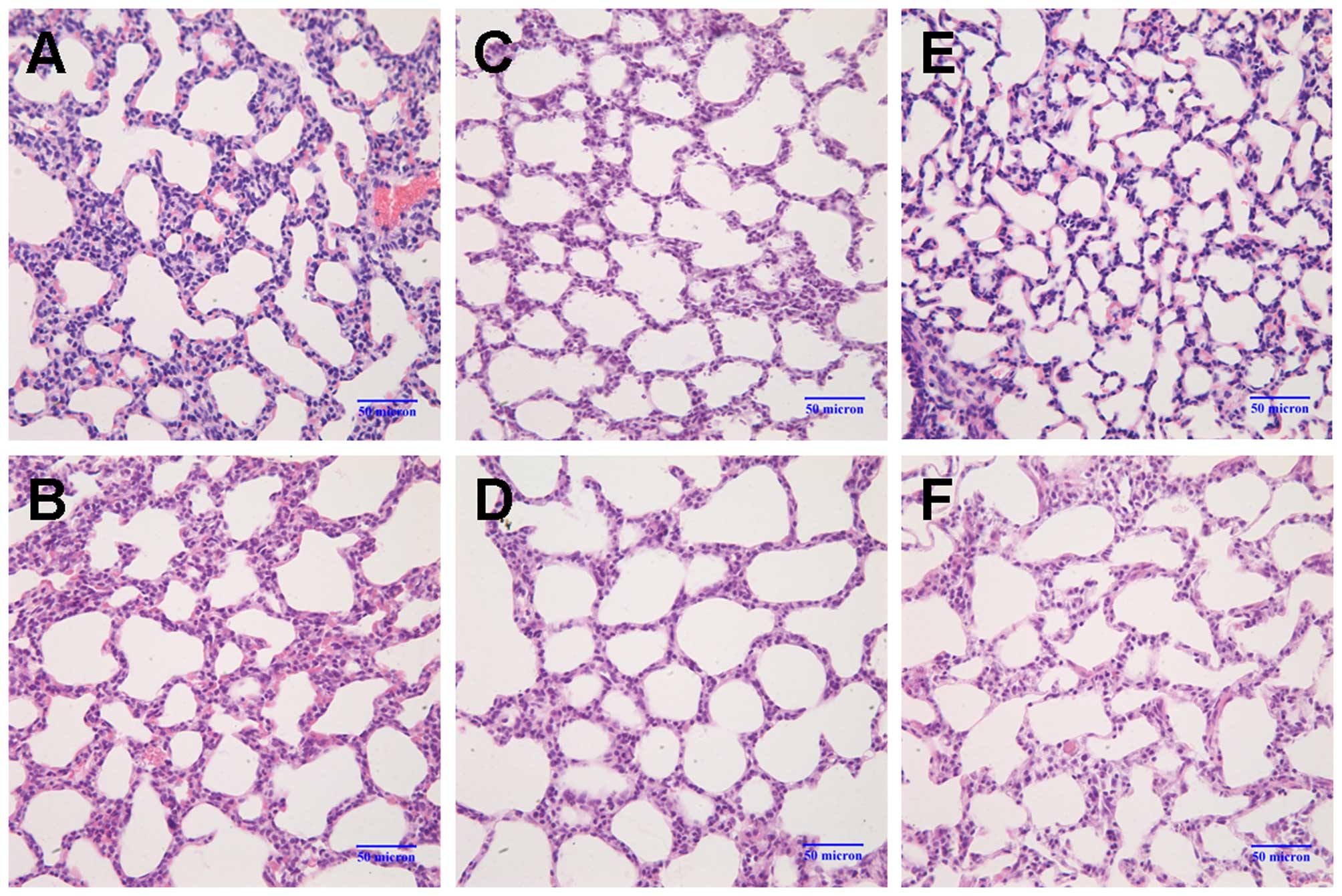
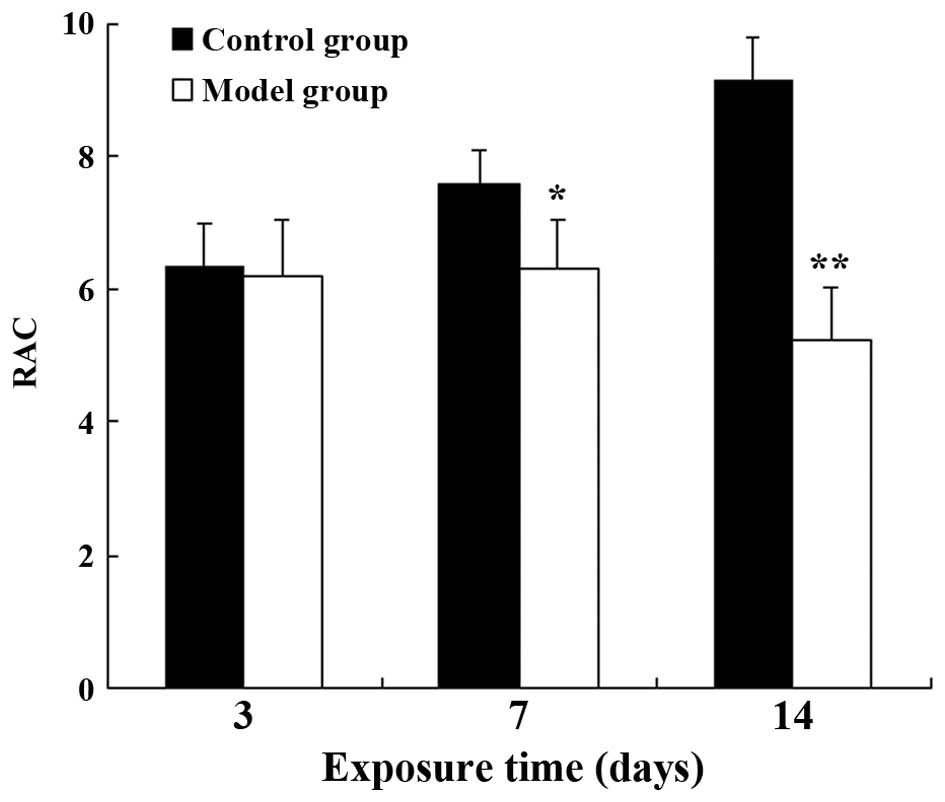
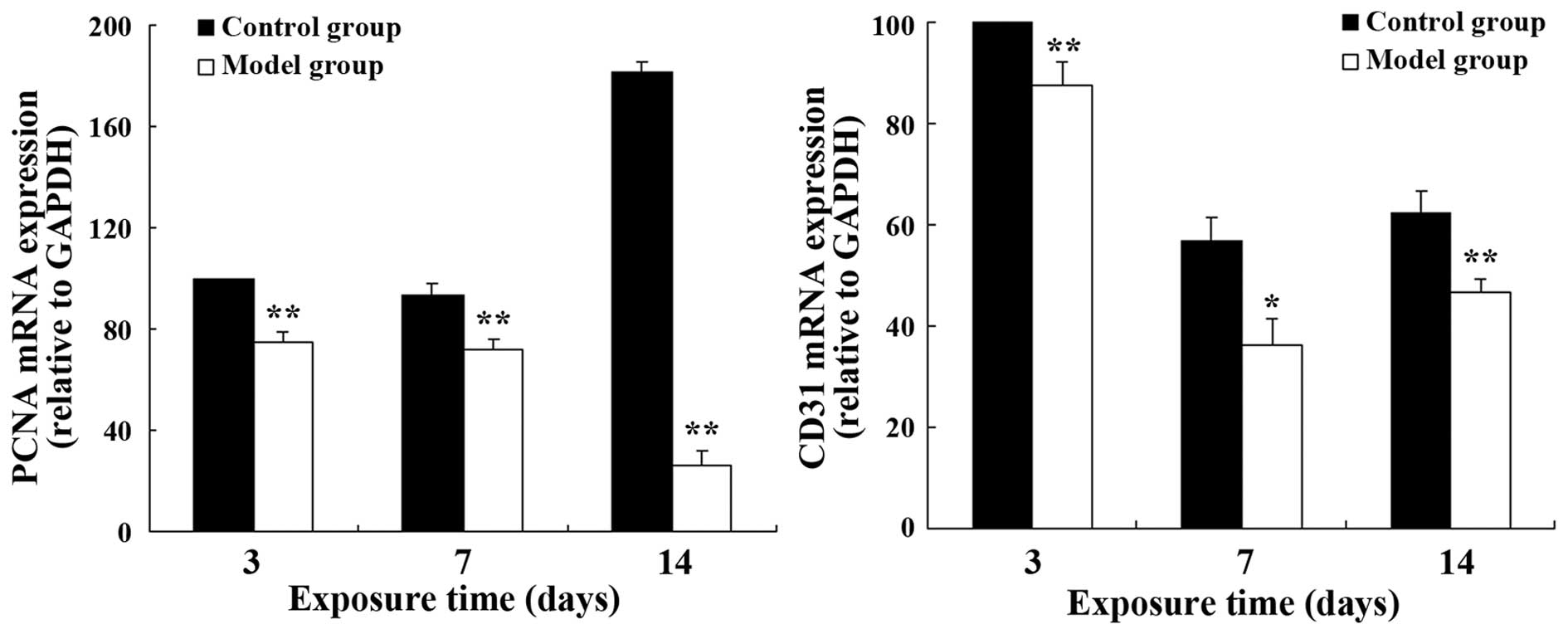
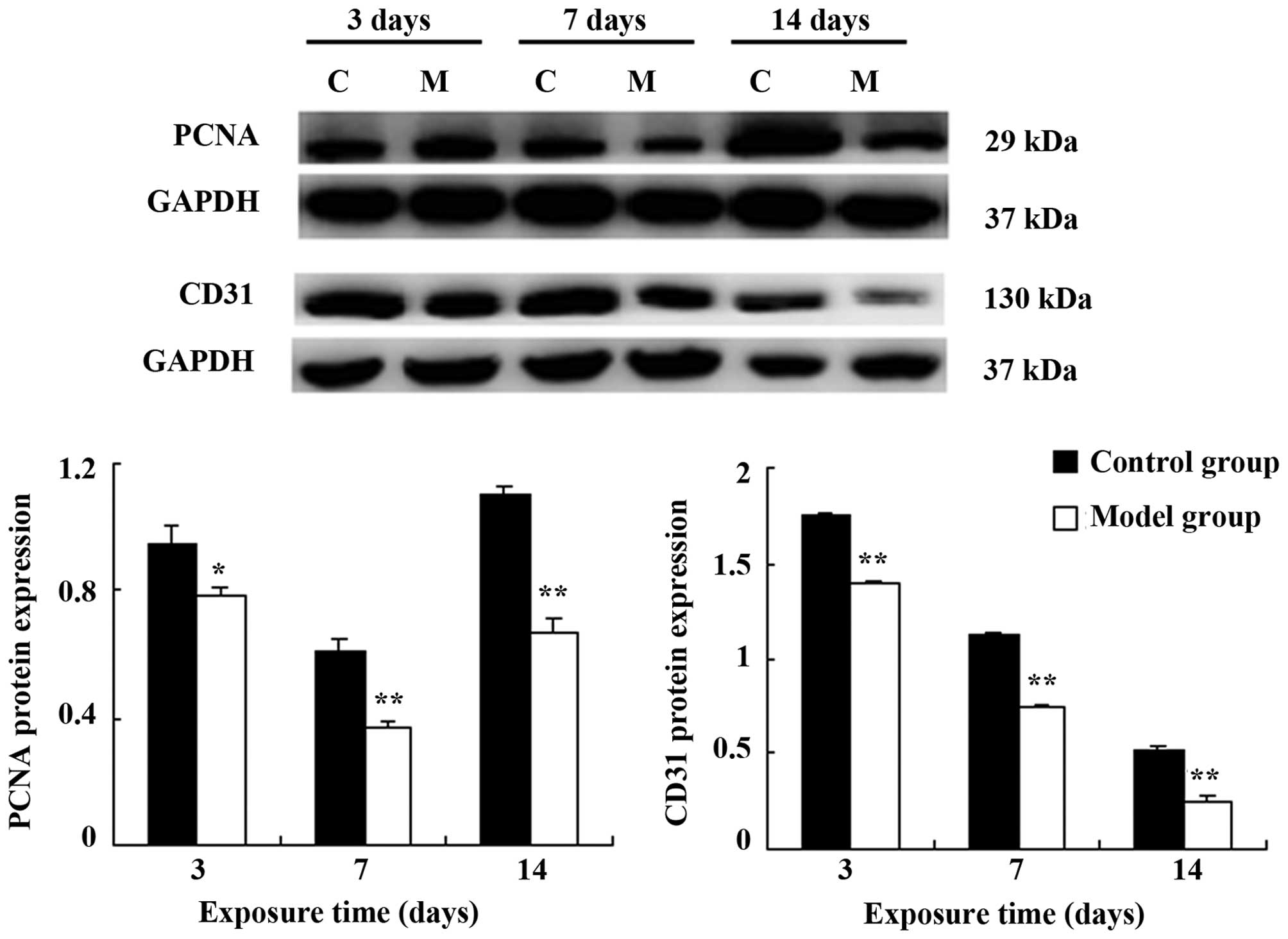
|
1
|
Hilgendorff A, Reiss I, Ehrhardt H,
Eickelberg O and Alvira CM: Chronic lung disease in the preterm
infant. Lessons learned from animal models. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 50:233–245. 2014.
|
|
2
|
Bhandari A and Bhandari V: Pitfalls,
problems, and progress in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics.
123:1562–1573. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bhandari A and McGrath-Morrow S: Long-term
pulmonary outcomes of patients with bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
Semin Perinatol. 37:132–137. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Anderson PJ and Doyle LW:
Neurodevelopmental outcome of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin
Perinatol. 30:227–232. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Herriges M and Morrisey EE: Lung
development: orchestrating the generation and regeneration of a
complex organ. Development. 141:502–513. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Warburton D, El-Hashash A, Carraro G,
Tiozzo C, Sala F, Rogers O, De Langhe S, Kemp PJ, Riccardi D,
Torday J, et al: Lung organogenesis. Curr Top Dev Biol. 90:73–158.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hadchouel A, Franco-Montoya ML and
Delacourt C: Altered lung development in bronchopulmonary
dysplasia. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 100:158–167. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Madurga A, Mizíková I, Ruiz-Camp J and
Morty RE: Recent advances in late lung development and the
pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell
Mol Physiol. 305:L893–L905. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Du T and Zamore PD: microPrimer: the
biogenesis and function of microRNA. Development. 132:4645–4652.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dong J, Jiang G, Asmann YW, Tomaszek S,
Jen J, Kislinger T and Wigle DA: MicroRNA networks in mouse lung
organogenesis. PLoS One. 5:e108542010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tay HL, Plank M, Collison A, Mattes J,
Kumar RK and Foster PS: MicroRNA: potential biomarkers and
therapeutic targets for allergic asthma? Ann Med. 46:633–639. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lino Cardenas CL, Kaminski N and Kass DJ:
Micromanaging microRNAs: using murine models to study microRNAs in
lung fibrosis. Drug Discov Today Dis Models. 10:e145–e151. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Joshi P, Middleton J, Jeon YJ and Garofalo
M: MicroRNAs in lung cancer. World J Methodol. 4:59–72. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu Y, Thomson JM, Wong HY, Hammond SM and
Hogan BL: Transgenic overexpression of the microRNA miR-17-92
cluster promotes proliferation and inhibits differentiation of lung
epithelial progenitor cells. Dev Biol. 310:442–453. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ventura A, Young AG, Winslow MM, Lintault
L, Meissner A, Erkeland SJ, Newman J, Bronson RT, Crowley D, Stone
JR, et al: Targeted deletion reveals essential and overlapping
functions of the miR-17 through 92 family of miRNA clusters. Cell.
132:875–886. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Carraro G, El-Hashash A, Guidolin D,
Tiozzo C, Turcatel G, Young BM, De Langhe SP, Bellusci S, Shi W,
Parnigotto PP and Warburton D: miR-17 family of microRNAs controls
FGF10-mediated embryonic lung epithelial branching morphogenesis
through MAPK14 and STAT3 regulation of E-Cadherin distribution. Dev
Biol. 333:238–250. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Navarro A, Marrades RM, Viñolas N, Quera
A, Agustí C, Huerta A, Ramirez J, Torres A and Monzo M: MicroRNAs
expressed during lung cancer development are expressed in human
pseudoglandular lung embryogenesis. Oncology. 76:162–169. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bhaskaran M, Wang Y, Zhang H, Weng T,
Baviskar P, Guo Y, Gou D and Liu L: MicroRNA-127 modulates fetal
lung development. Physiol Genomics. 37:268–278. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang X, Peng W, Zhang S, Wang C, He X,
Zhang Z, Zhu L, Wang Y and Feng Z: MicroRNA expression profile in
hyperoxia-exposed newborn mice during the development of
bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Respir Care. 56:1009–1015. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang H, Fu J, Xue X, Yao L, Qiao L, Hou A,
Jin L and Xing Y: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in
bronchopulmonary dysplasia of newborn rats. Pediatr Pulmonol.
49:1112–1123. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Northway WH Jr, Rosan RC and Porter DY:
Pulmonary disease following respirator therapy of hyaline-membrane
disease. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. N Engl J Med. 276:357–368.
1967. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bhaskaran M, Xi D, Wang Y, Huang C,
Narasaraju T, Shu W, Zhao C, Xiao X, More S, Breshears M and Liu L:
Identification of microRNAs changed in the neonatal lungs in
response to hyperoxia exposure. Physiol Genomics. 44:970–980. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dong J, Carey WA, Abel S, Collura C, Jiang
G, Tomaszek S, Sutor S, Roden AC, Asmann YW, Prakash YS and Wigle
DA: MicroRNA-mRNA interactions in a murine model of
hyperoxia-induced bronchopulmonary dysplasia. BMC Genomics.
13:2042012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Narasaraju T, Shukla D, More S, Huang C,
Zhang L, Xiao X and Liu L: Role of microRNA-150 and glycoprotein
nonmetastatic melanoma protein B in angiogenesis during
hyperoxia-induced neonatal lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
52:253–261. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Gu H, Yang T, Fu S, Chen X, Guo L and Ni
Y: MicroRNA-490-3p inhibits proliferation of A549 lung cancer cells
by targeting CCND1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 444:104–108. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bray I, Tivnan A, Bryan K, Foley NH,
Watters KM, Tracey L, Davidoff AM and Stallings RL: MicroRNA-542-5p
as a novel tumor suppressor in neuroblastoma. Cancer Lett.
303:56–64. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Song M, Yin Y, Zhang J, Zhang B, Bian Z,
Quan C, Zhou L, Hu Y, Wang Q, Ni S, et al: MiR-139-5p inhibits
migration and invasion of colorectal cancer by downregulating AMFR
and NOTCH1. Protein Cell. 5:851–861. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shen K, Mao R, Ma L, Li Y, Qiu Y, Cui D,
Le V, Yin P, Ni L and Liu J: Post-transcriptional regulation of the
tumor suppressor miR-139-5p and a network of miR-139-5p-mediated
mRNA interactions in colorectal cancer. FEBS J. 281:3609–3624.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu R, Yang M, Meng Y, Liao J, Sheng J, Pu
Y, Yin L and Kim SJ: Tumor-suppressive function of miR-139-5p in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e770682013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Krishnan K, Steptoe AL, Martin HC,
Pattabiraman DR, Nones K, Waddell N, Mariasegaram M, Simpson PT,
Lakhani SR, Vlassov A, et al: miR-139-5p is a regulator of
metastatic pathways in breast cancer. RNA. 19:1767–1780. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang H, Li M, Zhang R, Wang Y, Zang W, Ma
Y, Zhao G and Zhang G: Effect of miR-335 upregulation on the
apoptosis and invasion of lung cancer cell A549 and H1299. Tumour
Biol. 34:3101–3109. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jiang H, Hua D, Zhang J, Lan Q, Huang Q,
Yoon JG, Han X, Li L, Foltz G, Zheng S and Lin B: MicroRNA-127-3p
promotes glioblastoma cell migration and invasion by targeting the
tumor-suppressor gene SEPT7. Oncol Rep. 31:2261–2269.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jiang H, Jin C, Liu J, Hua D, Zhou F, Lou
X, Zhao N, Lan Q, Huang Q, Yoon JG, et al: Next generation
sequencing analysis of miRNAs: MiR-127-3p inhibits glioblastoma
proliferation and activates TGF-beta signaling by targeting SKI.
OMICS. 18:196–206. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zha R, Guo W, Zhang Z, Qiu Z, Wang Q, Ding
J, Huang S, Chen T, Gu J, Yao M and He X: Genome-wide screening
identified that miR-134 acts as a metastasis suppressor by
targeting integrin β1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One.
9:e876652014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Li H, Dai S, Zhen T, Shi H, Zhang F, Yang
Y, Kang L, Liang Y and Han A: Clinical and biological significance
of miR-378a-3p and miR-378a-5p in colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer.
50:1207–1221. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Megiorni F, Cialfi S, McDowell HP, Felsani
A, Camero S, Guffanti A, Pizer B, Clerico A, De Grazia A, Pizzuti
A, et al: Deep Sequencing the microRNA profile in rhabdomyosarcoma
reveals downregulation of miR-378 family members. BMC Cancer.
14:8802014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wu Z, Wu Y, Tian Y, Sun X, Liu J, Ren H,
Liang C, Song L, Hu H, Wang L and Jiao B: Differential effects of
miR-34c-3p and miR-34c-5p on the proliferation, apoptosis and
invasion of glioma cells. Oncol Lett. 6:1447–1452. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
López JA and Alvarez-Salas LM:
Differential effects of miR-34c-3p and miR-34c-5p on SiHa cells
proliferation apoptosis, migration and invasion. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 409:513–519. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xu H, Liu C, Zhang Y, Guo X, Liu Z, Luo Z,
Chang Y, Liu S, Sun Z and Wang X: Let-7b-5p regulates proliferation
and apoptosis in multiple myeloma by targeting IGF1R. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 46:965–972. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Zhu YJ, Xu B and Xia W: Hsa-miR-182
downregulates RASA1 and suppresses lung squamous cell carcinoma
cell proliferation. Clin Lab. 60:155–159. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Stenvold H, Donnem T, Andersen S, Al-Saad
S, Busund LT and Bremnes RM: Stage and tissue-specific prognostic
impact of miR-182 in NSCLC. BMC Cancer. 14:1382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yang WB, Chen PH, Hsu T, Fu TF, Su WC,
Liaw H, Chang WC and Hung JJ: Sp1-mediated microRNA-182 expression
regulates lung cancer progression. Oncotarget. 5:740–753. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang M1, Wang Y, Zang W, Wang H, Chu H, Li
P, Li M, Zhang G and Zhao G: Downregulation of microRNA-182
inhibits cell growth and invasion by targeting programmed cell
death 4 in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Tumour Biol. 35:39–46.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Zhang L, Liu T, Huang Y and Liu J:
microRNA-182 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of human lung
adenocarcinoma cells through its effect on human cortical
actin-associated protein. Int J Mol Med. 28:381–388.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sun Y, Fang R, Li C, Li L, Li F, Ye X and
Chen H: Hsa-miR-182 suppresses lung tumorigenesis through
downregulation of RGS17 expression in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 396:501–507. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lei Z, Xu G, Wang L, Yang H, Liu X, Zhao J
and Zhang HT: MiR-142-3p represses TGF-beta-induced growth
inhibition through repression of TGFbetaR1 in non-small cell lung
cancer. FASEB J. 28:2696–2704. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Carraro G, Shrestha A, Rostkovius J,
Contreras A, Chao CM, El Agha E, Mackenzie B, Dilai S, Guidolin D,
Taketo MM, et al: miR-142-3p balances proliferation and
differentiation of mesenchymal cells during lung development.
Development. 141:1272–1281. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ress AL, Stiegelbauer V, Winter E,
Schwarzenbacher D, Kiesslich T, Lax S, Jahn S, Deutsch A,
Bauernhofer T, Ling H, et al: MiR-96-5p influences cellular growth
and is associated with poor survival in colorectal cancer patients.
Mol Carcinog. Sep 25–2014.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li C, Du X, Tai S, Zhong X, Wang Z, Hu Z,
Zhang L, Kang P, Ji D, Jiang X, et al: GPC1 regulated by miR-96-5p,
rather than miR-182-5p, in inhibition of pancreatic carcinoma cell
proliferation. Int J Mol Sci. 15:6314–6327. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|