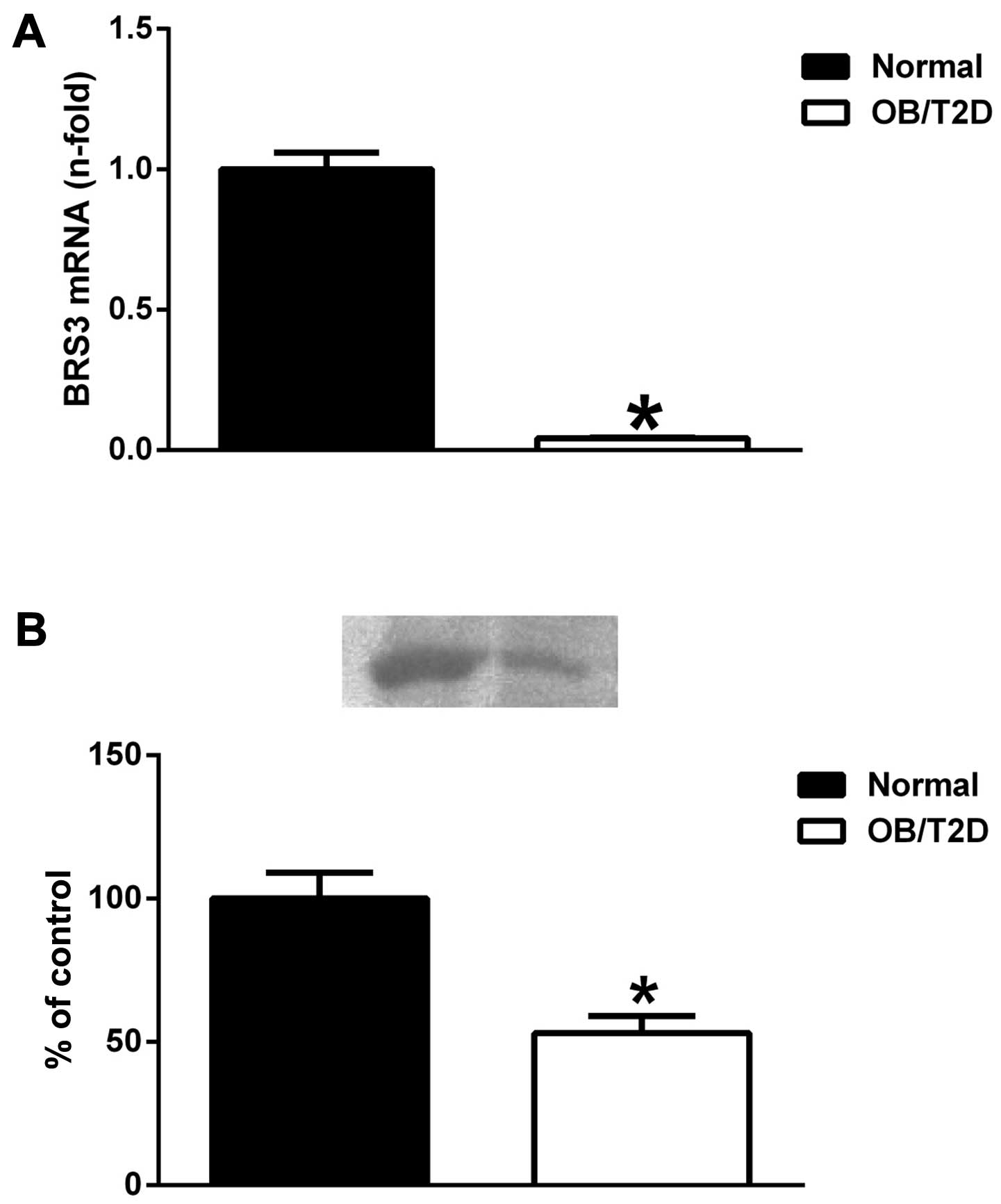
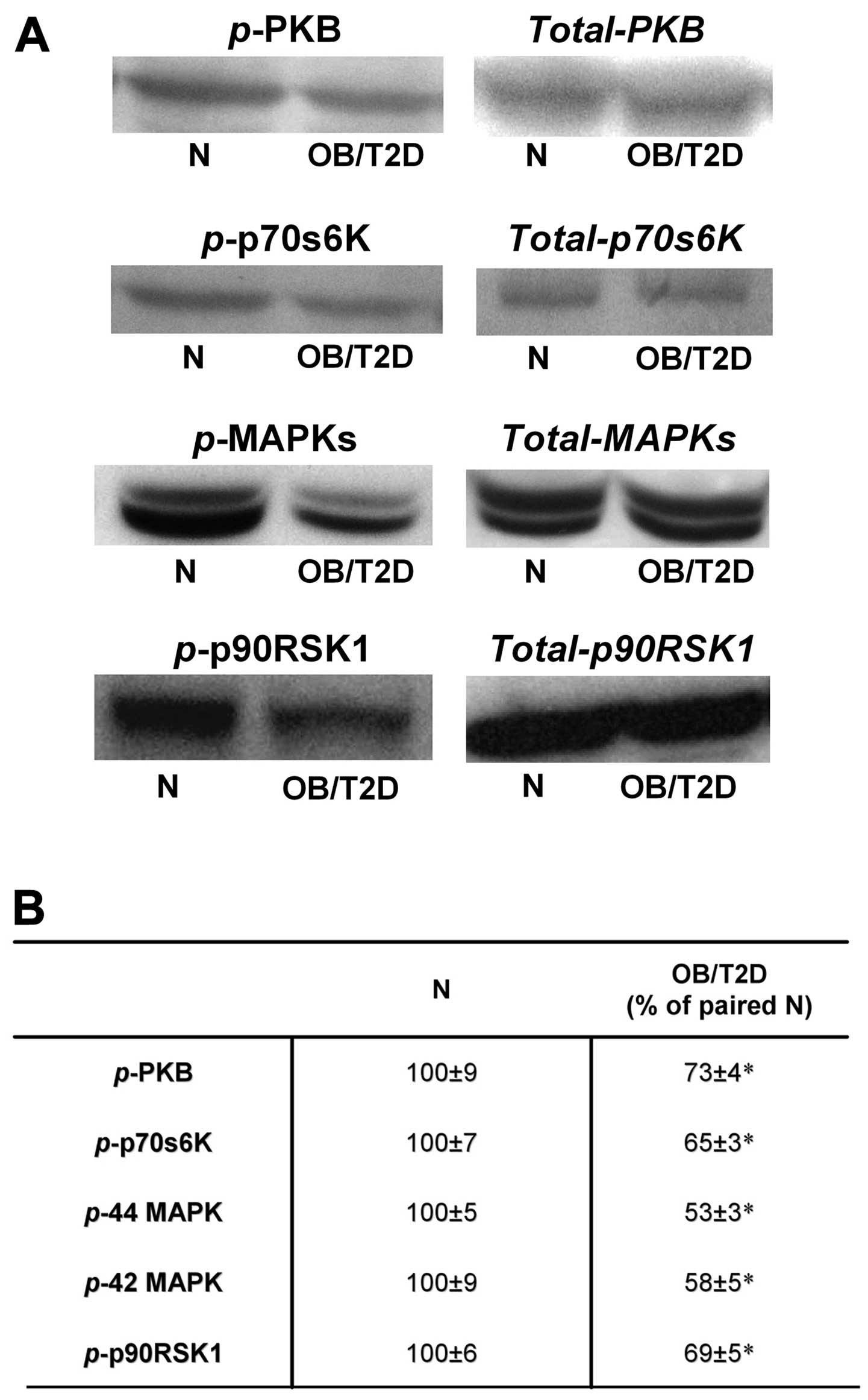
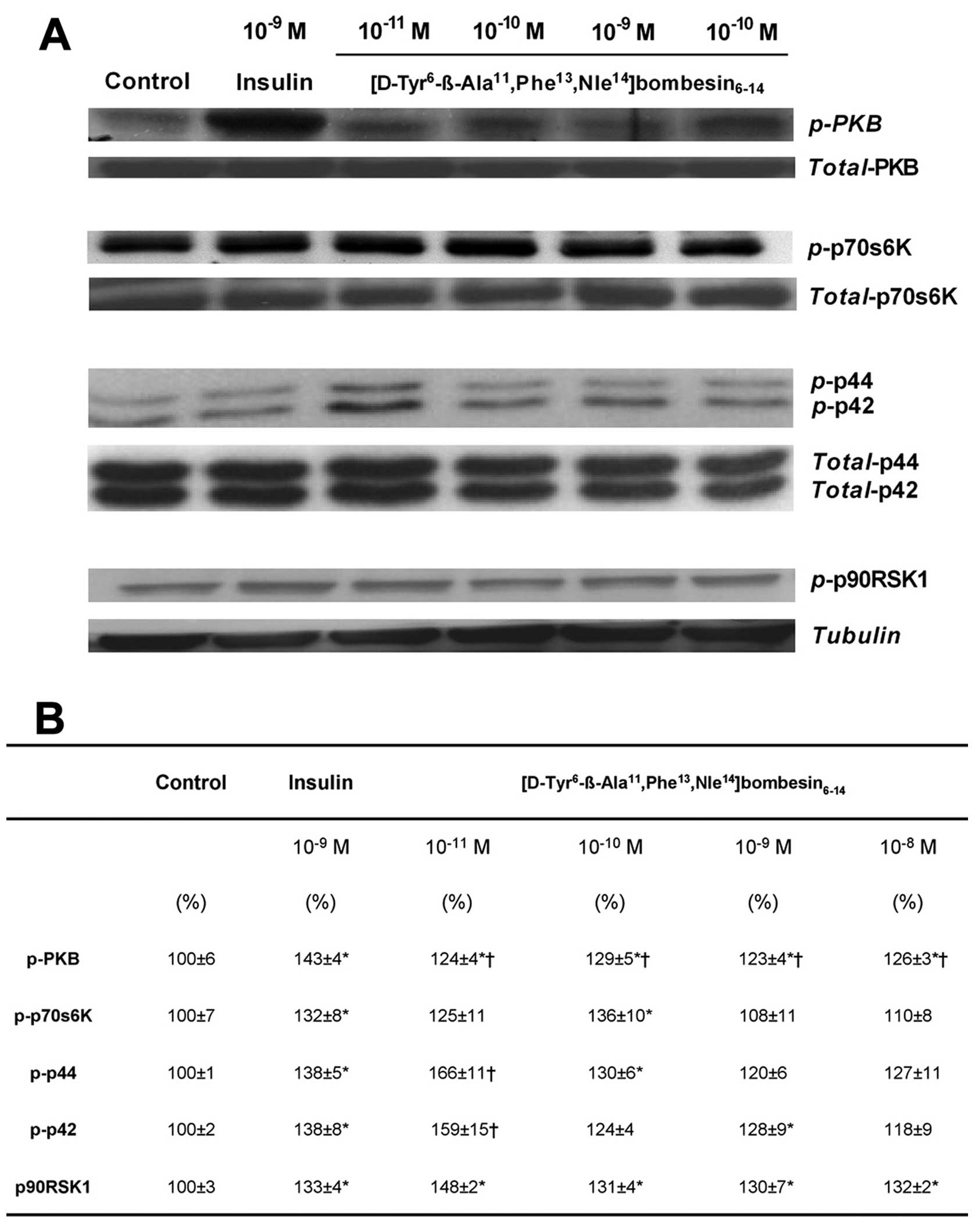
|
1
|
Fathi Z, Corjay MH, Shapira H, et al:
BRS-3: a novel bombesin receptor subtype selectively expressed in
testis and lung carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 268:5979–5984.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ohki-Hamazaki H, Watase K, Yamamoto K, et
al: Mice lacking bombesin receptor subtype-3 develop metabolic
defects and obesity. Nature. 390:165–169. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Porcher C, Juhem A, Peinnequin A and Bonaz
B: Bombesin receptor subtype-3 is expressed by the enteric nervous
system and by interstitial cells of Cajal in the rat
gastrointestinal tract. Cell Tissue Res. 320:21–31. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sano H, Feighner SD, Hreniuk DL, et al:
Characterization of the bombesin-like peptide receptor family in
primates. Genomics. 84:139–146. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ramos-Álvarez I, Martín-Duce A,
Moreno-Villegas Z, et al: Bombesin receptor subtype-3 (BRS-3), a
novel candidate as therapeutic molecular target in obesity and
diabetes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 367:109–115. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Moody TW and Jensen RT: Breast cancer
VPAC1 receptors. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1070:436–439. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schulz S, Röcken C and Schulz S:
Immunohistochemical detection of bombesin receptor subtypes GRP-R
and BRS-3 in human tumors using novel antipeptide antibodies.
Virchows Arch. 449:421–427. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jensen RT, Battey JF, Spindel ER and Benya
RV: International Union of Pharmacology. LXVIII. Mammalian bombesin
receptors: nomenclature, distribution, pharmacology, signaling, and
functions in normal and disease states. Pharmacol Rev. 60:1–42.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Guan XM, Chen H, Dobbelaar PH, et al:
Regulation of energy homeostasis by bombesin receptor subtype-3:
selective receptor agonists for the treatment of obesity. Cell
Metab. 11:101–112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Matsumoto K, Yamada K, Wada E, Hasegawa T,
Usui Y and Wada K: Bombesin receptor subtype-3 modulates plasma
insulin concentration. Peptides. 24:83–90. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nakamichi Y, Wada E, Aoki K, et al:
Functions of pancreatic beta cells and adipocytes in bombesin
receptor subtype-3-deficient mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
318:698–703. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ladenheim EE, Hamilton NL, Behles RR, et
al: Factors contributing to obesity in bombesin receptor
subtype-3-deficient mice. Endocrinology. 149:971–978. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Feng Y, Guan XM, Li J, et al: Bombesin
receptor subtype-3 (BRS-3) regulates glucose-stimulated insulin
secretion in pancreatic islets across multiple species.
Endocrinology. 152:4106–4115. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mantey SA, Weber HC, Sainz E, et al:
Discovery of a high affinity radioligand for the human orphan
receptor, bombesin receptor subtype 3, which demonstrates that it
has a unique pharmacology compared with other mammalian bombesin
receptors. J Biol Chem. 272:26062–26071. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guan XM, Metzger JM, Yang L, et al:
Antiobesity effect of MK-5046, a novel bombesin receptor subtype-3
agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 336:356–364. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Reitman ML, Dishy V, Moreau A, et al:
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of MK-5046, a bombesin
receptor subtype-3 (BRS-3) agonist, in healthy patients. J Clin
Pharmacol. 52:1306–1316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Moreno P, Mantey SA, Nuche-Berenguer B, et
al: Comparative pharmacology of bombesin receptor subtype-3,
nonpeptide agonist MK-5046, a universal peptide agonist, and
peptide antagonist Bantag-1 for human bombesin receptors. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 347:100–116. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ramos-Álvarez I, Moreno-Villegas Z,
Martin-Duce A, et al: Human BRS-3 receptor: functions/role in cell
signaling pathways and glucose metabolism in obese or diabetic
myocytes. Peptides. 51:91–99. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
González N, Acitores A, Sancho V, Valverde
I and Villanueva-Penacarrillo ML: Effect of GLP-1 on glucose
transport and its cell signalling in human myocytes. Regul Pept.
126:203–211. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural
proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.
Nature. 227:680–685. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Villanueva-Peñacarrillo ML, Puente J,
Redondo A, Clemente F and Valverde I: Effect of GLP-1 treatment on
GLUT2 and GLUT4 expression in type 1 and type 2 rat diabetic
models. Endocrine. 15:241–248. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fleig WE, Noether-Fleig G, Fussgaenger R
and Ditschuneit H: Modulation by a sulfonylurea of
insulin-dependent glycogenesis, but not of insulin binding, in
cultured rat hepatocytes. Evidence for a postreceptor mechanism of
action. Diabetes. 33:285–290. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Burgering BM, Medema RH, Maassen JA, et
al: Insulin stimulation of gene expression mediated by p21ras
activation. EMBO J. 10:1103–1109. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pandini G, Medico E, Conte E, Sciacca L,
Vigneri R and Belfiore A: Differential gene expression induced by
insulin and insulin-like growth factor-II through the insulin
receptor isoform A. J Biol Chem. 278:42178–42189. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Villanueva-Peñacarrillo ML, Martín-Duce A,
Ramos-Álvarez I, et al: Characteristic of GLP-1 effects on glucose
metabolism in human skeletal muscle from obese patients. Regul
Pept. 168:39–44. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
González N, Sancho V, Martín-Duce A, et
al: GLP-1 signalling and effects on glucose metabolism in myocytes
from type 2 diabetic patients. Int J Mol Med. 16:747–752.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sancho V, Trigo MV, González N, Valverde
I, Malaisse WJ and Villanueva-Penacarrillo ML: Effects of
glucagon-like peptide-1 and exendins on kinase activity, glucose
transport and lipid metabolism in adipocytes from normal and type-2
diabetic rats. J Mol Endocrinol. 35:27–38. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sancho V, Nuche B, Arnés L, et al: The
action of GLP-1 and exendins upon glucose transport in normal human
adipocytes, and on kinase activity as compared to morbidly obese
patients. Int J Mol Med. 19:961–966. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Arnés L1, González N, Tornero-Esteban P,
et al: Characteristics of GLP-1 and exendins action upon glucose
transport and metabolism in type 2 diabetic rat skeletal muscle.
Int J Mol Med. 22:127–132. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
MacAulay K, Blair AS, Hajduch E, et al:
Constitutive activation of GSK3 down-regulates glycogen synthase
abundance and glycogen deposition in rat skeletal muscle cells. J
Biol Chem. 280:9509–9518. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sutherland C and Cohen P: The
alpha-isoform of glycogen synthase kinase-3 from rabbit skeletal
muscle is inactivated by p70 S6 kinase or MAP kinase-activated
protein kinase-1 in vitro. FEBS Lett. 338:37–42. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sun LS and Quamina A: Extracellular
receptor kinase and cAMP response element binding protein
activation in the neonatal rat heart after perinatal cocaine
exposure. Pediatr Res. 56:947–952. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Qin X, Qu X, Coy D and Weber HC: A
selective human bombesin receptor subtype-3 peptide agonist
mediates CREB phosphorylation and transactivation. J Mol Neurosci.
46:88–99. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|