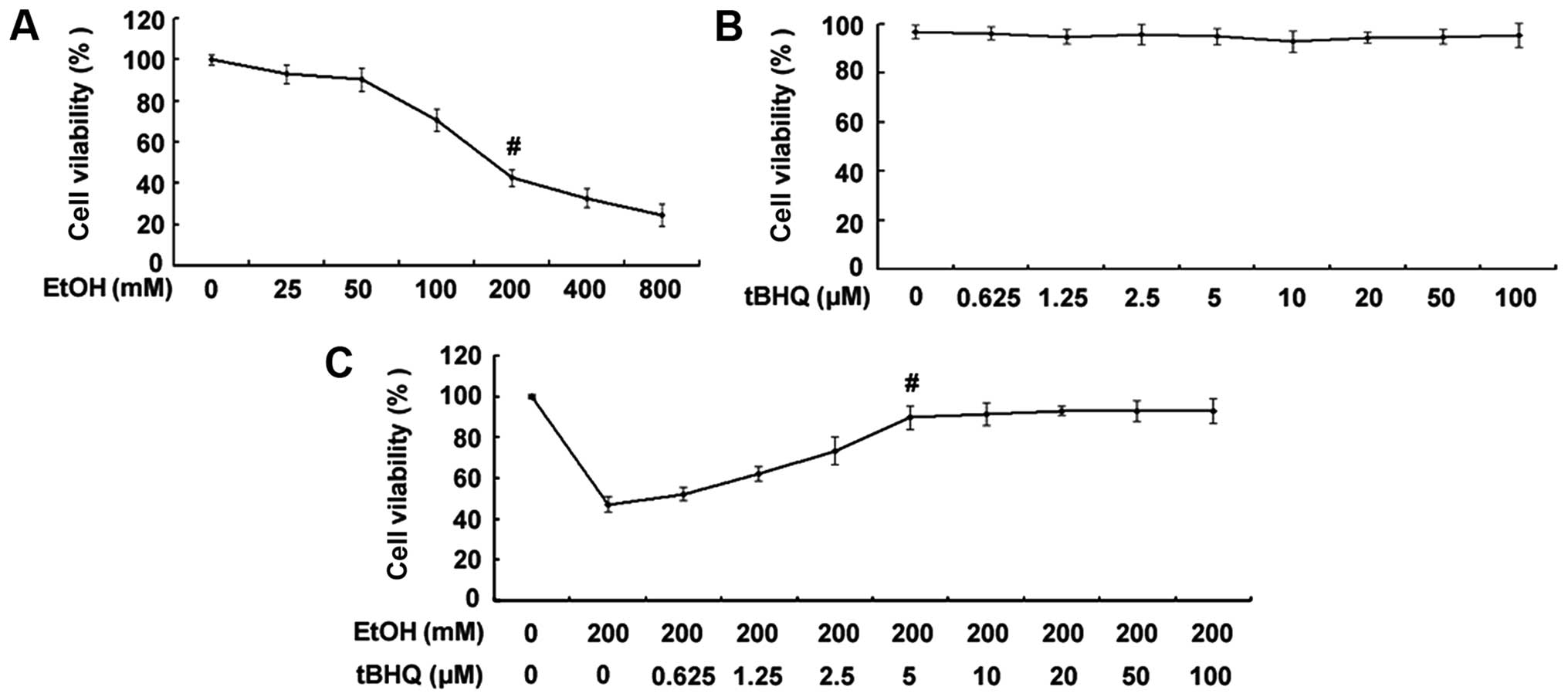
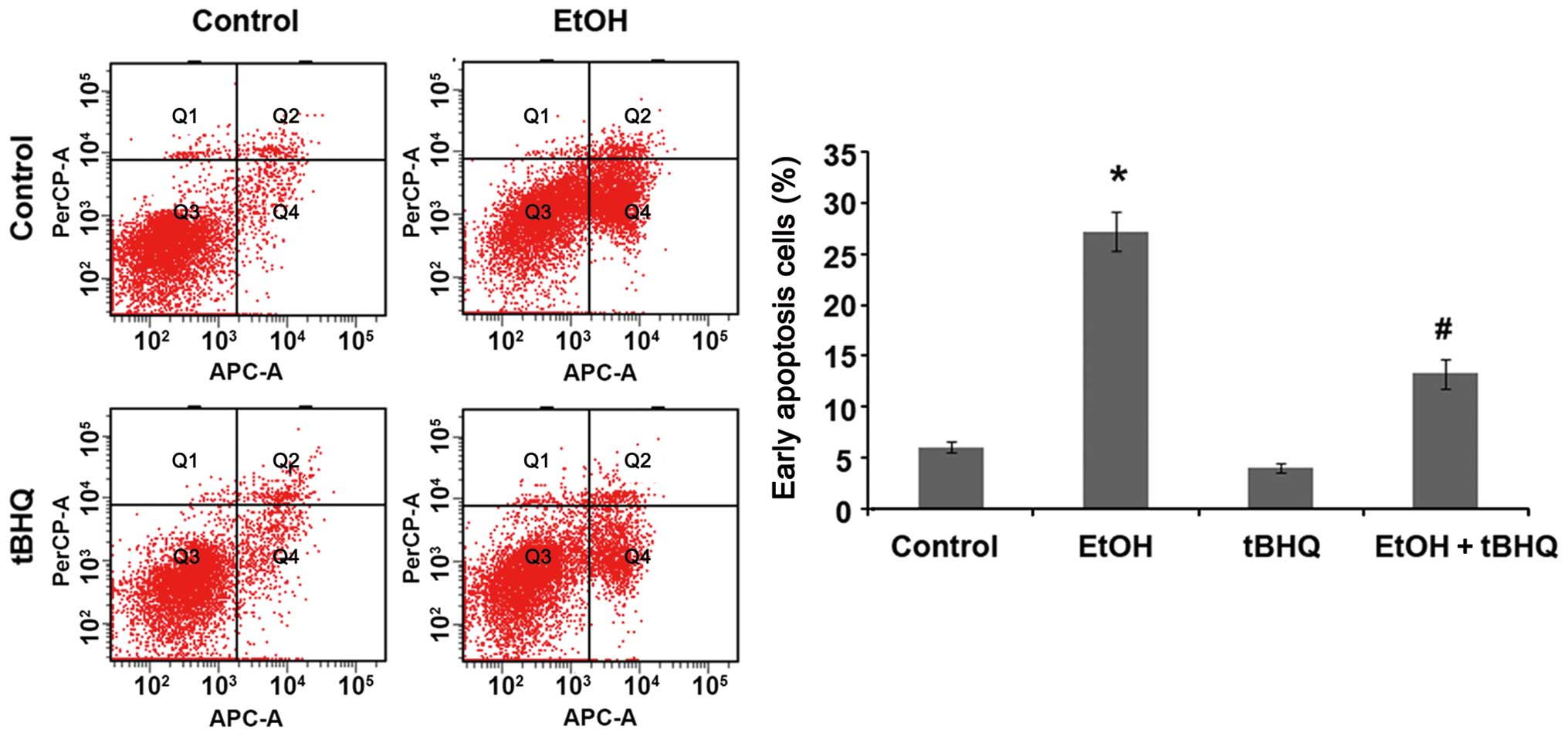
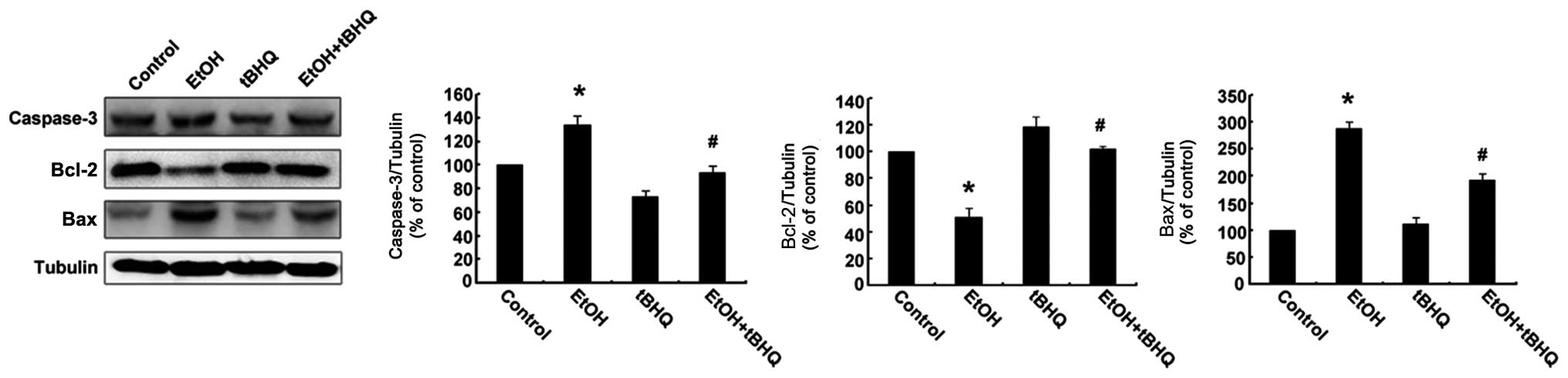
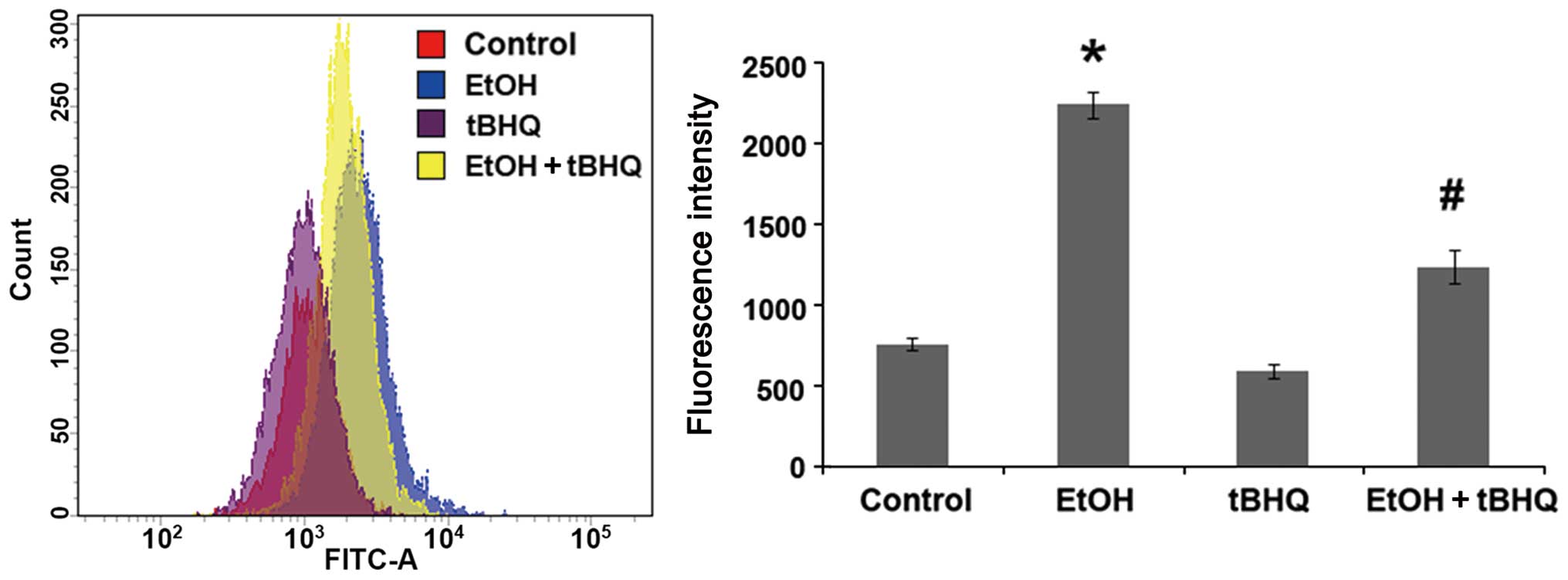
|
1
|
Piano MR and Phillips SA: Alcoholic
cardiomyopathy: pathophysiologic insights. Cardiovasc Toxicol.
14:291–308. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Capasso JM, Li P, Guideri G, Malhotra A,
Cortese R and Anversa P: Myocardial mechanical, biochemical, and
structural alterations induced by chronic ethanol ingestion in
rats. Circ Res. 71:346–356. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li SY, Li Q, Shen JJ, Dong F, Sigmon VK,
Liu Y and Ren J: Attenuation of acetaldehyde-induced cell injury by
overexpression of aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 (ALDH2) transgene in
human cardiac myocytes: role of MAP kinase signaling. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 40:283–294. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen DB, Wang L and Wang PH: Insulin-like
growth factor I retards apoptotic signaling induced by ethanol in
cardiomyocytes. Life Sci. 67:1683–1693. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tan Y, Li X, Prabhu SD, Brittian KR, Chen
Q, Yin X, McClain CJ, Zhou Z and Cai L: Angiotensin II plays a
critical role in alcohol- induced cardiac nitrative damage, cell
death, remodeling, and cardiomyopathy in a protein kinase
C/nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase-dependent
manner. J Am Coll Cardiol. 59:1477–1486. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fernández-Solà J, Fatjó F, Sacanella E,
Estruch R, Bosch X, Urbano-Márquez A and Nicolás JM: Evidence of
apoptosis in alcoholic cardiomyopathy. Hum Pathol. 37:1100–1110.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fernández-Solà J, Lluis M, Sacanella E,
Estruch R, Antúnez E and Urbano-Márquez A: Increased myostatin
activity and decreased myocyte proliferation in chronic alcoholic
cardiomyopathy. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 35:1220–1229. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kannan M, Wang L and Kang YJ: Myocardial
oxidative stress and toxicity induced by acute ethanol exposure in
mice. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 229:553–559. 2004.
|
|
9
|
Guan Z, Lui CY, Morkin E and Bahl JJ:
Oxidative stress and apoptosis in cardiomyocyte induced by
high-dose alcohol. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 44:696–702. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jing L, Jin CM, Li SS, Zhang FM, Yuan L,
Li WM, Sang Y, Li S and Zhou LJ: Chronic alcohol intake-induced
oxidative stress and apoptosis: role of CYP2E1 and calpain-1 in
alcoholic cardiomyopathy. Mol Cell Biochem. 359:283–292. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Umoh NA, Walker RK, Al-Rubaiee M, Jeffress
MA and Haddad GE: Acute alcohol modulates cardiac function as
PI3K/Akt regulates oxidative stress. Alcohol Clin Exp Res.
38:1847–1864. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ho E, Karimi Galougahi K, Liu CC, Bhindi R
and Figtree GA: Biological markers of oxidative stress:
applications to cardiovascular research and practice. Redox Biol.
1:483–491. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lucas DL, Brown RA, Wassef M and Giles TD:
Alcohol and the cardiovascular system: research challenges and
opportunities. J Am Coll Cardiol. 45:1916–1924. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang RH, Gao JY, Guo HT, Scott GI, Eason
AR, Wang XM and Ren J: Inhibition of CYP2E1 attenuates chronic
alcohol intake-induced myocardial contractile dysfunction and
apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1832:128–141. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kannan K and Jain SK: Oxidative stress and
apoptosis. Pathophysiology. 7:153–163. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zu L, Zheng X, Wang B, Parajuli N,
Steenbergen C, Becker LC and Cai ZP: Ischemic preconditioning
attenuates mitochondrial localization of PTEN induced by
ischemia-reperfusion. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
300:H2177–H2186. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kino M: Chronic effects of ethanol under
partial inhibition of catalase activity in the rat heart: light and
electron microscopic observations. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 13:5–21.
1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jaiswal AK: Nrf2 signaling in coordinated
activation of antioxidant gene expression. Free Radic Biol Med.
36:1199–1207. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li J, Ichikawa T, Villacorta L, Janicki
JS, Brower GL, Yamamoto M and Cui T: Nrf2 protects against
maladaptive cardiac responses to hemodynamic stress. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:1843–1850. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Calvert JW, Elston M, Nicholson CK,
Gundewar S, Jha S, Elrod JW, Ramachandran A and Lefer DJ: Genetic
and pharmacologic hydrogen sulfide therapy attenuates
ischemia-induced heart failure in mice. Circulation. 122:11–19.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li J, Zhang C, Xing Y, Janicki JS,
Yamamoto M, Wang XL, Tang DQ and Cui T: Up-regulation of p27(kip1)
contributes to Nrf2-mediated protection against angiotensin
II-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Cardiovasc Res. 90:315–324. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li S, Wang W, Niu T, Wang H, Li B, Shao L,
Lai Y, Li H, Janicki JS, Wang XL, et al: Nrf2 deficiency
exaggerates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and cardiac
dysfunction. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014:7485242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li J, Ichikawa T, Janicki JS and Cui T:
Targeting the Nrf2 pathway against cardiovascular disease. Expert
Opin Ther Targets. 13:785–794. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Walker RK, Cousins VM, Umoh NA, Jeffress
MA, Taghipour D, Al-Rubaiee M and Haddad GE: The good, the bad, and
the ugly with alcohol use and abuse on the heart. Alcohol Clin Exp
Res. 37:1253–1260. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dong J, Yan D and Chen SY: Stabilization
of Nrf2 protein by D3T provides protection against ethanol-induced
apoptosis in PC12 cells. PLoS One. 6:e168452011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen X, Liu J and Chen SY: Sulforaphane
protects against ethanol-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in
neural crest cells by the induction of Nrf2-mediated antioxidant
response. Br J Pharmacol. 169:437–448. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li J, Johnson D, Calkins M, Wright L,
Svendsen C and Johnson J: Stabilization of Nrf2 by tBHQ confers
protection against oxidative stress-induced cell death in human
neural stem cells. Toxicol Sci. 83:313–328. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kaspar JW and Jaiswal AK: An
autoregulatory loop between Nrf2 and Cul3-Rbx1 controls their
cellular abundance. J Biol Chem. 285:21349–21358. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu J, Cheng M, Liu Q, Yang J, Wu S, Lu X,
Jin C, Ma H and Cai Y: Protective role of tert-butylhydroquinone
against sodium fluoride-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in
PC12 cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 35:1017–1025. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li H, Zhang L, Wang F, Shi Y, Ren Y, Liu
Q, Cao Y and Duan H: Attenuation of glomerular injury in diabetic
mice with tert-butylhydroquinone through nuclear factor erythroid
2-related factor 2-dependent antioxidant gene activation. Am J
Nephrol. 33:289–297. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Z, Ji C, Wu L, Qiu J, Li Q, Shao Z
and Chen G: Tert-butylhydroquinone alleviates early brain injury
and cognitive dysfunction after experimental subarachnoid
hemorrhage: role of Keap1/Nrf2/ARE pathway. PLoS One. 9:e976852014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gharavi N, Haggarty S and El-Kadi AO:
Chemoprotective and carcinogenic effects of tert-butylhydroquinone
and its metabolites. Curr Drug Metab. 8:1–7. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yan D, Dong J, Sulik KK and Chen SY:
Induction of the Nrf2-driven antioxidant response by
tert-butylhydroquinone prevents ethanol-induced apoptosis in
cranial neural crest cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 80:144–149. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang Y, Zhao J, Yang W, Bi Y, Chi J, Tian
J and Li W: High-dose alcohol induces reactive oxygen
species-mediated apoptosis via PKC-β/p66Shc in mouse primary
cardiomyocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 456:656–661. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Jin W, Ni H, Dai Y, Wang H, Lu T, Wu J,
Jiang J and Liang W: Effects of tert-butylhydroquinone on
intestinal inflammatory response and apoptosis following traumatic
brain injury in mice. Mediators Inflamm. 2010:5025642010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kraft AD, Johnson DA and Johnson JA:
Nuclear factor E2-related factor 2-dependent antioxidant response
element activation by tert-butylhydroquinone and sulforaphane
occurring preferentially in astrocytes conditions neurons against
oxidative insult. J Neurosci. 24:1101–1112. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sun J, Ren X and Simpkins JW: Sequential
upregulation of superoxide dismutase 2 and heme oxygenase 1 by
tert-butylhy-droquinone protects mitochondria during oxidative
stress. Mol Pharmacol. 88:437–449. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Duan X, Liu D, Xing X, Li J, Zhao S, Nie
H, Zhang Y, Sun G and Li B: Tert-butylhydroquinone as a phenolic
activator of Nrf2 antagonizes arsenic-induced oxidative
cytotoxicity but promotes arsenic methylation and detoxication in
human hepatocyte cell line. Biol Trace Elem Res. 160:294–302. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang C, Li C, Peng H, Ye Z, Zhang J, Liu X
and Lou T: Activation of the Nrf2-ARE pathway attenuates
hyperglycemia-mediated injuries in mouse podocytes. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 34:891–902. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
He X, Kan H, Cai L and Ma Q: Nrf2 is
critical in defense against high glucose-induced oxidative damage
in cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 46:47–58. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Chen X, Liu J and Chen SY: Over-expression
of Nrf2 diminishes ethanol-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis
in neural crest cells by inducing an antioxidant response. Reprod
Toxicol. 42:102–109. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Huang XS, Chen HP, Yu HH, Yan YF, Liao ZP
and Huang QR: Nrf2-dependent upregulation of antioxidative enzymes:
a novel pathway for hypoxic preconditioning-mediated delayed
cardioprotection. Mol Cell Biochem. 385:33–41. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Calvert JW, Jha S, Gundewar S, Elrod JW,
Ramachandran A, Pattillo CB, Kevil CG and Lefer DJ: Hydrogen
sulfide mediates cardioprotection through Nrf2 signaling. Circ Res.
105:365–374. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li S, Li J, Shen C, Zhang X, Sun S, Cho M,
Sun C and Song Z: Tert-butylhydroquinone (tBHQ) protects
hepatocytes against lipotoxicity via inducing autophagy
independently of Nrf2 activation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1841:22–33.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Li T, Sun KJ, Wang HD, Zhou ML, Ding K, Lu
XY, Wei WT, Wang CX and Zhou XM: Tert-butylhydroquinone ameliorates
early brain injury after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in
mice by enhancing Nrf2-independent autophagy. Neurochem Res.
40:1829–1838. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang Y, Liu FF, Bi X, Wang S, Wu X and
Jiang F: The antioxidant compound tert-butylhydroquinone activates
Akt in myocardium, suppresses apoptosis and ameliorates pressure
overload-induced cardiac dysfunction. Sci Rep. 5:130052015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Reed JC: Double identity for proteins of
the Bcl-2 family. Nature. 387:773–776. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Niture SK and Jaiswal AK: INrf2 (Keap1)
targets Bcl-2 degradation and controls cellular apoptosis. Cell
Death Differ. 18:439–451. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Niture SK and Jaiswal AK: Inhibitor of
Nrf2 (INrf2 or Keap1) protein degrades Bcl-xL via phosphoglycerate
mutase 5 and controls cellular apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
286:44542–44556. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|