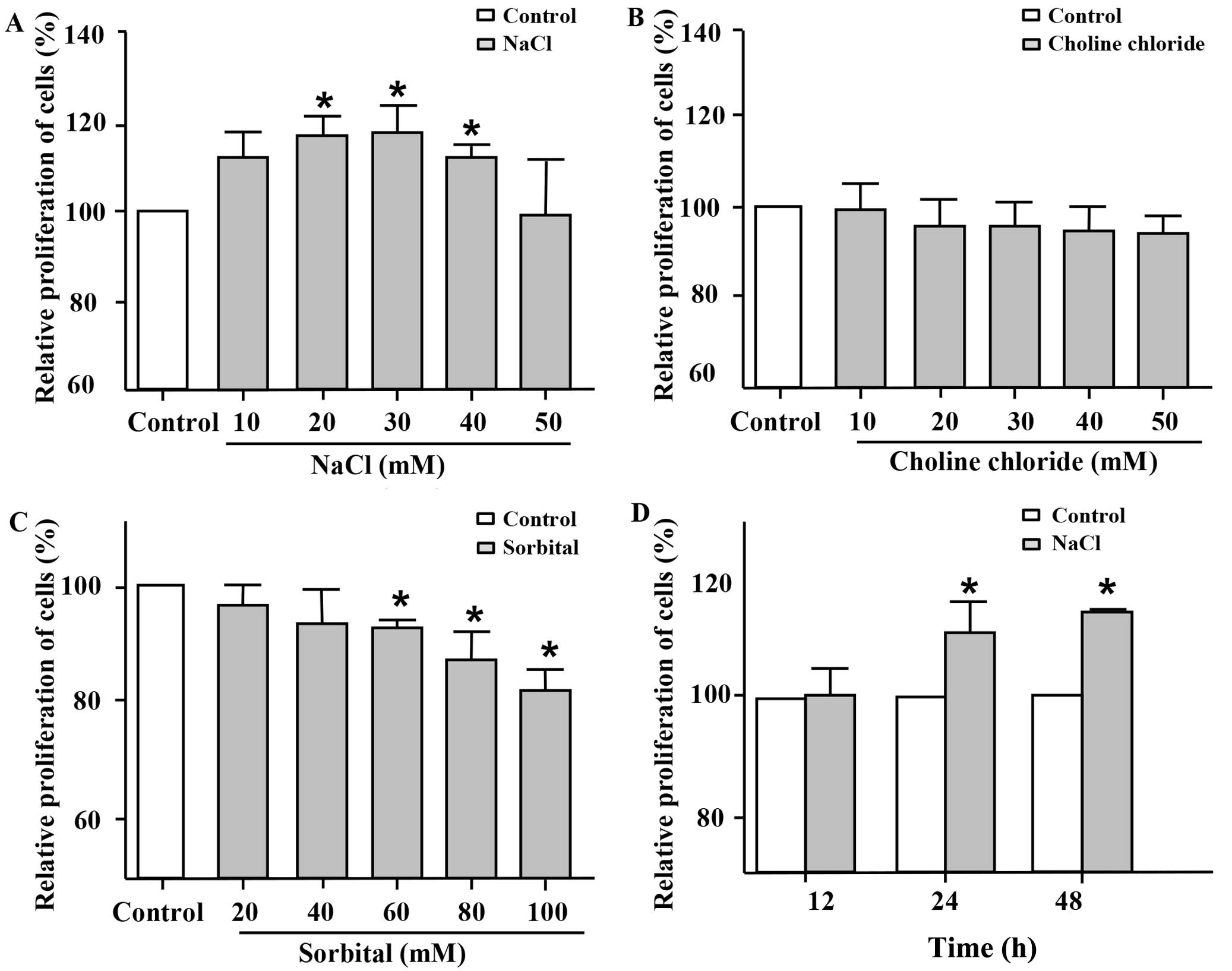
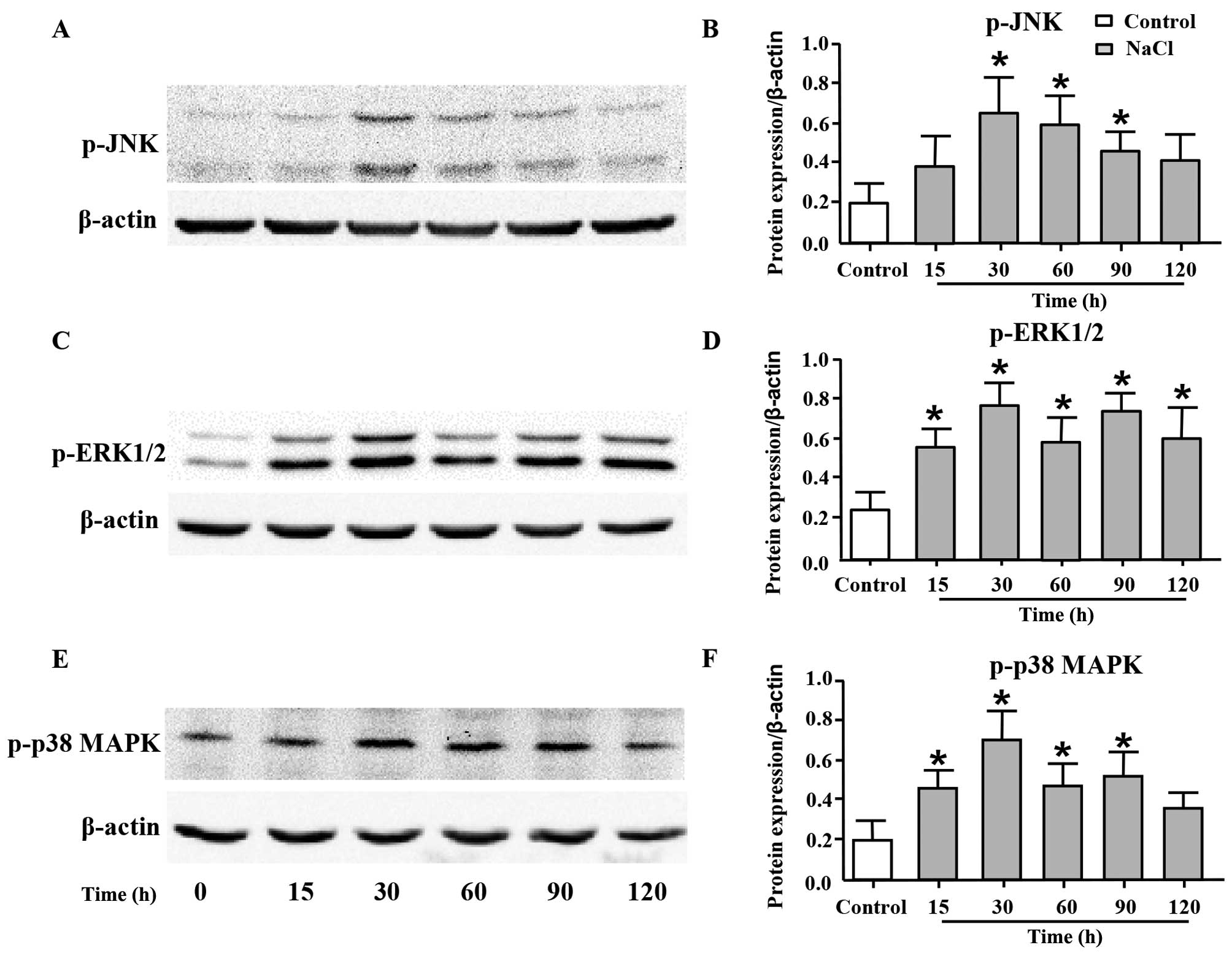
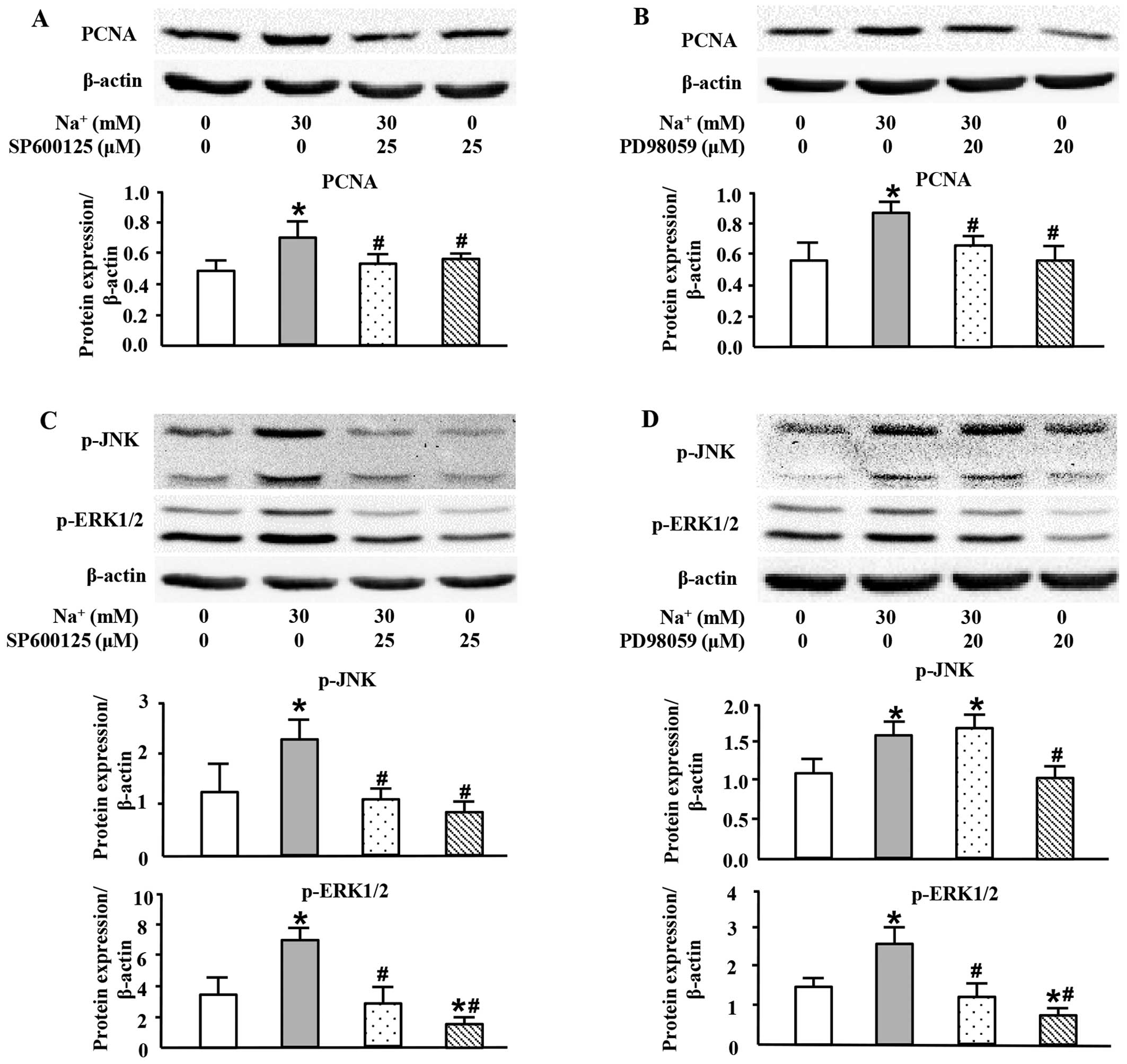
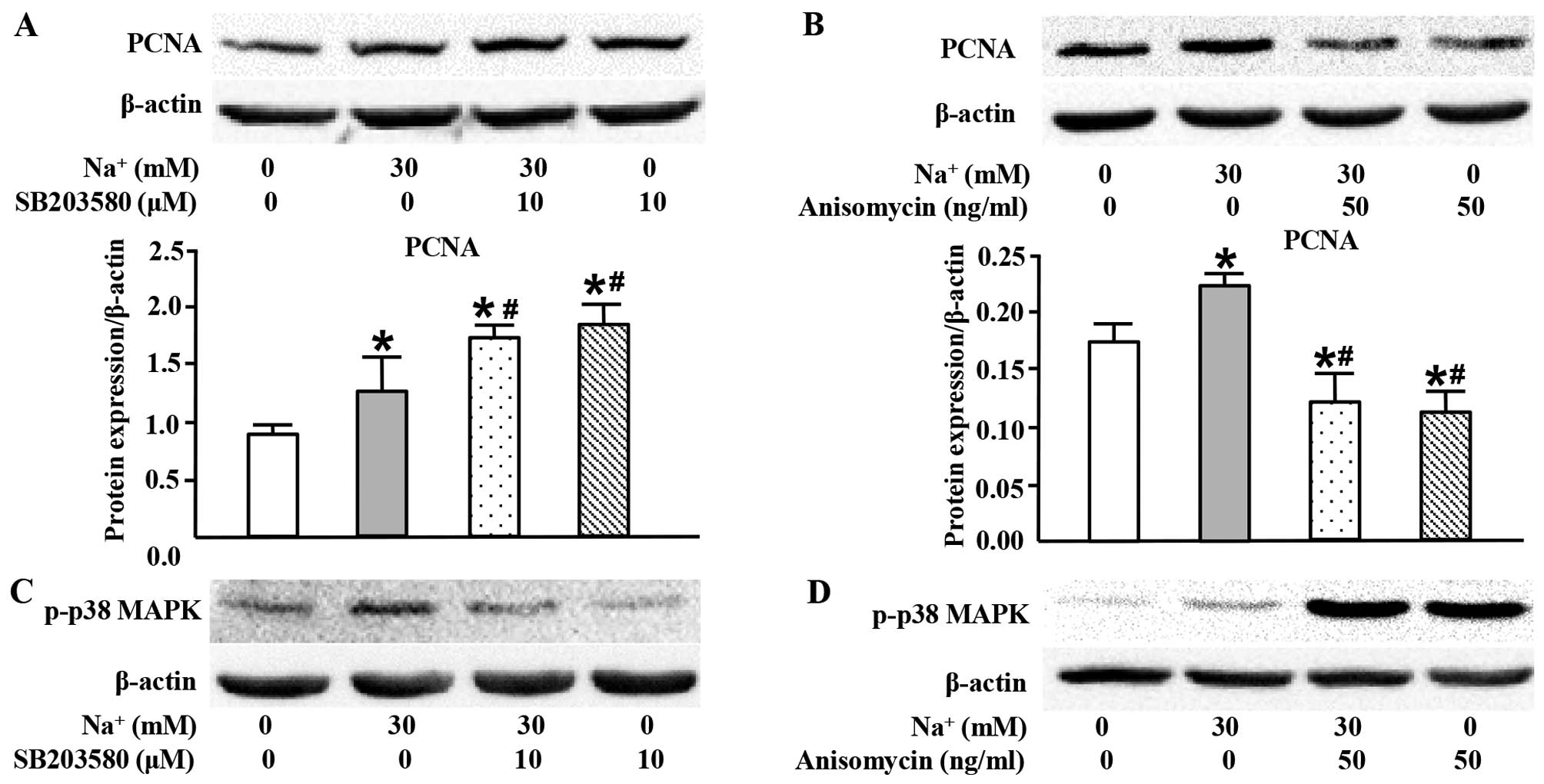
|
1
|
Aburto NJ, Ziolkovska A, Hooper L, Elliott
P, Cappuccio FP and Meerpohl JJ: Effect of lower sodium intake on
health: Systematic review and meta-analyses. BMJ. 346:f13262013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Graudal NA, Hubeck-Graudal T and Jürgens
G: Effects of low-sodium diet vs. high-sodium diet on blood
pressure, renin, aldosterone, catecholamines, cholesterol, and
triglyceride (Cochrane Review). Am J Hypertens. 25:1–15. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
He FJ, Li J and Macgregor GA: Effect of
longer term modest salt reduction on blood pressure: Cochrane
systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. BMJ.
346:f13252013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Taylor RS, Ashton KE, Moxham T, Hooper L
and Ebrahim S: Reduced dietary salt for the prevention of
cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled
trials (Cochrane review). Am J Hypertens. 24:843–853. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Neuhofer W and Beck FX: Cell survival in
the hostile environment of the renal medulla. Annu Rev Physiol.
67:531–555. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cha JH, Woo SK, Han KH, Kim YH, Handler
JS, Kim J and Kwon HM: Hydration status affects nuclear
distribution of transcription factor tonicity responsive enhancer
binding protein in rat kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol. 12:2221–2230.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kültz D and Chakravarty D: Hyperosmolality
in the form of elevated NaCl but not urea causes DNA damage in
murine kidney cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:1999–2004. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang Z, Dmitrieva NI, Park JH, Levine RL
and Burg MB: High urea and NaCl carbonylate proteins in renal cells
in culture and in vivo, and high urea causes 8-oxoguanine lesions
in their DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:9491–9496. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Santos BC, Chevaile A, Hébert MJ,
Zagajeski J and Gullans SR: A combination of NaCl and urea enhances
survival of IMCD cells to hyperosmolality. Am J Physiol.
274:F1167–F1173. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Machnik A, Neuhofer W, Jantsch J, Dahlmann
A, Tammela T, Machura K, Park JK, Beck FX, Müller DN, Derer W, et
al: Macrophages regulate salt-dependent volume and blood pressure
by a vascular endothelial growth factor-C-dependent buffering
mechanism. Nat Med. 15:545–552. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nijst P, Verbrugge FH, Grieten L, Dupont
M, Steels P, Tang WH and Mullens W: The pathophysiological role of
interstitial sodium in heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol.
65:378–388. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Heer M, Baisch F, Kropp J, Gerzer R and
Drummer C: High dietary sodium chloride consumption may not induce
body fluid retention in humans. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
278:F585–F595. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kirkendall AM, Connor WE, Abboud F,
Rastogi SP, Anderson TA and Fry M: The effect of dietary sodium
chloride on blood pressure, body fluids, electrolytes, renal
function, and serum lipids of normotensive man. J Lab Clin Med.
87:411–434. 1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Palacios C, Wigertz K, Martin BR, Jackman
L, Pratt JH, Peacock M, McCabe G and Weaver CM: Sodium retention in
black and white female adolescents in response to salt intake. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 89:1858–1863. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Titze J, Shakibaei M, Schafflhuber M,
Schulze-Tanzil G, Porst M, Schwind KH, Dietsch P and Hilgers KF:
Glycosaminoglycan polymerization may enable osmotically inactive
Na+ storage in the skin. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 287:H203–H208. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Singer DR, Markandu ND, Sugden AL, Miller
MA and MacGregor GA: Sodium restriction in hypertensive patients
treated with a converting enzyme inhibitor and a thiazide.
Hypertension. 17:798–803. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Matsushita N, Kitazato KT, Tada Y,
Sumiyoshi M, Shimada K, Yagi K, Kanematsu Y, Satomi J and Nagahiro
S: Increase in body Na+/water ratio is associated with
cerebral aneurysm formation in oophorectomized rats. Hypertension.
60:1309–1315. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lacolley P, Regnault V, Nicoletti A, Li Z
and Michel JB: The vascular smooth muscle cell in arterial
pathology: A cell that can take on multiple roles. Cardiovasc Res.
95:194–204. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shi N and Chen SY: Mechanisms
simultaneously regulate smooth muscle proliferation and
differentiation. J Biomed Res. 28:40–46. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu G, Hitomi H, Rahman A, Nakano D, Mori
H, Masaki T, Ma H, Iwamoto T, Kobori H and Nishiyama A: High sodium
augments angiotensin II-induced vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation through the ERK1/2-dependent pathway. Hypertens Res.
37:13–18. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Makita S, Nakamura M, Yoshida H and
Hiramori K: Effect of angiotensin II receptor blocker on
angiotensin II stimulated DNA synthesis of cultured human aortic
smooth muscle cells. Life Sci. 56:PL383–PL388. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Komuro I, Kurihara H, Sugiyama T,
Yoshizumi M, Takaku F and Yazaki Y: Endothelin stimulates c-fos and
c-myc expression and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells.
FEBS Lett. 238:249–252. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu J, Ren Y, Kang L and Zhang L: Oxidized
low-density lipoprotein increases the proliferation and migration
of human coronary artery smooth muscle cells through the
upregulation of osteopontin. Int J Mol Med. 33:1341–1347.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang H, Liu Y, Zhu L, Wang W, Wan Z, Chen
F, Wu Y, Zhou J and Yuan Z: 17β-estradiol promotes cholesterol
efflux from vascular smooth muscle cells through a liver X receptor
α-dependent pathway. Int J Mol Med. 33:550–558. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Weissberg PL, Cary NR and Shanahan CM:
Gene expression and vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype. Blood
Press Suppl. 2:68–73. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Salic A and Mitchison TJ: A chemical
method for fast and sensitive detection of DNA synthesis in vivo.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:2415–2420. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guzińska-Ustymowicz K, Pryczynicz A,
Kemona A and Czyzewska J: Correlation between proliferation
markers: PCNA, Ki-67, MCM-2 and antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 in
colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 29:3049–3052. 2009.
|
|
28
|
Liu D, Huang Y, Bu D, Liu AD, Holmberg L,
Jia Y, Tang C, Du J and Jin H: Sulfur dioxide inhibits vascular
smooth muscle cell proliferation via suppressing the Erk/MAP kinase
pathway mediated by cAMP/PKA signaling. Cell Death Dis.
5:e12512014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Boutros T, Chevet E and Metrakos P:
Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase/MAP kinase phosphatase
regulation: Roles in cell growth, death, and cancer. Pharmacol Rev.
60:261–310. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cargnello M and Roux PP: Activation and
function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated
protein kinases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 75:50–83. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Powles J, Fahimi S, Micha R, Khatibzadeh
S, Shi P, Ezzati M, Engell RE, Lim SS, Danaei G, Mozaffarian D, et
al Global Burden of Diseases Nutrition and Chronic Diseases Expert
Group (NutriCoDE): Global, regional and national sodium intakes in
1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis of 24 h urinary sodium
excretion and dietary surveys worldwide. BMJ Open. 3:e0037332013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Blaustein MP, Leenen FHH, Chen L, Golovina
VA, Hamlyn JM, Pallone TL, Van Huysse JW, Zhang J and Wier WG: How
NaCl raises blood pressure: A new paradigm for the pathogenesis of
salt-dependent hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
302:H1031–H1049. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Duzgun SA, Rasque H, Kito H, Azuma N, Li
W, Basson MD, Gahtan V, Dudrick SJ and Sumpio BE: Mitogen-activated
protein phosphorylation in endothelial cells exposed to
hyperosmolar conditions. J Cell Biochem. 76:567–571. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kleinewietfeld M, Manzel A, Titze J,
Kvakan H, Yosef N, Linker RA, Muller DN and Hafler DA: Sodium
chloride drives autoimmune disease by the induction of pathogenic
TH17 cells. Nature. 496:518–522. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhou X, Ferraris JD, Dmitrieva NI, Liu Y
and Burg MB: MKP-1 inhibits high NaCl-induced activation of p38 but
does not inhibit the activation of TonEBP/OREBP: Opposite roles of
p38alpha and p38delta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:5620–5625. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jaeschke A, Karasarides M, Ventura JJ,
Ehrhardt A, Zhang C, Flavell RA, Shokat KM and Davis RJ: JNK2 is a
positive regulator of the cJun transcription factor. Mol Cell.
23:899–911. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Meloche S and Pouysségur J: The ERK1/2
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway as a master regulator of
the G1- to S-phase transition. Oncogene. 26:3227–3239. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cuadrado A and Nebreda AR: Mechanisms and
functions of p38 MAPK signalling. Biochem J. 429:403–417. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mikhailov A, Shinohara M and Rieder CL:
The p38-mediated stress-activated checkpoint. A rapid response
system for delaying progression through antephase and entry into
mitosis. Cell Cycle. 4:57–62. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Perdiguero E, Ruiz-Bonilla V, Serrano AL
and Muñoz-Cánoves P: Genetic deficiency of p38alpha reveals its
critical role in myoblast cell cycle exit: The p38alpha-JNK
connection. Cell Cycle. 6:1298–1303. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|