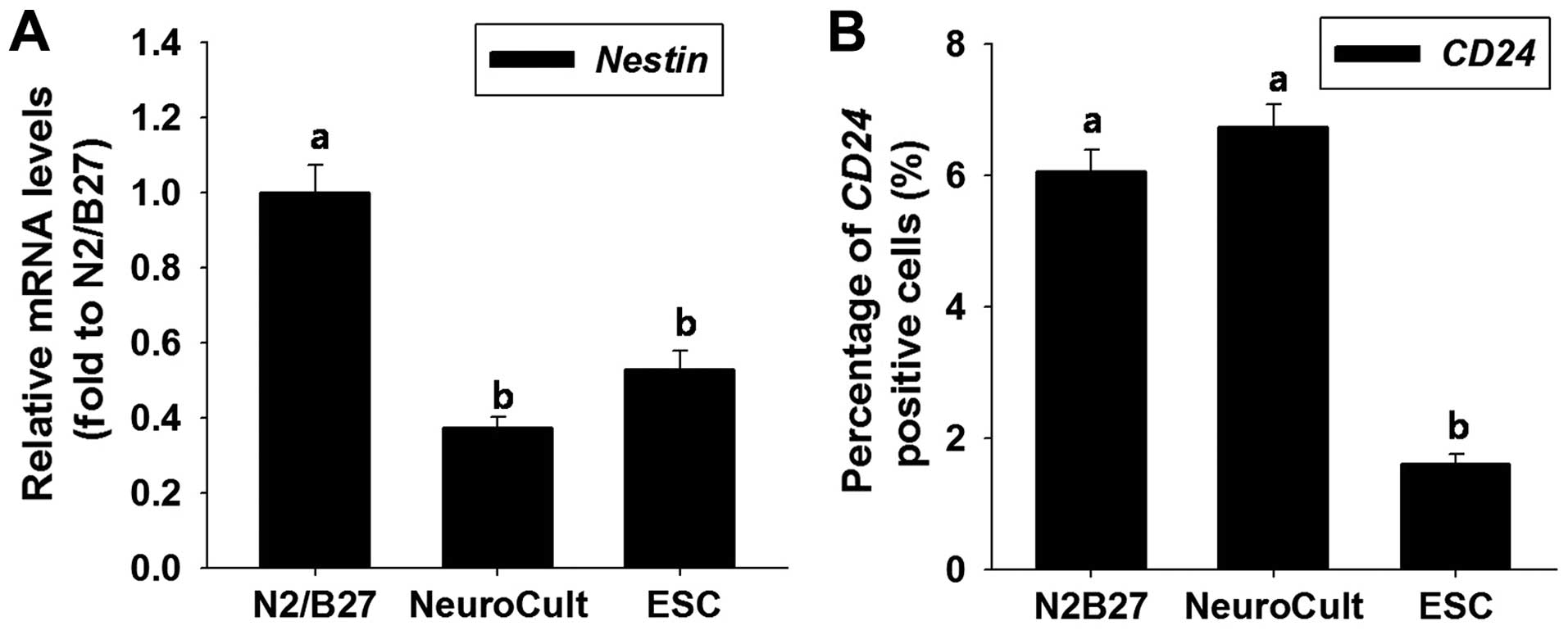
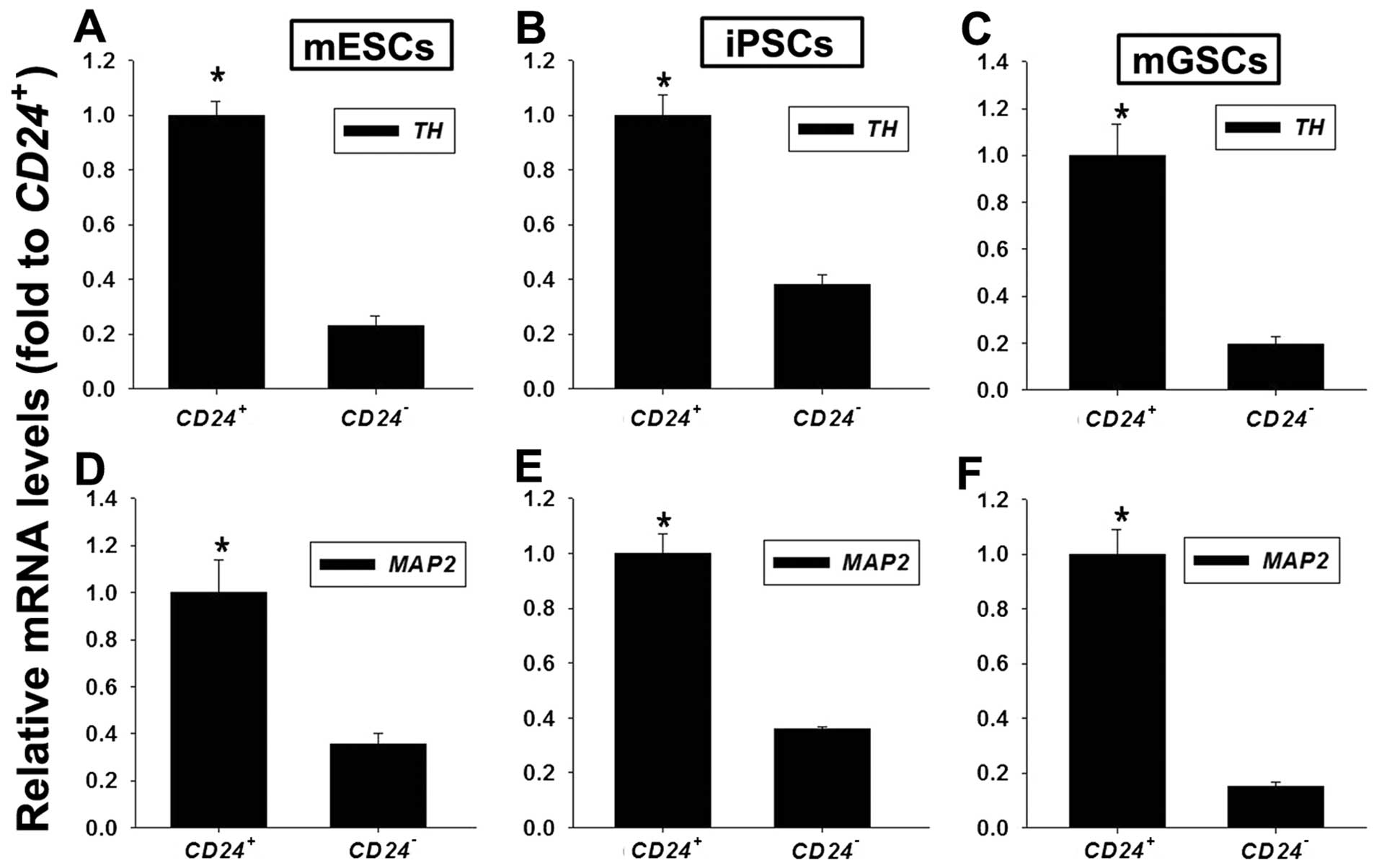
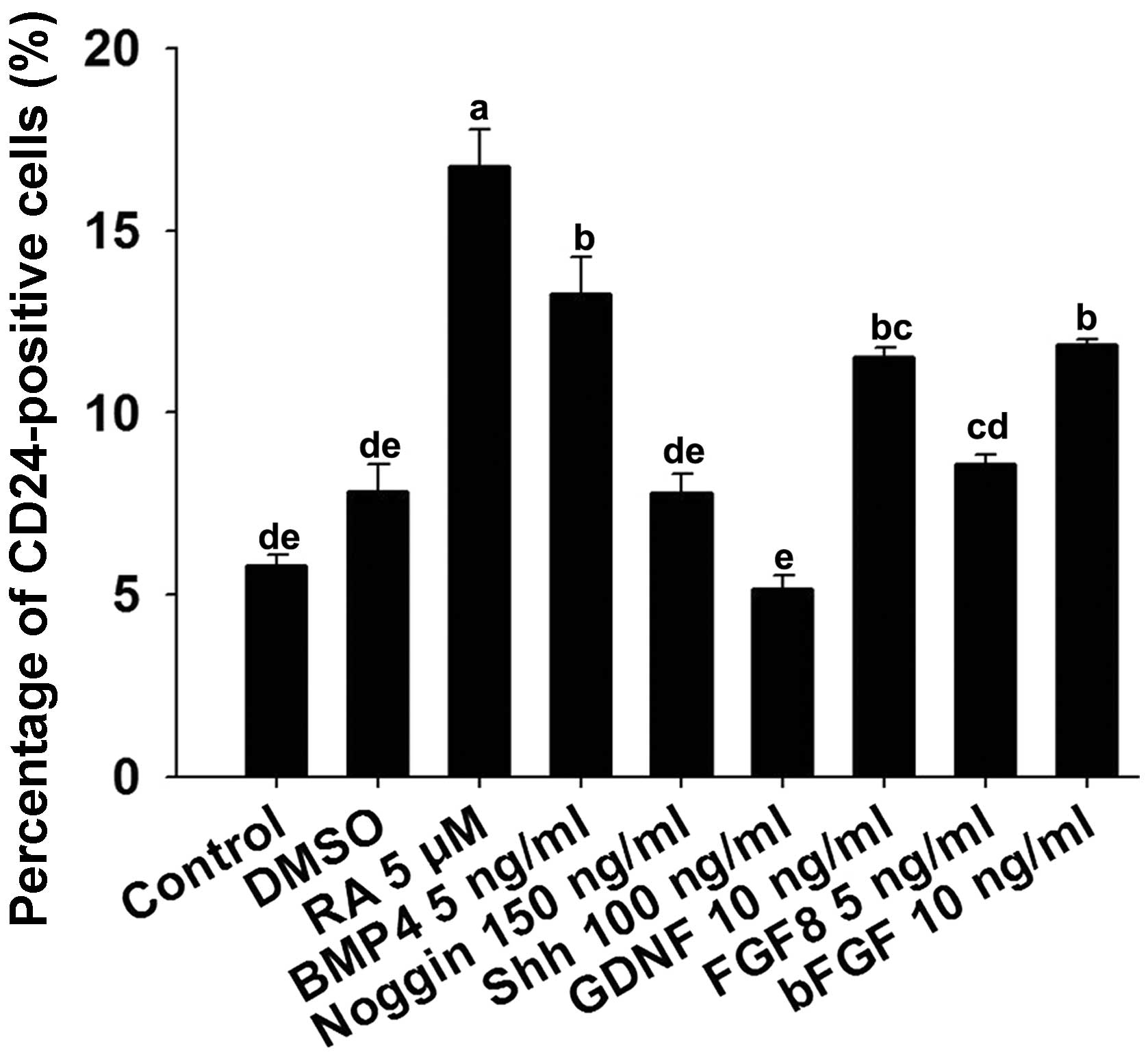
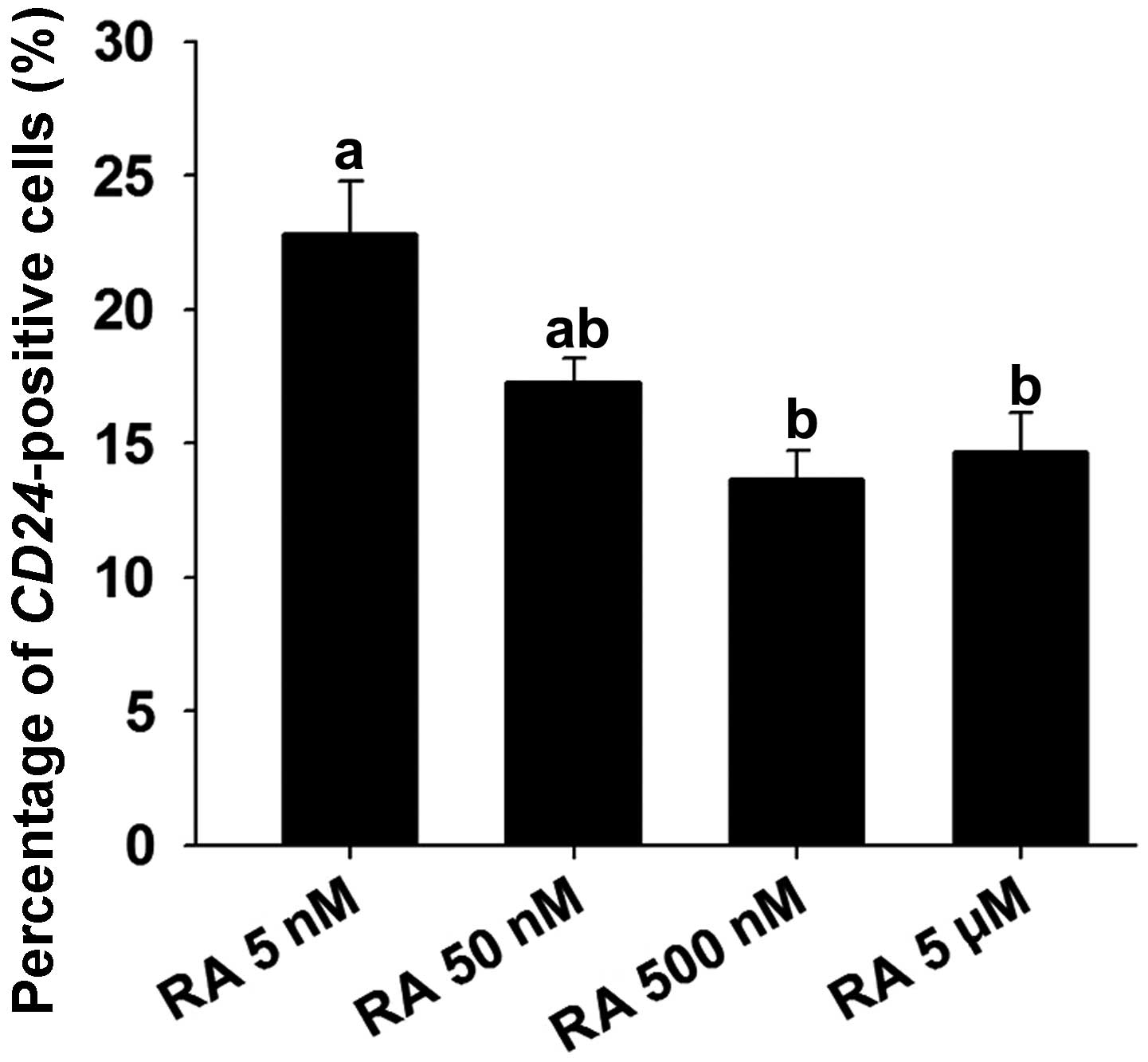
|
1
|
Hu BY, Du ZW, Li XJ, Ayala M and Zhang SC:
Human oligodendrocytes from embryonic stem cells: Conserved SHH
signaling networks and divergent FGF effects. Development.
136:1443–1452. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li XJ, Du ZW, Zarnowska ED, Pankratz M,
Hansen LO, Pearce RA and Zhang SC: Specification of motoneurons
from human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 23:215–221. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Perrier AL, Tabar V, Barberi T, Rubio ME,
Bruses J, Topf N, Harrison NL and Studer L: Derivation of midbrain
dopamine neurons from human embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 101:12543–12548. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Roy NS, Cleren C, Singh SK, Yang L, Beal
MF and Goldman SA: Functional engraftment of human ES cell-derived
dopaminergic neurons enriched by coculture with
telomerase-immortalized midbrain astrocytes. Nat Med. 12:1259–1268.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Watanabe K, Ueno M, Kamiya D, Nishiyama A,
Matsumura M, Wataya T, Takahashi JB, Nishikawa S, Nishikawa S,
Muguruma K and Sasai Y: A ROCK inhibitor permits survival of
dissociated human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 25:681–686.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang L, Soonpaa MH, Adler ED, Roepke TK,
Kattman SJ, Kennedy M, Henckaerts E, Bonham K, Abbott GW, Linden
RM, et al: Human cardiovascular progenitor cells develop from a
KDR+ embryonic-stem-cell-derived population. Nature.
453:524–528. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nishikawa S, Goldstein RA and Nierras CR:
The promise of human induced pluripotent stem cells for research
and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:725–729. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Takahashi K and Yamanaka S: Induction of
pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast
cultures by defined factors. Cell. 126:663–676. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Spradling A, Drummond-Barbosa D and Kai T:
Stem cells find their niche. Nature. 414:98–104. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Conrad S, Renninger M, Hennenlotter J,
Wiesner T, Just L, Bonin M, Aicher W, Bühring HJ, Mattheus U, Mack
A, et al: Generation of pluripotent stem cells from adult human
testis. Nature. 456:344–349. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guan K, Nayernia K, Maier LS, Wagner S,
Dressel R, Lee JH, Nolte J, Wolf F, Li M, Engel W and Hasenfuss G:
Pluripotency of spermatogonial stem cells from adult mouse testis.
Nature. 440:1199–1203. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Izadyar F, Pau F, Marh J, Slepko N, Wang
T, Gonzalez R, Ramos T, Howerton K, Sayre C and Silva F: Generation
of multipotent cell lines from a distinct population of male germ
line stem cells. Reproduction. 135:771–784. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kanatsu-Shinohara M, Inoue K, Lee J,
Yoshimoto M, Ogonuki N, Miki H, Baba S, Kato T, Kazuki Y, Toyokuni
S, et al: Generation of pluripotent stem cells from neonatal mouse
testis. Cell. 119:1001–1012. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kanatsu-Shinohara M, Lee J, Inoue K,
Ogonuki N, Miki H, Toyokuni S, Ikawa M, Nakamura T, Ogura A and
Shinohara T: Pluripotency of a single spermatogonial stem cell in
mice. Biol Reprod. 78:681–687. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ko K, Tapia N, Wu G, Kim JB, Bravo MJ,
Sasse P, Glaser T, Ruau D, Han DW, Greber B, et al: Induction of
pluripotency in adult unipotent germline stem cells. Cell Stem
Cell. 5:87–96. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Seandel M, James D, Shmelkov SV,
Falciatori I, Kim J, Chaval S, Scherr DS, Zhang F, Torres R, Gale
NW, et al: Generation of functional multipotent adult stem cells
from GPR125+ germline progenitors. Nature. 449:346–350.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim BJ, Lee YA, Kim YH, Kim KJ, Jung MS,
Ha SJ, Kang HG, Kim BG, Do JT, Yang HS and Ryu BY: Establishment of
adult mouse testis-derived multipotent germ line stem cells and
comparison of lineage-specific differentiation potential. Tissue
Eng Regen Med. 11:121–130. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Glaser T, Opitz T, Kischlat T, Konang R,
Sasse P, Fleischmann BK, Engel W, Nayernia K and Brüstle O: Adult
germ line stem cells as a source of functional neurons and glia.
Stem Cells. 26:2434–2443. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Baumgarth N and Roederer M: A practical
approach to multi-color flow cytometry for immunophenotyping. J
Immunol Methods. 243:77–97. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kantor AB and Roederer M: FACS analysis of
leukocytes. Handbook of Experimental Immunology. Herzenberg LA,
Weir DM and Blackwell C: Blackwell Science; Boston: pp. 43–49.
1996
|
|
21
|
Morrison SJ, Uchida N and Weissman IL: The
biology of hematopoietic stem cells. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
11:35–71. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zola H: Medical applications of leukocyte
surface molecules-the CD molecules. Mol Med. 12:312–316. 2006.
|
|
23
|
Iversen SD and Iversen LL: Dopamine: 50
years in perspective. Trends Neurosci. 30:188–193. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fraichard A, Chassande O, Bilbaut G, Dehay
C, Savatier P and Samarut J: In vitro differentiation of embryonic
stem cells into glial cells and functional neurons. J Cell Sci.
108:3181–3188. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Megiorni F, Mora B, Indovina P and
Mazzilli MC: Expression of neuronal markers during NTera2/cloneD1
differentiation by cell aggregation method. Neurosci Lett.
373:105–109. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Caceres A, Mautino J and Kosik KS:
Suppression of MAP2 in cultured cerebellar macroneurons inhibits
minor neurite formation. Neuron. 9:607–618. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dehmelt L, Smart FM, Ozer RS and Halpain
S: The role of microtubule-associated protein 2c in the
reorganization of microtubules and lamellipodia during neurite
initiation. J Neurosci. 23:9479–9490. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Harada A, Teng J, Takei Y, Oguchi K and
Hirokawa N: MAP2 is required for dendrite elongation, PKA anchoring
in dendrites, and proper PKA signal transduction. J Cell Biol.
158:541–549. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tesar PJ, Chenoweth JG, Brook FA, Davies
TJ, Evans EP, Mack DL, Gardner RL and McKay RD: New cell lines from
mouse epiblast share defining features with human embryonic stem
cells. Nature. 448:196–199. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang SC: Defining glial cells during CNS
development. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2:840–843. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bouhon IA, Kato H, Chandran S and Allen
ND: Neural differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells in
chemically defined medium. Brain Res Bull. 68:62–75. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Finley MF, Devata S and Huettner JE: BMP-4
inhibits neural differentiation of murine embryonic stem cells. J
Neurobiol. 40:271–287. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Okabe S, Forsberg-Nilsson K, Spiro AC,
Segal M and McKay RD: Development of neuronal precursor cells and
functional postmitotic neurons from embryonic stem cells in vitro.
Mech Dev. 59:89–102. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tropepe V, Hitoshi S, Sirard C, Mak TW,
Rossant J and van der Kooy D: Direct neural fate specification from
embryonic stem cells: A primitive mammalian neural stem cell stage
acquired through a default mechanism. Neuron. 30:65–78. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Watanabe K, Kamiya D, Nishiyama A,
Katayama T, Nozaki S, Kawasaki H, Watanabe Y, Mizuseki K and Sasai
Y: Directed differentiation of telencephalic precursors from
embryonic stem cells. Nat Neurosci. 8:288–296. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wiles MV and Johansson BM: Embryonic stem
cell development in a chemically defined medium. Exp Cell Res.
247:241–248. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ying QL, Stavridis M, Griffiths D, Li M
and Smith A: Conversion of embryonic stem cells into
neuroectodermal precursors in adherent monoculture. Nat Biotechnol.
21:183–186. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kawasaki H, Mizuseki K, Nishikawa S,
Kaneko S, Kuwana Y, Nakanishi S, Nishikawa SI and Sasai Y:
Induction of midbrain dopaminergic neurons from ES cells by stromal
cell-derived inducing activity. Neuron. 28:31–40. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lee SH, Lumelsky N, Studer L, Auerbach JM
and McKay RD: Efficient generation of midbrain and hindbrain
neurons from mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol.
18:675–679. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wichterle H, Lieberam I, Porter JA and
Jessell TM: Directed differentiation of embryonic stem cells into
motor neurons. Cell. 110:385–397. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cai C and Grabel L: Directing the
differentiation of embryonic stem cells to neural stem cells. Dev
Dyn. 236:3255–3266. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kay R, Rosten PM and Humphries RK: CD24, a
signal transducer modulating B cell activation responses, is a very
short peptide with a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor.
J Immunol. 147:1412–1416. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Williams LA, McLellan AD, Summers KL, Sorg
RV, Fearnley DB and Hart DN: Identification of a novel dendritic
cell surface antigen defined by carbohydrate specific CD24 antibody
cross-reactivity. Immunology. 89:120–125. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Calaora V, Chazal G, Nielsen PJ, Rougon G
and Moreau H: mCD24 expression in the developing mouse brain and in
zones of secondary neurogenesis in the adult. Neuroscience.
73:581–594. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Axell MZ, Zlateva S and Curtis M: A method
for rapid derivation and propagation of neural progenitors from
human embryonic stem cells. J Neurosci Methods. 184:275–284. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Do JT, Joo JY, Han DW, Araúzo-Bravo MJ,
Kim MJ, Greber B, Zaehres H, Sobek-Klocke I, Chung HM and Schöler
HR: Generation of parthenogenetic induced pluripotent stem cells
from parthenogenetic neural stem cells. Stem Cells. 27:2962–2968.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gerrard L, Rodgers L and Cui W:
Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to neural lineages in
adherent culture by blocking bone morphogenetic protein signaling.
Stem Cells. 23:1234–1241. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hicks AU, Lappalainen RS, Narkilahti S,
Suuronen R, Corbett D, Sivenius J, Hovatta O and Jolkkonen J:
Transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived neural
precursor cells and enriched environment after cortical stroke in
rats: Cell survival and functional recovery. Eur J Neurosci.
29:562–574. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Koch P, Opitz T, Steinbeck JA, Ladewig J
and Brüstle O: A rosette-type, self-renewing human ES cell-derived
neural stem cell with potential for in vitro instruction and
synaptic integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:3225–3230. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Maden M: Retinoid signalling in the
development of the central nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci.
3:843–853. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Pierani A, Brenner-Morton S, Chiang C and
Jessell TM: A sonic hedgehog-independent, retinoid-activated
pathway of neurogenesis in the ventral spinal cord. Cell.
97:903–915. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hirsinger E, Duprez D, Jouve C, Malapert
P, Cooke J and Pourquié O: Noggin acts downstream of Wnt and Sonic
Hedgehog to antagonize BMP4 in avian somite patterning.
Development. 124:4605–4614. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Marcelino J, Sciortino CM, Romero MF,
Ulatowski LM, Ballock RT, Economides AN, Eimon PM, Harland RM and
Warman ML: Human disease-causing NOG missense mutations: Effects on
noggin secretion, dimer formation, and bone morphogenetic protein
binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:11353–11358. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Sasai Y, Lu B, Steinbeisser H and De
Robertis EM: Regulation of neural induction by the Chd and Bmp-4
antagonistic patterning signals in Xenopus. Nature. 376:333–336.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|