|
1
|
Mymrikov EV, Seit-Nebi AS and Gusev NB:
Large potentials of small heat shock proteins. Physiol Rev.
91:1123–1159. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kampinga HH, Hageman J, Vos MJ, Kubota H,
Tanguay RM, Bruford EA, Cheetham ME, Chen B and Hightower LE:
Guidelines for the nomenclature of the human heat shock proteins.
Cell Stress Chaperones. 14:105–111. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Kriehuber T, Rattei T, Weinmaier T,
Bepperling A, Haslbeck M and Buchner J: Independent evolution of
the core domain and its flanking sequences in small heat shock
proteins. FASEB J. 24:3633–3642. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dubińska-Magiera M, Jabłońska J, Saczko J,
Kulbacka J, Jagla T and Daczewska M: Contribution of small heat
shock proteins to muscle development and function. FEBS Lett.
588:517–530. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kostenko S and Moens U: Heat shock protein
27 phosphorylation: Kinases, phosphatases, functions and pathology.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 66:3289–3307. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Landry J, Lambert H, Zhou M, Lavoie JN,
Hickey E, Weber LA and Anderson CW: Human HSP27 is phosphorylated
at serines 78 and 82 by heat shock and mitogen-activated kinases
that recognize the same amino acid motif as S6 kinase II. J Biol
Chem. 267:794–803. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hayes D, Napoli V, Mazurkie A, Stafford WF
and Graceffa P: Phosphorylation dependence of hsp27 multimeric size
and molecular chaperone function. J Biol Chem. 284:18801–18807.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Takai S, Adachi S,
Minamitani C, Yasuda E, Noda T, Kato K, Toyoda H, Kaneoka Y,
Yamaguchi A, et al: Phosphorylated heat shock protein 27 represses
growth of hepatocellular carcinoma via inhibition of extracellular
signal-regulated kinase. J Biol Chem. 283:18852–18860. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kular J, Tickner J, Chim SM and Xu J: An
overview of the regulation of bone remodelling at the cellular
level. Clin Biochem. 45:863–873. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chim SM, Tickner J, Chow ST, Kuek V, Guo
B, Zhang G, Rosen V, Erber W and Xu J: Angiogenic factors in bone
local environment. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 24:297–310. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Uozaki H, Horiuchi H, Ishida T, Iijima T,
Imamura T and Machinami R: Overexpression of resistance-related
proteins (metallothioneins, glutathione-S-transferase pi, heat
shock protein 27, and lung resistance-related protein) in
osteosarcoma. Relationship with poor prognosis Cancer.
79:2336–2344. 1997.
|
|
12
|
Tiffee JC, Griffin JP and Cooper LF:
Immunolocalization of stress proteins and extracellular matrix
proteins in the rat tibia. Tissue Cell. 32:141–147. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Leonardi R, Barbato E, Paganelli C and Lo
Muzio L: Immunolocalization of heat shock protein 27 in developing
jaw bones and tooth germs of human fetuses. Calcif Tissue Int.
75:509–516. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shakoori AR, Oberdorf AM, Owen TA, Weber
LA, Hickey E, Stein JL, Lian JB and Stein GS: Expression of heat
shock genes during differentiation of mammalian osteoblasts and
promyelocytic leukemia cells. J Cell Biochem. 48:277–287. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kozawa O, Niwa M, Matsuno H, Ishisaki A,
Kato K and Uematsu T: Stimulatory effect of basic fibroblast growth
factor on induction of heat shock protein 27 in osteoblasts: Role
of protein kinase C. Arch Biochem Biophys. 388:237–242. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kozawa O, Niwa M, Matsuno H, Tokuda H,
Miwa M, Ito H, Kato K and Uematsu T: Sphingosine 1-phosphate
induces heat shock protein 27 via p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase activation in osteoblasts. J Bone Miner Res. 14:1761–1767.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kato K, Adachi S, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R,
Minamitani C, Natsume H, Katagiri Y, Hirose Y, Mizutani J, Tokuda
H, Kozawa O, et al: Regulation by heat shock protein 27 of
osteocalcin synthesis in osteoblasts. Endocrinology. 152:1872–1882.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Arrigo AP and Gibert B: HspB1, HspB5 and
HspB4 in human cancers: Potent oncogenic role of some of their
client proteins. Cancers (Basel). 6:333–365. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gibert B, Eckel B, Fasquelle L, Moulin M,
Bouhallier F, Gonin V, Mellier G, Simon S, Kretz-Remy C, Arrigo AP,
et al: Knock down of heat shock protein 27 (HspB1) induces
degradation of several putative client proteins. PLoS One.
7:e297192012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Andrieu C, Taieb D, Baylot V, Ettinger S,
Soubeyran P, De-Thonel A, Nelson C, Garrido C, So A, Fazli L, et
al: Heat shock protein 27 confers resistance to androgen ablation
and chemotherapy in prostate cancer cells through eIF4E. Oncogene.
29:1883–1896. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kong J and Lasko P: Translational control
in cellular and developmental processes. Nat Rev Genet. 13:383–394.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gilbert RJ, Gordiyenko Y, von der Haar T,
Sonnen AF, Hofmann G, Nardelli M, Stuart DI and McCarthy JE:
Reconfiguration of yeast 40S ribosomal subunit domains by the
translation initiation multifactor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:5788–5793. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sonenberg N and Gingras AC: The mRNA 5′
cap-binding protein eIF4E and control of cell growth. Curr Opin
Cell Biol. 10:268–275. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jia Y, Polunovsky V, Bitterman PB and
Wagner CR: Cap-dependent translation initiation factor eIF4E: An
emerging anticancer drug target. Med Res Rev. 32:786–814. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kubisch C, Dimagno MJ, Tietz AB, Welsh MJ,
Ernst SA, Brandt-Nedelev B, Diebold J, Wagner AC, Göke B, Williams
JA, et al: Overexpression of heat shock protein Hsp27 protects
against cerulein-induced pancreatitis. Gastroenterology.
127:275–286. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sudo H, Kodama HA, Amagai Y, Yamamoto S
and Kasai S: In vitro differentiation and calcification in a new
clonal osteogenic cell line derived from newborn mouse calvaria. J
Cell Biol. 96:191–198. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kozawa O, Tokuda H, Miwa M, Kotoyori J and
Oiso Y: Cross-talk regulation between cyclic AMP production and
phosphoinositide hydrolysis induced by prostaglandin E2
in osteoblast-like cells. Exp Cell Res. 198:130–134. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Kumada T, Nagasawa
T, Suzuki M, Yasuda E, Okuda S, Maeda A, Kaneoka Y, Toyoda H and
Kozawa O: Direct association of heat shock protein 20 (HSPB6) with
phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) in human hepatocellular carcinoma:
Regulation of the PI3K activity. PLoS One. 8:e784402013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang W, Yang N and Shi XM: Regulation of
mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic differentiation by
glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper (GILZ). J Biol Chem.
283:4723–4729. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Simpson DA, Feeney S, Boyle C and Stitt
AW: Retinal VEGF mRNA measured by SYBR green I fluorescence: A
versatile approach to quantitative PCR. Mol Vis. 6:178–183.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural
proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.
Nature. 227:680–685. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
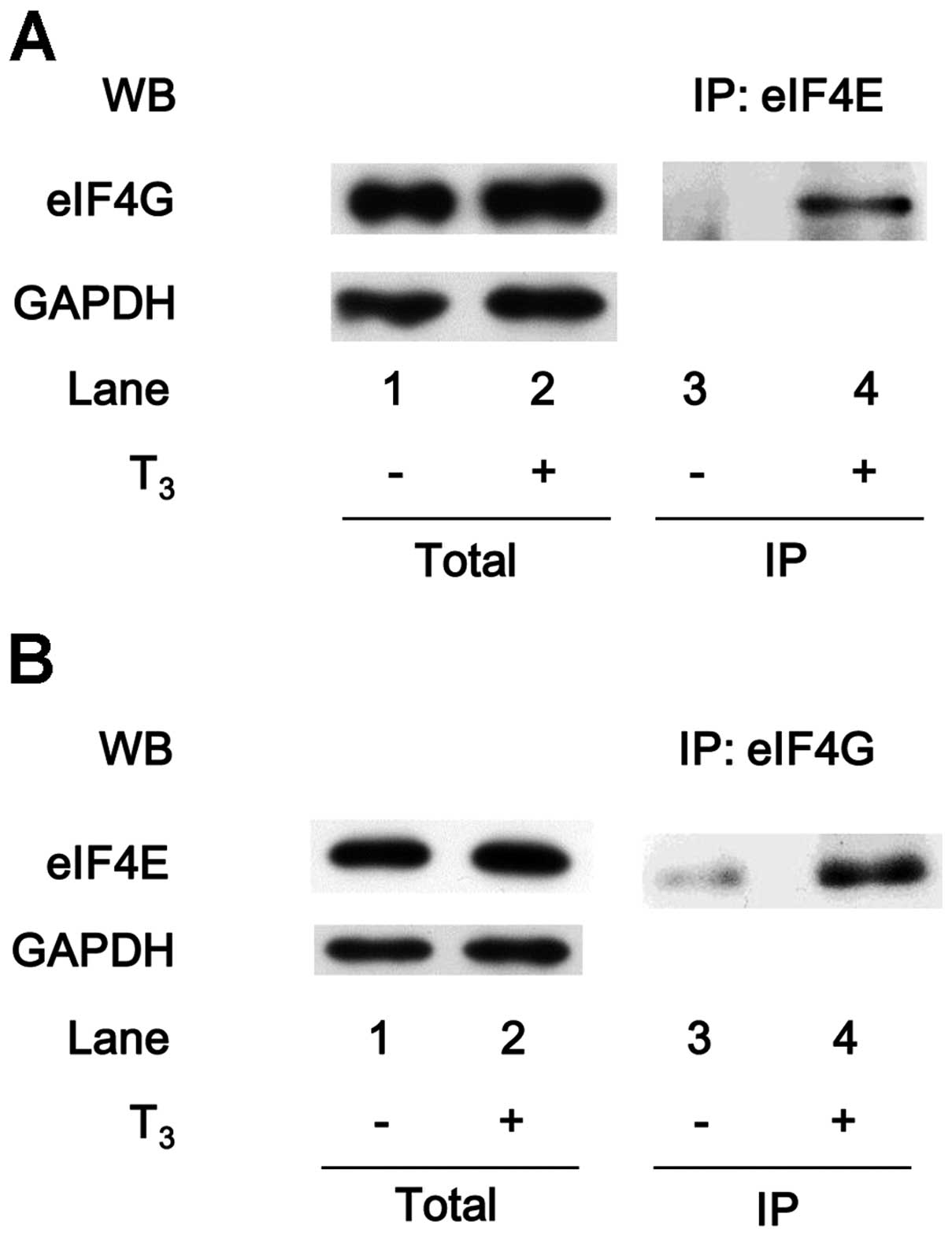
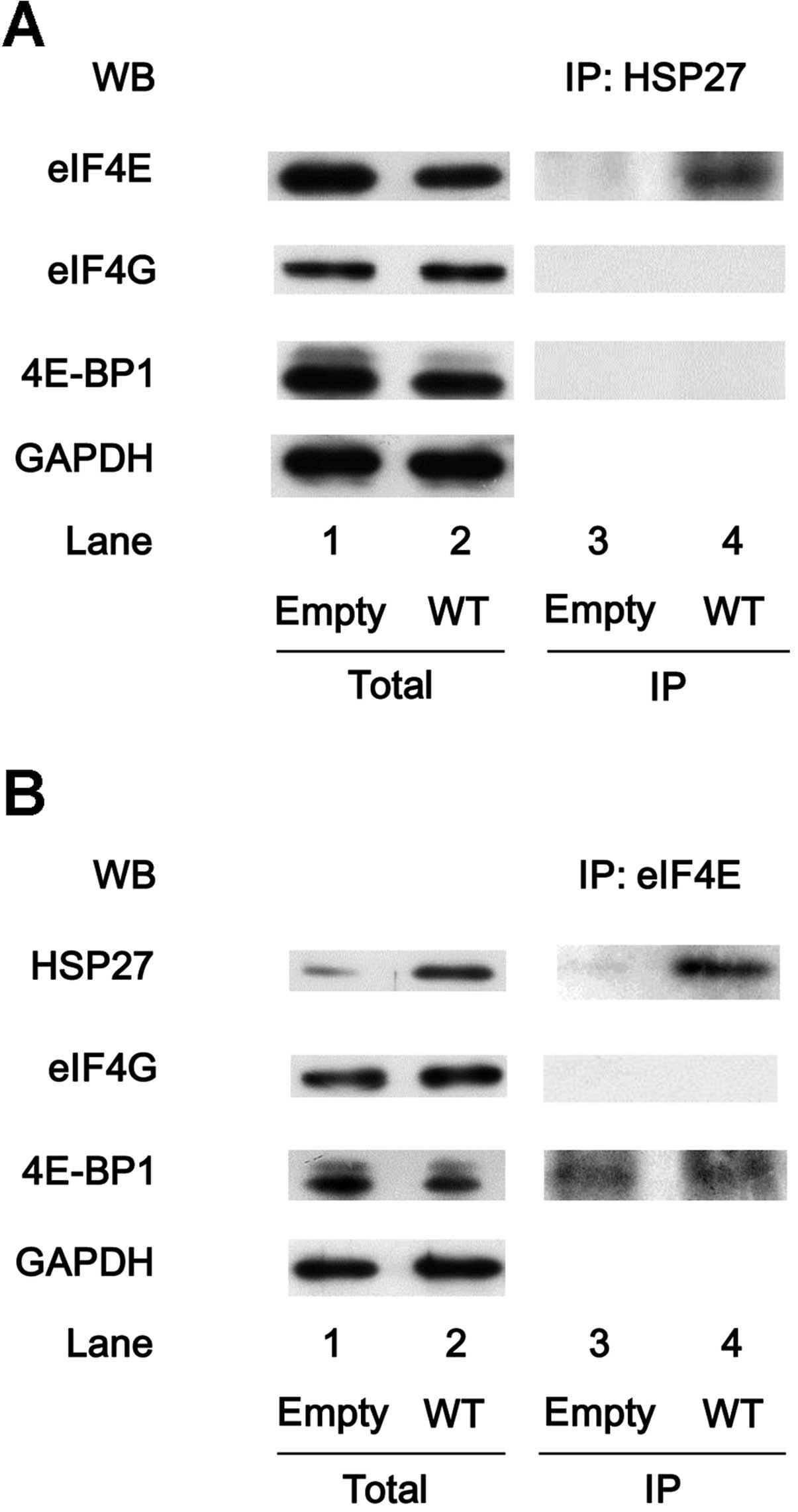
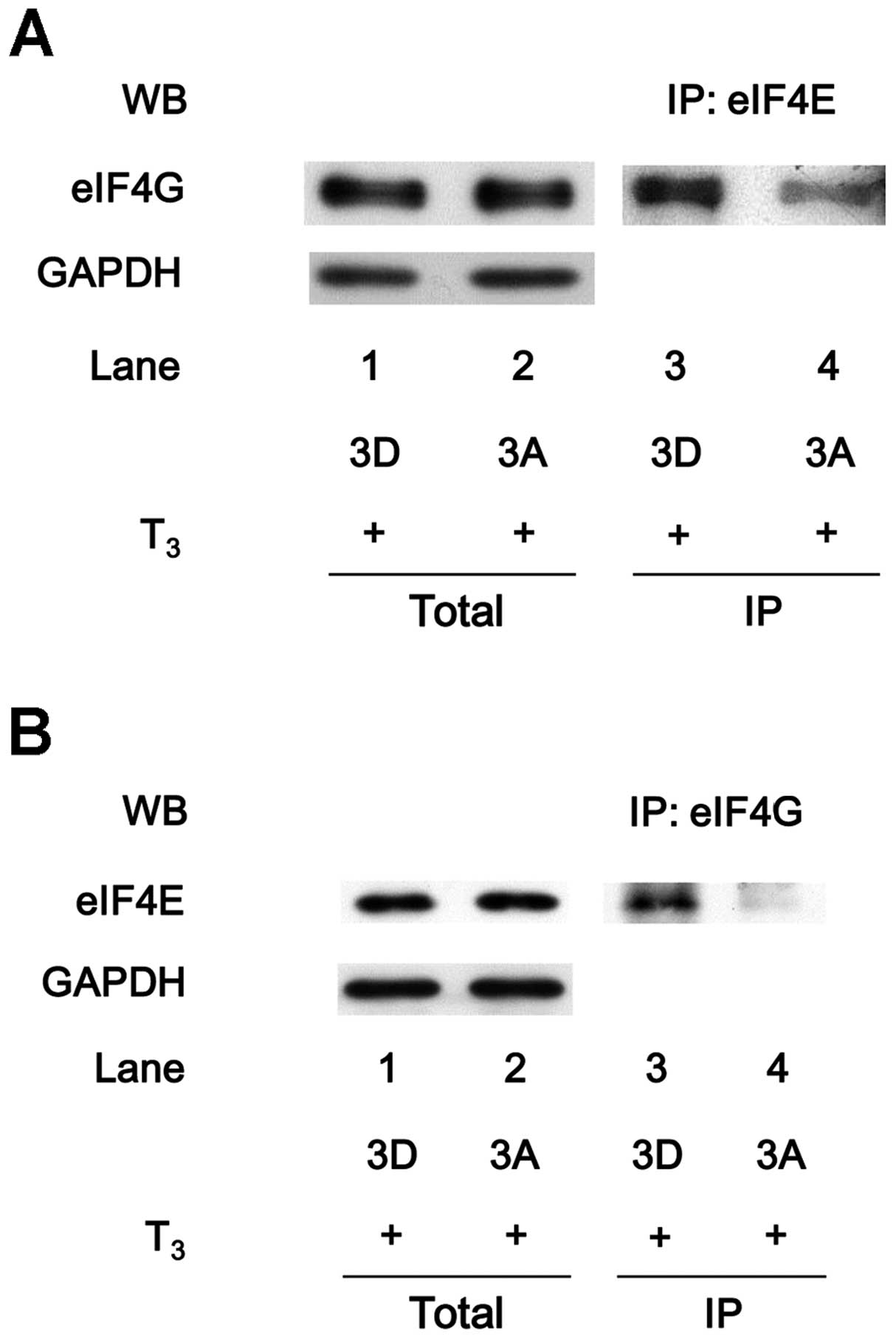
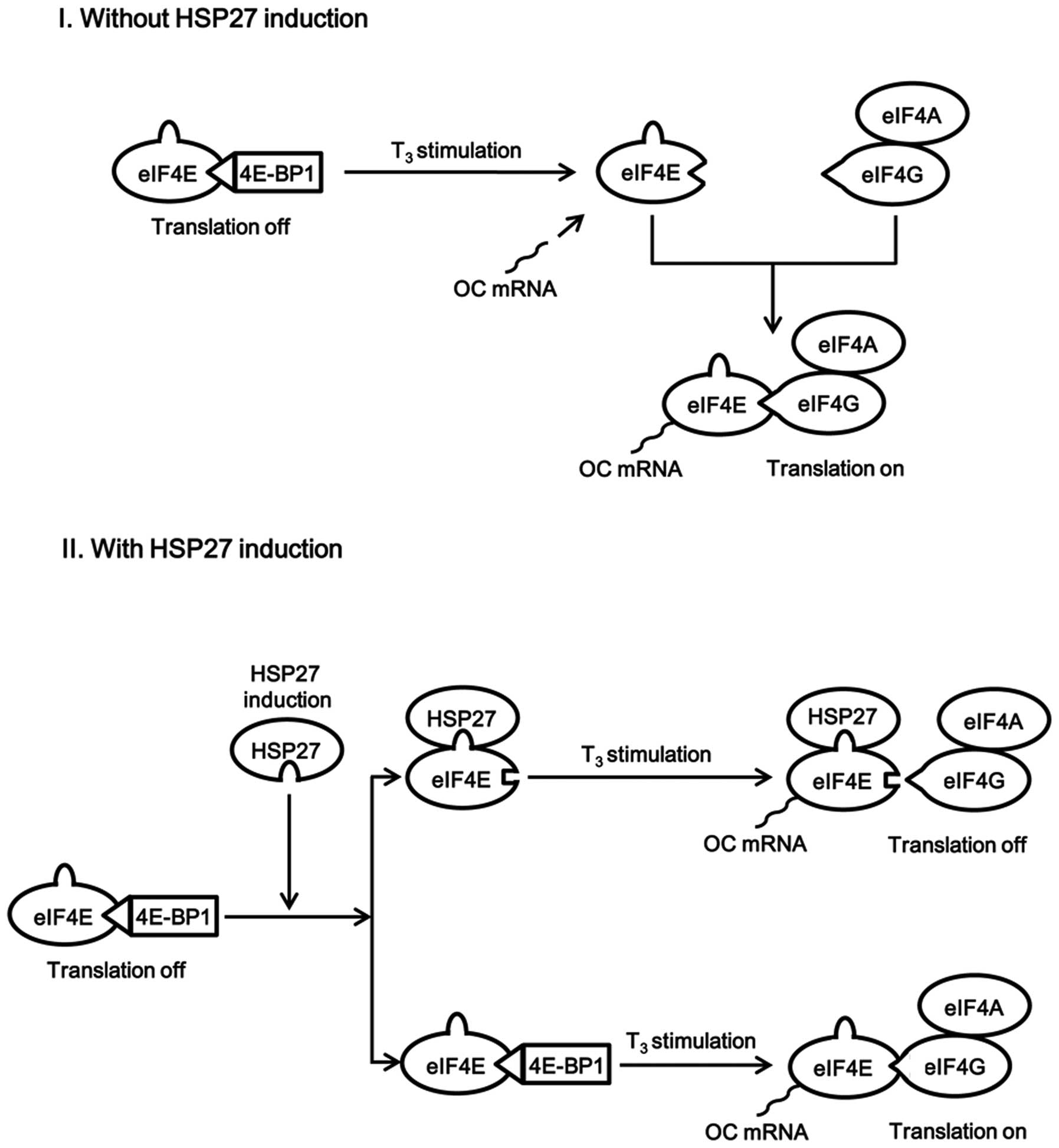
Cuesta R, Laroia G and Schneider RJ:
Chaperone hsp27 inhibits translation during heat shock by binding
eIF4G and facilitating dissociation of cap-initiation complexes.
Genes Dev. 14:1460–1470. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kato K, Tokuda H, Adachi S,
Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Yamauchi J, Natsume H, Minamitani C,
Mizutani J, Otsuka T and Kozawa O: Role of heat shock protein 27 in
transforming growth factor-β-stimulated vascular endothelial growth
factor release in osteoblasts. Int J Mol Med. 27:423–428.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Barutta F, Pinach S, Giunti S, Vittone F,
Forbes JM, Chiarle R, Arnstein M, Perin PC, Camussi G, Cooper ME,
et al: Heat shock protein expression in diabetic nephropathy. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 295:F1817–F1824. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Singh D, McCann KL and Imani F: MAPK and
heat shock protein 27 activation are associated with respiratory
syncytial virus induction of human bronchial epithelial monolayer
disruption. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 293:L436–L445.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|