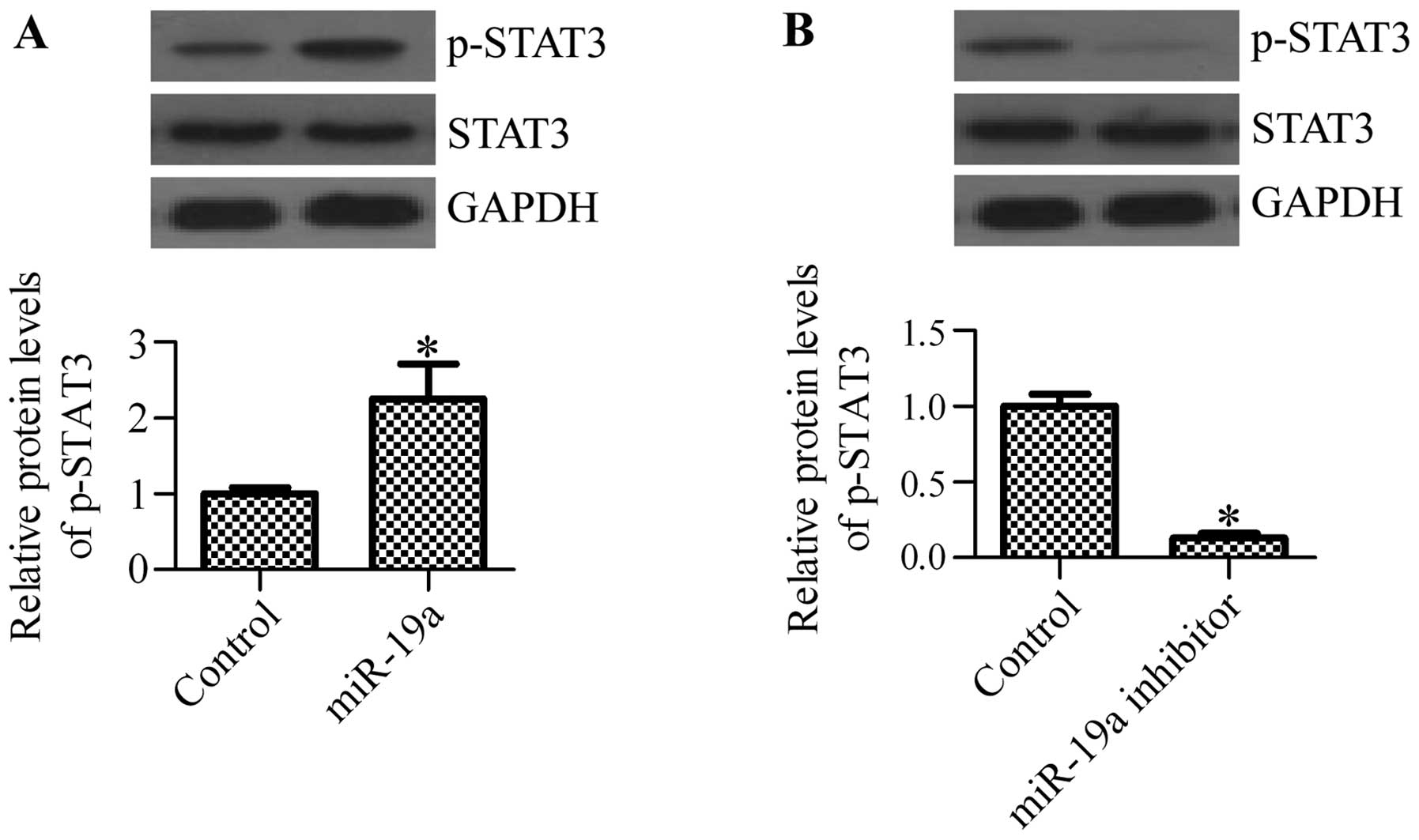
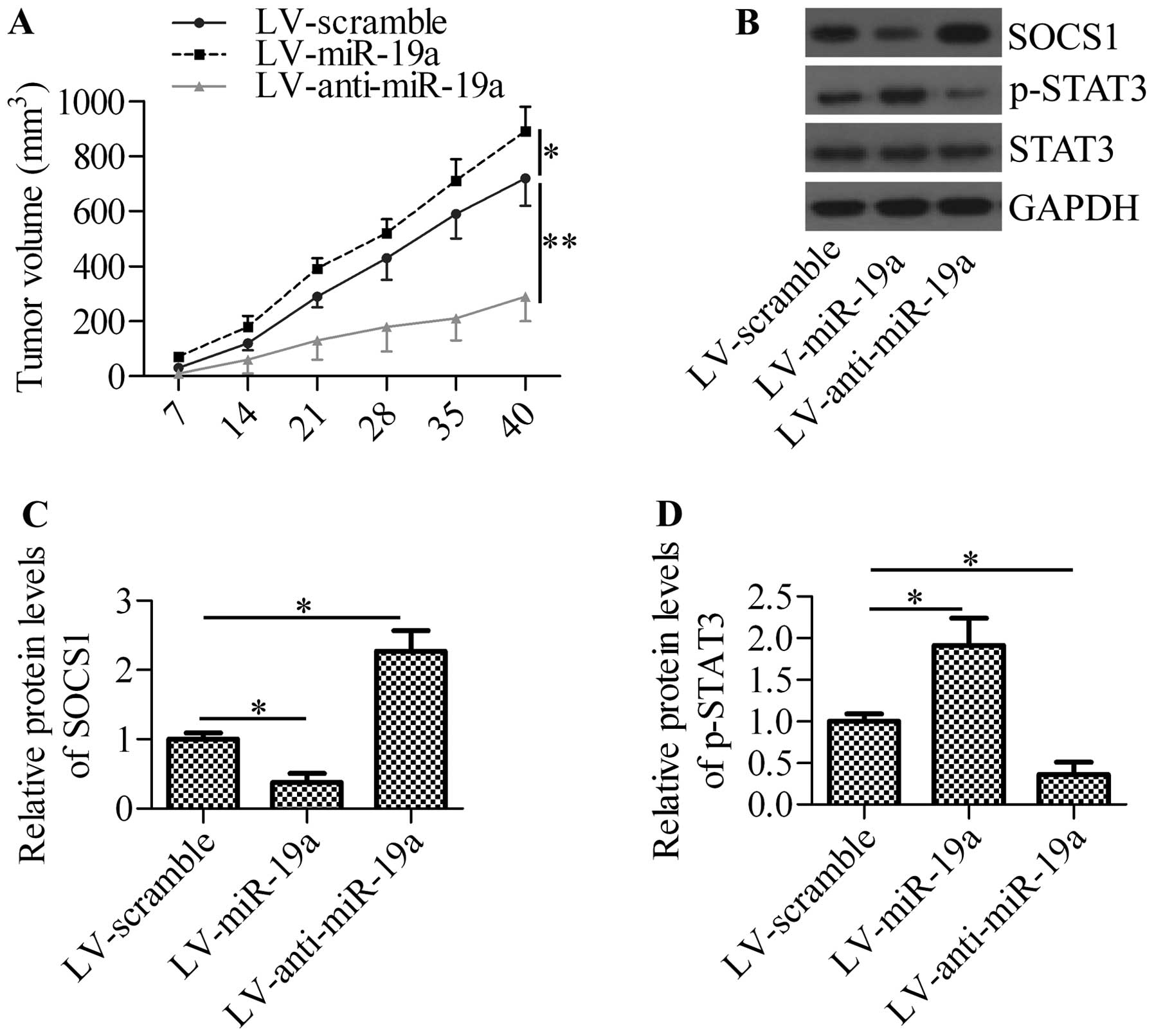
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Claassens L, van Meerbeeck J, Coens C, et
al: Health-related quality of life in non-small-cell lung cancer:
an update of a systematic review on methodologic issues in
randomized controlled trials. J Clin Oncol. 29:2104–2120. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hu Z, Chen X, Zhao Y, et al: Serum
microRNA signatures identified in a genome-wide serum microRNA
expression profiling predict survival of non-small-cell lung
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 28:1721–1726. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, et al:
Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 355:2542–2550. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Blumenschein GR Jr and Herbst RS:
Integration of targeted therapies in gemcitabine chemotherapy
regimens. Clin Lung Cancer. 4:217–223. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cabebe E and Wakelee H: Role of
anti-angiogenesis agents in treating NSCLC: focus on bevacizumab
and VEGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Curr Treat Options Oncol.
8:15–27. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ranganathan K and Sivasankar V: MicroRNAs
- Biology and clinical applications. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol.
18:229–234. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI and
Diederichs S: Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways
and their regulation. Nat Cell Biol. 11:228–234. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rottiers V, Najafi-Shoushtari SH, Kristo
F, et al: MicroRNAs in metabolism and metabolic diseases. Cold
Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 76:225–233. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Aigner A: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) in cancer
invasion and metastasis: therapeutic approaches based on
metastasis-related miRNAs. J Mol Med (Berl). 89:445–457. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zimmerman AL and Wu S: MicroRNAs, cancer
and cancer stem cells. Cancer Lett. 300:10–19. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang P, Chen L, Zhang J, et al:
Methylation-mediated silencing of the miR-124 genes facilitates
pancreatic cancer progression and metastasis by targeting Rac1.
Oncogene. 33:514–524. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Oh JS, Kim JJ, Byun JY and Kim IA:
Lin28-let7 modulates radiosensitivity of human cancer cells with
activation of K-Ras. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 76:5–8. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang P, Zhuang L, Zhang J, et al: The
serum miR-21 level serves as a predictor for the chemosensitivity
of advanced pancreatic cancer, and miR-21 expression confers
chemoresistance by targeting FasL. Mol Oncol. 7:334–345. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Petrocca F, Visone R, Onelli MR, et al:
E2F1-regulated microRNAs impair TGFbeta-dependent cell-cycle arrest
and apoptosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Cell. 13:272–286. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu Q, Yang Z, An Y, et al: MiR-19a/b
modulate the metastasis of gastric cancer cells by targeting the
tumour suppressor MXD1. Cell Death Dis. 5:e11442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu XM, Wang XB, Chen MM, et al:
MicroRNA-19a and -19b regulate cervical carcinoma cell
proliferation and invasion by targeting CUL5. Cancer Lett.
322:148–158. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu G, Li H, Wang X, et al: MicroRNA-19a
targets tissue factor to inhibit colon cancer cells migration and
invasion. Mol Cell Biochem. 380:239–247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lin Q, Chen T, Lin Q, Lin G, et al: Serum
miR-19a expression correlates with worse prognosis of patients with
non-small cell lung cancer. J Surg Oncol. 107:767–771. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu H and Jove R: The STATs of cancer - new
molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:97–105. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tian M, Wan Y, Tang J, et al: Depletion of
tissue factor suppresses hepatic metastasis and tumor growth in
colorectal cancer via the downregulation of MMPs and the induction
of autophagy and apoptosis. Cancer Biol Ther. 12:896–907. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang J, Li H, Yu JP, Wang SE and Ren XB:
Role of SOCS1 in tumor progression and therapeutic application. Int
J Cancer. 130:1971–1980. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Huang C, Li H, Wu W, Jiang T and Qiu Z:
Regulation of miR-155 affects pancreatic cancer cell invasiveness
and migration by modulating the STAT3 signaling pathway through
SOCS1. Oncol Rep. 30:1223–1230. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cittadini A, Monti MG, Iaccarino G, et al:
SOCS1 gene transfer accelerates the transition to heart failure
through the inhibition of the gp130/JAK/STAT pathway. Cardiovasc
Res. 96:381–390. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu L, Li W, Wei X, et al: Potent
antitumor activity of oncolytic adenovirus-mediated SOCS1 for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Gene Ther. 20:84–92. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Xu XL, Jiang YH, Feng JG, et al:
MicroRNA-17, microRNA-18a, and microRNA-19a are prognostic
indicators in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Thorac Surg.
97:1037–1045. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sochor M, Basova P, Pesta M, et al:
Oncogenic MicroRNAs: miR-155, miR-19a, miR-181b, and miR-24 enable
monitoring of early breast cancer in serum. BMC Cancer. 14:4482014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Navarro A, Marrades RM, Vinolas N, et al:
MicroRNAs expressed during lung cancer development are expressed in
human pseudoglandular lung embryogenesis. Oncology. 76:162–169.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen Q, Xia HW, Ge XJ, et al: Serum
miR-19a predicts resistance to FOLFOX chemotherapy in advanced
colorectal cancer cases. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:7421–7426.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Murphy BL, Obad S, Bihannic L, et al:
Silencing of the miR-17~92 cluster family inhibits medulloblastoma
progression. Cancer Res. 73:7068–7078. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li X, Xie W, Xie C, et al: Curcumin
modulates miR-19/PTEN/AKT/p53 axis to suppress bisphenol A-induced
MCF-7 breast cancer cell proliferation. Phytother Res.
28:1553–1560. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wu TY, Zhang TH, Qu LM, et al: MiR-19a is
correlated with prognosis and apoptosis of laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma by regulating TIMP-2 expression. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:56–63. 2013.
|
|
35
|
Wang F, Li T, Zhang B, et al:
MicroRNA-19a/b regulates multidrug resistance in human gastric
cancer cells by targeting PTEN. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
434:688–694. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Krebs DL and Hilton DJ: SOCS proteins:
negative regulators of cytokine signaling. Stem Cells. 19:378–387.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yasukawa H, Sasaki A and Yoshimura A:
Negative regulation of cytokine signaling pathways. Annu Rev
Immunol. 18:143–164. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
He Y, Zhang W, Zhang R, Zhang H and Min W:
SOCS1 inhibits tumor necrosis factor-induced activation of ASK1-JNK
inflammatory signaling by mediating ASK1 degradation. J Biol Chem.
281:5559–5566. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hanada T, Yoshida H, Kato S, et al:
Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 is essential for suppressing
dendritic cell activation and systemic autoimmunity. Immunity.
19:437–450. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chinen T, Kobayashi T, Ogata H, et al:
Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 regulates inflammatory bowel
disease in which both IFNgamma and IL-4 are involved.
Gastroenterology. 130:373–388. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sasi W, Sharma AK and Mokbel K: The role
of suppressors of cytokine signalling in human neoplasms. Mol Biol
Int. 2014:6307972014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chu PY, Yeh CM, Hsu NC, et al: Epigenetic
alteration of the SOCS1 gene in hepatocellular carcinoma. Swiss Med
Wkly. 140:w130652010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Neuwirt H, Puhr M, Santer FR, et al:
Suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)-1 is expressed in human
prostate cancer and exerts growth-inhibitory function through
down-regulation of cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases. Am J
Pathol. 174:1921–1930. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Komazaki T, Nagai H, Emi M, et al:
Hypermethylation-associated inactivation of the SOCS-1 gene, a
JAK/STAT inhibitor, in human pancreatic cancers. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
34:191–194. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lesinski GB, Zimmerer JM, Kreiner M, et
al: Modulation of SOCS protein expression influences the interferon
responsiveness of human melanoma cells. BMC Cancer. 10:1422010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zitzmann K, Brand S, De Toni EN, et al:
SOCS1 silencing enhances antitumor activity of type I IFNs by
regulating apoptosis in neuroendocrine tumor cells. Cancer Res.
67:5025–5032. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhao M, Gao FH, Wang JY, et al: JAK2/STAT3
signaling pathway activation mediates tumor angiogenesis by
upregulation of VEGF and bFGF in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung
Cancer. 73:366–374. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yu H, Pardoll D and Jove R: STATs in
cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:798–809. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Souma Y, Nishida T, Serada S, et al:
Antiproliferative effect of SOCS-1 through the suppression of STAT3
and p38 MAPK activation in gastric cancer cells. Int J Cancer.
131:1287–1296. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Xu Y, Xu X, Gao X, Chen H and Geng L:
Shikonin suppresses IL-17-induced VEGF expression via blockage of
JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 19:327–333. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Shimada K, Serada S, Fujimoto M, et al:
Molecular mechanism underlying the antiproliferative effect of
suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 in non-small-cell lung cancer
cells. Cancer Sci. 104:1483–1491. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|