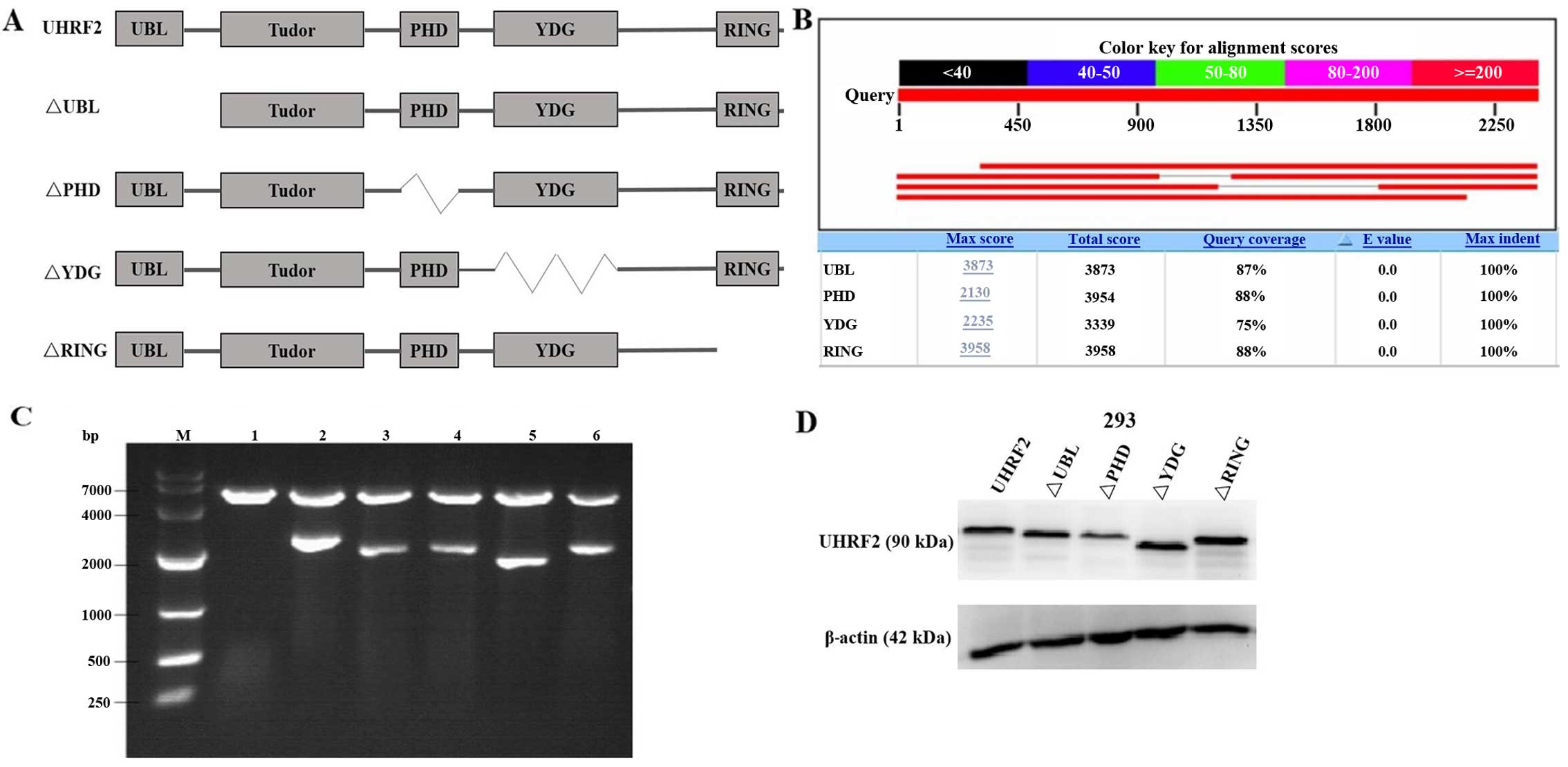
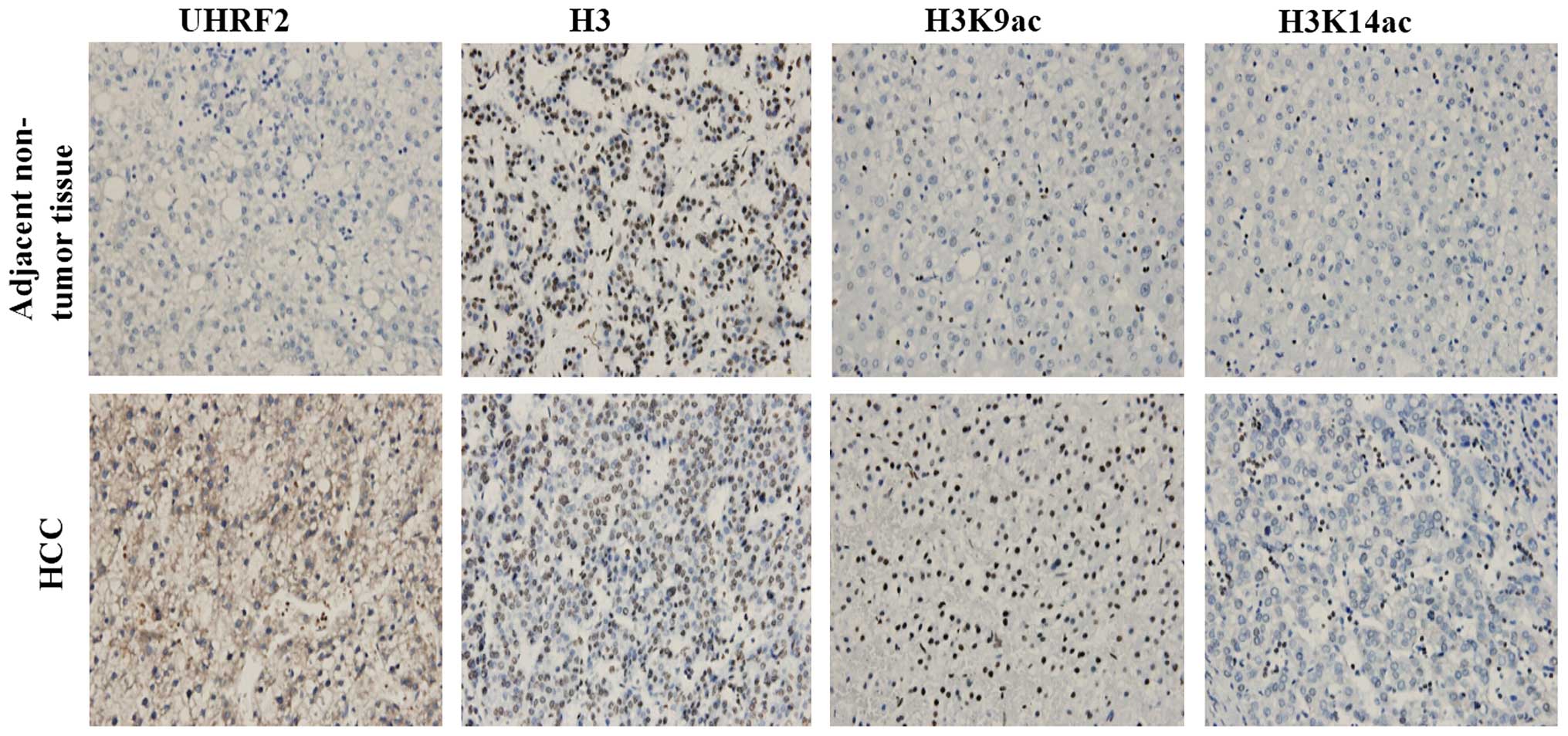
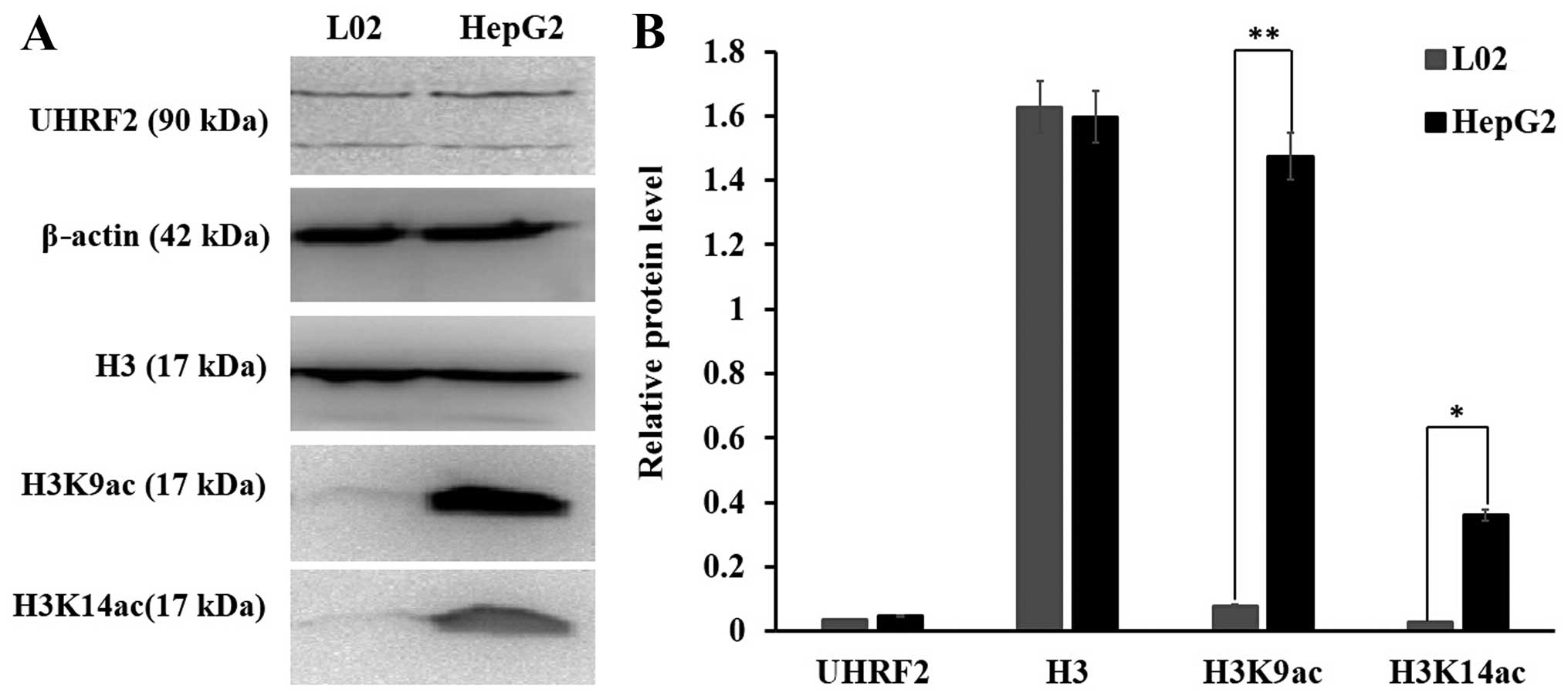
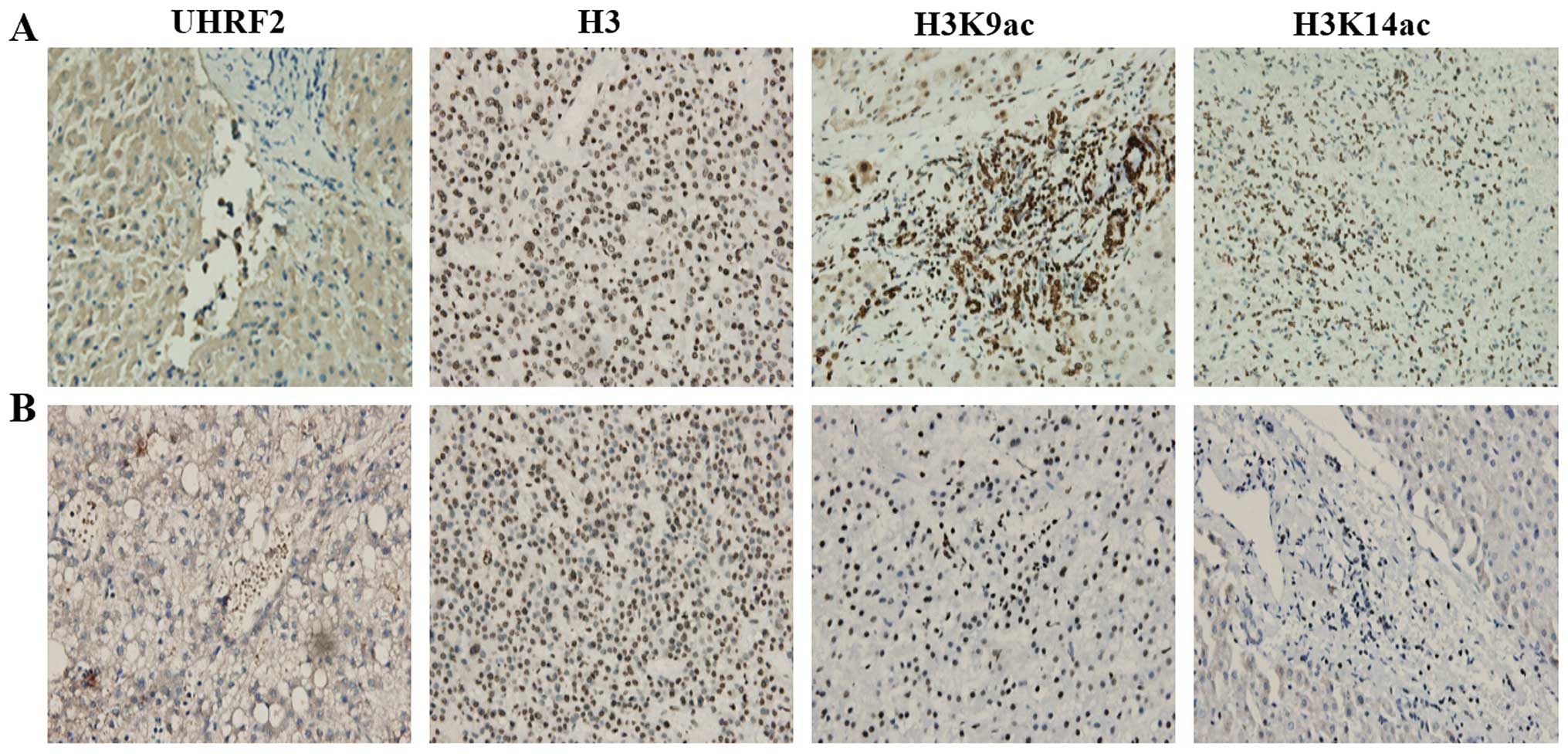
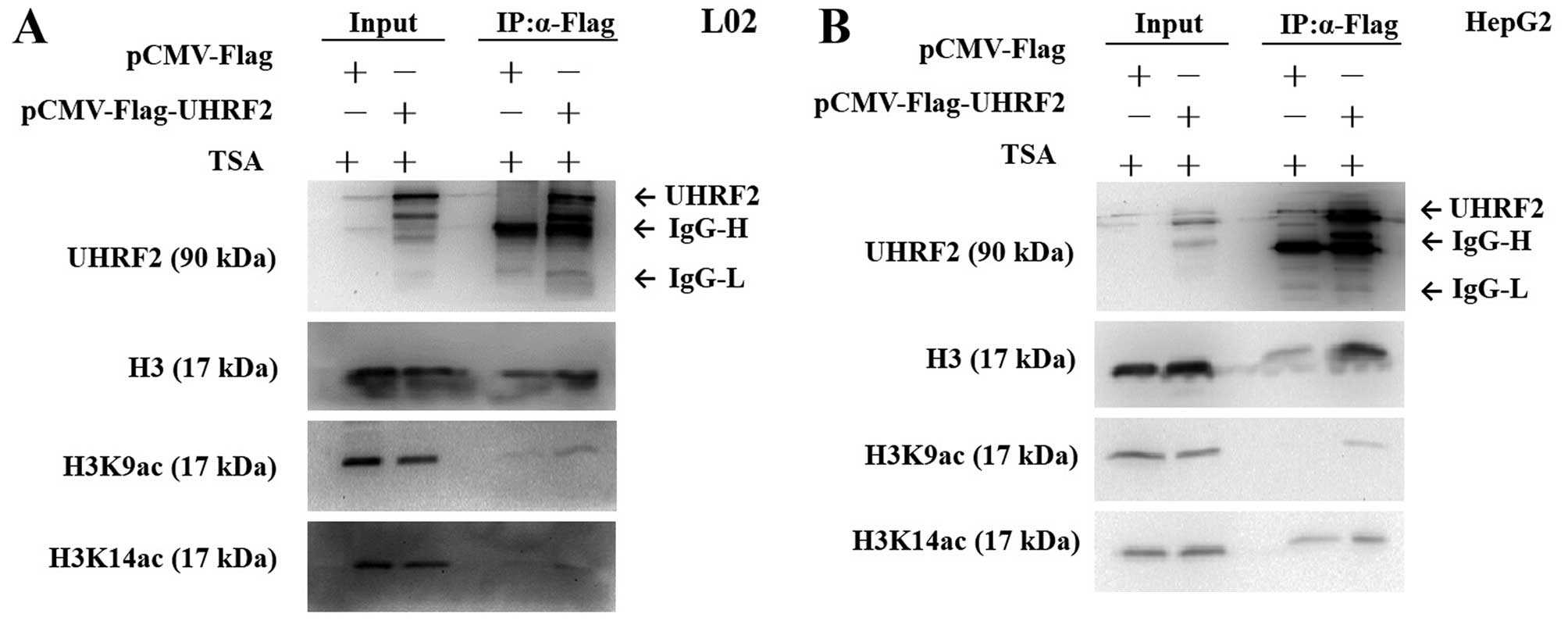
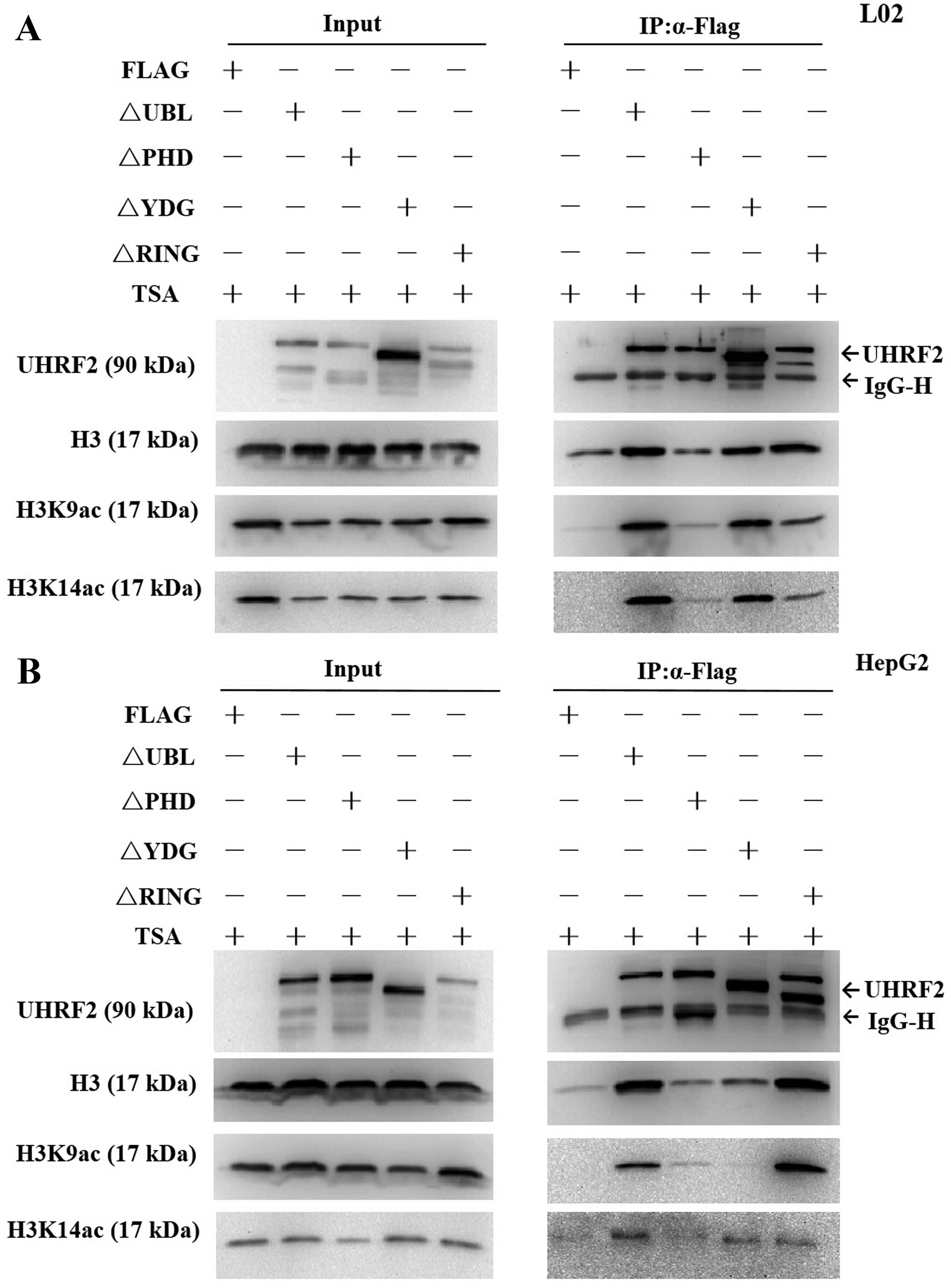
|
1
|
Ma L, Chua MS, Andrisani O and So S:
Epigenetics in hepatocellular carcinoma: An update and future
therapy perspectives. World J Gastroenterol. 20:333–345. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Puszyk WM, Trinh TL, Chapple SJ and Liu C:
Linking metabolism and epigenetic regulation in development of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Lab Invest. 93:983–990. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kratz A, Arner E, Saito R, Kubosaki A,
Kawai J, Suzuki H, Carninci P, Arakawa T, Tomita M, Hayashizaki Y
and Daub CO: Core promoter structure and genomic context reflect
histone 3 lysine 9 acetylation patterns. BMC Genomics. 11:2572010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shahbazian MD and Grunstein M: Functions
of site-specific histone acetylation and deacetylation. Annu Rev
Biochem. 76:75–100. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Elsheikh SE, Green AR, Rakha EA, Powe DG,
Ahmed RA, Collins HM, Soria D, Garibaldi JM, Paish CE, Ammar AA, et
al: Global histone modifications in breast cancer correlate with
tumor phenotypes, prognostic factors, and patient outcome. Cancer
Res. 69:3802–3809. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
He C, Xu J, Zhang J, Xie D, Ye H, Xiao Z,
Cai M, Xu K, Zeng Y, Li H and Wang J: High expression of
trimethylated histone H3 lysine 4 is associated with poor prognosis
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 43:1425–1435. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Neureiter D, Jäger T, Ocker M and
Kiesslich T: Epigenetics and pancreatic cancer: Pathophysiology and
novel treatment aspects. World J Gastroenterol. 20:7830–7848. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hung SY, Lin HH, Yeh KT and Chang JG:
Histone-modifying genes as biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:2496–2507. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Karmodiya K, Krebs AR, Oulad-Abdelghani M,
Kimura H and Tora L: H3K9 and H3K14 acetylation co-occur at many
gene regulatory elements, while H3K14ac marks a subset of inactive
inducible promoters in mouse embryonic stem cells. BMC Genomics.
13:4242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pokholok DK, Harbison CT, Levine S, Cole
M, Hannett NM, Lee TI, Bell GW, Walker K, Rolfe PA, Herbolsheimer
E, et al: Genome-wide map of nucleosome acetylation and methylation
in yeast. Cell. 122:517–527. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang Z, Zang C, Rosenfeld JA, Schones DE,
Barski A, Cuddapah S, Cui K, Roh TY, Peng W, Zhang MQ and Zhao K:
Combinatorial patterns of histone acetylations and methylations in
the human genome. Nat Genet. 40:897–903. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mori T, Ikeda DD, Yamaguchi Y and Unoki M:
NIRF/UHRF2 occupies a central position in the cell cycle network
and allows coupling with the epigenetic landscape. FEBS Lett.
586:1570–1583. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang J, Gao Q, Li P, Liu X, Jia Y, Wu W,
Li J, Dong S, Koseki H and Wong J: S phase-dependent interaction
with DNMT1 dictates the role of UHRF1 but not UHRF2 in DNA
methylation maintenance. Cell Res. 21:1723–1739. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bronner C, Achour M, Arima Y, Chataigneau
T, Saya H and Schini-Kerth VB: The UHRF family: Oncogenes that are
drugable targets for cancer therapy in the near future? Pharmacol
Ther. 115:419–434. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Karagianni P, Amazit L, Qin J and Wong J:
ICBP90, a novel methyl K9 H3 binding protein linking protein
ubiquitination with heterochromatin formation. Mol Cell Biol.
28:705–717. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Pichler G, Wolf P, Schmidt CS, Meilinger
D, Schneider K, Frauer C, Fellinger K, Rottach A and Leonhardt H:
Cooperative DNA and histone binding by Uhrf2 links the two major
repressive epigenetic pathways. J Cell Biochem. 112:2585–2593.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qian G, Jin F, Chang L, Yang Y, Peng H and
Duan C: NIRF, a novel ubiquitin ligase, interacts with hepatitis B
virus core protein and promotes its degradation. Biotechnol Lett.
34:29–36. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Qian G, Hu B, Zhou D, Xuan Y, Bai L and
Duan C: NIRF, a novel ubiquitin ligase, inhibits hepatitis B virus
replication through effect on HBV core protein and H3 histones. DNA
Cell Biol. 34:327–332. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lu JC, Chang YT, Wang CT, Lin YC, Lin CK
and Wu ZS: Trichostatin A modulates thiazolidinedione-mediated
suppression of tumor necrosis factor α-induced lipolysis in 3T3-L1
adipocytes. PLoS One. 8:e715172013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sailaja BS, Cohen-Carmon D, Zimmerman G,
Soreq H and Meshorer E: Stress-induced epigenetic transcriptional
memory of acetylcholinesterase by HDAC4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:E3687–E3695. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Musselman CA and Kutateladze TG:
Handpicking epigenetic marks with PHD fingers. Nucleic Acids Res.
39:9061–9071. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
He X, Duan C, Chen J, Ou-Yang X, Zhang Z,
Li C and Peng H: Let-7a elevates p21(WAF1) levels by targeting of
NIRF and suppresses the growth of A549 lung cancer cells. FEBS
Lett. 583:3501–3507. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu J, Liu S, Liu G, Dombkowski A, Abrams
J, Martin-Trevino R, Wicha MS, Ethier SP and Yang ZQ:
Identification and functional analysis of 9p24 amplified genes in
human breast cancer. Oncogene. 333–341. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang F, Zhang P, Ma Y, Yang J, Moyer MP,
Shi C, Peng J and Qin H: NIRF is frequently upregulated in
colorectal cancer and its oncogenicity can be suppressed by let-7a
microRNA. Cancer Lett. 314:223–231. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lu S, Yan D, Wu Z, Jiang T, Chen J, Yuan
L, Lin J, Peng Z and Tang H: Ubiquitin-like with PHD and ring
finger domains 2 is a predictor of survival and a potential
therapeutic target in colon cancer. Oncol Rep. 31:1802–1810.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu TF, Zhang W, Su ZP, Chen SS, Chen GL,
Wei YX, Sun T, Xie XS, Li B, Zhou YX, et al: UHRF2 mRNA expression
is low in malignant glioma but silencing inhibits the growth of
U251 glioma cells in vitro. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:5137–5142.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Venturelli S, Armeanu S, Pathil A, Hsieh
CJ, Weiss TS, Vonthein R, Wehrmann M, Gregor M, Lauer UM and Bitzer
M: Epigenetic combination therapy as a tumor-selective treatment
approach for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 109:2132–2141. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nightingale KP, Gendreizig S, White DA,
Bradbury C, Hollfelder F and Turner BM: Cross-talk between histone
modifications in response to histone deacetylase inhibitors: MLL4
links histone H3 acetylation and histone H3K4 methylation. J Biol
Chem. 282:4408–4416. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Luo T, Cui S, Bian C and Yu X: Uhrf2 is
important for DNA damage response in vascular smooth muscle cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 441:65–70. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rajakumara E, Wang Z, Ma H, Hu L, Chen H,
Lin Y, Guo R, Wu F, Li H, Lan F, et al: PHD finger recognition of
unmodified histone H3R2 links UHRF1 to regulation of euchromatic
gene expression. Mol Cell. 43:275–284. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Citterio E, Papait R, Nicassio F, Vecchi
M, Gomiero P, Mantovani R, Di Fiore PP and Bonapace IM: Np95 is a
histone-binding protein endowed with ubiquitin ligase activity. Mol
Cell Biol. 24:2526–2535. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|