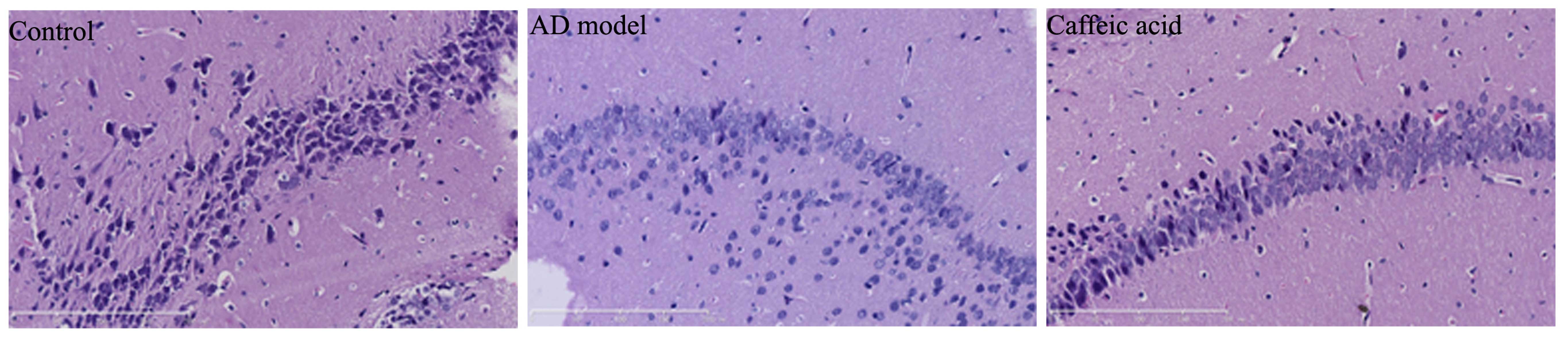
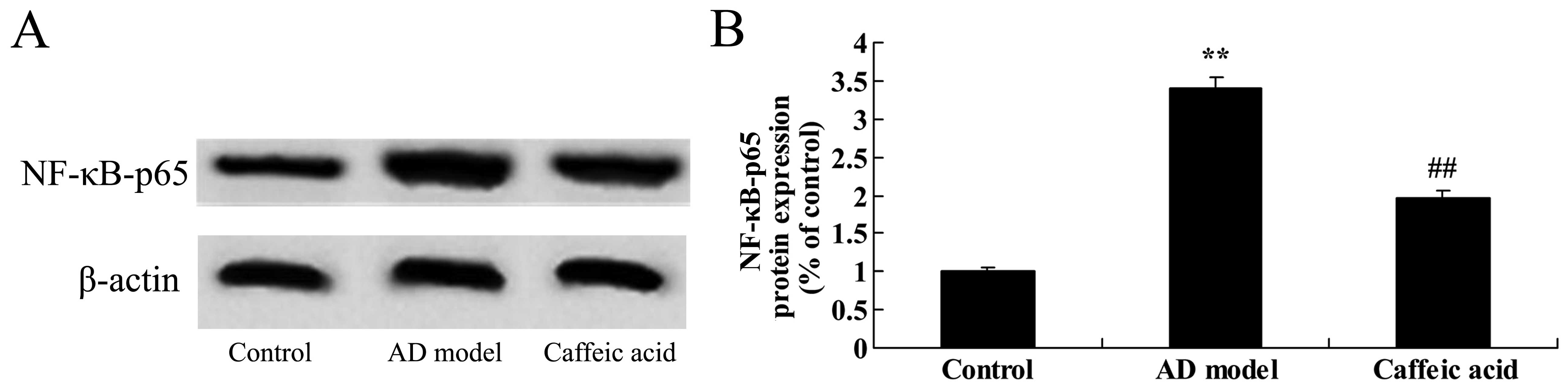
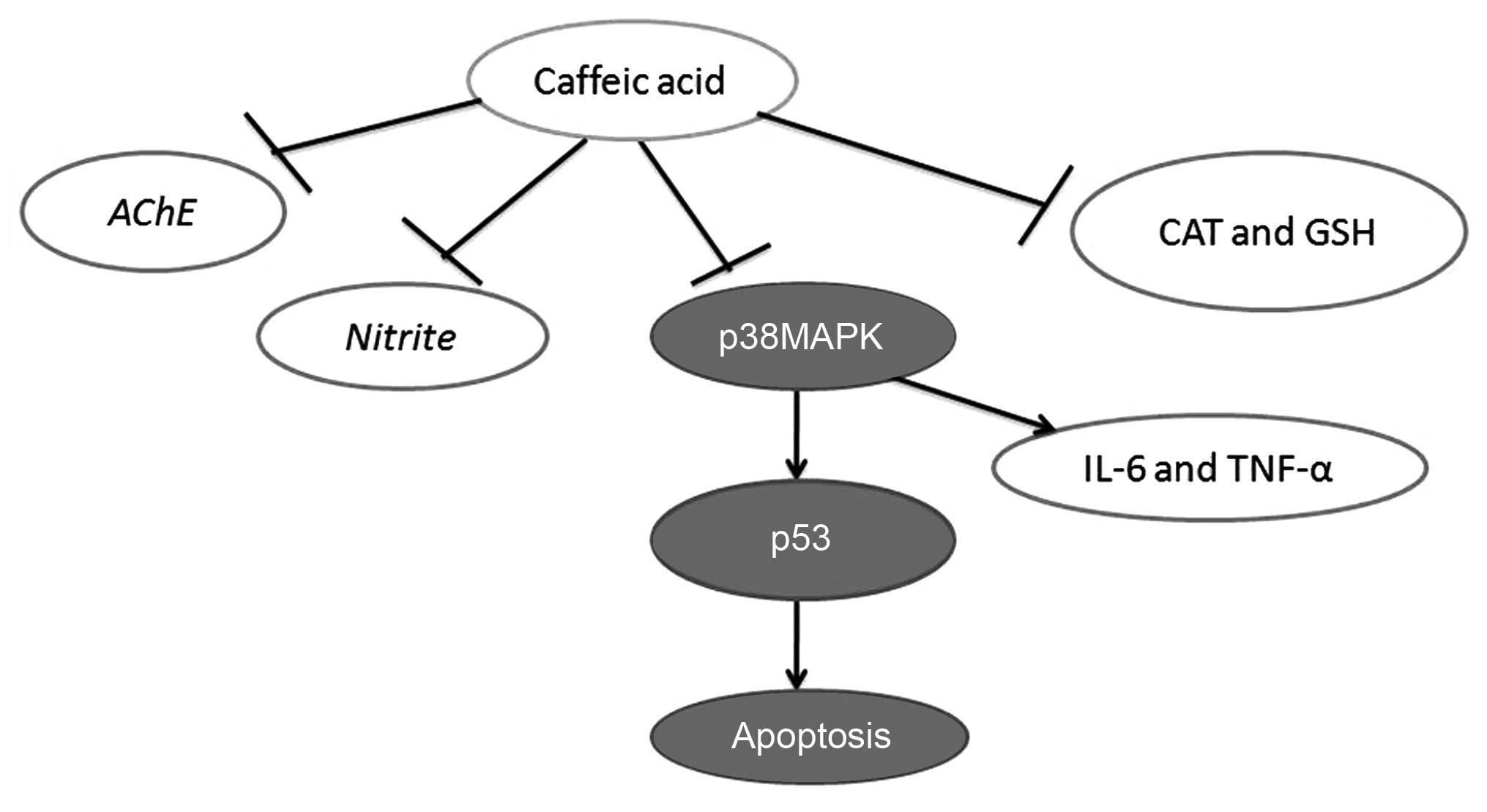
|
1
|
Muir SW, Speechley M, Wells J, Borrie M,
Gopaul K and Montero-Odasso M: Gait assessment in mild cognitive
impairment and Alzheimer's disease: the effect of dual-task
challenges across the cognitive spectrum. Gait Posture. 35:96–100.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Pitkala KH, Raivio MM, Laakkonen ML,
Tilvis RS, Kautiainen H and Strandberg TE: Exercise rehabilitation
on home-dwelling patients with Alzheimer's disease - a randomized,
controlled trial. Study protocol. Trials. 11:922010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Spires-Jones TL, Mielke ML, Rozkalne A,
Meyer-Luehmann M, de Calignon A, Bacskai BJ, Schenk D and Hyman BT:
Passive immunotherapy rapidly increases structural plasticity in a
mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Neurobiol Dis. 33:213–220. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Olazarán J, Reisberg B, Clare L, Cruz I,
Peña-Casanova J, Del Ser T, Woods B, Beck C, Auer S, Lai C, et al:
Nonpharmacological therapies in Alzheimer's disease: a systematic
review of efficacy. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 30:161–178. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang WY, Tan MS, Yu JT and Tan L: Role of
pro-inflammatory cytokines released from microglia in Alzheimer's
disease. Ann Transl Med. 3:1362015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Götz J, Ittner LM, Schonrock N and Cappai
R: An update on the toxicity of Abeta in Alzheimer's disease.
Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 4:1033–1042. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Pittalà V, Salerno L, Romeo G, Siracusa
MA, Modica MN, Romano GL, Salomone S, Drago F and Bucolo C: Effects
of novel hybrids of caffeic acid phenethyl ester and NSAIDs on
experimental ocular inflammation. Eur J Pharmacol. 752:78–83. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pinho E, Henriques M and Soares G: Caffeic
acid loading wound dressing: Physicochemical and biological
characterization. Ther Deliv. 5:1063–1075. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tanida I, Shirasago Y, Suzuki R, Abe R,
Wakita T, Hanada K and Fukasawa M: Inhibitory effects of caffeic
acid, a coffee-related organic acid, on the propagation of
hepatitis C virus. Jpn J Infect Dis. 68:268–275. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Paracatu LC, Faria CM, Quinello C, Rennó
C, Palmeira P, Zeraik ML, da Fonseca LM and Ximenes VF: Caffeic
Acid phenethyl ester: consequences of its hydrophobicity in the
oxidative functions and cytokine release by leukocytes. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2014:7936292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bailly F and Cotelle P: Anti-HIV
activities of natural antioxidant caffeic acid derivatives: toward
an antiviral supplementation diet. Curr Med Chem. 12:1811–1818.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang Y, Li Y, Wang K, Wang Y, Yin W and Li
L: P38/NF-κB/snail pathway is involved in caffeic acid-induced
inhibition of cancer stem cells-like properties and migratory
capacity in malignant human keratinocyte. PLoS One. 8:e589152013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr and
Feather-Stone RM: A new and rapid colorimetric determination of
acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 7:88–95. 1961.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Paillard T, Rolland Y and de Souto Barreto
P: Protective effects of physical exercise in Alzheimer's disease
and Parkinson's disease: a narrative review. J Clin Neurol.
11:212–219. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu H, Finkelstein DI and Adlard PA:
Interactions of metals and Apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer's disease.
Front Aging Neurosci. 6:1212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Khan KA, Kumar N, Nayak PG, Nampoothiri M,
Shenoy RR, Krishnadas N, Rao CM and Mudgal J: Impact of caffeic
acid on aluminium chloride-induced dementia in rats. J Pharm
Pharmacol. 65:1745–1752. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pinheiro Fernandes FD, Fontenele Menezes
AP, de Sousa Neves JC, Fonteles AA, da Silva AT, de Araújo
Rodrigues P, Santos do Carmo MR, de Souza CM and de Andrade GM:
Caffeic acid protects mice from memory deficits induced by focal
cerebral ischemia. Behav Pharmacol. 25:637–647. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yousof Ali M, Jung HA and Choi JS:
Anti-diabetic and anti-Alzheimer's disease activities of Angelica
decursiva. Arch Pharm Res. 38:2216–2227. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zimmermann M: Neuronal AChE splice
variants and their non-hydrolytic functions: redefining a target of
AChE inhibitors? Br J Pharmacol. 170:953–967. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mehrotra A, Shanbhag R, Chamallamudi MR,
Singh VP and Mudgal J: Ameliorative effect of caffeic acid against
inflammatory pain in rodents. Eur J Pharmacol. 666:80–86. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sassi C, Ridge PG, Nalls MA, Gibbs R, Ding
J, Lupton MK, Troakes C, Lunnon K, Al-Sarraj S, Brown KS, et al:
Influence of coding variability in APP-Aβ metabolism genes in
sporadic Alzheimer's disease. PLoS One. 11:e01500792016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Gonzalez P, da Costa VC, Hyde K, Wu Q,
Annunziata O, Rizo J, Akkaraju G and Green KN: Bimodal-hybrid
heterocyclic amine targeting oxidative pathways and copper
mis-regulation in Alzheimer's disease. Metallomics. 6:2072–2082.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hatanaka H, Hanyu H, Hirose D, Fukusawa R,
Namioka N and Iwamoto T: Peripheral oxidative stress markers in
individuals with Alzheimer's disease with or without
cerebrovascular disease. J Am Geriatr Soc. 63:1472–1474. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim H, Kim W, Yum S, Hong S, Oh JE, Lee
JW, Kwak MK, Park EJ, Na DH and Jung Y: Caffeic acid phenethyl
ester activation of Nrf2 pathway is enhanced under oxidative state:
structural analysis and potential as a pathologically targeted
therapeutic agent in treatment of colonic inflammation. Free Radic
Biol Med. 65:552–562. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ashabi G, Alamdary SZ, Ramin M and
Khodagholi F: Reduction of hippocampal apoptosis by
intracerebroventricular administration of extracellular
signal-regulated protein kinase and/or p38 inhibitors in amyloid
beta rat model of Alzheimer's disease: involvement of
nuclear-related factor-2 and nuclear factor-κB. Basic Clin
Pharmacol Toxicol. 112:145–155. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yang WN, Ma KG, Qian YH, Zhang JS, Feng
GF, Shi LL, Zhang ZC and Liu ZH: Mitogen-activated protein kinase
signaling pathways promote low-density lipoprotein receptor-related
protein 1-mediated internalization of beta-amyloid protein in
primary cortical neurons. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 64:252–264.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim TI, Lee YK, Park SG, Choi IS, Ban JO,
Park HK, Nam SY, Yun YW, Han SB, Oh KW and Hong JT: L-Theanine, an
amino acid in green tea, attenuates beta-amyloid-induced cognitive
dysfunction and neurotoxicity: reduction in oxidative damage and
inactivation of ERK/p38 kinase and NF-kappaB pathways. Free Radic
Biol Med. 47:1601–1610. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee MS, Kim YH, Lee BR, Kwon SH, Moon WJ,
Hong KS, Song YS, Morita K, Hahm DH, Shim I and Her S: Novel
antidepressant-like activity of caffeic acid phenethyl ester is
mediated by enhanced glucocorticoid receptor function in the
hippocampus. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014:6460392014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|