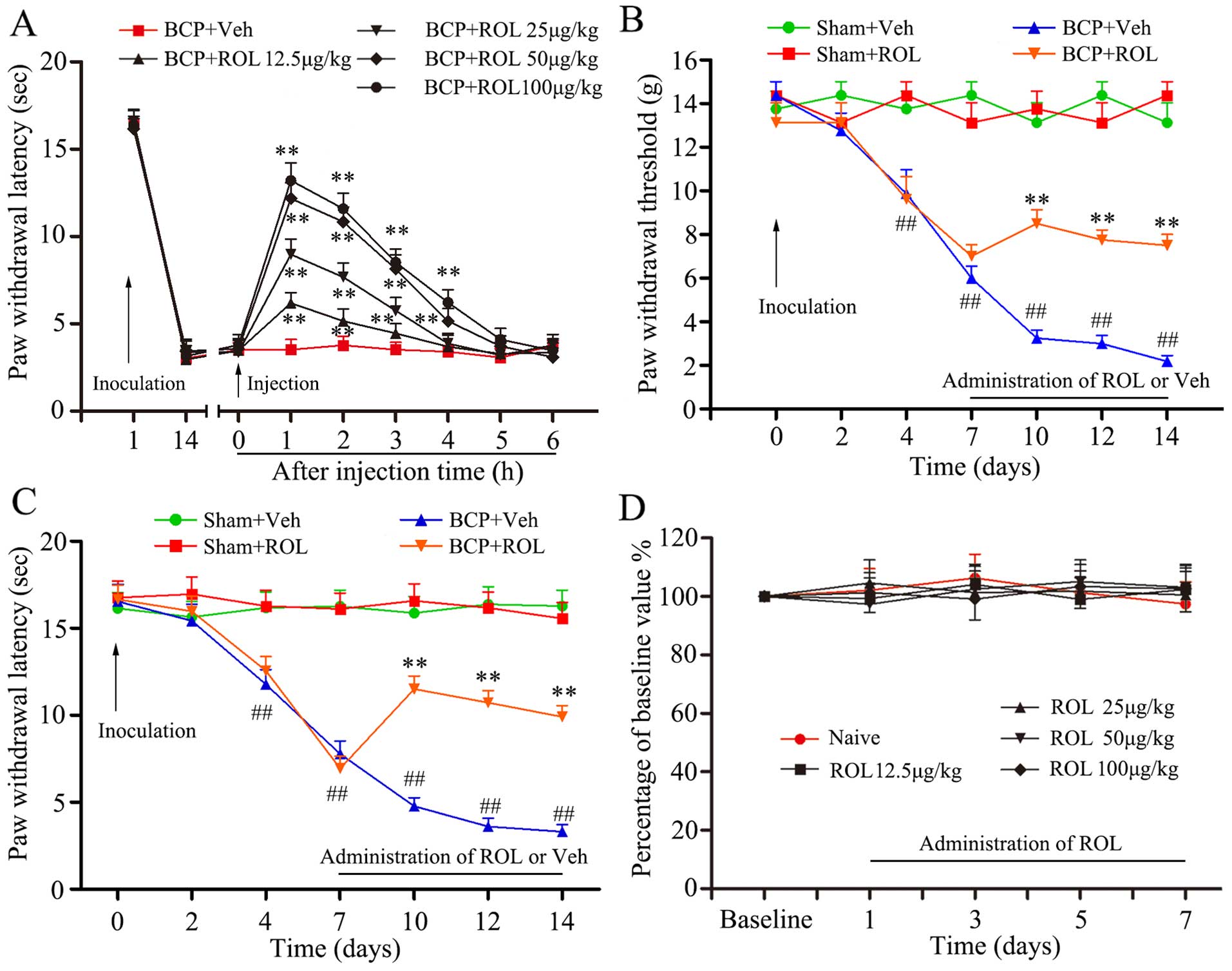
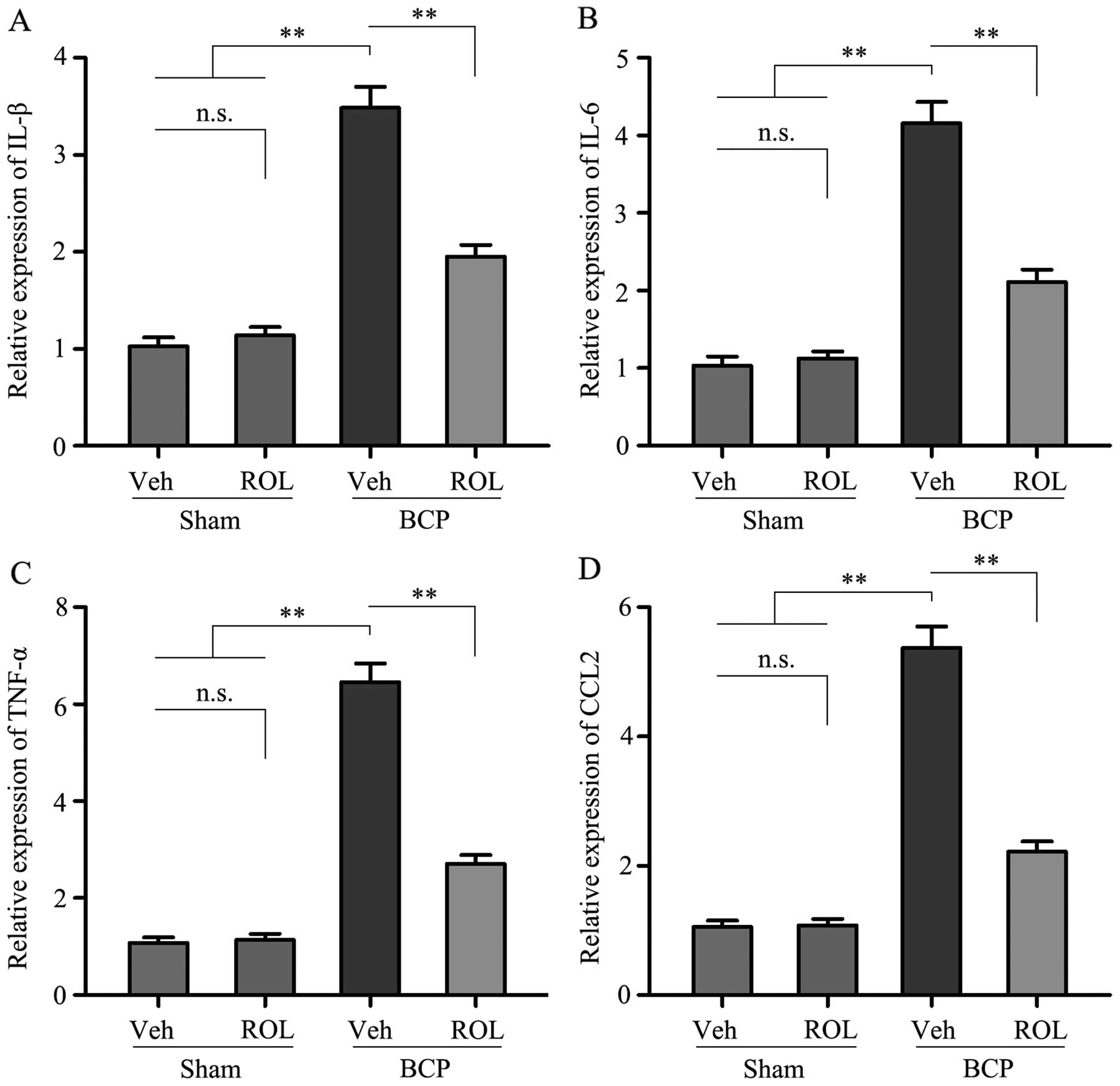
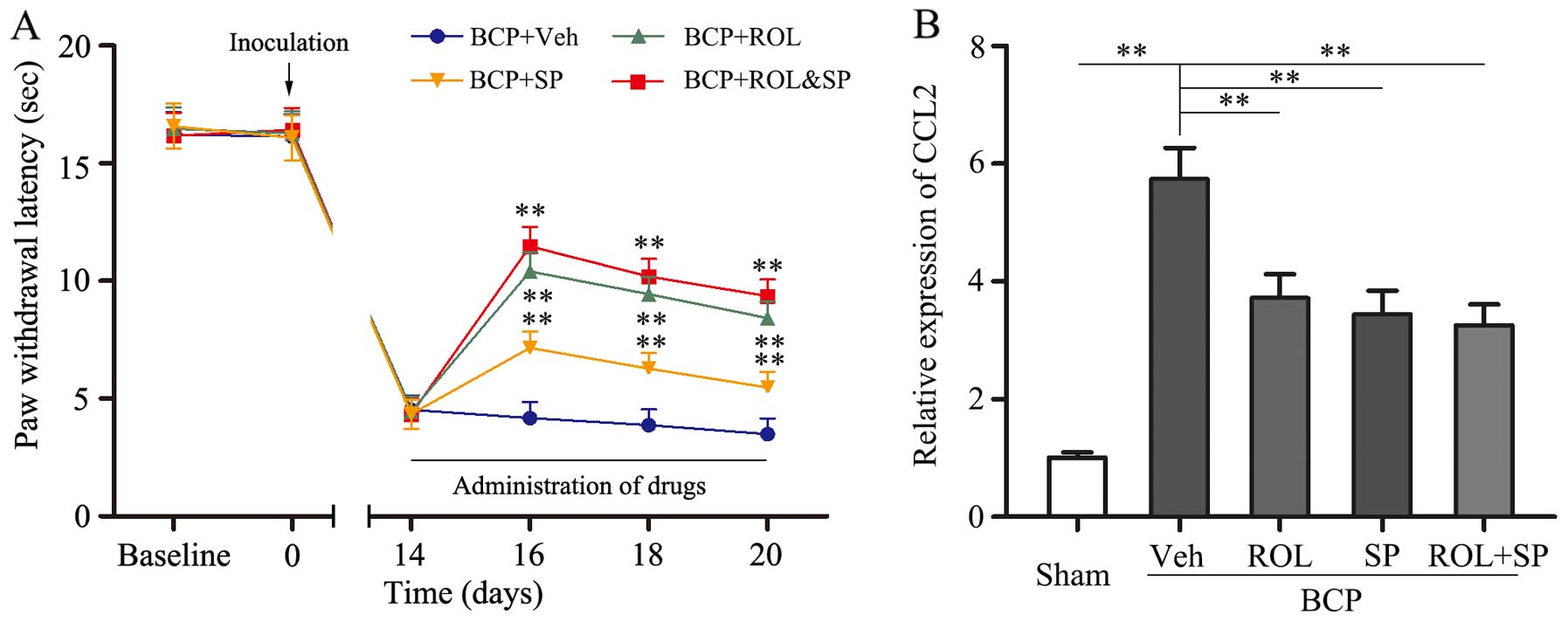
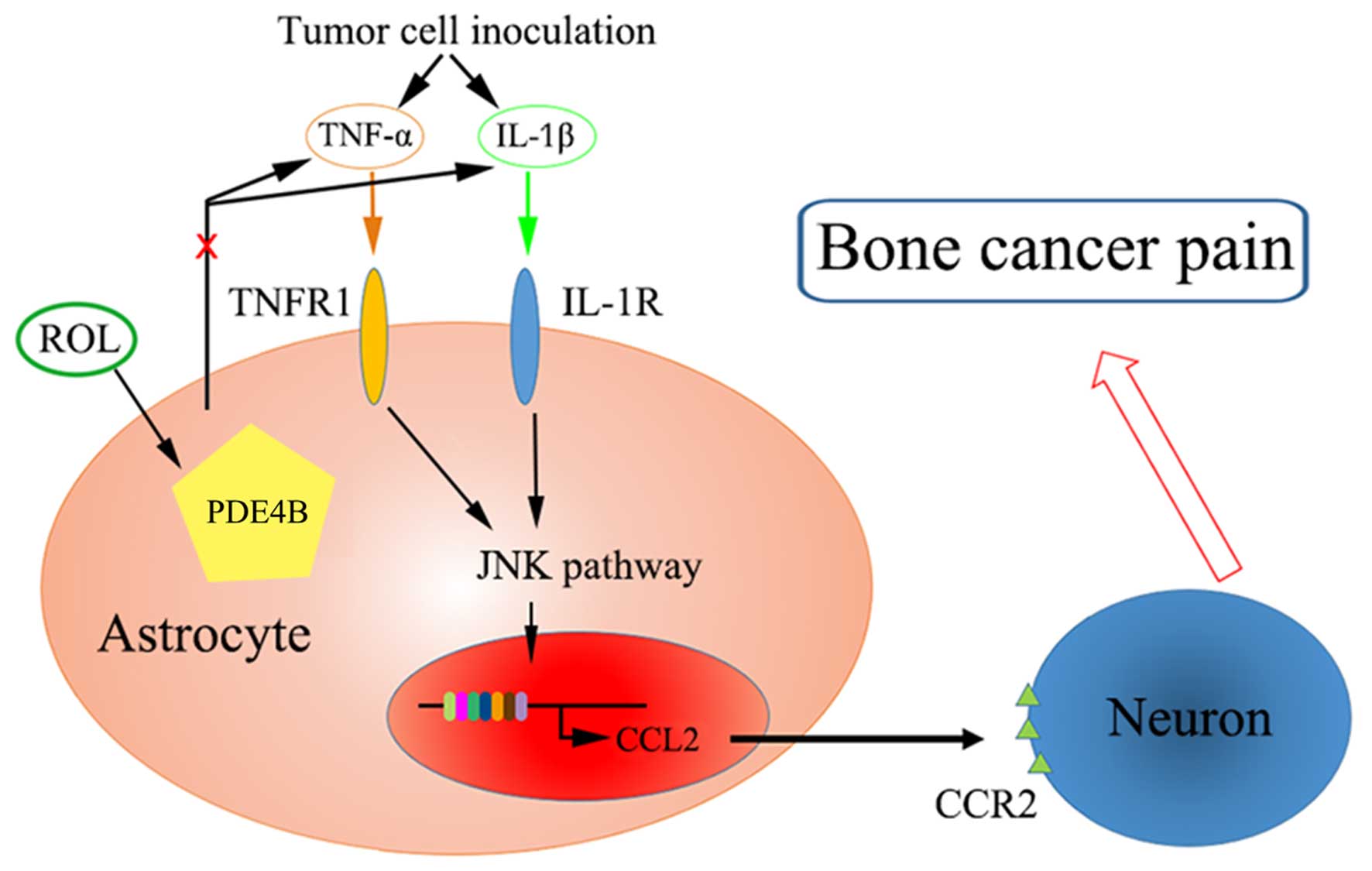
|
1
|
Lozano-Ondoua AN, Symons-Liguori AM and
Vanderah TW: Cancer-induced bone pain: Mechanisms and models.
Neurosci Lett. 557:52–59. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bennett MI, Rayment C, Hjermstad M, Aass
N, Caraceni A and Kaasa S: Prevalence and aetiology of neuropathic
pain in cancer patients: A systematic review. Pain. 153:359–365.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mantyh PW: Cancer pain and its impact on
diagnosis, survival and quality of life. Nat Rev Neurosci.
7:797–809. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ji RR, Berta T and Nedergaard M: Glia and
pain: Is chronic pain a gliopathy? Pain. 154(Suppl 1): S10–S28.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang Y, Li H, Li TT, Luo H, Gu XY, Lü N,
Ji RR and Zhang YQ: Delayed activation of spinal microglia
contributes to the maintenance of bone cancer pain in female Wistar
rats via P2X7 receptor and IL-18. J Neurosci. 35:7950–7963. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Remeniuk B, Sukhtankar D, Okun A,
Navratilova E, Xie JY, King T and Porreca F: Behavioral and
neurochemical analysis of ongoing bone cancer pain in rats. Pain.
156:1864–1873. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Oprée A and Kress M: Involvement of the
proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha, IL-1 beta,
and IL-6 but not IL-8 in the development of heat hyperalgesia:
Effects on heat-evoked calcitonin gene-related peptide release from
rat skin. J Neurosci. 20:6289–6293. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chichorro JG, Lorenzetti BB and Zampronio
AR: Involvement of bradykinin, cytokines, sympathetic amines and
prostaglandins in formalin-induced orofacial nociception in rats.
Br J Pharmacol. 141:1175–1184. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhou L, Huang J, Gao J, Zhang G and Jiang
J: NMDA and AMPA receptors in the anterior cingulate cortex
mediates visceral pain in visceral hypersensitivity rats. Cell
Immunol. 287:86–90. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guo W, Miyoshi K, Dubner R, Gu M, Li M,
Liu J, Yang J, Zou S, Ren K, Noguchi K and Wei F: Spinal 5-HT3
receptors mediate descending facilitation and contribute to
behavioral hypersensitivity via a reciprocal neuron-glial signaling
cascade. Mol Pain. 10:352014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang XW, Hu S, Mao-Ying QL, Li Q, Yang CJ,
Zhang H, Mi WL, Wu GC and Wang YQ: Activation of c-jun N-terminal
kinase in spinal cord contributes to breast cancer induced bone
pain in rats. Mol Brain. 5:212012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tang J, Zhu C, Li ZH, Liu XY, Sun SK,
Zhang T, Luo ZJ, Zhang H and Li WY: Inhibition of the spinal
astrocytic JNK/MCP-1 pathway activation correlates with the
analgesic effects of tanshinone IIA sulfonate in neuropathic pain.
J Neuroinflammation. 12:572015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Houslay MD and Adams DR: PDE4 cAMP
phosphodiesterases: Modular enzymes that orchestrate signalling
cross-talk, desensitization and compartmentalization. Biochem J.
370:1–18. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Pearse DD and Hughes ZA: PDE4B as a
microglia target to reduce neuroinflammation. Glia. 64:1698–1709.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kumar A, Jain NK and Kulkarni SK:
Analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of phosphodiesterase
inhibitors. Indian J Exp Biol. 38:26–30. 2000.
|
|
16
|
Francischi JN, Yokoro CM, Poole S, Tafuri
WL, Cunha FQ and Teixeira MM: Anti-inflammatory and analgesic
effects of the phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor rolipram in a rat
model of arthritis. Eur J Pharmacol. 399:243–249. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim HK, Kwon JY, Yoo C and Abdi S: The
analgesic effect of rolipram, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, on
chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Anesth Analg.
121:822–828. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rock EM, Benzaquen J, Limebeer CL and
Parker LA: Potential of the rat model of conditioned gaping to
detect nausea produced by rolipram, a phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4)
inhibitor. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 91:537–541. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Sanna MD, Ghelardini C and Galeotti N:
Blockade of the spinal BDNF-activated JNK pathway prevents the
development of anti-retroviral-induced neuropathic pain.
Neuropharmacology. 105:543–552. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Q, Wang J, Duan MT, Han SP, Zeng XY
and Wang JY: NF-κB, ERK, p38 MAPK and JNK contribute to the
initiation and/or maintenance of mechanical allodynia induced by
tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the red nucleus. Brain Res Bull.
99:132–139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hu XM, Liu YN, Zhang HL, Cao SB, Zhang T,
Chen LP and Shen W: CXCL12/CXCR4 chemokine signaling in spinal glia
induces pain hypersensitivity through MAPKs-mediated
neuroinflammation in bone cancer rats. J Neurochem. 132:452–463.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wu HH, Yin JB, Zhang T, Cui YY, Dong YL,
Chen GZ and Wang W: Inhibiting spinal neuron-astrocytic activation
correlates with synergistic analgesia of dexmedetomidine and
ropivacaine. PLoS One. 9:e923742014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu S, Liu YP, Song WB and Song XJ:
EphrinB-EphB receptor signaling contributes to bone cancer pain via
Toll-like receptor and proinflammatory cytokines in rat spinal
cord. Pain. 154:2823–2835. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dixon WJ: Efficient analysis of
experimental observations. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 20:441–462.
1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, Flores C
and Joris J: A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal
nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain. 32:77–88. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hamm RJ, Pike BR, O'Dell DM, Lyeth BG and
Jenkins LW: The rotarod test: An evaluation of its effectiveness in
assessing motor deficits following traumatic brain injury. J
Neurotrauma. 11:187–196. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mei XP, Zhang H, Wang W, Wei YY, Zhai MZ,
Wang W, Xu LX and Li YQ: Inhibition of spinal astrocytic c-Jun
N-terminal kinase (JNK) activation correlates with the analgesic
effects of ketamine in neuropathic pain. J Neuroinflammation.
8:62011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gao YJ and Ji RR: Activation of JNK
pathway in persistent pain. Neurosci Lett. 437:180–183. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li ZY, Zhang YP, Zhang J, Zhang SB, Li D,
Huang ZZ and Xin WJ: The possible involvement of JNK activation in
the spinal dorsal horn in bortezomib-induced allodynia: the role of
TNF-α and IL-1β. J Anesth. 30:55–63. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang ZZ, Zhang Y, Liu YQ, Zhao N, Zhang
YZ, Yuan L, An L, Li J, Wang XY, Qin JJ, et al: RNA
interference-mediated phosphodiesterase 4D splice variants
knock-down in the prefrontal cortex produces antidepressant-like
and cognition-enhancing effects. Br J Pharmacol. 168:1001–1014.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
García-Osta A, Cuadrado-Tejedor M,
García-Barroso C, Oyarzábal J and Franco R: Phosphodiesterases as
therapeutic targets for Alzheimer's disease. ACS Chem Neurosci.
3:832–844. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang ZZ, Yang WX, Zhang Y, Zhao N, Zhang
YZ, Liu YQ, Xu Y, Wilson SP, O'Donnell JM, Zhang HT and Li YF:
Phosphodiesterase-4D knock-down in the prefrontal cortex alleviates
chronic unpredictable stress-induced depressive-like behaviors and
memory deficits in mice. Sci Rep. 5:113322015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Huang Z and Mancini JA: Phosphodiesterase
4 inhibitors for the treatment of asthma and COPD. Curr Med Chem.
13:3253–3262. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bolger GB, Dunlop AJ, Meng D, Day JP,
Klussmann E, Baillie GS, Adams DR and Houslay MD: Dimerization of
cAMP phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) in living cells requires interfaces
located in both the UCR1 and catalytic unit domains. Cell Signal.
27:756–769. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Christiansen SH, Selige J, Dunkern T,
Rassov A and Leist M: Combined anti-inflammatory effects of
β2-adrenergic agonists and PDE4 inhibitors on astrocytes by
upregulation of intracellular cAMP. Neurochem Int. 59:837–846.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ji Q, Di Y, He X, Liu Q, Liu J, Li W and
Zhang L: Intrathecal injection of phosphodiesterase 4B-specific
siRNA attenuates neuropathic pain in rats with L5 spinal nerve
ligation. Mol Med Rep. 13:1914–1922. 2016.
|
|
37
|
Nunes AR, Sample V, Xiang YK, Monteiro EC,
Gauda E and Zhang J: Effect of oxygen on phosphodiesterases (PDE) 3
and 4 isoforms and PKA activity in the superior cervical ganglia.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 758:287–294. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Perez-Aso M, Montesinos MC, Mediero A,
Wilder T, Schafer PH and Cronstein B: Apremilast, a novel
phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor, regulates inflammation
through multiple cAMP downstream effectors. Arthritis Res Ther.
17:2492015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Old EA, Clark AK and Malcangio M: The role
of glia in the spinal cord in neuropathic and inflammatory pain.
Handb Exp Pharmacol. 227:145–170. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Alfonso Romero-Sandoval E and Sweitzer S:
Nonneuronal central mechanisms of pain: Glia and immune response.
Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 131:325–358. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Romero-Alejo E, Puig MM and Romero A:
Inhibition of astrocyte activation is involved in the prevention of
postoperative latent pain sensitization by ketamine and gabapentin
in mice. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 7:22–24. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li W, Zhang Y, Xing C and Zhang M:
Tanshinone IIA represses inflammatory response and reduces
radiculopathic pain by inhibiting IRAK-1 and NF-κB/p38/JNK
signaling. Int Immunopharmacol. 28:382–389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gao YJ, Zhang L, Samad OA, Suter MR,
Yasuhiko K, Xu ZZ, Park JY, Lind AL, Ma Q and Ji RR: JNK-induced
MCP-1 production in spinal cord astrocytes contributes to central
sensitization and neuropathic pain. J Neurosci. 29:4096–4108. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lu Y, Jiang BC, Cao DL, Zhang ZJ, Zhang X,
Ji RR and Gao YJ: TRAF6 upregulation in spinal astrocytes maintains
neuropathic pain by integrating TNF-α and IL-1β signaling. Pain.
155:2618–2629. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lu C, Liu Y, Sun B, Sun Y, Hou B, Zhang Y,
Ma Z and Gu X: Intrathecal injection of JWH-015 attenuates bone
cancer pain via time-dependent modification of pro-inflammatory
cytokines expression and astrocytes activity in spinal cord.
Inflammation. 38:1880–1890. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pillarisetti S: Targeting interleukin-1β
for pain. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 10:571–575. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Narita M, Shimamura M, Imai S, Kubota C,
Yajima Y, Takagi T, Shiokawa M, Inoue T, Suzuki M and Suzuki T:
Role of interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha-dependent
expression of cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA in thermal hyperalgesia induced
by chronic inflammation in mice. Neuroscience. 152:477–486. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Pevida M, González-Rodríguez S, Lastra A,
García-Suárez O, Hidalgo A, Menéndez L and Baamonde A: Involvement
of spinal chemokine CCL2 in the hyperalgesia evoked by bone cancer
in mice: A role for astroglia and microglia. Cell Mol Neurobiol.
34:143–156. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|