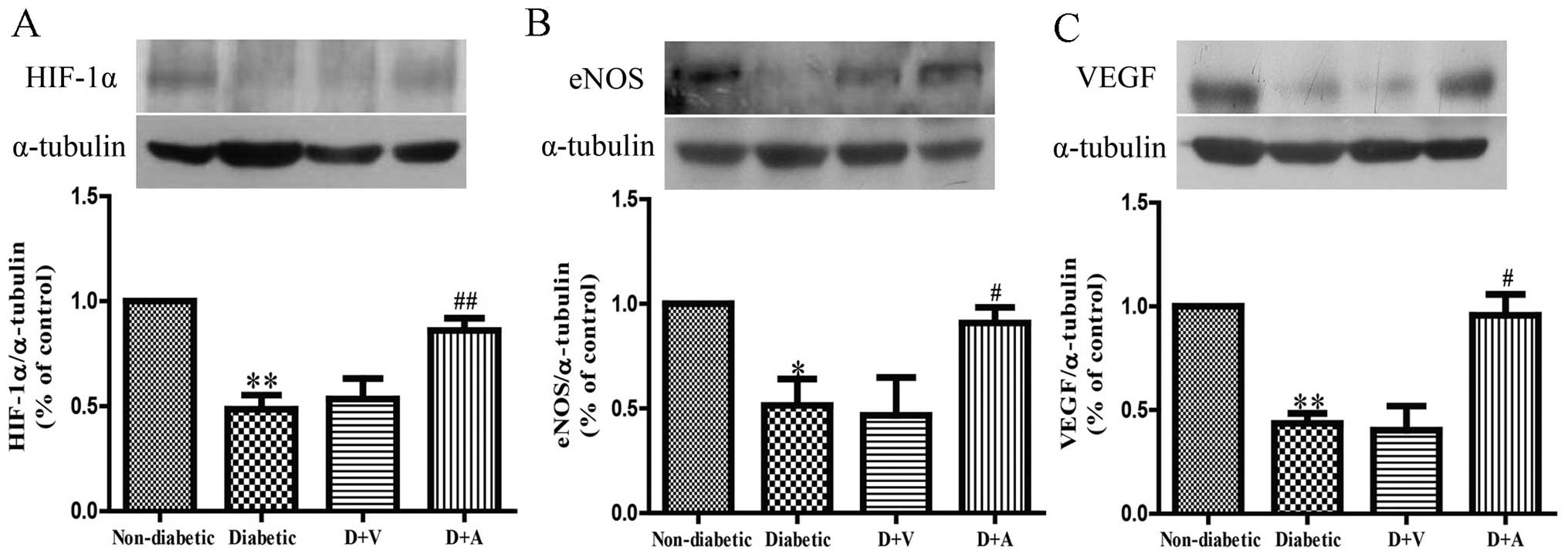
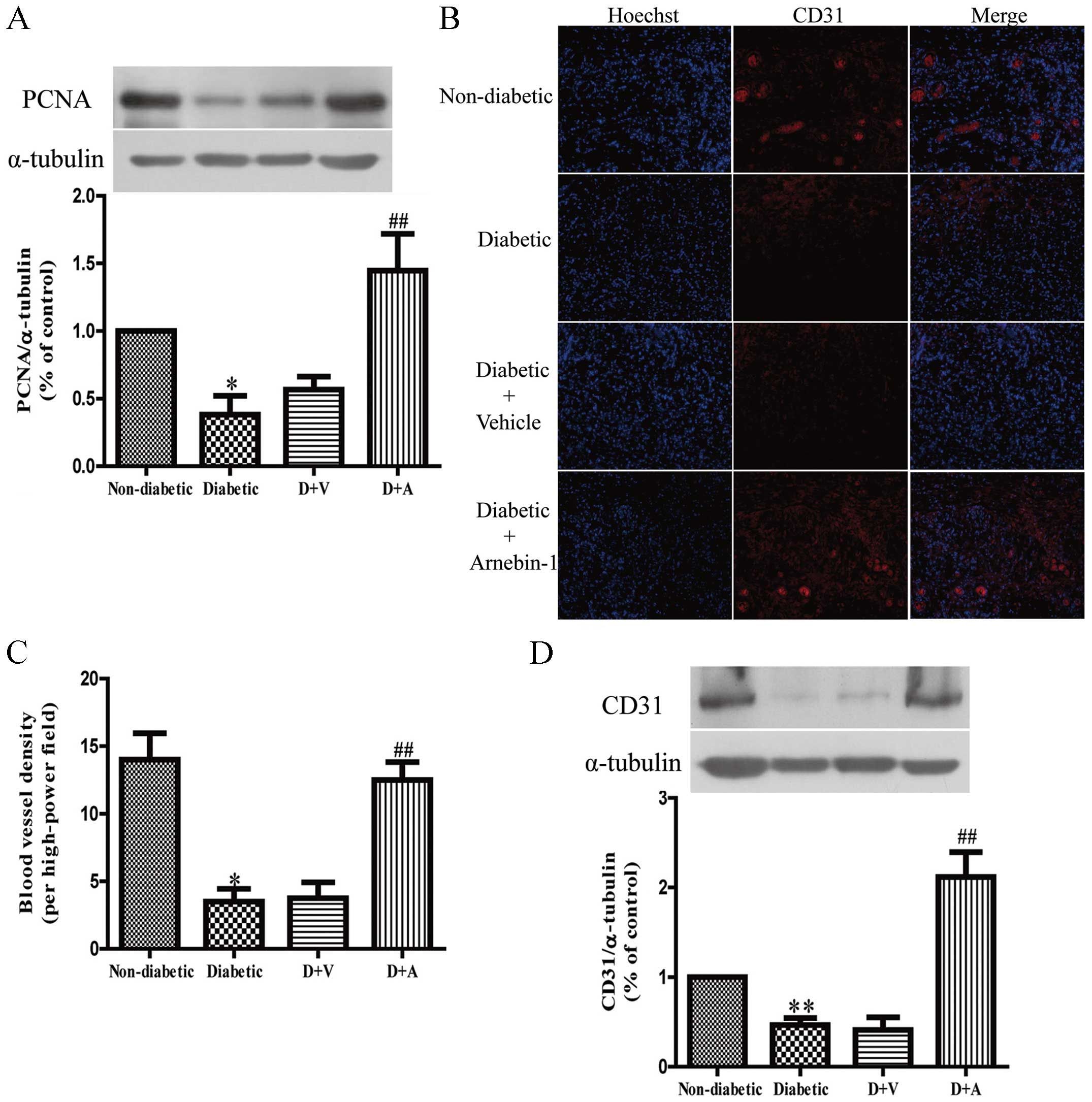
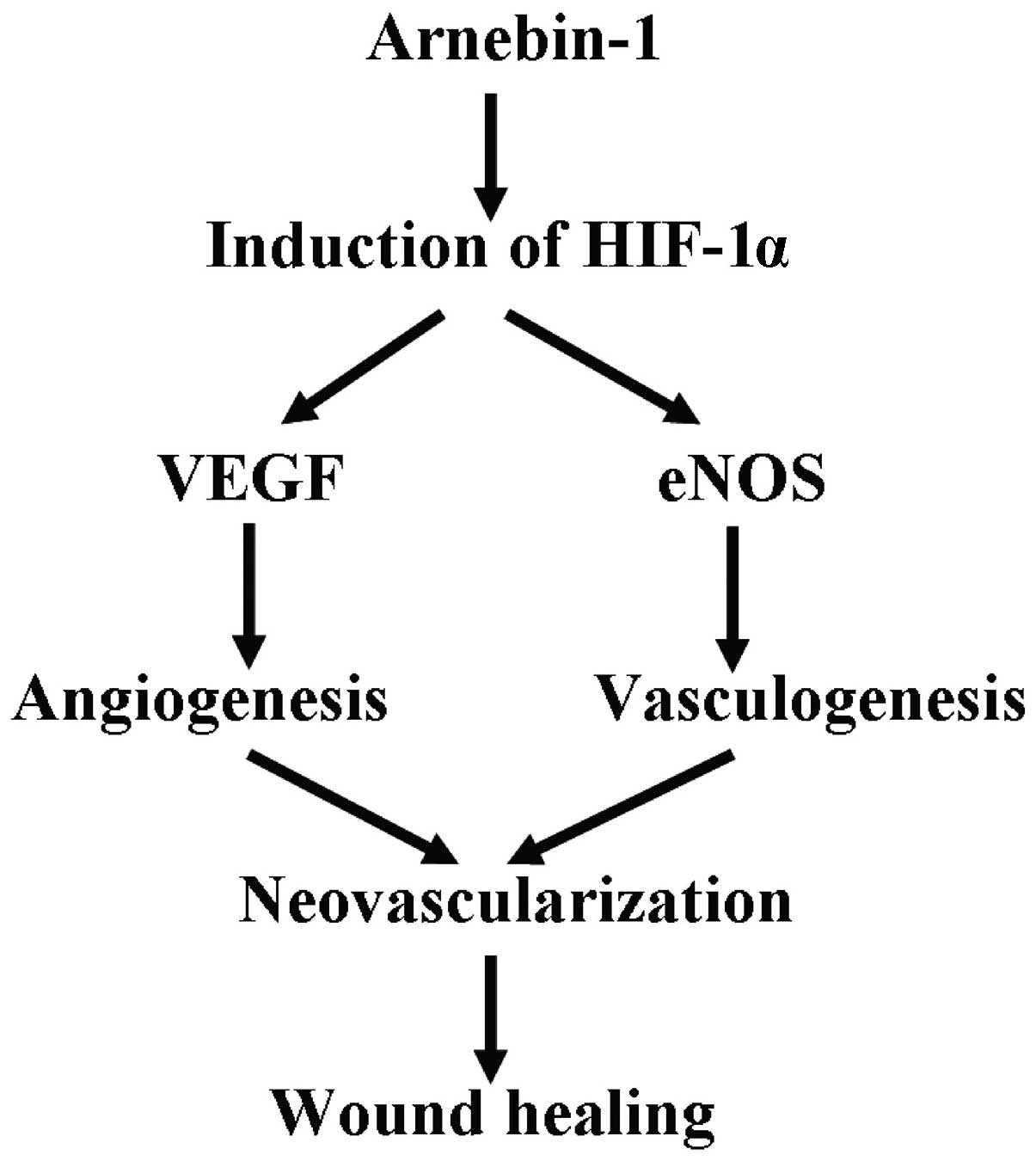
|
1
|
Boulton AJ: The diabetic foot: Grand
overview, epidemiology and pathogenesis. Diabetes Metab Res Rev.
24(Suppl 1): S3–S6. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Boulton AJ, Vileikyte L,
Ragnarson-Tennvall G and Apelqvist J: The global burden of diabetic
foot disease. Lancet. 366:1719–1724. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bartus CL and Margolis DJ: Reducing the
incidence of foot ulceration and amputation in diabetes. Curr Diab
Rep. 4:413–418. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Macfarlane RM and Jeffcoate WJ: Factors
contributing to the presentation of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabet
Med. 14:867–870. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ruffieux P, Hommel L and Saurat JH:
Long-term assessment of chronic leg ulcer treatment by autologous
skin grafts. Dermatology. 195:77–80. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tandara AA and Mustoe TA: Oxygen in wound
healing - more than a nutrient. World J Surg. 28:294–300. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Covello KL and Simon MC: HIFs, hypoxia,
and vascular development. Curr Top Dev Biol. 62:37–54. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ceradini DJ, Kulkarni AR, Callaghan MJ,
Tepper OM, Bastidas N, Kleinman ME, Capla JM, Galiano RD, Levine JP
and Gurtner GC: Progenitor cell trafficking is regulated by hypoxic
gradients through HIF-1 induction of SDF-1. Nat Med. 10:858–864.
2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kelly BD, Hackett SF, Hirota K, Oshima Y,
Cai Z, Berg-Dixon S, Rowan A, Yan Z, Campochiaro PA and Semenza GL:
Cell type-specific regulation of angiogenic growth factor gene
expression and induction of angiogenesis in nonischemic tissue by a
constitutively active form of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Circ Res.
93:1074–1081. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li W, Li Y, Guan S, Fan J, Cheng CF,
Bright AM, Chinn C, Chen M and Woodley DT: Extracellular heat shock
protein-90alpha: Linking hypoxia to skin cell motility and wound
healing. EMBO J. 26:1221–1233. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Thangarajah H, Yao D, Chang EI, Shi Y,
Jazayeri L, Vial IN, Galiano RD, Du XL, Grogan R, Galvez MG, et al:
The molecular basis for impaired hypoxia-induced VEGF expression in
diabetic tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:13505–13510. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Carmeliet P: VEGF as a key mediator of
angiogenesis in cancer. Oncology. 69(Suppl 3): 4–10. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ferrara N, Gerber HP and LeCouter J: The
biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 9:669–676. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Neufeld G, Cohen T, Gengrinovitch S and
Poltorak Z: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its
receptors. FASEB J. 13:9–22. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Frank S, Hübner G, Breier G, Longaker MT,
Greenhalgh DG and Werner S: Regulation of vascular endothelial
growth factor expression in cultured keratinocytes. Implications
for normal and impaired wound healing. J Biol Chem.
270:12607–12613. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Holmes K, Roberts OL, Thomas AM and Cross
MJ: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2: Structure,
function, intracellular signalling and therapeutic inhibition. Cell
Signal. 19:2003–2012. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J and
Claesson-Welsh L: VEGF receptor signalling - in control of vascular
function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:359–371. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Meadows KN, Bryant P and Pumiglia K:
Vascular endothelial growth factor induction of the angiogenic
phenotype requires Ras activation. J Biol Chem. 276:49289–49298.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Takahashi T, Ueno H and Shibuya M: VEGF
activates protein kinase C-dependent, but Ras-independent
Raf-MEK-MAP kinase pathway for DNA synthesis in primary endothelial
cells. Oncogene. 18:2221–2230. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ko SH, Nauta A, Morrison SD, Zhou H,
Zimmermann A, Gurtner GC, Ding S and Longaker MT: Antimycotic
ciclopirox olamine in the diabetic environment promotes
angiogenesis and enhances wound healing. PLoS One. 6:e278442011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Papageorgiou VP, Assimopoulou AN and
Ballis AC: Alkannins and shikonins: a new class of wound healing
agents. Curr Med Chem. 15:3248–3267. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sidhu GS, Singh AK, Banaudha KK, Gaddipati
JP, Patnaik GK and Maheshwari RK: Arnebin-1 accelerates normal and
hydrocortisone-induced impaired wound healing. J Invest Dermatol.
113:773–781. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zeng Z and Zhu BH: Arnebin-1 promotes the
angiogenesis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells and
accelerates the wound healing process in diabetic rats. J
Ethnopharmacol. 154:653–662. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Oyibo SO, Jude EB, Tarawneh I, Nguyen HC,
Armstrong DG, Harkless LB and Boulton AJ: The effects of ulcer size
and site, patient's age, sex and type and duration of diabetes on
the outcome of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabet Med. 18:133–138. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Armstrong DG, Lavery LA and Harkless LB:
Validation of a diabetic wound classification system. The
contribution of depth, infection, and ischemia to risk of
amputation. Diabetes Care. 21:855–859. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jeffcoate WJ, Chipchase SY, Ince P and
Game FL: Assessing the outcome of the management of diabetic foot
ulcers using ulcer-related and person-related measures. Diabetes
Care. 29:1784–1787. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Martin A, Komada MR and Sane DC: Abnormal
angiogenesis in diabetes mellitus. Med Res Rev. 23:117–145. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Falanga V: Wound healing and its
impairment in the diabetic foot. Lancet. 366:1736–1743. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hinchliffe RJ, Valk GD, Apelqvist J,
Armstrong DG, Bakker K, Game FL, Hartemann-Heurtier A, Löndahl M,
Price PE, van Houtum WH and Jeffcoate WJ: A systematic review of
the effectiveness of interventions to enhance the healing of
chronic ulcers of the foot in diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev.
24(Suppl 1): S119–S144. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bao P, Kodra A, Tomic-Canic M, Golinko MS,
Ehrlich HP and Brem H: The role of vascular endothelial growth
factor in wound healing. J Surg Res. 153:347–358. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Xie L, Zhang M, Dong B, Guan M, Lu M,
Huang Z, Gao H and Li X: Improved refractory wound healing with
administration of acidic fibroblast growth factor in diabetic rats.
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 93:396–403. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Botusan IR, Sunkari VG, Savu O, Catrina
AI, Grünler J, Lindberg S, Pereira T, Ylä-Herttuala S, Poellinger
L, Brismar K, et al: Stabilization of HIF-1α is critical to improve
wound healing in diabetic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:19426–19431. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Stroka DM, Burkhardt T, Desbaillets I,
Wenger RH, Neil DA, Bauer C, Gassmann M and Candinas D: HIF-1 is
expressed in normoxic tissue and displays an organ-specific
regulation under systemic hypoxia. FASEB J. 15:2445–2453.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Galiano RD, Tepper OM, Pelo CR, Bhatt KA,
Callaghan M, Bastidas N, Bunting S, Steinmetz HG and Gurtner GC:
Topical vascular endothelial growth factor accelerates diabetic
wound healing through increased angiogenesis and by mobilizing and
recruiting bone marrow-derived cells. Am J Pathol. 164:1935–1947.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Carmeliet P: Mechanisms of angiogenesis
and arteriogenesis. Nat Med. 6:389–395. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vranckx JJ, Yao F, Petrie N, Augustinova
H, Hoeller D, Visovatti S, Slama J and Eriksson E: In vivo gene
delivery of Ad-VEGF121 to full-thickness wounds in aged pigs
results in high levels of VEGF expression but not in accelerated
healing. Wound Repair Regen. 13:51–60. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rey S and Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible
factor-1-dependent mechanisms of vascularization and vascular
remodelling. Cardiovasc Res. 86:236–242. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bitto A, Irrera N, Minutoli L, Calò M, Lo
Cascio P, Caccia P, Pizzino G, Pallio G, Micali A, Vaccaro M, et
al: Relaxin improves multiple markers of wound healing and
ameliorates the disturbed healing pattern of genetically diabetic
mice. Clin Sci (Lond). 125:575–585. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Liu J and Agarwal S: Mechanical signals
activate vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 to
upregulate endothelial cell proliferation during inflammation. J
Immunol. 185:1215–1221. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Takahashi T, Yamaguchi S, Chida K and
Shibuya M: A single autophosphorylation site on KDR/Flk-1 is
essential for VEGF-A-dependent activation of PLC-gamma and DNA
synthesis in vascular endothelial cells. EMBO J. 20:2768–2778.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Eliceiri BP, Puente XS, Hood JD, Stupack
DG, Schlaepfer DD, Huang XZ, Sheppard D and Cheresh DA:
Src-mediated coupling of focal adhesion kinase to integrin
alpha(v)beta5 in vascular endothelial growth factor signaling. J
Cell Biol. 157:149–160. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Holmqvist K, Cross MJ, Rolny C, Hägerkvist
R, Rahimi N, Matsumoto T, Claesson-Welsh L and Welsh M: The adaptor
protein shb binds to tyrosine 1175 in vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF) receptor-2 and regulates VEGF-dependent cellular
migration. J Biol Chem. 279:22267–22275. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Abedi H and Zachary I: Vascular
endothelial growth factor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation and
recruitment to new focal adhesions of focal adhesion kinase and
paxillin in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 272:15442–15451. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Avraham HK, Lee TH, Koh Y, Kim TA, Jiang
S, Sussman M, Samarel AM and Avraham S: Vascular endothelial growth
factor regulates focal adhesion assembly in human brain
microvascular endothelial cells through activation of the focal
adhesion kinase and related adhesion focal tyrosine kinase. J Biol
Chem. 278:36661–36668. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Aicher A, Heeschen C, Mildner-Rihm C,
Urbich C, Ihling C, Technau-Ihling K, Zeiher AM and Dimmeler S:
Essential role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase for
mobilization of stem and progenitor cells. Nat Med. 9:1370–1376.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Everaert BR, Van Craenenbroeck EM, Hoymans
VY, Haine SE, Van Nassauw L, Conraads VM, Timmermans JP and Vrints
CJ: Current perspective of pathophysiological and interventional
effects on endothelial progenitor cell biology: focus on
PI3K/AKT/eNOS pathway. Int J Cardiol. 144:350–366. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|