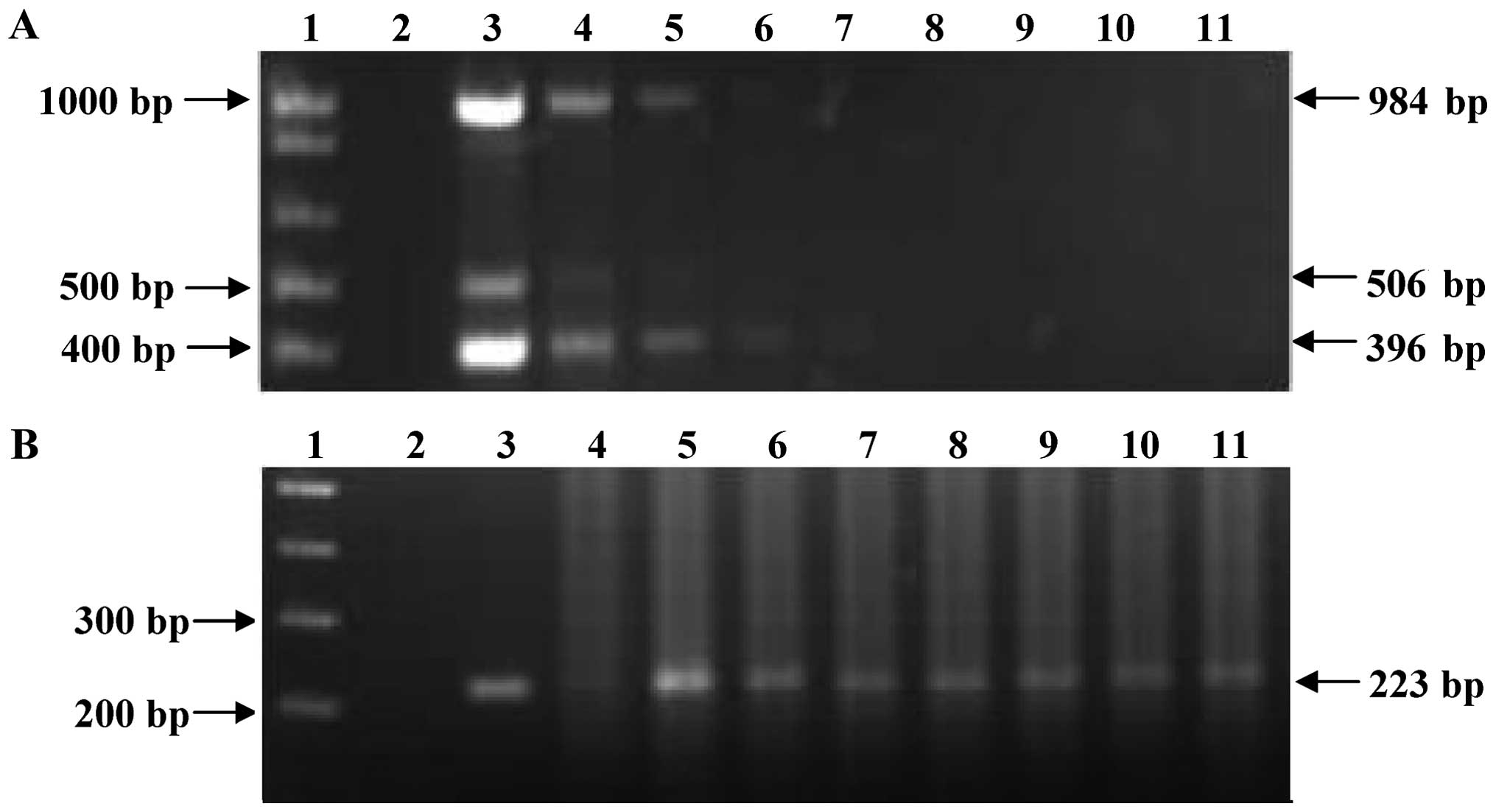
|
1
|
Mazars E, Lesjean S, Banuls AL, Gilbert M,
Vincent V, Gicquel B, Tibayrenc M, Locht C and Supply P:
High-resolution minisatellite-based typing as a portable approach
to global analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis molecular
epidemiology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:1901–1906. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Puccioni-Sohler M and Brandão CO: Factors
associated to the positive cerebrospinal fluid culture in the
tuberculous meningitis. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 65:48–53. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
World Health Organization: Global
tuberculosis report. 2015, http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/.
Accessed August, 2015.
|
|
4
|
Ministry of Health in Mexico: National
system of epidemiological surveillance. Single system of
information (Sistema Nacional de Vigilancia Epidemiológica. Sistema
Único de Información. Secretaría de Salud, México). Epidemiologia.
29:5–6. 2006.
|
|
5
|
Procedures manual of standards for
epidemiological surveillance of mycobacteriosis (tuberculosis and
leprosy). Available: http://www.epidemiologia.salud.gob.mx/doctos/infoepid/vig_epid_manuales/17_2012_Manual_Micobacteriosis_vFinal_9nov12.pdf
(In Spanish).
|
|
6
|
Abter EIM, Schaening O, Barbour RL and
Lutwick LI: Tuberculosis in the adult. Tuberculosis: A Clinical
Handbook. Lutwicick LI: Chapman and Hall Medical; London: pp.
54–101. 1995, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Golden MP and Vikram HR: Extrapulmonary
tuberculosis: an overview. Am Fam Physician. 72:1761–1768.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Donald PR and Schoeman JF: Tuberculous
meningitis. N Engl J Med. 351:1719–1720. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ahuja GK, Mohan KK, Prasad K and Behari M:
Diagnostic criteria for tuberculous meningitis and their
validation. Tuber Lung Dis. 75:149–152. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
González-Martín J, García-García JM,
Anibarro L, Vidal R, Esteban J, Blanquer R, Moreno S and
Ruiz-Manzano J: Consensus document on the diagnosis, treatment and
prevention of tuberculosis. Arch Bronconeumol. 46:255–274. 2010.In
Spanish. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Haldar S, Sharma N, Gupta VK and Tyagi JS:
Efficient diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis by detection of
Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA in cerebrospinal fluid filtrates
using PCR. J Med Microbiol. 58:616–624. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rock RB, Olin M, Baker CA, Molitor TW and
Peterson PK: Central nervous system tuberculosis: Pathogenesis and
clinical aspects. Clin Microbiol Rev. 21:243–261. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Thwaites GE and Tran TH: Tuberculous
meningitis: many questions, too few answers. Lancet Neurol.
4:160–170. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Venkataswamy MM, Rafi W, Nagarathna S,
Ravi V and Chandramuki A: Comparative evaluation of BACTEC 460TB
system and Lowenstein-Jensen medium for the isolation of M.
tuberculosis from cerebrospinal fluid samples of tuberculous
meningitis patients. Indian J Med Microbiol. 25:236–240. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Delidow B, Lynch JP, Peluso JJ and White
BA: Polymerase chain reaction. Methods in Molecular Biology, PCR
Protocols: Methods and Application. White B: Humana Press Inc;
Totowa, NJ: pp. 1–30. 1998
|
|
16
|
Kox LF, Rhienthong D, Miranda AM,
Udomsantisuk N, Ellis K, van Leeuwen J, van Heusden S, Kuijper S
and Kolk AH: A more reliable PCR for detection of Mycobacterium
tuberculosis in clinical samples. J Clin Microbiol. 32:672–678.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ritacco V and de Kantor IN: Simultaneous
detection of Mycobacterium bovis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis in
human cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 45:6842007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Takahashi T and Nakayama T: Novel
technique of quantitative nested real-time PCR assay for
Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA. J Clin Microbiol. 44:1029–1039.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cole ST, Brosch R, Parkhill J, Garnier T,
Churcher C, Harris D, Gordon SV, Eiglmeier K, Gas S, Barry CE III,
et al: Deciphering the biology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from
the complete genome sequence. Nature. 393:537–544. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kato-Maeda M, Rhee JT, Gingeras TR,
Salamon H, Drenkow J, Smittipat N and Small PM: Comparing genomes
within the species Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Genome Res.
11:547–554. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tsolaki AG, Hirsh AE, DeRiemer K, Enciso
JA, Wong MZ, Hannan M, Goguet de la Salmoniere YO, Aman K,
Kato-Maeda M and Small PM: Functional and evolutionary genomics of
Mycobacterium tuberculosis: insights from genomic deletions in 100
strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:4865–4870. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Palma-Nicolás JP and Bocanegra-García V:
Innovative strategies to diagnose and monitor tuberculosis
patients. Arch Bronconeumol. 43:225–232. 2007.In Spanish.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Parrado R, Lozano D, Garcia L, Torrico MC,
Delgado R, Torrico F, Laserna M and Reithinger R: Multiprimer PCR
system diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in Cochabamba, Bolivia.
J Clin Microbiol. 46:830–831. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Richardson ET, Samson D and Banaei N:
Rapid Identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and
nontuberculous mycobacteria by multiplex, real-time PCR. J Clin
Microbiol. 47:1497–1502. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Siddiqi SH, Hawkins JE and Laszlo A:
Interlaboratory drug susceptibility testing of Mycobacterium
tuberculosis by a radiometric procedure and two conventional
methods. J Clin Microbiol. 22:919–923. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fuentelsaz Gallego C: Sample size
calculation. Matronas Profesion. 5:pp. 5–13. 2004, Available:
https://ecaths1.s3.amazonaws.com/seminarioi/1400533589.1%20Muestreo.pdf.
(In Spanish).
|
|
27
|
Chomczynski P and Sacchi N: Single-step
method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium
thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem.
162:156–159. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chomczynski P: A reagent for the
single-step simultaneous isolation of RNA, DNA and proteins from
cell and tissue samples. Biotechniques. 15:532–534. 536–537.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dawson B and Trapp RG: Biostatistics. 4th
edition. New York: McGraw Hill; 2004
|
|
30
|
Del Portillo P, Murillo LA and Patarroyo
ME: Amplification of a species-specific DNA fragment of
Mycobacterium tuberculosis and its possible use in diagnosis. J
Clin Microbiol. 29:2163–2168. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Del Portillo P, Thomas MC, Martínez E,
Marañón C, Valladares B, Patarroyo ME and Carlos López M:
Multiprimer PCR system for differential identification of
mycobacteria in clinical samples. J Clin Microbiol. 34:324–328.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Herrera EA and Segovia M: Evaluation of
mtp40 genomic fragment amplification for specific detection of
Mycobacterium tuberculosis in clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol.
34:1108–1113. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nava PO, Manssur H and Prieto L:
Evaluation of bacilloscopy, cultivation and polymerase chain
reaction for the diagnostic of lung tuberculosis. Kasmera.
33:119–131. 2005.In Spanish.
|
|
34
|
Ling DI, Flores LL, Riley LW and Pai M:
Commercial nucleic-acid amplification tests for diagnosis of
pulmonary tuberculosis in respiratory specimens: meta-analysis and
meta-regression. PLoS One. 3:e15362008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gori A, Franzetti F, Marchetti G, Catozzi
L and Corbellino M: Specific detection of Mycobacterium
tuberculosis by mtp40 nested PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 34:2866–2867.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kolk AH, Schuitema AR, Kuijper S, van
Leeuwen J, Hermans PW, van Embden JD and Hartskeerl RA: Detection
of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in clinical samples by using
polymerase chain reaction and a nonradioactive detection system. J
Clin Microbiol. 30:2567–2575. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lima JF, Montenegro LM, Montenegro RA,
Cabral MM, Lima AS, Abath FG and Schindler HC: Performance of
nested PCR in the specific detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
complex in blood samples of pediatric patients. J Bras Pneumol.
35:690–697. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Koivula T, Svenson SB and Källenius G: The
mtp40 gene is not present in Mycobacterium bovis. Tuberculosis
(Edinb). 82:183–185. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Vera-Cabrera L, Howard ST, Laszlo A and
Johnson WM: Analysis of genetic polymorphism in the phospholipase
region of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol.
35:1190–1195. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Seth P, Ahuja GK, Bhanu NV, Behari M,
Bhowmik S, Broor S, Dar L and Chakraborty M: Evaluation of
polymerase chain reaction for rapid diagnosis of clinically
suspected tuberculous meningitis. Tuber Lung Dis. 77:353–357. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bonington A, Strang JI, Klapper PE, Hood
SV, Rubombora W, Penny M, Willers R and Wilkins EG: Use of Roche
AMPLICOR Mycobacterium tuberculosis PCR in early diagnosis of
tuberculous meningitis. J Clin Microbiol. 36:1251–1254.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Vera-Cabrera L, Hernández-Vera MA, Welsh
O, Johnson WM and Castro-Garza J: Phospholipase region of
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a preferential locus for IS6110
transposition. J Clin Microbiol. 39:3499–3504. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Weil A, Plikaytis BB, Butler WR, Woodley
CL and Shinnick TM: The mtp40 gene is not present in all strains of
Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 34:2309–2311.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|