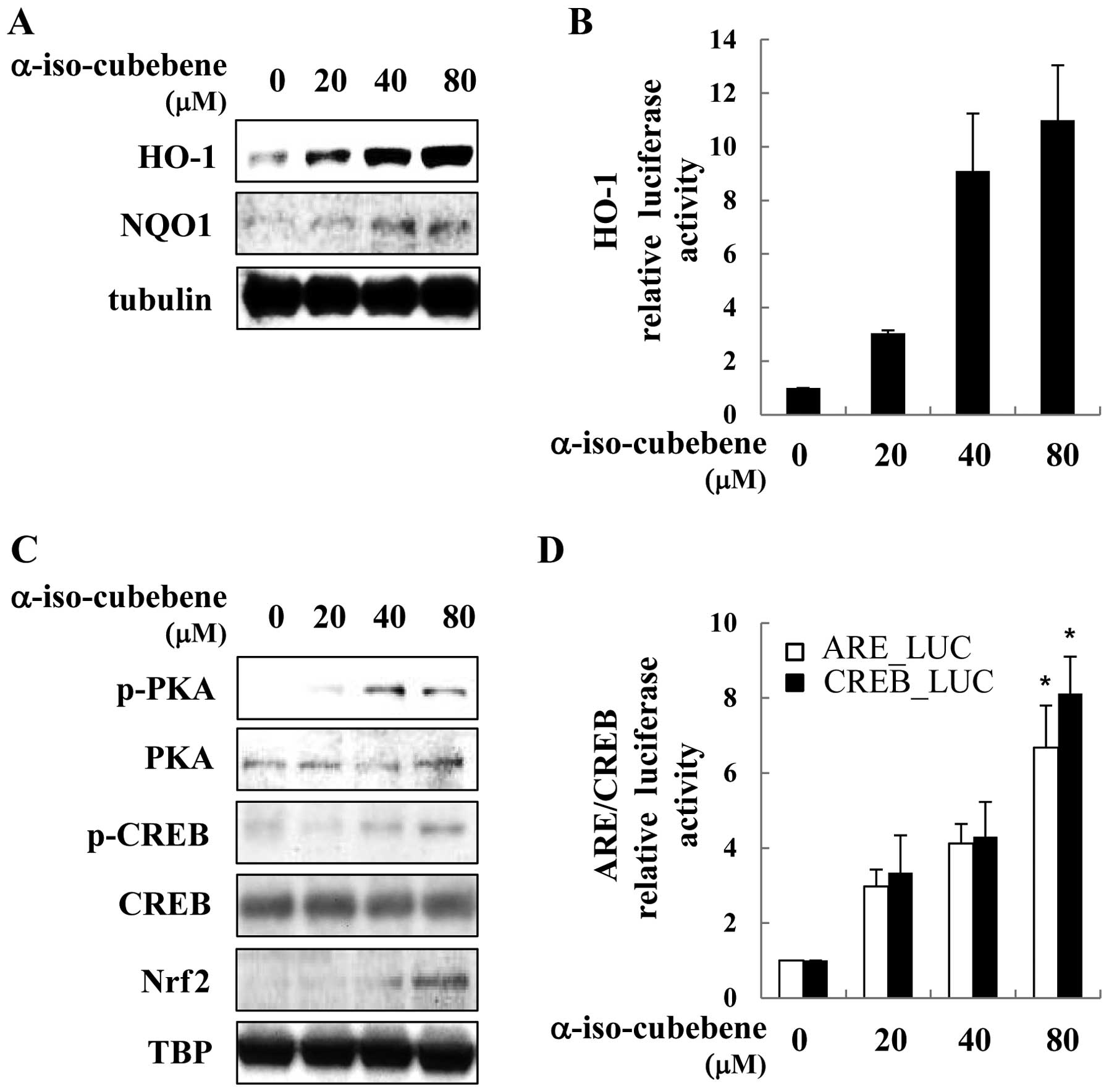
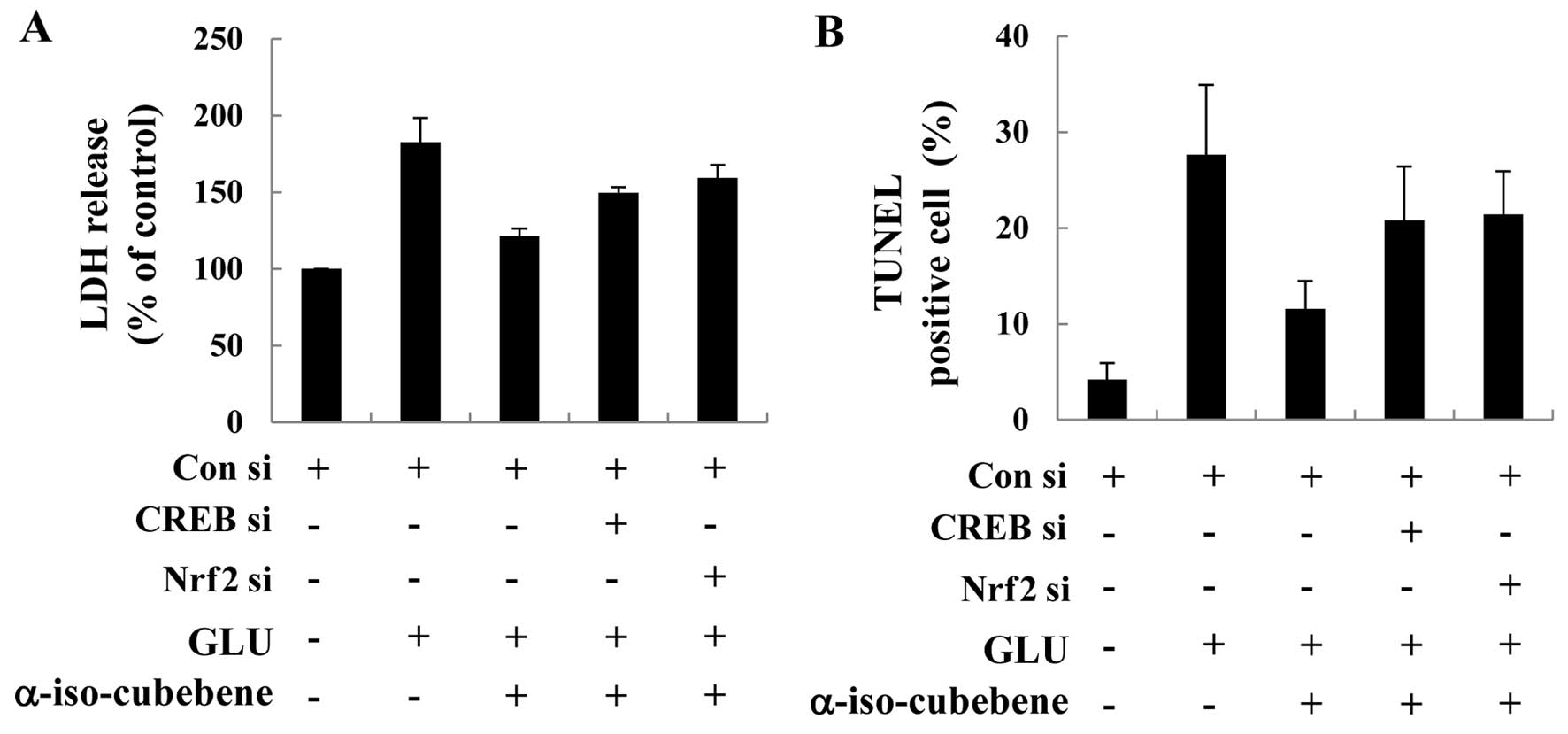
|
1
|
Coyle JT and Puttfarcken P: Oxidative
stress, glutamate, and neurodegenerative disorders. Science.
262:689–695. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tan S, Sagara Y, Liu Y, Maher P and
Schubert D: The regulation of reactive oxygen species production
during programmed cell death. J Cell Biol. 141:1423–1432. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Elphick LM, Hawat M, Toms NJ, Meinander A,
Mikhailov A, Eriksson JE and Kass GE: Opposing roles for caspase
and calpain death proteases in L-glutamate-induced oxidative
neurotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 232:258–267. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Murphy TH, Miyamoto M, Sastre A, Schnaar
RL and Coyle JT: Glutamate toxicity in a neuronal cell line
involves inhibition of cystine transport leading to oxidative
stress. Neuron. 2:1547–1558. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Behl C, Lezoualc’h F, Trapp T, Widmann M,
Skutella T and Holsboer F: Glucocorticoids enhance oxidative
stress-induced cell death in hippocampal neurons in vitro.
Endocrinology. 138:101–106. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Maher P and Schubert D: Signaling by
reactive oxygen species in the nervous system. Cell Mol Life Sci.
57:1287–1305. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stanciu M, Wang Y, Kentor R, et al:
Persistent activation of ERK contributes to glutamate-induced
oxidative toxicity in a neuronal cell line and primary cortical
neuron cultures. J Biol Chem. 275:12200–12206. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ravassard P, Pachoud B, Comte JC, et al:
Paradoxical (REM) sleep deprivation causes a large and rapidly
reversible decrease in long-term potentiation, synaptic
transmission, glutamate receptor protein levels, and ERK/MAPK
activation in the dorsal hippocampus. Sleep. 32:227–240.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kumamaru E, Numakawa T, Adachi N, et al:
Glucocorticoid prevents brain-derived neurotrophic factor-mediated
maturation of synaptic function in developing hippocampal neurons
through reduction in the activity of mitogen-activated protein
kinase. Mol Endocrinol. 22:546–558. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Fukui M, Song JH, Choi J, Choi HJ and Zhu
BT: Mechanism of glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in HT22 mouse
hippocampal cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 617:1–11. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Choi DW: Calcium-mediated neurotoxicity:
Relationship to specific channel types and role in ischemic damage.
Trends Neurosci. 11:465–469. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ankarcrona M, Dypbukt JM, Bonfoco E,
Zhivotovsky B, Orrenius S, Lipton SA and Nicotera P:
Glutamate-induced neuronal death: a succession of necrosis or
apoptosis depending on mitochondrial function. Neuron. 15:961–973.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gunter TE and Pfeiffer DR: Mechanisms by
which mitochondria transport calcium. Am J Physiol. 258:C755–C786.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang Y and Bhavnani BR: Glutamate-induced
apoptosis in neuronal cells is mediated via caspase-dependent and
independent mechanisms involving calpain and caspase-3 proteases as
well as apoptosis inducing factor (AIF) and this process is
inhibited by equine estrogens. BMC Neurosci. 7:492006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Calkins MJ, Johnson DA, Townsend JA, et
al: The Nrf2/ARE pathway as a potential therapeutic target in
neurodegenerative disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 11:497–508. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
van Muiswinkel FL and Kuiperij HB: The
Nrf2-ARE signalling pathway: promising drug target to combat
oxidative stress in neurodegenerative disorders. Curr Drug Targets
CNS Neurol Disord. 4:267–281. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Satoh T, McKercher SR and Lipton SA:
Nrf2/ARE-mediated antioxidant actions of pro-electrophilic drugs.
Free Radic Biol Med. 65:645–657. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee J, Kim CH, Simon DK, et al:
Mitochondrial cyclic AMP response element-binding protein (CREB)
mediates mitochondrial gene expression and neuronal survival. J
Biol Chem. 280:40398–40401. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Baxter PS, Martel MA, McMahon A, Kind PC
and Hardingham GE: Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide
induces long-lasting neuroprotection through the induction of
activity-dependent signaling via the cyclic AMP response
element-binding protein-regulated transcription co-activator 1. J
Neurochem. 118:365–378. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Park SY, Kim JH, Lee SJ and Kim Y:
Involvement of PKA and HO-1 signaling in anti-inflammatory effects
of surfactin in BV-2 microglial cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
268:68–78. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Choi YW, Kim HJ, Park SS, et al:
Inhibition of endothelial cell adhesion by the new
anti-inflammatory agent alpha-iso-cubebene. Vascul Pharmacol.
51:215–224. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee SK, Kim SD, Lee HY, et al:
α-Iso-cubebene, a natural compound isolated from Schisandra
chinensis fruit, has therapeutic benefit against polymicrobial
sepsis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 426:226–231. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee YJ, Shim JW, Lee YJ, et al:
Identification of a novel compound that stimulates intracellular
calcium increase and CXCL8 production in human neutrophils from
Schisandra chinensis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 379:928–932.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Park SY, Park SJ, Park NJ, Joo WH, Lee SJ
and Choi YW: α-Iso-cubebene exerts neuroprotective effects in
amyloid beta stimulated microglia activation. Neurosci Lett.
555:143–148. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Maher P and Davis JB: The role of
monoamine metabolism in oxidative glutamate toxicity. J Neurosci.
16:6394–6401. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ziady AG, Sokolow A, Shank S, Corey D, et
al: Interaction with CREB binding protein modulates the activities
of Nrf2 and NF-κB in cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 302:L1221–L1231. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang T, Gu J, Wu PF, et al: Protection by
tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside against cerebral ischemia:
Involvement of JNK, SIRT1, and NF-kappaB pathways and inhibition of
intracellular ROS/RNS generation. Free Radic Biol Med. 47:229–240.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Katoh Y, Itoh K, Yoshida E, Miyagishi M,
Fukamizu A and Yamamoto M: Two domains of Nrf2 cooperatively bind
CBP, a CREB binding protein, and synergistically activate
transcription. Genes Cells. 6:857–868. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Arundine M and Tymianski M: Molecular
mechanisms of glutamate-dependent neurodegeneration in ischemia and
traumatic brain injury. Cell Mol Life Sci. 61:657–668. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tofighi R, Johansson C, Goldoni M, Ibrahim
WN, Gogvadze V, Mutti A and Ceccatelli S: Hippocampal neurons
exposed to the environmental contaminants methylmercury and
polychlorinated biphenyls undergo cell death via parallel
activation of calpains and lysosomal proteases. Neurotox Res.
19:183–194. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhang H, Liu H, Davies KJ, Sioutas C,
Finch CE, Morgan TE and Forman HJ: Nrf2-regulated phase II enzymes
are induced by chronic ambient nanoparticle exposure in young mice
with age-related impairments. Free Radic Biol Med. 52:2038–2046.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang H, Guo Z, Wu F, et al: PKA-mediated
protein phosphorylation protects ezrin from calpain I cleavage.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 333:496–501. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|