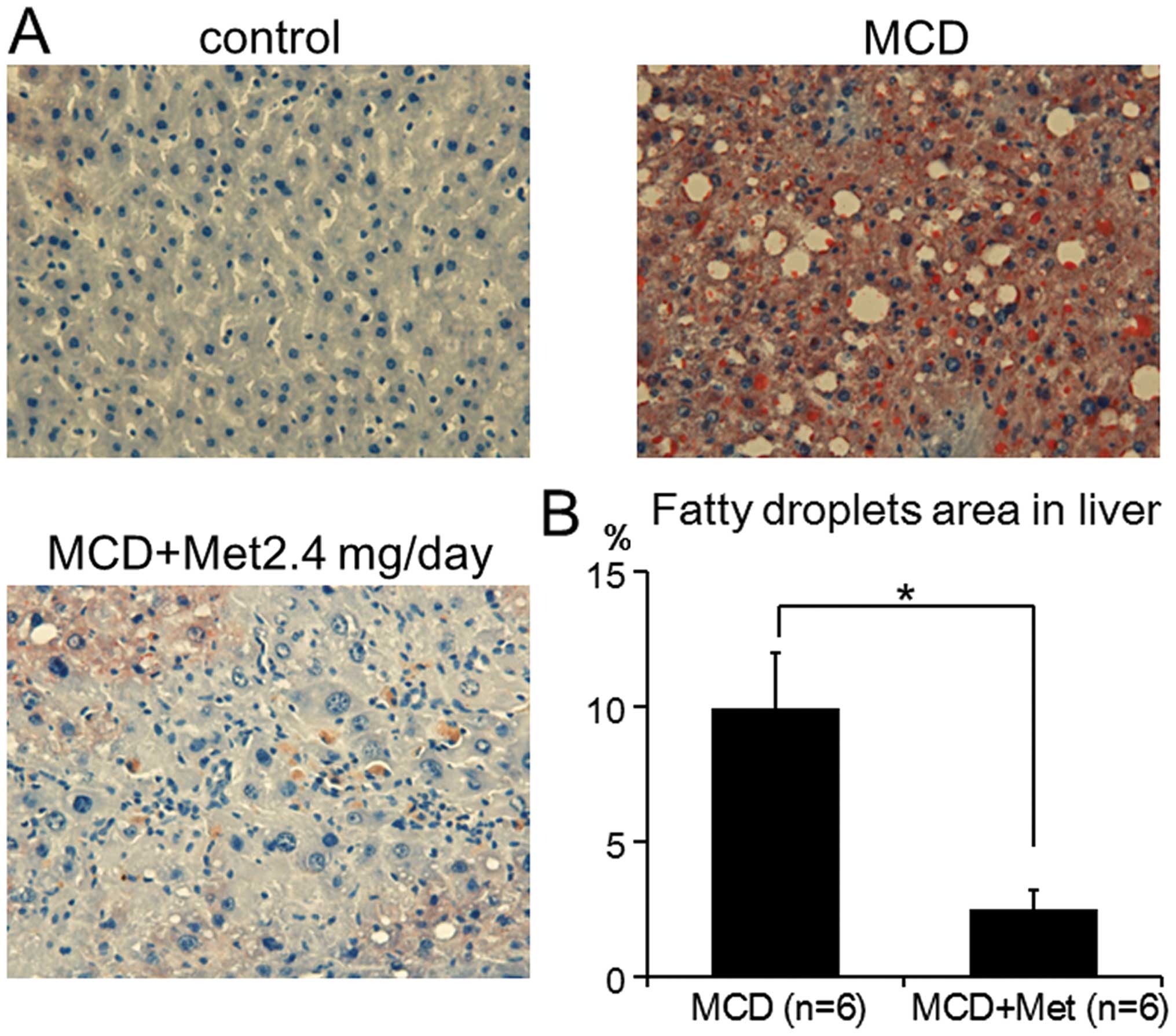
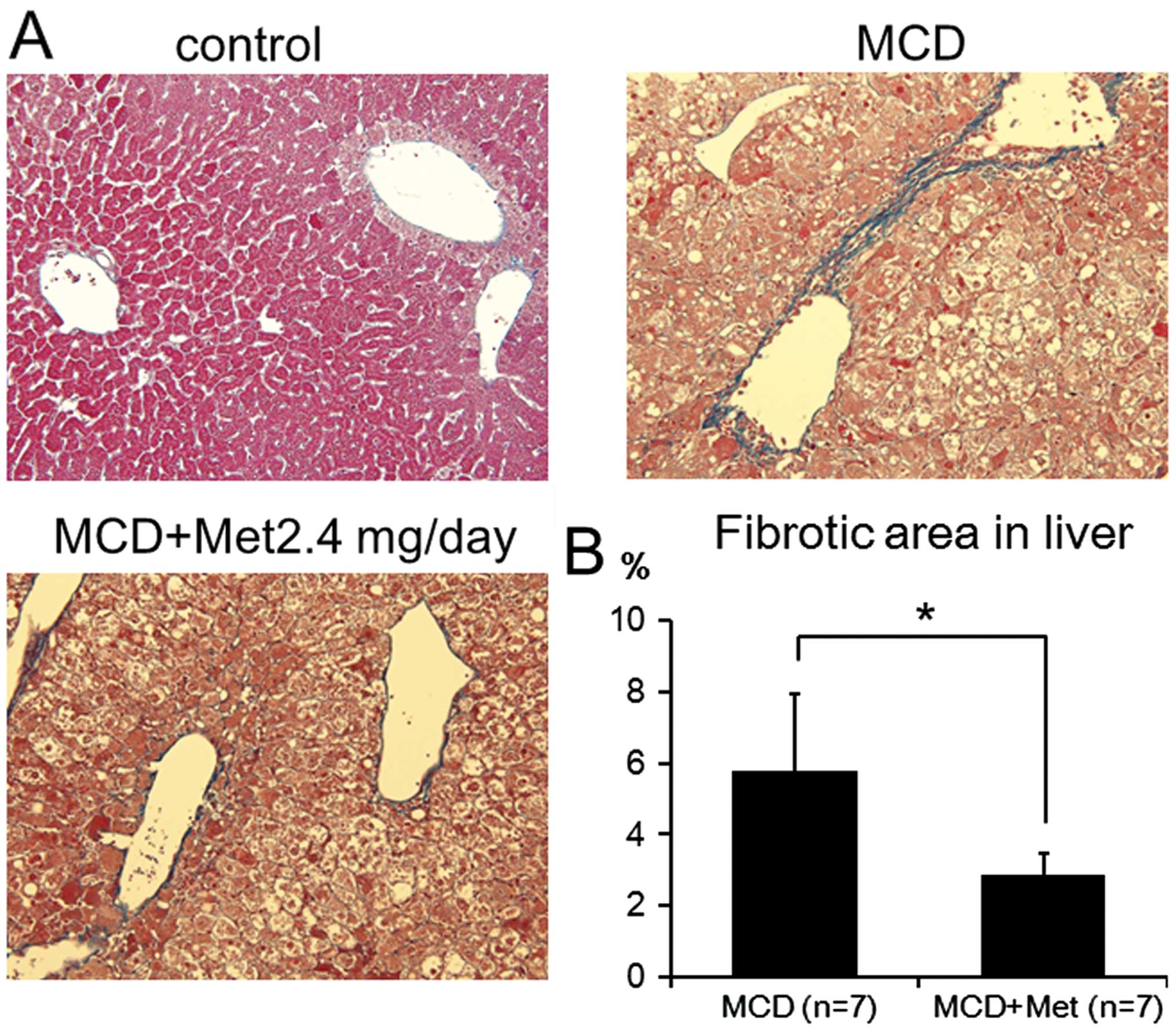
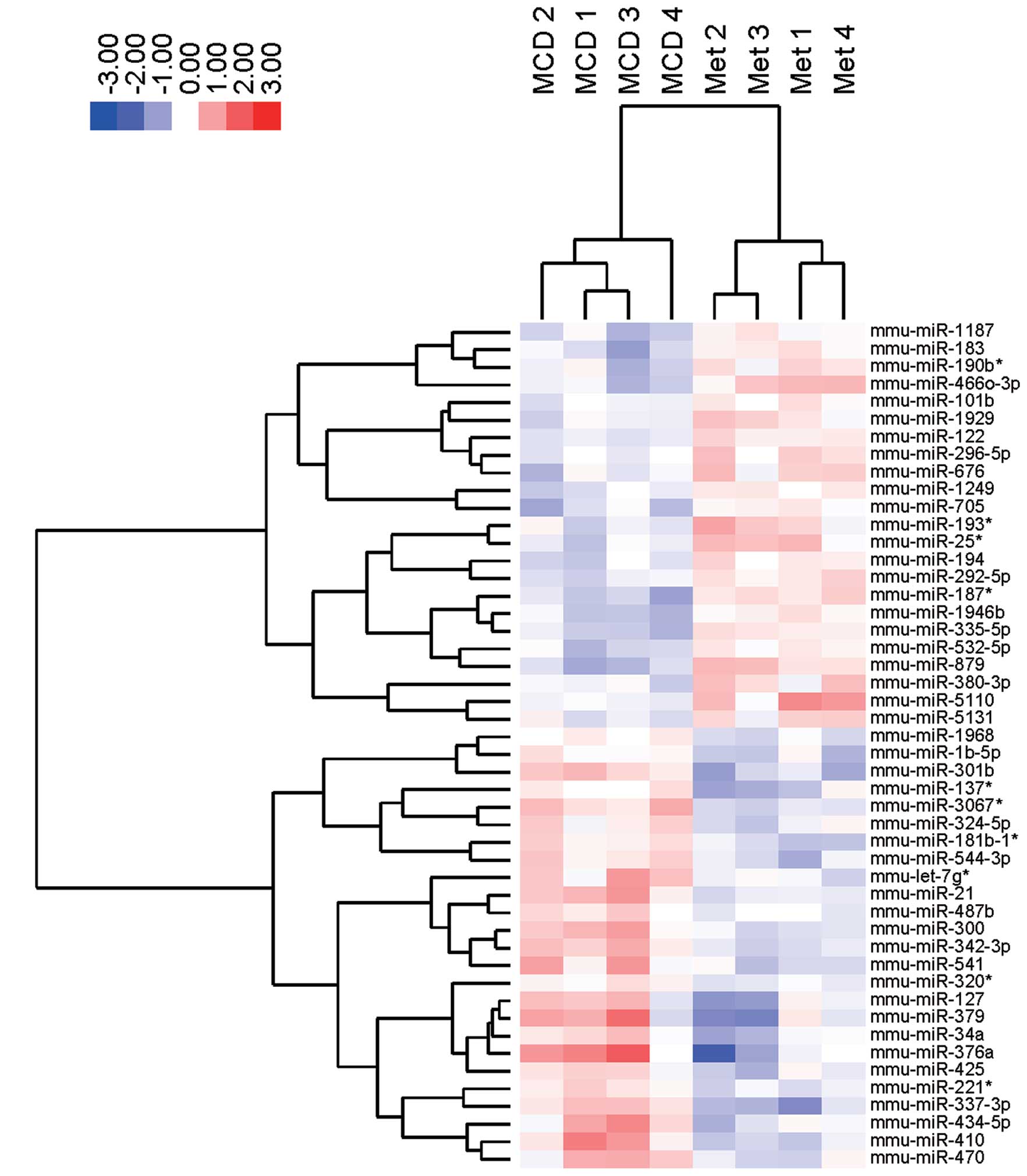
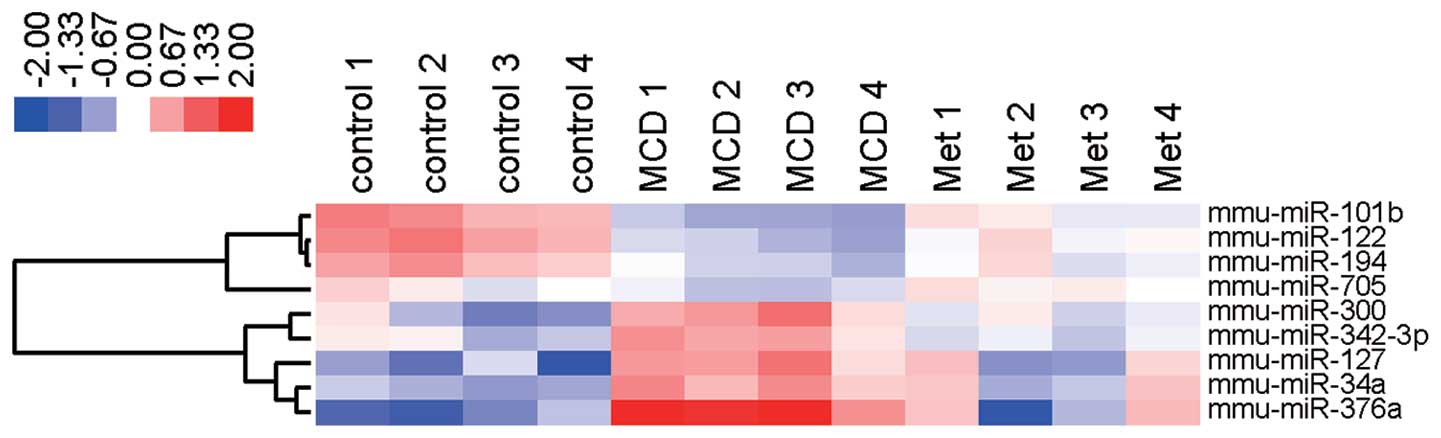
Spandidos Publications style
Katsura A, Morishita A, Iwama H, Tani J, Sakamoto T, Tatsuta M, Toyota Y, Fujita K, Kato K, Maeda E, Maeda E, et al: MicroRNA profiles following metformin treatment in a mouse model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Int J Mol Med 35: 877-884, 2015.
APA
Katsura, A., Morishita, A., Iwama, H., Tani, J., Sakamoto, T., Tatsuta, M. ... Masaki, T. (2015). MicroRNA profiles following metformin treatment in a mouse model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 35, 877-884. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2015.2092
MLA
Katsura, A., Morishita, A., Iwama, H., Tani, J., Sakamoto, T., Tatsuta, M., Toyota, Y., Fujita, K., Kato, K., Maeda, E., Nomura, T., Miyoshi, H., Yoneyama, H., Himoto, T., Fujiwara, S., Kobara, H., Mori, H., Niki, T., Ono, M., Hirashima, M., Masaki, T."MicroRNA profiles following metformin treatment in a mouse model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis". International Journal of Molecular Medicine 35.4 (2015): 877-884.
Chicago
Katsura, A., Morishita, A., Iwama, H., Tani, J., Sakamoto, T., Tatsuta, M., Toyota, Y., Fujita, K., Kato, K., Maeda, E., Nomura, T., Miyoshi, H., Yoneyama, H., Himoto, T., Fujiwara, S., Kobara, H., Mori, H., Niki, T., Ono, M., Hirashima, M., Masaki, T."MicroRNA profiles following metformin treatment in a mouse model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis". International Journal of Molecular Medicine 35, no. 4 (2015): 877-884. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2015.2092