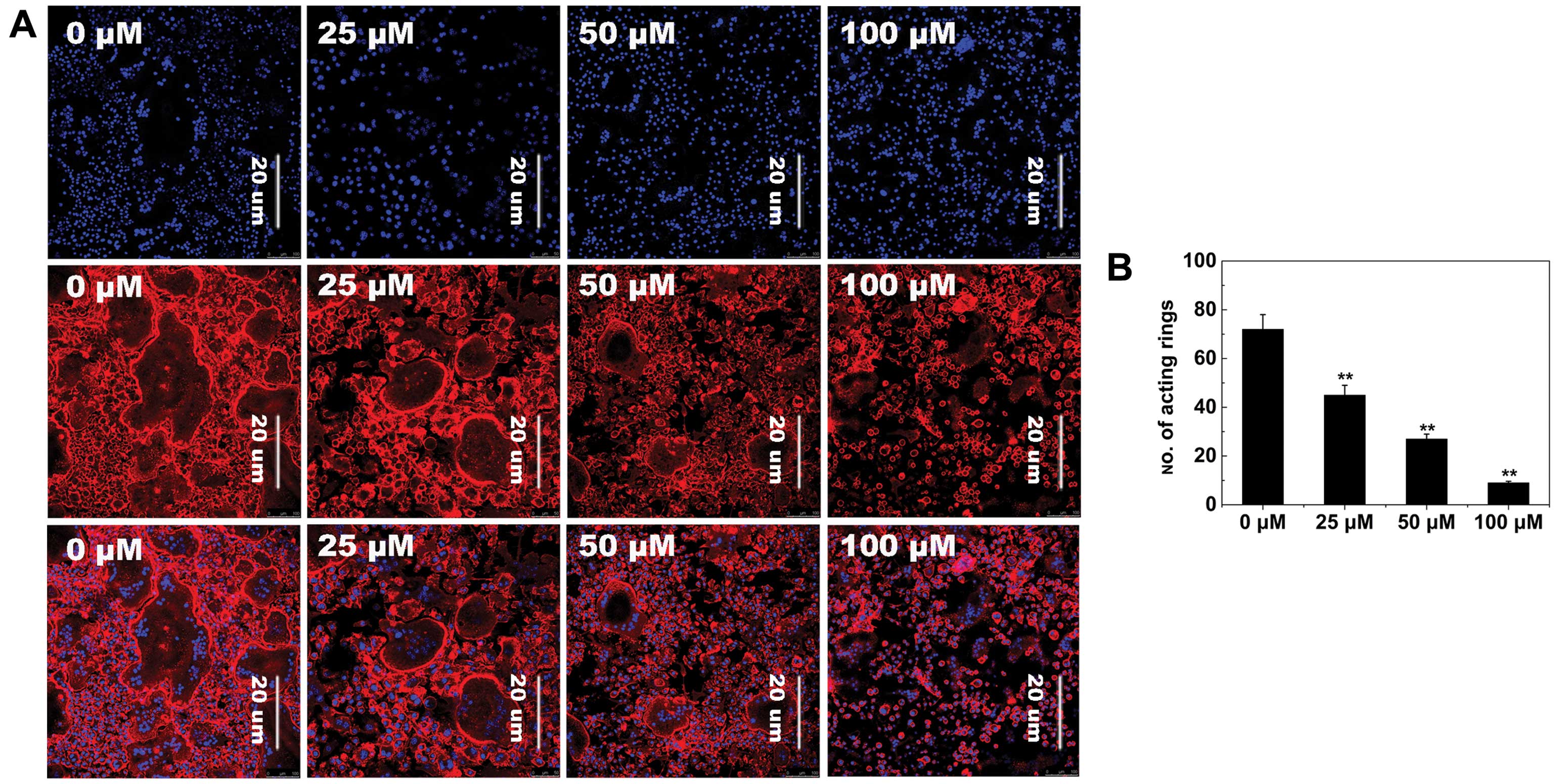
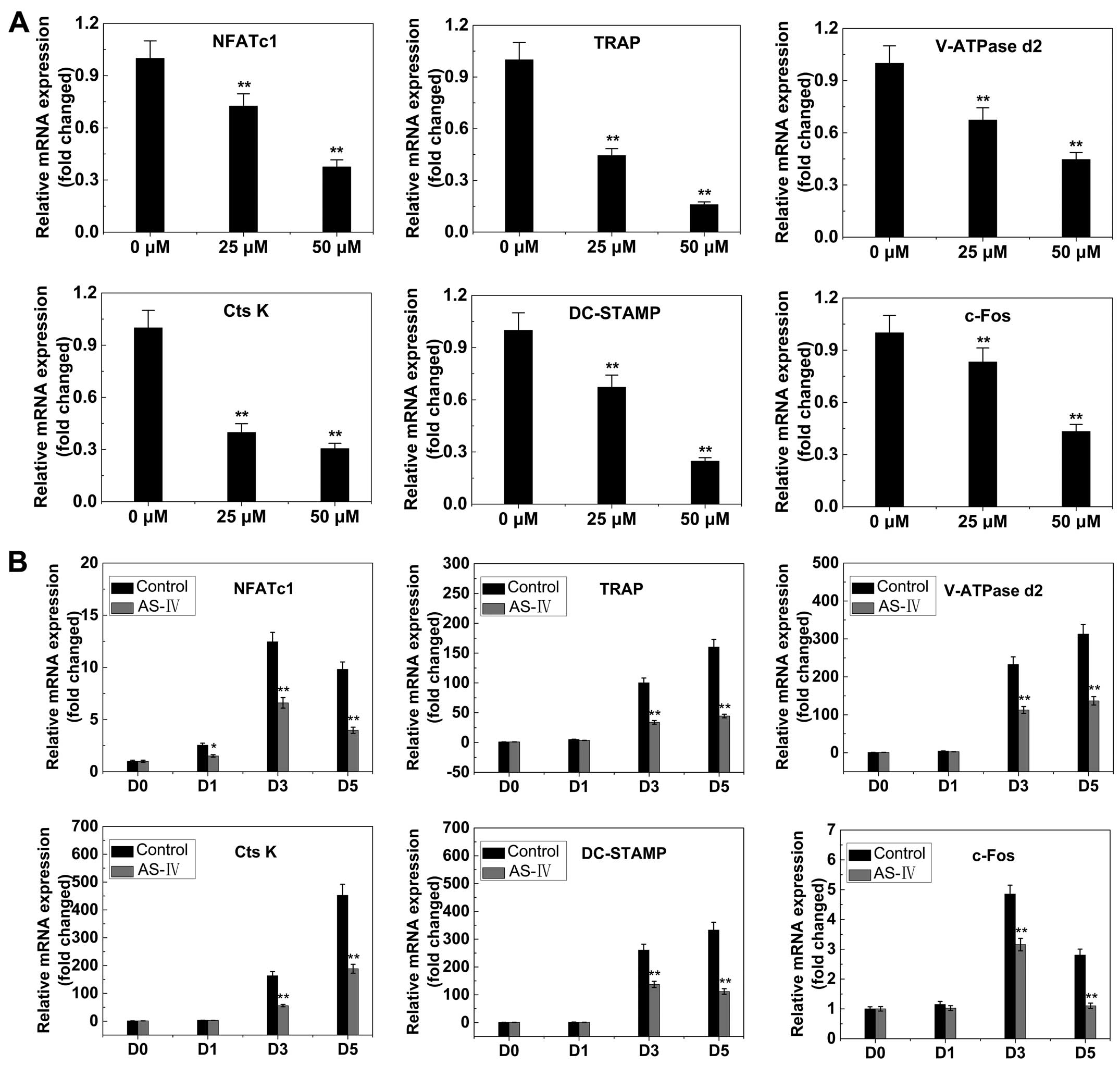
|
1
|
Kim HS, Suh KS, Sul D, Kim BJ, Lee SK and
Jung WW: The inhibitory effect and the molecular mechanism of
glabridin on RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cells.
Int J Mol Med. 29:169–177. 2012.
|
|
2
|
Rodan GA and Martin TJ: Therapeutic
approaches to bone diseases. Science. 289:1508–1514. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim TH, Kim HJ, Lee SH and Kim SY: Potent
inhibitory effect of Foeniculum vulgare Miller extract on
osteoclast differentiation and ovariectomy-induced bone loss. Int J
Mol Med. 29:1053–1059. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guo H, Zhang J, Hao S and Jin Q:
Adenovirus-mediated small interfering RNA targeting tumor necrosis
factor-α inhibits titanium particle-induced osteoclastogenesis and
bone resorption. Int J Mol Med. 32:296–306. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hou GQ, Guo C, Song GH, Fang N, Fan WJ,
Chen XD, Yuan L and Wang ZQ: Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) promotes
osteoclast differentiation and activation by enhancing the MAPK
pathway and COX-2 expression in RAW264.7 cells. Int J Mol Med.
32:503–510. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kanis JA: Assessment of fracture risk and
its application to screening for postmenopausal osteoporosis:
Synopsis of a WHO report. Osteoporos Int. 4:368–381. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Akatsu T, Tanaka
H, Sasaki T, Nishihara T, Koga T, Martin TJ and Suda T: Origin of
osteoclasts: Mature monocytes and macrophages are capable of
differentiating into osteoclasts under a suitable microenvironment
prepared by bone marrow-derived stromal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 87:7260–7264. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Purdue PE, Koulouvaris P, Potter HG,
Nestor BJ and Sculco TP: The cellular and molecular biology of
periprosthetic osteolysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 454:251–261.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ren W, Wu B, Peng X, Hua J, Hao HN and
Wooley PH: Implant wear induces inflammation, but not osteoclastic
bone resorption, in RANK(−/−) mice. J Orthop Res. 24:1575–1586.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Raggatt LJ and Partridge NC: Cellular and
molecular mechanisms of bone remodeling. J Biol Chem.
285:25103–25108. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS and Lacey DL:
Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 423:337–342.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Asagiri M and Takayanagi H: The molecular
understanding of osteoclast differentiation. Bone. 40:251–264.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Strait K, Li Y, Dillehay DL and Weitzmann
MN: Suppression of NF-kappaB activation blocks osteoclastic bone
resorption during estrogen deficiency. Int J Mol Med. 21:521–525.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zwerina J, Hayer S, Redlich K, Bobacz K,
Kollias G, Smolen JS and Schett G: Activation of p38 MAPK is a key
step in tumor necrosis factor-mediated inflammatory bone
destruction. Arthritis Rheum. 54:463–472. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Meissner JD, Freund R, Krone D, Umeda PK,
Chang KC, Gros G and Scheibe RJ: Extracellular signal-regulated
kinase 1/2-mediated phosphorylation of p300 enhances myosin heavy
chain I/beta gene expression via acetylation of nuclear factor of
activated T cells c1. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:5907–5925. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Grigoriadis AE, Wang ZQ, Cecchini MG,
Hofstetter W, Felix R, Fleisch HA and Wagner EF: c-Fos: A key
regulator of osteoclast-macrophage lineage determination and bone
remodeling. Science. 266:443–448. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mansky KC, Sankar U, Han J and Ostrowski
MC: Microphthalmia transcription factor is a target of the p38 MAPK
pathway in response to receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand
signaling. J Biol Chem. 277:11077–11083. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim YW, Baek SH, Lee SH, Kim TH and Kim
SY: Fucoidan, a sulfated polysaccharide, inhibits osteoclast
differentiation and function by modulating RANKL signaling. Int J
Mol Sci. 15:18840–18855. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xuying W, Jiangbo Z, Yuping Z, Xili M,
Yiwen Z, Tianbao Z and Weidong Z: Effect of astragaloside IV on the
general and peripartum reproductive toxicity in Sprague-Dawley
rats. Int J Toxicol. 29:505–516. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ren S, Zhang H, Mu Y, Sun M and Liu P:
Pharmacological effects of astragaloside IV: A literature review. J
Tradit Chin Med. 33:413–416. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jia Y, Zuo D, Li Z, Liu H, Dai Z, Cai J,
Pang L and Wu Y: Astragaloside IV inhibits doxorubicin-induced
cardiomyocyte apoptosis mediated by mitochondrial apoptotic pathway
via activating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo).
62:45–53. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Tan S, Wang G, Guo Y, Gui D and Wang N:
Preventive effects of a natural anti-inflammatory agent,
astragaloside IV, on ischemic acute kidney injury in rats. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013:2840252013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hu JY, Han J, Chu ZG, Song HP, Zhang DX,
Zhang Q and Huang YS: Astragaloside IV attenuates hypoxia-induced
cardiomyocyte damage in rats by upregulating superoxide dismutase-1
levels. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 36:351–357. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Huang X, Tang L, Wang F and Song G:
Astragaloside IV attenuates allergic inflammation by regulation
Th1/Th2 cytokine and enhancement CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3 T cells in
ovalbumin-induced asthma. Immunobiology. 219:565–571. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Qi H, Wei L, Han Y, Zhang Q, Lau AS and
Rong J: Proteomic characterization of the cellular response to
chemopreventive triterpenoid astragaloside IV in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2. Int J Oncol. 36:725–735.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
He CL, Yi PF, Fan QJ, Shen HQ, Jiang XL,
Qin QQ, Song Z, Zhang C, Wu SC, Wei XB, et al: Xiang-Qi-Tang and
its active components exhibit anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant
properties by inhibiting MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways in
LPS-treated rat cardiac microvascular endothelial cells.
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 35:215–224. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang Q, Shao X, Xu W, Qi C, Gu L, Ni Z and
Mou S: Astragalosides IV inhibits high glucose-induced cell
apoptosis through HGF activation in cultured human tubular
epithelial cells. Ren Fail. 36:400–406. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zheng R, Deng Y, Chen Y, Fan J, Zhang M,
Zhong Y, Zhu R and Wang L: Astragaloside IV attenuates complement
membranous attack complex induced podocyte injury through the MAPK
pathway. Phytother Res. 26:892–898. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Gui D, Huang J, Guo Y, Chen J, Chen Y,
Xiao W, Liu X and Wang N: Astragaloside IV ameliorates renal injury
in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats through inhibiting
NF-κB-mediated inflammatory genes expression. Cytokine. 61:970–977.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li M, Yu L, She T, Gan Y, Liu F, Hu Z,
Chen Y, Li S and Xia H: Astragaloside IV attenuates Toll-like
receptor 4 expression via NF-κB pathway under high glucose
condition in mesenchymal stem cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 696:203–209.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun L, Li W, Li W, Xiong L, Li G and Ma R:
Astragaloside IV prevents damage to human mesangial cells through
the inhibition of the NADPH oxidase/ROS/Akt/NF-κB pathway under
high glucose conditions. Int J Mol Med. 34:167–176. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bian Q, Huang JH, Liang QQ, Shu B, Hou W,
Xu H, Zhao YJ, Lu S, Shi Q and Wang YJ: The osteogenetic effect of
astragaloside IV with centrifugating pressure on the OCT-1 cells.
Pharmazie. 66:63–68. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang B and Chen MZ: Astragaloside IV
possesses antiarthritic effect by preventing interleukin 1β-induced
joint inflammation and cartilage damage. Arch Pharm Res.
37:793–802. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xie J, Wang H, Song T, Wang Z, Li F, Ma J,
Chen J, Nan Y, Yi H and Wang W: Tanshinone IIA and astragaloside IV
promote the migration of mesenchymal stem cells by up-regulation of
CXCR4. Protoplasma. 250:521–530. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Qin A, Cheng TS, Lin Z, Cao L, Chim SM,
Pavlos NJ, Xu J, Zheng MH and Dai KR: Prevention of wear
particle-induced osteolysis by a novel V-ATPase inhibitor
saliphenylhalamide through inhibition of osteoclast bone
resorption. PLoS One. 7:e341322012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wedemeyer C, Xu J, Neuerburg C,
Landgraeber S, Malyar NM, von Knoch F, Gosheger G, von Knoch M,
Löer F and Saxler G: Particle-induced osteolysis in
three-dimensional micro-computed tomography. Calcif Tissue Int.
81:394–402. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Qin A, Cheng TS, Pavlos NJ, Lin Z, Dai KR
and Zheng MH: V-ATPases in osteoclasts: Structure, function and
potential inhibitors of bone resorption. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
44:1422–1435. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Monje P, Hernández-Losa J, Lyons RJ,
Castellone MD and Gutkind JS: Regulation of the transcriptional
activity of c-Fos by ERK. A novel role for the prolyl isomerase
PIN1. J Biol Chem. 280:35081–35084. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Seo SW, Lee D, Minematsu H, Kim AD, Shin
M, Cho SK, Kim DW, Yang J and Lee FY: Targeting extracellular
signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling has therapeutic
implications for inflammatory osteolysis. Bone. 46:695–702. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Takayanagi H, Kim S, Koga T, Nishina H,
Isshiki M, Yoshida H, Saiura A, Isobe M, Yokochi T and Inoue J:
Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2)
integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of
osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 3:889–901. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Franzoso G, Carlson L, Xing L, Poljak L,
Shores EW, Brown KD, Leonardi A, Tran T, Boyce BF and Siebenlist U:
Requirement for NF-kappaB in osteoclast and B-cell development.
Genes Dev. 11:3482–3496. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Iotsova V, Caamaño J, Loy J, Yang Y, Lewin
A and Bravo R: Osteopetrosis in mice lacking NF-kappaB1 and
NF-kappaB2. Nat Med. 3:1285–1289. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lee SH, Kim JK and Jang HD: Genistein
inhibits osteoclastic differentiation of RAW 264.7 cells via
regulation of ROS production and scavenging. Int J Mol Sci.
15:10605–10621. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Inacio MC, Ake CF, Paxton EW, Khatod M,
Wang C, Gross TP, Kaczmarek RG, Marinac-Dabic D and Sedrakyan A:
Sex and risk of hip implant failure: Assessing total hip
arthroplasty outcomes in the United States. JAMA Intern Med.
173:435–441. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rizzoli R: A new treatment for
post-menopausal osteoporosis: Strontium ranelate. J Endocrinol
Invest. 28(Suppl): 50–57. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Weitzmann MN and Pacifici R: Estrogen
regulation of immune cell bone interactions. Ann NY Acad Sci.
1068:256–274. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Marx RE: The deception and fallacies of
sponsored randomized prospective double-blinded clinical trials:
The bisphosphonate research example. Int J Oral Maxillofac
Implants. 29:e37–e44. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Maeda SS and Lazaretti-Castro M: An
overview on the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Arq Bras
Endocrinol Metabol. 58:162–171. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Nakamura T, Sugimoto T, Nakano T,
Kishimoto H, Ito M, Fukunaga M, Hagino H, Sone T, Yoshikawa H,
Nishizawa Y, et al: Randomized Teriparatide [human parathyroid
hormone (PTH) 1-34] Once-Weekly Efficacy Research (TOWER) trial for
examining the reduction in new vertebral fractures in subjects with
primary osteoporosis and high fracture risk. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 97:3097–3106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Cummings SR, San Martin J, McClung MR,
Siris ES, Eastell R, Reid IR, Delmas P, Zoog HB, Austin M, Wang A,
et al: FREEDOM Trial: Denosumab for prevention of fractures in
postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 361:756–765.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hiligsmann M, Boonen A, Dirksen CD, Ben
Sedrine W and Reginster JY: Cost-effectiveness of denosumab in the
treatment of postmenopausal osteoporotic women. Expert Rev
Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 13:19–28. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Meunier PJ, Roux C, Ortolani S,
Diaz-Curiel M, Compston J, Marquis P, Cormier C, Isaia G, Badurski
J, Wark JD, et al: Effects of long-term strontium ranelate
treatment on vertebral fracture risk in postmenopausal women with
osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 20:1663–1673. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gingery A, Bradley E, Shaw A and Oursler
MJ: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase coordinately activates the
MEK/ERK and AKT/NFkappaB pathways to maintain osteoclast survival.
J Cell Biochem. 89:165–179. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Liu X, Qu X, Wu C, Zhai Z, Tian B, Li H,
Ouyang Z, Xu X, Wang W, Fan Q, et al: The effect of enoxacin on
osteoclastogenesis and reduction of titanium particle-induced
osteolysis via suppression of JNK signaling pathway. Biomaterials.
35:5721–5730. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhai Z, Qu X, Li H, Yang K, Wan P, Tan L,
Ouyang Z, Liu X, Tian B, Xiao F, et al: The effect of metallic
magnesium degradation products on osteoclast-induced osteolysis and
attenuation of NF-κB and NFATc1 signaling. Biomaterials.
35:6299–6310. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liu F, Zhu Z, Mao Y, Liu M, Tang T and Qiu
S: Inhibition of titanium particle-induced osteoclastogenesis
through inactivation of NFATc1 by VIVIT peptide. Biomaterials.
30:1756–1762. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|