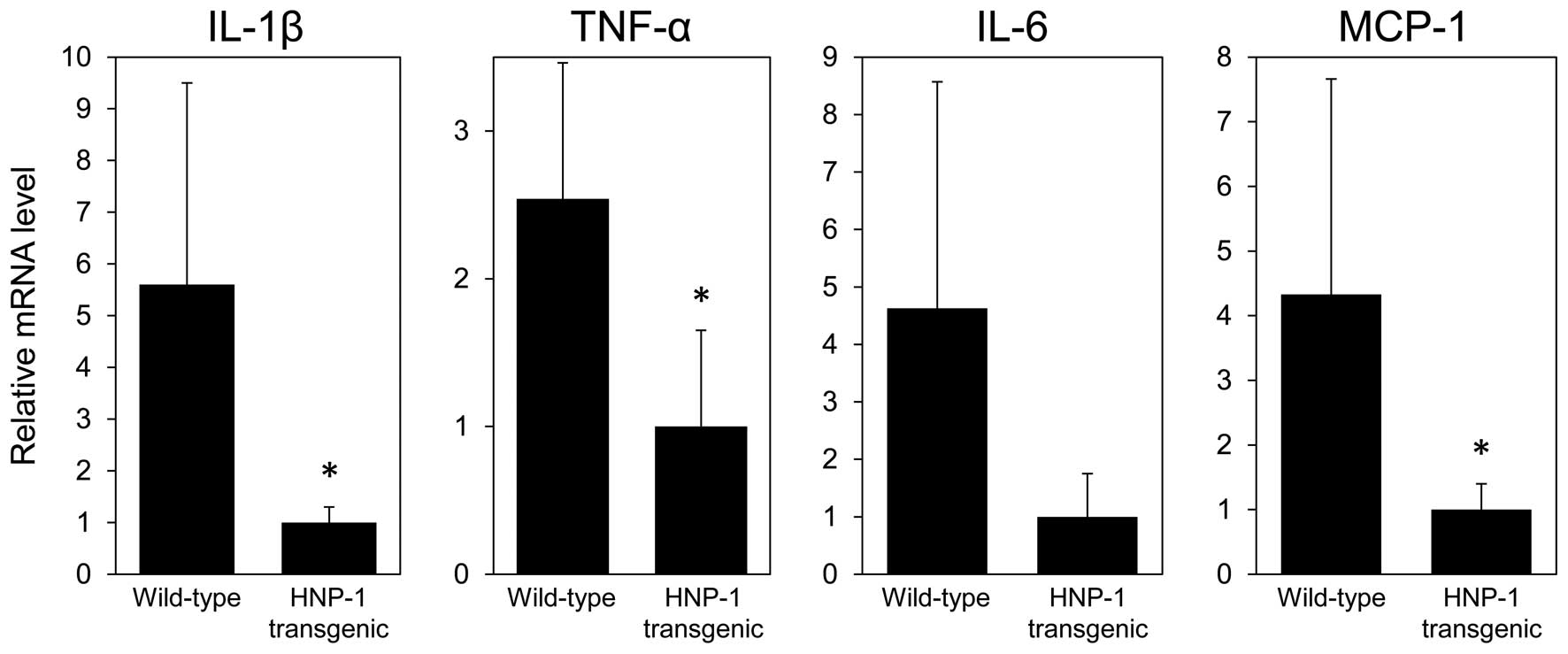
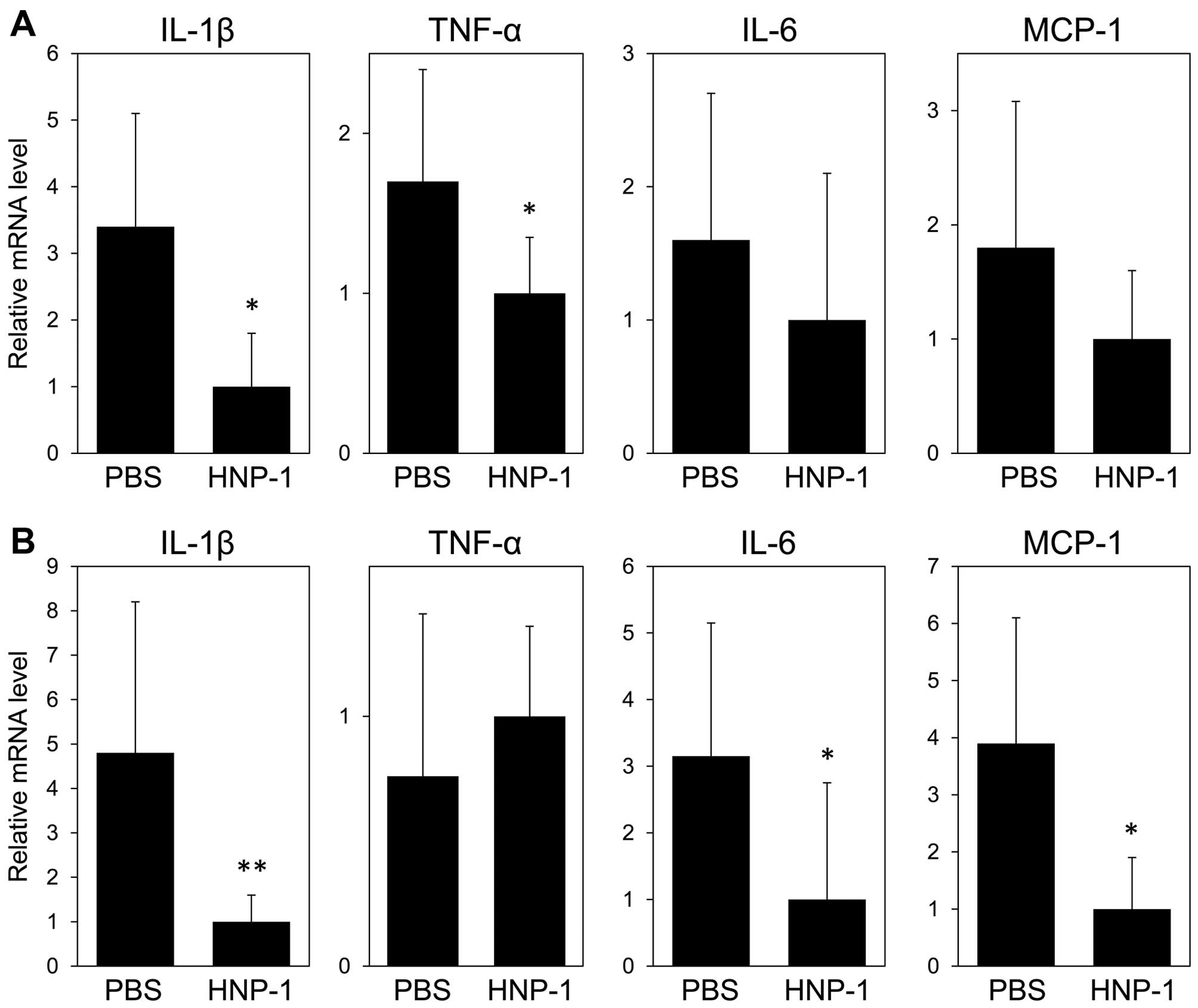
|
1
|
Fournier BM and Parkos CA: The role of
neutrophils during intestinal inflammation. Mucosal Immunol.
5:354–366. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Levy O: Antimicrobial proteins and
peptides: Anti-infective molecules of mammalian leukocytes. J
Leukoc Biol. 76:909–925. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Selsted ME, Harwig SS, Ganz T, Schilling
JW and Lehrer RI: Primary structures of three human neutrophil
defensins. J Clin Invest. 76:1436–1439. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wilde CG, Griffith JE, Marra MN, Snable JL
and Scott RW: Purification and characterization of human neutrophil
peptide 4, a novel member of the defensin family. J Biol Chem.
264:11200–11203. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ganz T, Selsted ME, Szklarek D, Harwig
SSL, Daher K, Bainton DF and Lehrer RI: Defensins. Natural peptide
antibiotics of human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 76:1427–1435.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lehrer RI, Ganz T, Szklarek D and Selsted
ME: Modulation of the in vitro candidacidal activity of human
neutrophil defensins by target cell metabolism and divalent
cations. J Clin Invest. 81:1829–1835. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Daher KA, Selsted ME and Lehrer RI: Direct
inactivation of viruses by human granulocyte defensins. J Virol.
60:1068–1074. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Turner J, Cho Y, Dinh NN, Waring AJ and
Lehrer RI: Activities of LL-37, a cathelin-associated antimicrobial
peptide of human neutrophils. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
42:2206–2214. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Territo MC, Ganz T, Selsted ME and Lehrer
R: Monocyte-chemotactic activity of defensins from human
neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 84:2017–2020. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang D, Chen Q, Chertov O and Oppenheim
JJ: Human neutrophil defensins selectively chemoattract naive T and
immature dendritic cells. J Leukoc Biol. 68:9–14. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Murphy CJ, Foster BA, Mannis MJ, Selsted
ME and Reid TW: Defensins are mitogenic for epithelial cells and
fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 155:408–413. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Aarbiou J, Ertmann M, van Wetering S, van
Noort P, Rook D, Rabe KF, Litvinov SV, van Krieken JH, de Boer WI
and Hiemstra PS: Human neutrophil defensins induce lung epithelial
cell proliferation in vitro. J Leukoc Biol. 72:167–174.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Müller CA, Markovic-Lipkovski J, Klatt T,
Gamper J, Schwarz G, Beck H, Deeg M, Kalbacher H, Widmann S,
Wessels JT, et al: Human alpha-defensins HNPs-1, -2, and -3 in
renal cell carcinoma: Influences on tumor cell proliferation. Am J
Pathol. 160:1311–1324. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hashimoto S, Uto H, Kanmura S, Sakiyama T,
Oku M, Iwashita Y, Ibusuki R, Sasaki F, Ibusuki K, Takami Y, et al:
Human neutrophil peptide-1 aggravates dextran sulfate
sodium-induced colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 18:667–675. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lehrer RI: Questions and answers about
defensins. Clin Infect Dis. 25:1141–1142. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Panyutich AV, Panyutich EA, Krapivin VA,
Baturevich EA and Ganz T: Plasma defensin concentrations are
elevated in patients with septicemia or bacterial meningitis. J Lab
Clin Med. 122:202–207. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Albrethsen J, Møller CH, Olsen J, Raskov H
and Gammeltoft S: Human neutrophil peptides 1, 2 and 3 are
biochemical markers for metastatic colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer.
42:3057–3064. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kanmura S, Uto H, Numata M, Hashimoto S,
Moriuchi A, Fujita H, Oketani M, Ido A, Kodama M, Ohi H and
Tsubouchi H: Human neutrophil peptides 1–3 are useful biomarkers in
patients with active ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis.
15:909–917. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Mukae H, Iiboshi H, Nakazato M, Hiratsuka
T, Tokojima M, Abe K, Ashitani J, Kadota J, Matsukura S and Kohno
S: Raised plasma concentrations of α-defensins in patients with
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax. 57:623–628. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ashitani J, Mukae H, Hiratsuka T, Nakazato
M, Kumamoto K and Matsukura S: Elevated levels of α-defensins in
plasma and BAL fluid of patients with active pulmonary
tuberculosis. Chest. 121:519–526. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xavier RJ and Podolsky DK: Unravelling the
pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 448:427–434.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Eisenhauer PB and Lehrer RI: Mouse
neutrophils lack defensins. Infect Immun. 60:3446–3447.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ibusuki R, Uto H, Arima S, Mawatari S,
Setoguchi Y, Iwashita Y, Hashimoto S, Maeda T, Tanoue S, Kanmura S,
et al: Transgenic expression of human neutrophil peptide-1 enhances
hepatic fibrosis in mice fed a choline-deficient, L-amino
acid-defined diet. Liver Int. 33:1549–1556. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Murthy SN, Cooper HS, Shim H, Shah RS,
Ibrahim SA and Sedergran DJ: Treatment of dextran sulfate
sodium-induced murine colitis by intracolonic cyclosporin. Dig Dis
Sci. 38:1722–1734. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cooper HS, Murthy SN, Shah RS and
Sedergran DJ: Clinicopathologic study of dextran sulfate sodium
experimental murine colitis. Lab Invest. 69:238–249.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kamada N, Hisamatsu T, Okamoto S, Sato T,
Matsuoka K, Arai K, Nakai T, Hasegawa A, Inoue N, Watanabe N, et
al: Abnormally differentiated subsets of intestinal macrophage play
a key role in Th1-dominant chronic colitis through excess
production of IL-12 and IL-23 in response to bacteria. J Immunol.
175:6900–6908. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shanahan MT, Tanabe H and Ouellette AJ:
Strain-specific polymorphisms in Paneth cell α-defensins of C57BL/6
mice and evidence of vestigial myeloid α-defensin pseudogenes.
Infect Immun. 79:459–473. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Perše M and Cerar A: Dextran sodium
sulphate colitis mouse model: Traps and tricks. J Biomed
Biotechnol. 2012:7186172012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Welling MM, Hiemstra PS, van den Barselaar
MT, Paulusma-Annema A, Nibbering PH, Pauwels EK and Calame W:
Antibacterial activity of human neutrophil defensins in
experimental infections in mice is accompanied by increased
leukocyte accumulation. J Clin Invest. 102:1583–1590. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chaly YV, Paleolog EM, Kolesnikova TS,
Tikhonov II, Petratchenko EV and Voitenok NN: Neutrophil
alpha-defensin human neutrophil peptide modulates cytokine
production in human monocytes and adhesion molecule expression in
endothelial cells. Eur Cytokine Netw. 11:257–266. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shi J, Aono S, Lu W, Ouellette AJ, Hu X,
Ji Y, Wang L, Lenz S, van Ginkel FW, Liles M, et al: A novel role
for defensins in intestinal homeostasis: Regulation of IL-1β
secretion. J Immunol. 179:1245–1253. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kohlgraf KG, Ackermann A, Lu X, Burnell K,
Bélanger M, Cavanaugh JE, Xie H, Progulske-Fox A and Brogden KA:
Defensins attenuate cytokine responses yet enhance antibody
responses to Porphyromonas gingivalis adhesins in mice. Future
Microbiol. 5:115–125. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Miles K, Clarke DJ, Lu W, Sibinska Z,
Beaumont PE, Davidson DJ, Barr TA, Campopiano DJ and Gray M: Dying
and necrotic neutrophils are anti-inflammatory secondary to the
release of α-defensins. J Immunol. 183:2122–2132. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kuhn KA, Manieri NA, Liu TC and
Stappenbeck TS: IL-6 stimulates intestinal epithelial proliferation
and repair after injury. PLoS One. 9:e1141952014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Murai M, Turovskaya O, Kim G, Madan R,
Karp CL, Cheroutre H and Kronenberg M: Interleukin 10 acts on
regulatory T cells to maintain expression of the transcription
factor Foxp3 and suppressive function in mice with colitis. Nat
Immunol. 10:1178–1184. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ibusuki K, Sakiyama T, Kanmura S, Maeda T,
Iwashita Y, Nasu Y, Sasaki F, Taguchi H, Hashimoto S, Numata M, et
al: Human neutrophil peptides induce interleukin-8 in intestinal
epithelial cells through the P2 receptor and ERK1/2 signaling
pathways. Int J Mol Med. 35:1603–1609. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Scott MG, Davidson DJ, Gold MR, Bowdish D
and Hancock RE: The human antimicrobial peptide LL-37 is a
multifunctional modulator of innate immune responses. J Immunol.
169:3883–3891. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shaykhiev R, Beisswenger C, Kändler K,
Senske J, Püchner A, Damm T, Behr J and Bals R: Human endogenous
antibiotic LL-37 stimulates airway epithelial cell proliferation
and wound closure. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
289:L842–L848. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Aarbiou J, Verhoosel RM, Van Wetering S,
De Boer WI, Van Krieken JH, Litvinov SV, Rabe KF and Hiemstra PS:
Neutrophil defensins enhance lung epithelial wound closure and
mucin gene expression in vitro. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
30:193–201. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Nagaoka I, Suzuki K, Niyonsaba F, Tamura H
and Hirata M: Modulation of neutrophil apoptosis by antimicrobial
peptides. ISRN Microbiol. 2012:3457912012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Schauber J, Rieger D, Weiler F, Wehkamp J,
Eck M, Fellermann K, Scheppach W, Gallo RL and Stange EF:
Heterogeneous expression of human cathelicidin hCAP18/LL-37 in
inflammatory bowel diseases. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
18:615–621. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Brannigan AE, O'Connell PR, Hurley H,
O'Neill A, Brady HR, Fitzpatrick JM and Watson RW: Neutrophil
apoptosis is delayed in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
Shock. 13:361–366. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Altznauer F, Martinelli S, Yousefi S,
Thürig C, Schmid I, Conway EM, Schöni MH, Vogt P, Mueller C, Fey
MF, et al: Inflammation-associated cell cycle-independent block of
apoptosis by survivin in terminally differentiated neutrophils. J
Exp Med. 199:1343–1354. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liles WC, Dale DC and Klebanoff SJ:
Glucocorticoids inhibit apoptosis of human neutrophils. Blood.
86:3181–3188. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Amulic B, Cazalet C, Hayes GL, Metzler KD
and Zychlinsky A: Neutrophil function: From mechanisms to disease.
Annu Rev Immunol. 30:459–489. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sacco R, Romano A, Mazzoni A, Bertini M,
Federici G, Metrangolo S, Parisi G, Nencini C, Giampietro C,
Bertoni M, et al: Granulocytapheresis in steroid-dependent and
steroid-resistant patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A
prospective observational study. J Crohn's Colitis. 7:e692–e697.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|