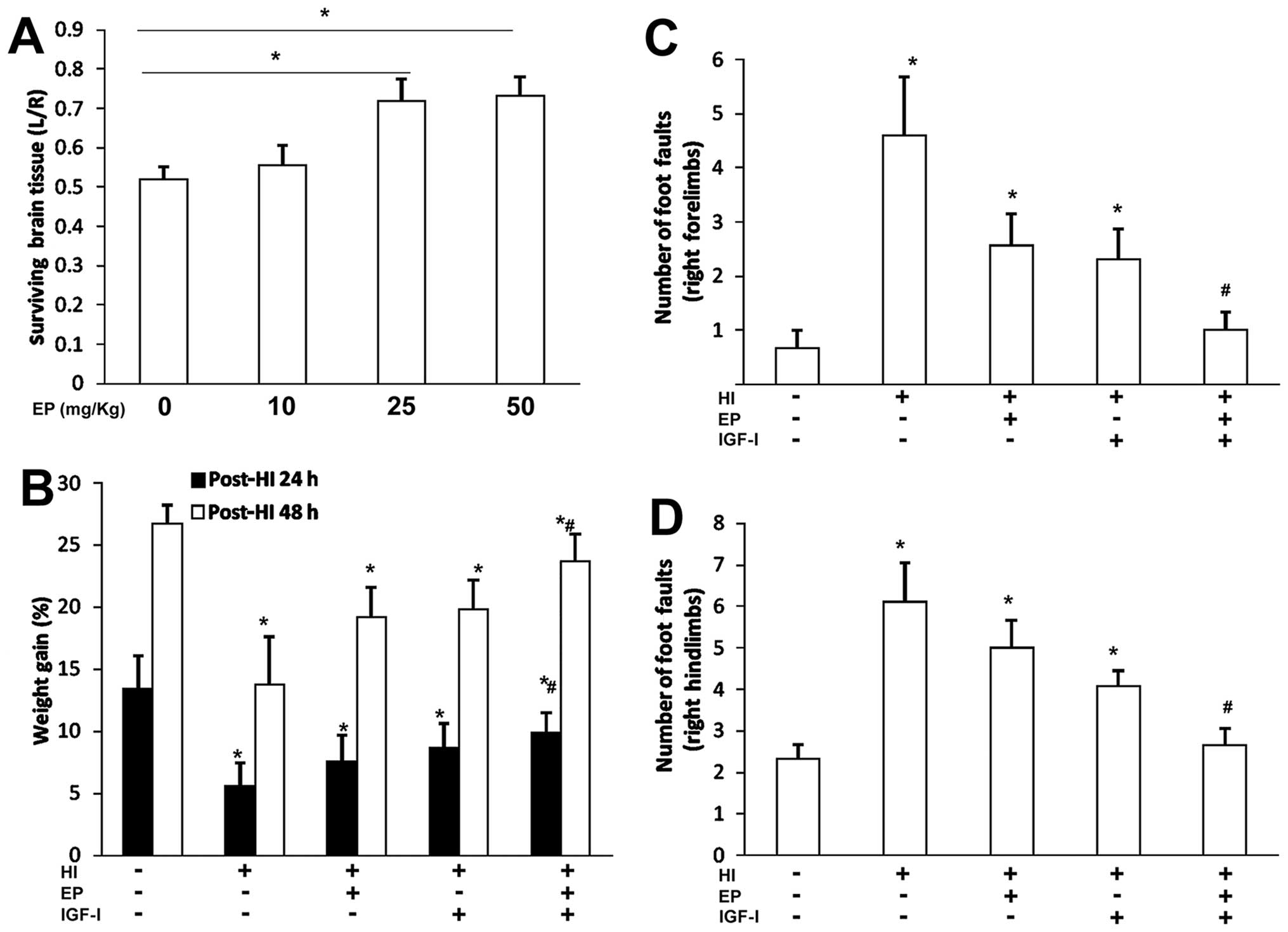
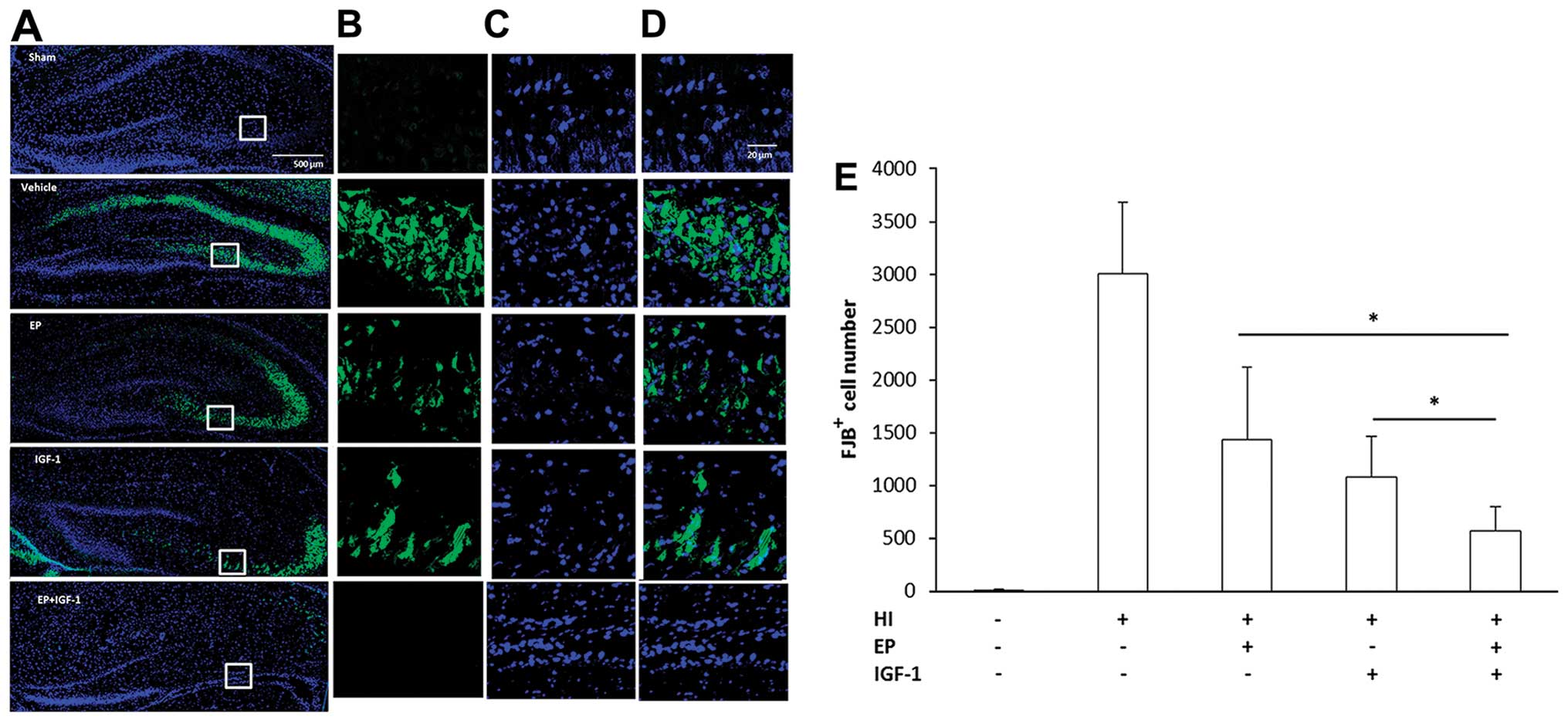
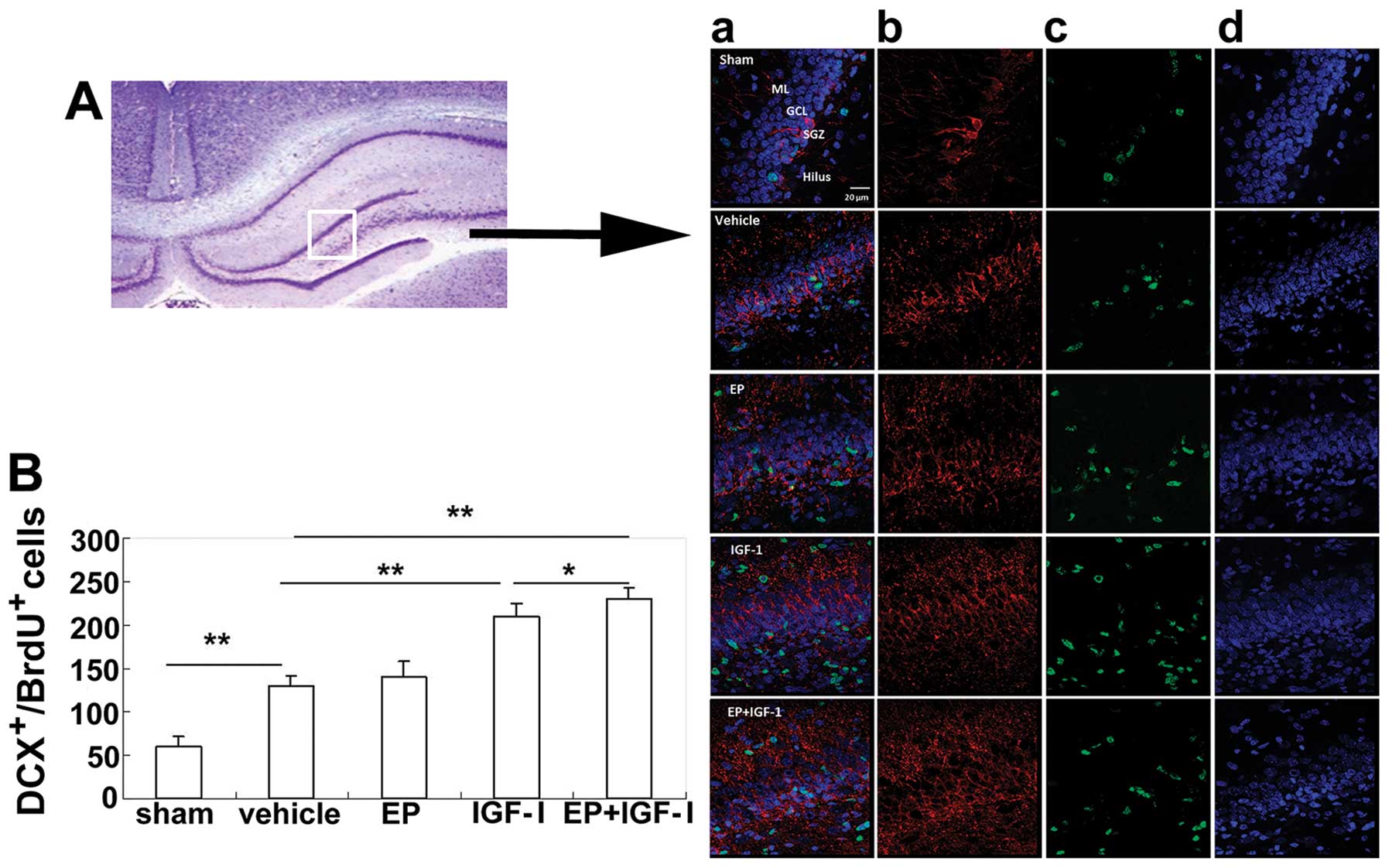
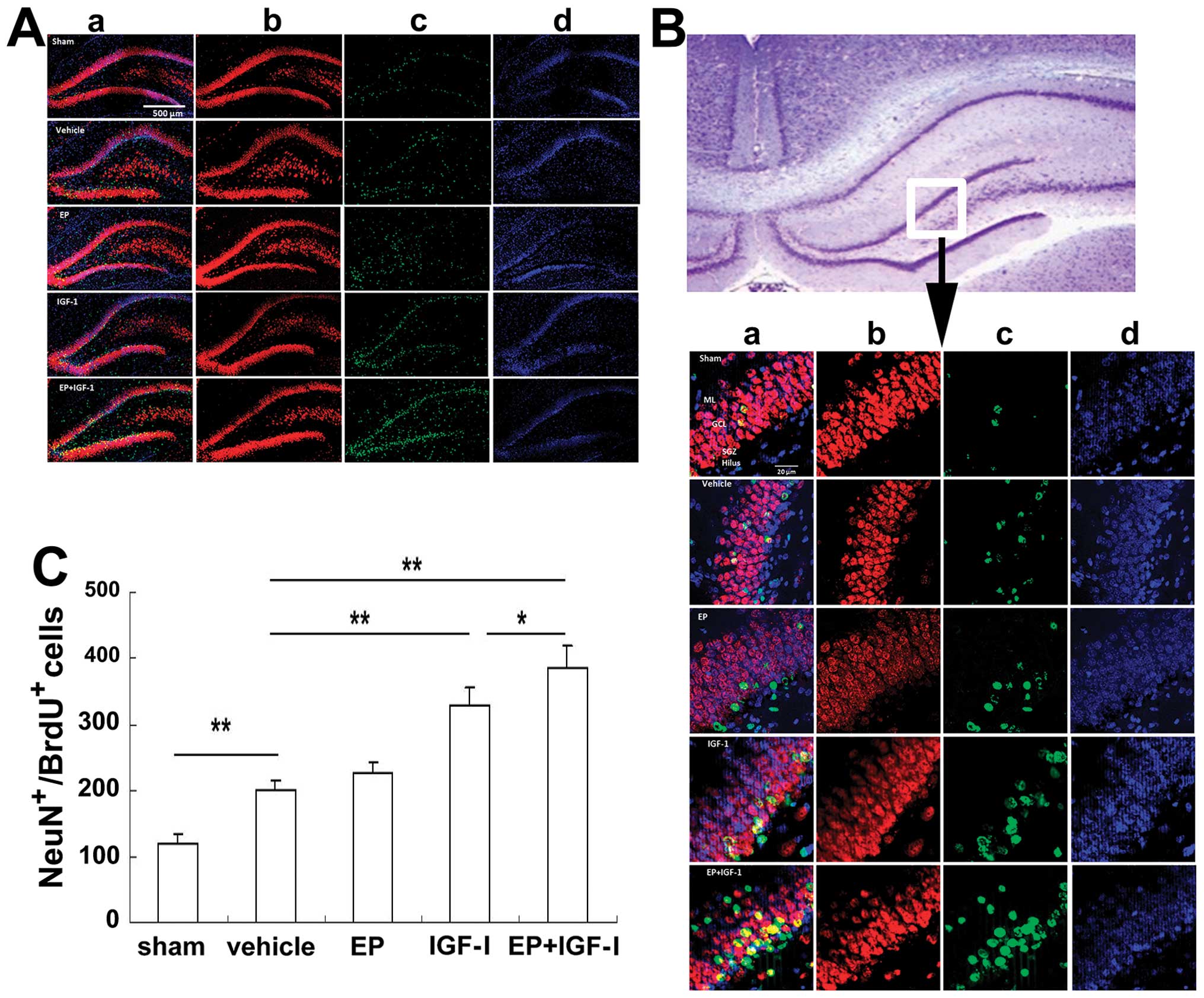
|
1
|
Ikonomidou C, Mosinger JL, Salles KS,
Labruyere J and Olney JW: Sensitivity of the developing rat brain
to hypobaric/ischemic damage parallels sensitivity to
N-methyl-aspartate neurotoxicity. J Neurosci. 9:2809–2818.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jiang X, Mu D, Manabat C, et al:
Differential vulnerability of immature murine neurons to
oxygen-glucose deprivation. Exp Neurol. 190:224–232. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ikonomidou C and Kaindl AM: Neuronal death
and oxidative stress in the developing brain. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 14:1535–1550. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Berger R and Garnier Y: Perinatal brain
injury. J Perinat Med. 28:261–285. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
du Plessis AJ and Volpe JJ: Perinatal
brain injury in the preterm and term newborn. Curr Opin Neurol.
15:151–157. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Logitharajah P, Rutherford MA and Cowan
FM: Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in preterm infants: antecedent
factors, brain imaging, and outcome. Pediatr Res. 66:222–229. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vannucci RC: Hypoxic-ischemic
encephalopathy. Am J Perinatol. 17:113–120. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Russo VC, Gluckman PD, Feldman EL and
Werther GA: The insulin-like growth factor system and its
pleiotropic functions in brain. Endocr Rev. 26:916–943. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Aberg ND, Brywe KG and Isgaard J: Aspects
of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-I related to
neuroprotection, regeneration, and functional plasticity in the
adult brain. ScientificWorldJournal. 6:53–80. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guan J, Bennet L, George S, et al:
Insulin-like growth factor-1 reduces postischemic white matter
injury in fetal sheep. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 21:493–502. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guan J: Insulin-like growth factor-1 and
its derivatives: potential pharmaceutical application for ischemic
brain injury. Recent Pat CNS Drug Discov. 3:112–127. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Desagher S, Glowinski J and Premont J:
Pyruvate protects neurons against hydrogen peroxide-induced
toxicity. J Neurosci. 17:9060–9067. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mazzio E and Soliman KF: Pyruvic acid
cytoprotection against 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium,
6-hydroxydopamine and hydrogen peroxide toxicities in vitro.
Neurosci Lett. 337:77–80. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pan R, Rong Z, She Y, Cao Y, Chang LW and
Lee WH: Sodium pyruvate reduces hypoxic-ischemic injury to neonatal
rat brain. Pediatr Res. 72:479–489. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shen H, Hu X, Liu C, et al: Ethyl pyruvate
protects against hypoxic-ischemic brain injury via anti-cell death
and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Neurobiol Dis. 37:711–722. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Rong Z, Pan R, Xu Y, Zhang C, Cao Y and
Liu D: Hesperidin pretreatment protects hypoxia-ischemic brain
injury in neonatal rat. Neuroscience. 255:292–299. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Goldberg MP and Choi DW: Combined oxygen
and glucose deprivation in cortical cell culture: calcium-dependent
and calcium-independent mechanisms of neuronal injury. J Neurosci.
13:3510–3524. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rice JE III, Vannucci RC and Brierley JB:
The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the
rat. Ann Neurol. 9:131–141. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhong J, Zhao L, Du Y, Wei G, Yao WG and
Lee WH: Delayed IGF-1 treatment reduced long-term
hypoxia-ischemia-induced brain damage and improved behavior
recovery of immature rats. Neurol Res. 31:483–489. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Northington FJ, Chavez-Valdez R and Martin
LJ: Neuronal cell death in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Ann Neurol.
69:743–758. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Perlman JM: Intervention strategies for
neonatal hypoxic-ischemic cerebral injury. Clin Ther. 28:1353–1365.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Savman K and Brown KL: Treating neonatal
brain injury - promise and inherent research challenges. Recent Pat
Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 4:16–24. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Buonocore G and Groenendaal F:
Anti-oxidant strategies. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 12:287–295.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hobbs CE and Oorschot DE: Neonatal rat
hypoxia-ischemia: long-term rescue of striatal neurons and motor
skills by combined antioxidant-hypothermia treatment. Brain Pathol.
18:443–454. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cruz RJ Jr, Harada T, Sasatomi E and Fink
MP: Effects of ethyl pyruvate and other α-keto carboxylic acid
derivatives in a rat model of multivisceral ischemia and
reperfusion. J Surg Res. 165:151–157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kao KK and Fink MP: The biochemical basis
for the anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective actions of ethyl
pyruvate and related compounds. Biochem Pharmacol. 80:151–159.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gressens P, Le Verche V, Fraser M, Rousset
CI, Schwendimann L, Bennet L, George SA, Wang X, Mallard C, Tilley
BC, et al: Pitfalls in the quest of neuroprotectants for the
perinatal brain. Dev Neurosci. 33:189–198. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Werner H and Leroith D: Insulin and
insulin-like growth factor receptors in the brain: Physiological
and pathological aspects. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. Jan
31–2014.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Satar M, Ozcan K, Yapicioglu H and Narli
N: Serum insulin-like growth factor 1 and growth hormone levels of
hypoxic-ischemic newborns. Biol Neonate. 85:15–20. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lee WH, Wang GM, Seaman LB and Vannucci
SJ: Coordinate IGF-I and IGFBP5 gene expression in perinatal rat
brain after hypoxia-ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 16:227–236.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Clawson TF, Vannucci SJ, Wang GM, Seaman
LB, Yang XL and Lee WH: Hypoxia-ischemia-induced apoptotic cell
death correlates with IGF-I mRNA decrease in neonatal rat brain.
Biol Signals Recept. 8:281–293. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Brywe KG, Mallard C, Gustavsson M, et al:
IGF-I neuroprotection in the immature brain after hypoxia-ischemia,
involvement of Akt and GSK3beta? Eur J Neurosci. 21:1489–1502.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lin S, Fan LW, Rhodes PG and Cai Z:
Intranasal administration of IGF-1 attenuates hypoxic-ischemic
brain injury in neonatal rats. Exp Neurol. 217:361–370. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wood TL, Loladze V, Altieri S, Gangoli N,
Levison SW, Brywe KG, Mallard C and Hagberg H: Delayed IGF-1
administration rescues oligodendrocyte progenitors from
glutamate-induced cell death and hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Dev
Neurosci. 29:302–310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pazos MR, Cinquina V, Gomez A, et al:
Cannabidiol administration after hypoxia-ischemia to newborn rats
reduces long-term brain injury and restores neurobehavioral
function. Neuropharmacology. 63:776–783. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Towfighi J, Mauger D, Vannucci RC and
Vannucci SJ: Influence of age on the cerebral lesions in an
immature rat model of cerebral hypoxia-ischemia: a light
microscopic study. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 100:149–160. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shrivastava K, Chertoff M, Llovera G,
Recasens M and Acarin L: Short and long-term analysis and
comparison of neurodegeneration and inflammatory cell response in
the ipsilateral and contralateral hemisphere of the neonatal mouse
brain after hypoxia/ischemia. Neurol Res Int. 2012:7815122012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dudek H, Datta SR, Franke TF, et al:
Regulation of neuronal survival by the serine-threonine protein
kinase Akt. Science. 275:661–665. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Aberg MA, Aberg ND, Hedbacker H, Oscarsson
J and Eriksson PS: Peripheral infusion of IGF-I selectively induces
neurogenesis in the adult rat hippocampus. J Neurosci.
20:2896–2903. 2000.
|
|
40
|
D’Ercole AJ, Ye P and O’Kusky JR: Mutant
mouse models of insulin-like growth factor actions in the central
nervous system. Neuropeptides. 36:209–220. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Gao X, Enikolopov G and Chen J: Moderate
traumatic brain injury promotes proliferation of quiescent neural
progenitors in the adult hippocampus. Exp Neurol. 219:516–523.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bartley J, Soltau T, Wimborne H, et al:
BrdU-positive cells in the neonatal mouse hippocampus following
hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. BMC Neurosci. 6:152005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bayer SA: Development of the hippocampal
region in the rat. I. Neurogenesis examined with 3H-thymidine
autoradiography. J Comp Neurol. 190:87–114. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|