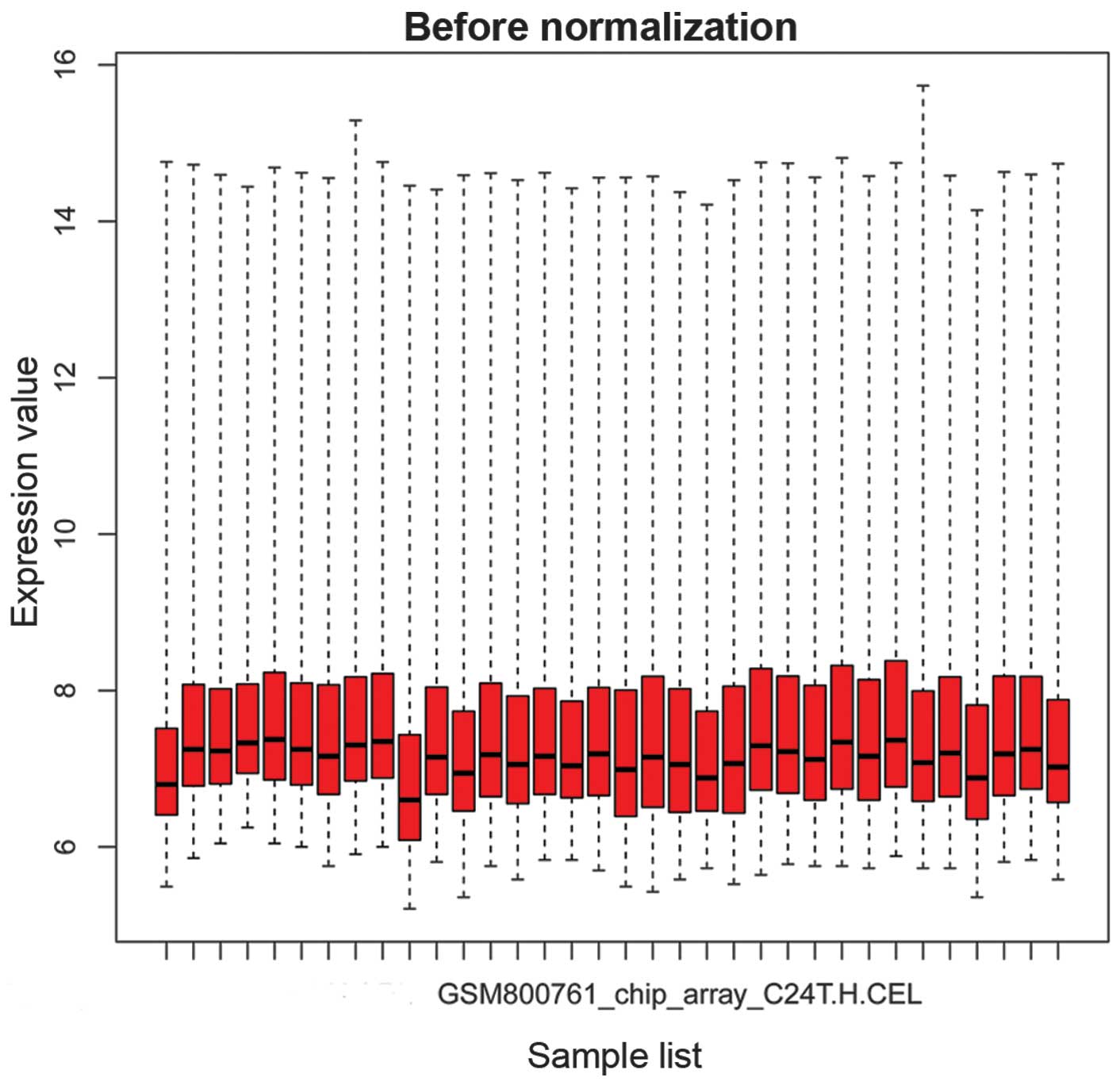
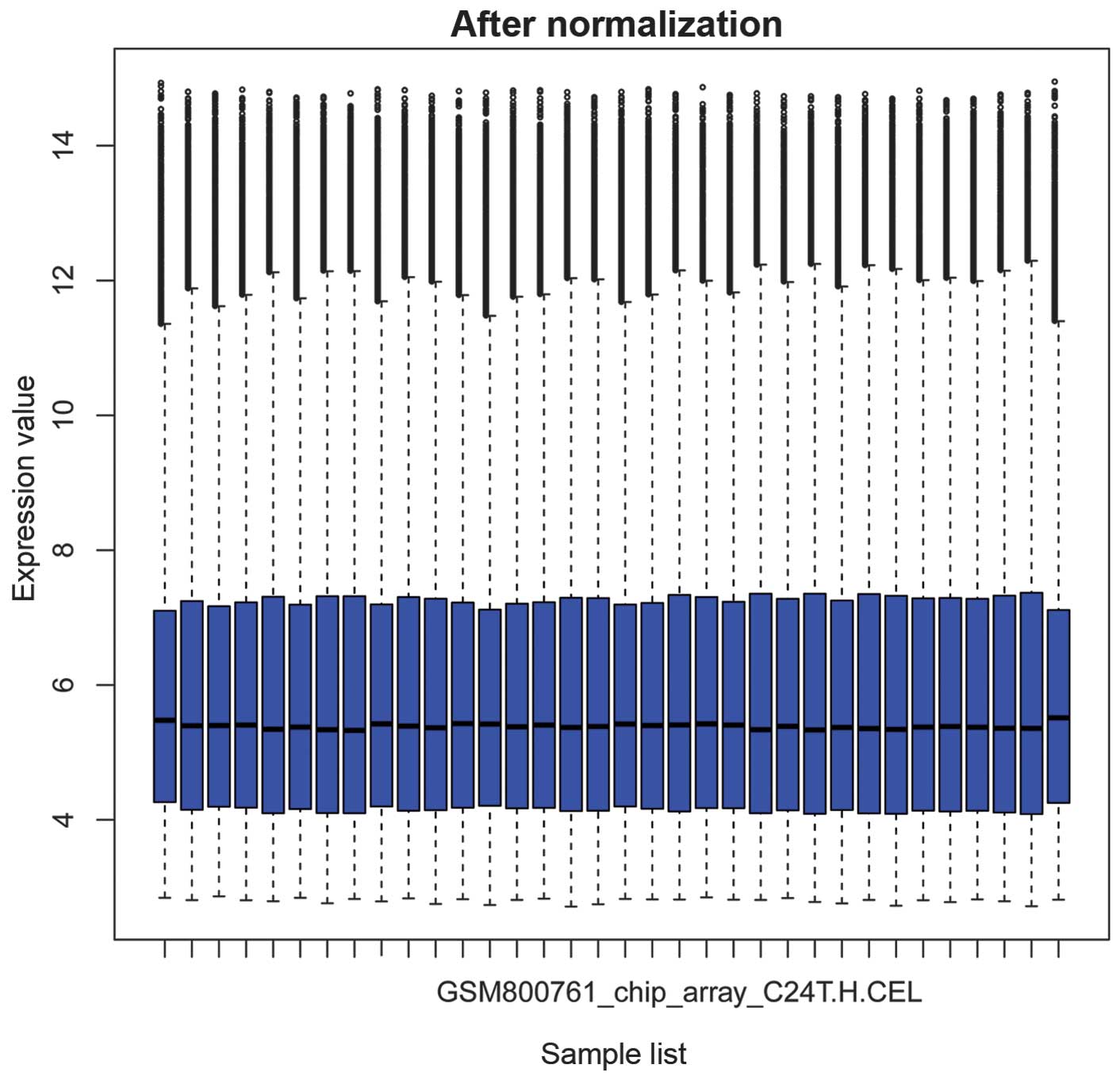
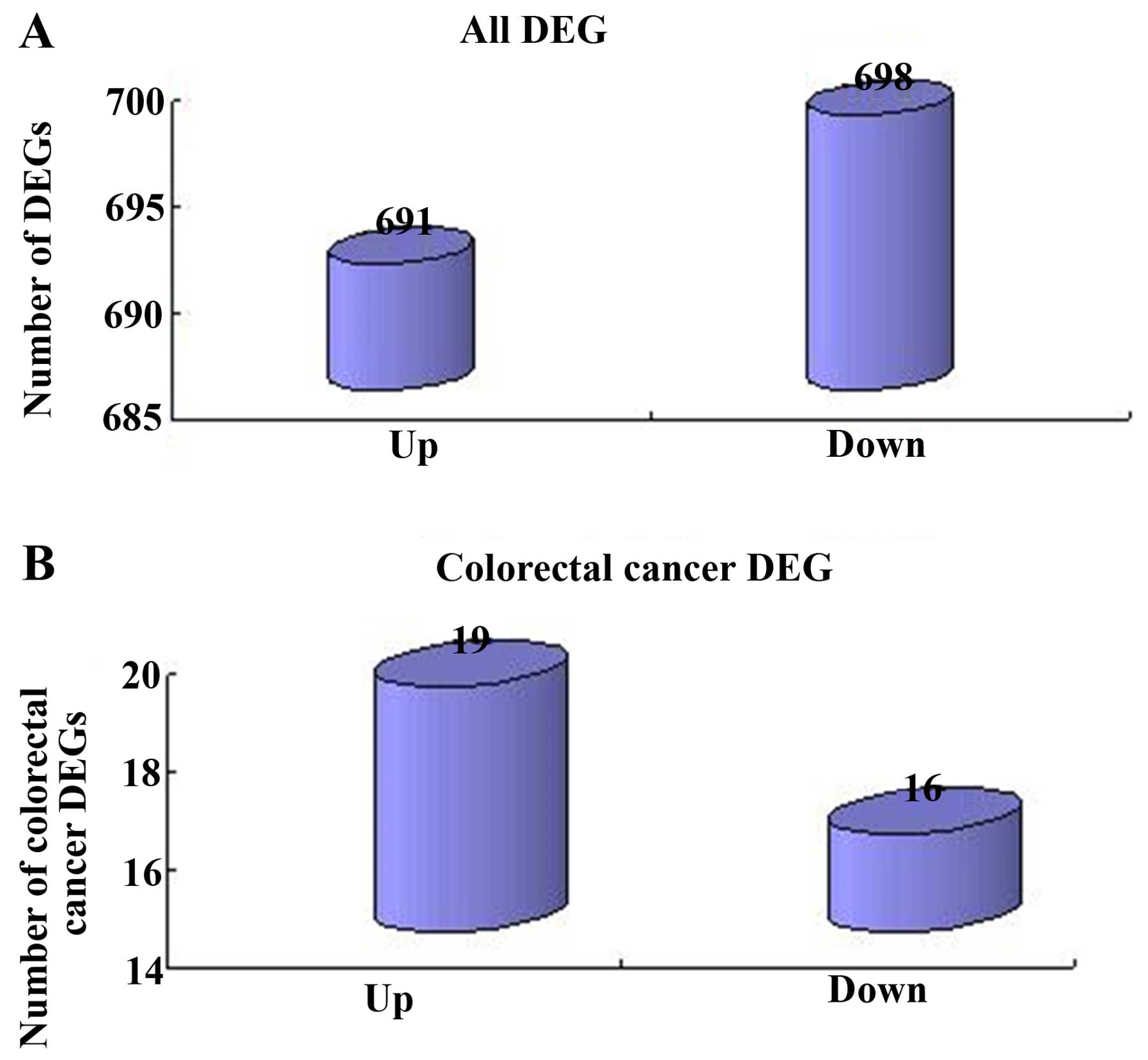
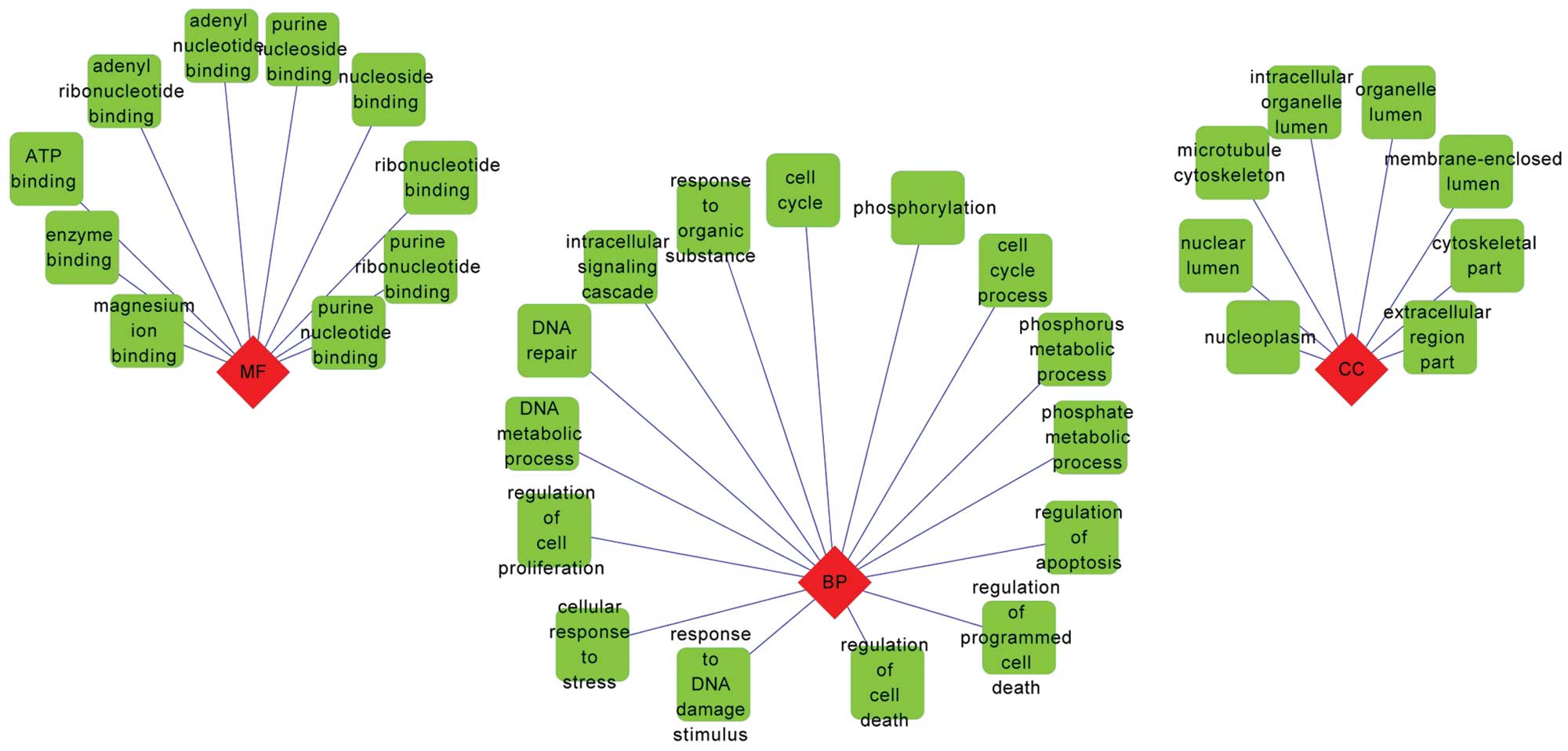
|
1
|
Stewart BW and Wild C: World Cancer Report
2014. World Health Organization; 2014
|
|
2
|
Stegeman I, de Wijkerslooth TR, Stoop EM,
van Leerdam ME, Dekker E, van Ballegooijen M, Kuipers EJ, Fockens
P, Kraaijenhagen RA and Bossuyt PM: Colorectal cancer risk factors
in the detection of advanced adenoma and colorectal cancer. Cancer
Epidemiol. 37:278–283. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nelson H, Petrelli N, Carlin A, Couture J,
Fleshman J, Guillem J, Miedema B, Ota D and Sargent D; National
Cancer Institute Expert Panel: Guidelines 2000 for colon and rectal
cancer surgery. J Natl Cancer Inst. 93:583–596. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Markowitz SD and Bertagnolli MM: Molecular
origins of cancer: Molecular basis of colorectal cancer. N Engl J
Med. 361:2449–2460. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Goyette MC, Cho K, Fasching CL, Levy DB,
Kinzler KW, Paraskeva C, Vogelstein B and Stanbridge EJ:
Progression of colorectal cancer is associated with multiple tumor
suppressor gene defects but inhibition of tumorigenicity is
accomplished by correction of any single defect via chromosome
transfer. Mol Cell Biol. 12:1387–1395. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vermeulen L, De Sousa E, Melo F, van der
Heijden M, Cameron K, de Jong JH, Borovski T, Tuynman JB, Todaro M,
Merz C, Rodermond H, et al: Wnt activity defines colon cancer stem
cells and is regulated by the microenvironment. Nat Cell Biol.
12:468–476. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Segditsas S and Tomlinson I: Colorectal
cancer and genetic alterations in the Wnt pathway. Oncogene.
25:7531–7537. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fodde R, Smits R and Clevers H: APC,
signal transduction and genetic instability in colorectal cancer.
Nat Rev Cancer. 1:55–67. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yoshie T, Nishiumi S, Izumi Y, Sakai A,
Inoue J, Azuma T and Yoshida M: Regulation of the metabolite
profile by an APC gene mutation in colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci.
103:1010–1021. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Voorneveld PW, Kodach LL, Jacobs RJ, Liv
N, Zonnevylle AC, Hoogenboom JP, Biemond I, Verspaget HW, Hommes
DW, de Rooij K, et al: Loss of SMAD4 alters BMP signaling to
promote colorectal cancer cell metastasis via activation of Rho and
ROCK. Gastroenterology. 147:196–208. e132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rokavec M, Öner MG, Li H, Jackstadt R,
Jiang L, Lodygin D, Kaller M, Horst D, Ziegler PK, Schwitalla S, et
al: IL-6R/STAT3/miR-34a feedback loop promotes EMT-mediated
colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis. J Clin Invest.
124:1853–67. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
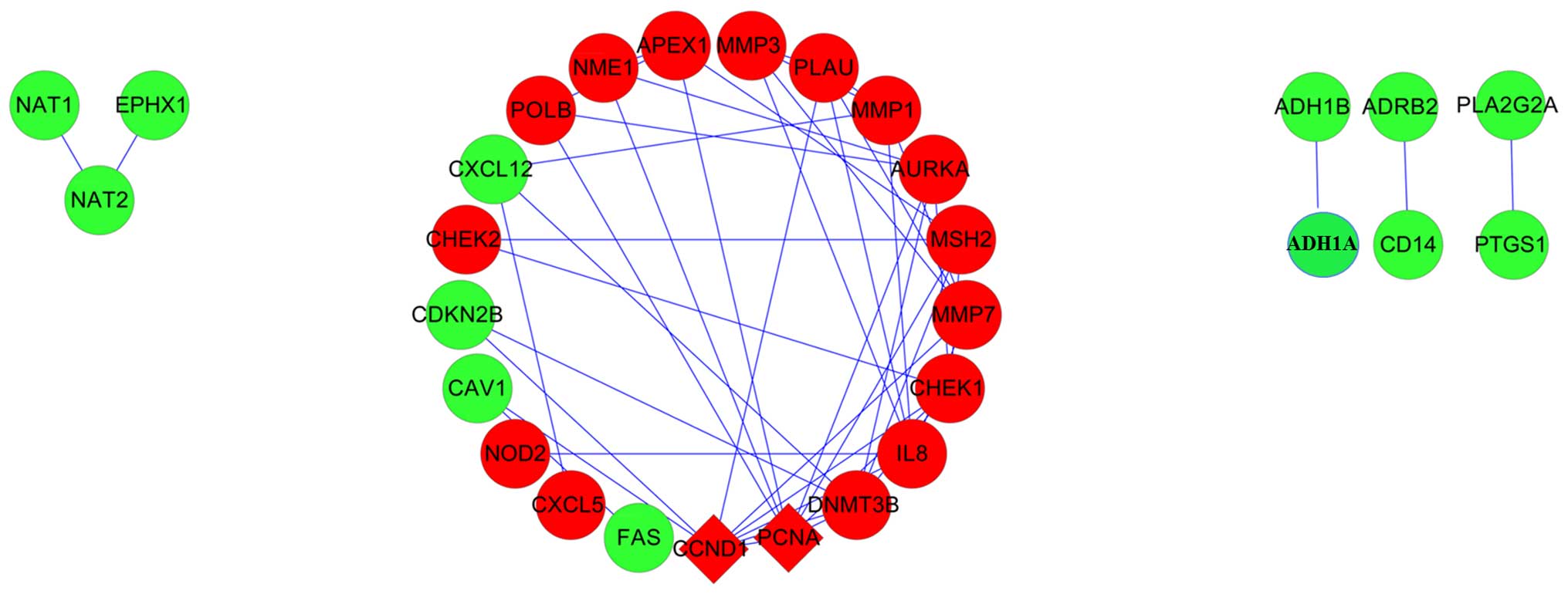
Khamas A, Ishikawa T, Shimokawa K, Mogushi
K, Iida S, Ishiguro M, Mizushima H, Tanaka H, Uetake H and Sugihara
K: Screening for epigenetically masked genes in colorectal cancer
Using 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine, microarray and gene expression
profile. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 9:67–75. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM and Irizarry
RA: affy - analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level.
Bioinformatics. 20:307–315. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tibshirani R, Hastie T and Narasimhan B:
samr: SAM: Significance Analysis of Microarrays. R package version
1.26. 2011, http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/samr/index.html;
Date accessed June 29, 2011.
|
|
15
|
Thissen D, Steinberg L and Kuang D: Quick
and easy implementation of the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure for
controlling the false positive rate in multiple comparisons. J Educ
Behav Stat. 27:77–83. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4(3)2003.
|
|
17
|
Huang W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Harris MA, Clark J, Ireland A, Lomax J,
Ashburner M, Foulger R, Eilbeck K, Lewis S, Marshall B, Mungall C,
et al: Gene Ontology Consortium: The Gene Ontology (GO) database
and informatics resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 32:D258–D261. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Sato Y, Furumichi M
and Tanabe M: KEGG for integration and interpretation of
large-scale molecular data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:D109–D114.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering
C, et al: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks, with
increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Saito R, Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J,
Wang P-L, Lotia S, Pico AR, Bader GD and Ideker T: A travel guide
to Cytoscape plugins. Nat Methods. 9:1069–1076. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Burge C and Karlin S: Prediction of
complete gene structures in human genomic DNA. J Mol Biol.
268:78–94. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Marasco E, Ross A, Dawson J, Moroose T and
Ambrose T: Detecting STR peaks in degraded DNA samples. Proceedings
of the 4th International Conference of Bioinformatics and
Computational Biology; pp. 1–8. LasVegas, USA. 2012
|
|
24
|
McEvoy CR, Seshadri R and Firgaira FA:
Large DNA fragment sizing using native acrylamide gels on an
automated DNA sequencer and GENESCAN software. Biotechniques.
25:464–470. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Punta M, Coggill PC, Eberhardt RY, Mistry
J, Tate J, Boursnell C, Pang N, Forslund K, Ceric G, Clements J, et
al: The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res.
40:D290–D301. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Wang Y, Geer LY, Chappey C, Kans JA and
Bryant SH: Cn3D: sequence and structure views for Entrez. Trends
Biochem Sci. 25:300–302. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jemal A, Ward E and Thun M: Declining
death rates reflect progress against cancer. PLoS One. 5. pp.
e95842010, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Evans DA: N-acetyltransferase. Pharmacol
Ther. 42:157–234. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Minchin RF, Hanna PE, Dupret J-M, Wagner
CR, Rodrigues-Lima F and Butcher NJ: Arylamine N-acetyltransferase
I. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 39:1999–2005. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Butcher NJ and Minchin RF: Arylamine
N-acetyltransferase 1: A novel drug target in cancer development.
Pharmacol Rev. 64:147–165. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhang L, Zhou J, Wang J, Liang G, Li J,
Zhu Y and Su Y: Absence of association between N-acetyltransferase
2 acetylator status and colorectal cancer susceptibility: Based on
evidence from 40 studies. PLoS One. 7:e324252012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lilla C, Verla-Tebit E, Risch A, Jäger B,
Hoffmeister M, Brenner H and Chang-Claude J: Effect of NAT1 and
NAT2 genetic polymorphisms on colorectal cancer risk associated
with exposure to tobacco smoke and meat consumption. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 15:99–107. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sinha R, Cross AJ, Daniel CR, Graubard BI,
Wu JW, Hollenbeck AR, Gunter MJ, Park Y and Freedman ND:
Caffeinated and decaffeinated coffee and tea intakes and risk of
colorectal cancer in a large prospective study. Am J Clin Nutr.
96:374–381. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Baldin V, Lukas J, Marcote MJ, Pagano M
and Draetta G: Cyclin D1 is a nuclear protein required for cell
cycle progression in G1. Genes Dev. 7:812–821. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jirawatnotai S, Hu Y, Michowski W, Elias
JE, Becks L, Bienvenu F, Zagozdzon A, Goswami T, Wang YE, Clark AB,
et al: A function for cyclin D1 in DNA repair uncovered by protein
interactome analyses in human cancers. Nature. 474:230–234. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang W, Gordon M, Press OA, Rhodes K,
Vallböhmer D, Yang DY, Park D, Fazzone W, Schultheis A, Sherrod AE,
et al: Cyclin D1 and epidermal growth factor polymorphisms
associated with survival in patients with advanced colorectal
cancer treated with Cetuximab. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 16:475–483.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yang Y, Wang F, Shi C, Zou Y, Qin H and Ma
Y: Cyclin D1 G870A polymorphism contributes to colorectal cancer
susceptibility: Evidence from a systematic review of 22
case-control studies. PLoS One. 7:e368132012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wangefjord S, Manjer J, Gaber A, Nodin B,
Eberhard J and Jirström K: Cyclin D1 expression in colorectal
cancer is a favorable prognostic factor in men but not in women in
a prospective, population-based cohort study. Biol Sex Differ.
2(10)2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nie J, Liu L, Zheng W, Chen L, Wu X, Xu Y,
Du X and Han W: microRNA-365, downregulated in colon cancer,
inhibits cell cycle progression and promotes apoptosis of colon
cancer cells by probably targeting Cyclin D1 and Bcl-2.
Carcinogenesis. 33:220–225. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Maga G and Hübscher U: Proliferating cell
nuclear antigen (PCNA): A dancer with many partners. J Cell Sci.
116:3051–3060. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Teixeira CR, Tanaka S, Haruma K, Yoshihara
M, Sumii K and Kajiyama G: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen
expression at the invasive tumor margin predicts malignant
potential of colorectal carcinomas. Cancer. 73:575–579. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sumiyoshi Y, Yamashita Y, Maekawa T, Sakai
N, Shirakusa T and Kikuchi M: Expression of CD44, vascular
endothelial growth factor, and proliferating cell nuclear antigen
in severe venous invasional colorectal cancer and its ionship to
liver metastasis. Surg Today. 30:323–327. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Yu SJ, Yu JK, Ge WT, Hu HG, Yuan Y and
Zheng S: SPARCL1, Shp2, MSH2, E-cadherin, p53, ADCY-2 and MAPK are
prognosis-related in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol.
17:2028–2036. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|