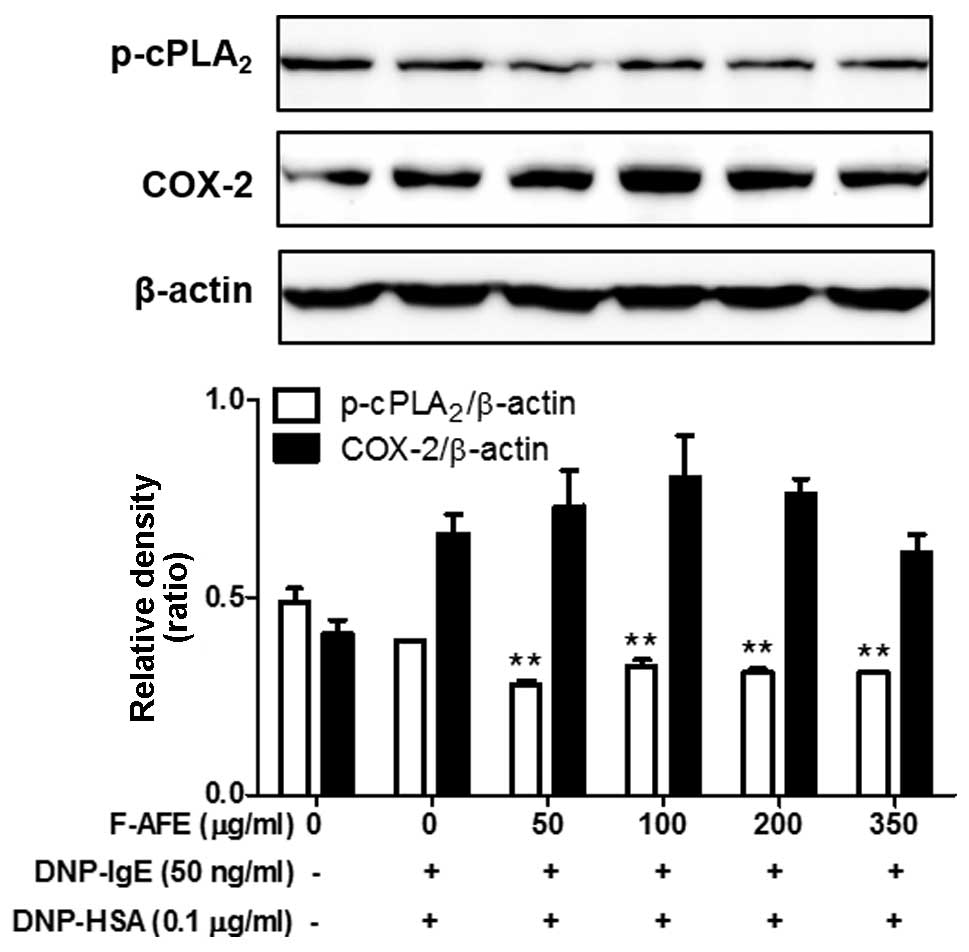
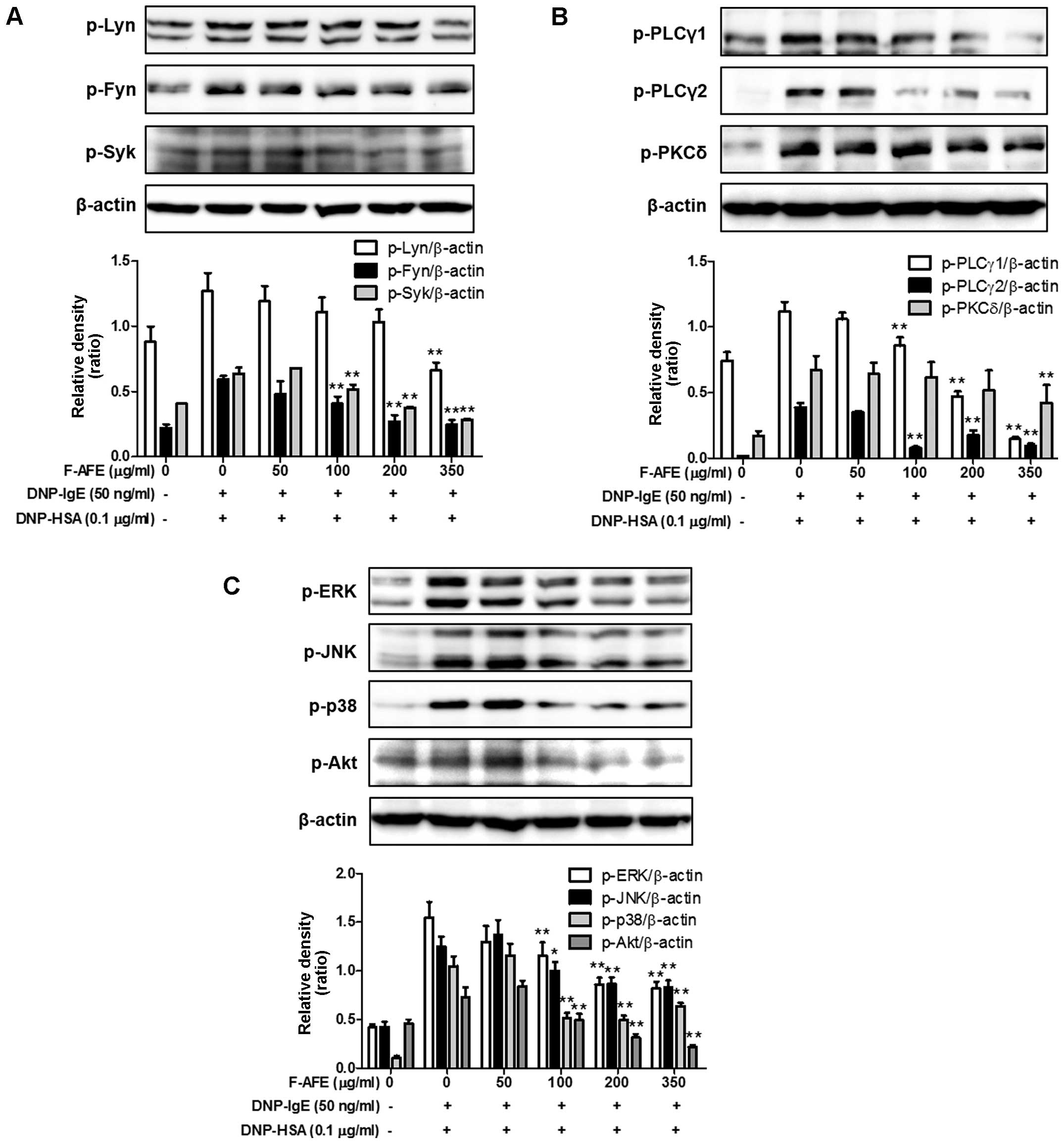
|
1
|
Liu J, Cai YZ, Wong RN, Lee CK, Tang SC,
Sze SC, Tong Y and Zhang Y: Comparative analysis of caffeoylquinic
acids and lignans in roots and seeds among various burdock (Arctium
lappa) genotypes with high antioxidant activity. J Agric Food Chem.
60:4067–4075. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Matsumoto T, Hosono-Nishiyama K and Yamada
H: Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of butyrolactone lignans
from Arctium lappa on leukemic cells. Planta Med. 72:276–278. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Knott A, Reuschlein K, Mielke H, Wensorra
U, Mummert C, Koop U, Kausch M, Kolbe L, Peters N, Stäb F, et al:
Natural Arctium lappa fruit extract improves the clinical signs of
aging skin. J Cosmet Dermatol. 7:281–289. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Xu Z, Wang X, Zhou M, Ma L, Deng Y, Zhang
H, Zhao A, Zhang Y and Jia W: The antidiabetic activity of total
lignan from Fructus Arctii against alloxan-induced diabetes in mice
and rats. Phytother Res. 22:97–101. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lee IA, Joh EH and Kim DH: Arctigenin
isolated from the seeds of Arctium lappa ameliorates memory
deficits in mice. Planta Med. 77:1525–1527. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang YN, Huang XY, Feng ZM, Jiang JS and
Zhang PC: Hepatoprotective activity of twelve novel 7′-hydroxy
lignan glucosides from Arctii Fructus. J Agric Food Chem.
62:9095–9102. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu X, Yang Y, Dou Y, Ye J, Bian D, Wei Z,
Tong B, Kong L, Xia Y and Dai Y: Arctigenin but not arctiin acts as
the major effective constituent of Arctium lappa L. fruit for
attenuating colonic inflammatory response induced by dextran
sulfate sodium in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 23:505–515. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Boldizsár I, Füzfai Z, Tóth F, Sedlák E,
Borsodi L and Molnár-Perl I: Mass fragmentation study of the
trimethylsilyl derivatives of arctiin, matairesinoside, arctigenin,
phylligenin, matairesinol, pinoresinol and methylarctigenin: Their
gas and liquid chromatographic analysis in plant extracts. J
Chromatogr A. 1217:1674–1682. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Oh YC, Cho WK, Oh JH, Im GY, Jeong YH,
Yang MC and Ma JY: Fermentation by Lactobacillus enhances
anti-inflammatory effect of Oyaksungisan on LPS-stimulated RAW
264.7 mouse macrophage cells. BMC Complement Altern Med. 12:172012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim A, Im M, Hwang YH, Yang HJ and Ma JY:
Jaeumganghwa-tang induces apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway
and Lactobacillus fermentation enhances its anticancer activity in
HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cells. PLoS One. 10:e01278982015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kim JH, Park TS, Yang SH, Suh JW and Shim
SM: Microbial bioconversion and processing methods enhance the
phenolic acid and flavonoids and the radical scavenging capacity of
Smilax china L. leaf. J Sci Food Agric. Mar 5–2015.Epub ahead of
print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sheih IC, Fang TJ, Wu TK, Chang CH and
Chen RY: Purification and properties of a novel phenolic
antioxidant from Radix astragali fermented by Aspergillus oryzae
M29. J Agric Food Chem. 59:6520–6525. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Uzzaman A and Cho SH: Chapter 28:
Classification of hypersensitivity reactions. Allergy Asthma Proc.
33(Suppl 1): S96–S99. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Theoharides TC and Kalogeromitros D: The
critical role of mast cells in allergy and inflammation. Ann NY
Acad Sci. 1088:78–99. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gilfillan AM and Tkaczyk C: Integrated
signalling pathways for mast-cell activation. Nat Rev Immunol.
6:218–230. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chung TH, Kang TJ, Cho WK, Im GY, Lee GS,
Yang MC, Cho CW and Ma JY: Effectiveness of the novel herbal
medicine, KIOM-MA, and its bioconversion product, KIOM-MA128, on
the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2012:7629182012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang W, Pan Q, Han XY, Wang J, Tan RQ, He
F, Dou DQ and Kang TG: Simultaneous determination of arctiin and
its metabolites in rat urine and feces by HPLC. Fitoterapia.
86:6–12. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Morita Y and Siraganian RP: Inhibition of
IgE-mediated histamine release from rat basophilic leukemia cells
and rat mast cells by inhibitors of transmethylation. J Immunol.
127:1339–1344. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ishiyama M, Tominaga H, Shiga M, Sasamoto
K, Ohkura Y and Ueno K: A combined assay of cell viability and in
vitro cytotoxicity with a highly water-soluble tetrazolium salt,
neutral red and crystal violet. Biol Pharm Bull. 19:1518–1520.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yoo JM, Kim NY, Seo JM, Kim SJ, Lee SY,
Kim SK, Kim HD, Lee SW and Kim MR: Inhibitory effects of mulberry
fruit extract in combination with naringinase on the allergic
response in IgE-activated RBL-2H3 cells. Int J Mol Med. 33:469–477.
2014.
|
|
21
|
Russo C and Polosa R: TNF-alpha as a
promising therapeutic target in chronic asthma: A lesson from
rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Sci (Lond). 109:135–142. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yoo JM, Sok DE and Kim MR: Anti-allergic
action of aged black garlic extract in RBL-2H3 cells and passive
cutaneous anaphylaxis reaction in mice. J Med Food. 17:92–102.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
van der Pouw Kraan TC, Boeije LC, Smeenk
RJ, Wijdenes J and Aarden LA: Prostaglandin-E2 is a
potent inhibitor of human interleukin 12 production. J Exp Med.
181:775–779. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ford-Hutchinson AW, Bray MA, Doig MV,
Shipley ME and Smith MJ: Leukotriene B, a potent chemokinetic and
aggregating substance released from polymorphonuclear leukocytes.
Nature. 286:264–265. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Arima M and Fukuda T: Prostaglandin
D2 and T(H)2 inflammation in the pathogenesis of
bronchial asthma. Korean J Intern Med. 26:8–18. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nettis E, D'Erasmo M, Di Leo E, Calogiuri
G, Montinaro V, Ferrannini A and Vacca A: The employment of
leukotriene antagonists in cutaneous diseases belonging to
allergological field. Mediators Inflamm. 2010:6281712010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kawakami Y, Kitaura J, Satterthwaite AB,
Kato RM, Asai K, Hartman SE, Maeda-Yamamoto M, Lowell CA, Rawlings
DJ, Witte ON, et al: Redundant and opposing functions of two
tyrosine kinases, Btk and Lyn, in mast cell activation. J Immunol.
165:1210–1219. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Choi SY, Hwang JH, Park SY, Jin YJ, Ko HC,
Moon SW and Kim SJ: Fermented guava leaf extract inhibits
LPS-induced COX-2 and iNOS expression in mouse macrophage cells by
inhibition of transcription factor NF-kappaB. Phytother Res.
22:1030–1034. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu H, Zhang Y, Sun Y, Wang X, Zhai Y, Sun
Y, Sun S, Yu A, Zhang H and Wang Y: Determination of the major
constituents in fruit of Arctium lappa L. by matrix solid-phase
dispersion extraction coupled with HPLC separation and fluorescence
detection. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.
878:2707–2711. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao F, Wang L and Liu K: In vitro
anti-inflammatory effects of arctigenin, a lignan from Arctium
lappa L., through inhibition on iNOS pathway. J Ethnopharmacol.
122:457–462. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Theoharides TC, Alysandratos KD, Angelidou
A, Delivanis DA, Sismanopoulos N, Zhang B, Asadi S, Vasiadi M, Weng
Z, Miniati A, et al: Mast cells and inflammation. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1822:21–33. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Roth K, Chen WM and Lin TJ: Positive and
negative regulatory mechanisms in high-affinity IgE
receptor-mediated mast cell activation. Arch Immunol Ther Exp
(Warsz). 56:385–399. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Gomez G, Gonzalez-Espinosa C, Odom S, Baez
G, Cid ME, Ryan JJ and Rivera J: Impaired FcepsilonRI-dependent
gene expression and defective eicosanoid and cytokine production as
a consequence of Fyn deficiency in mast cells. J Immunol.
175:7602–7610. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fanning LB and Boyce JA: Lipid mediators
and allergic diseases. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 111:155–162.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|