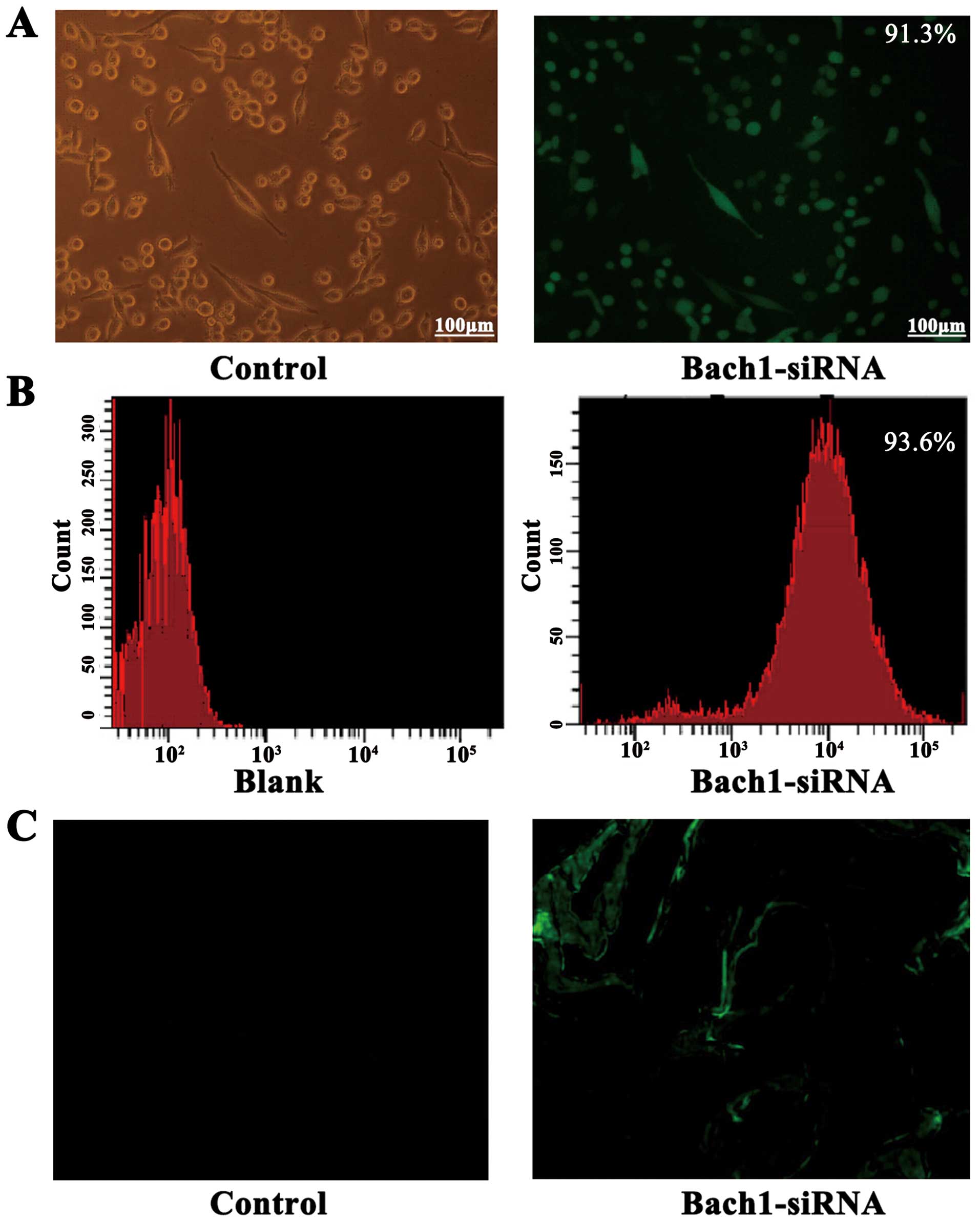
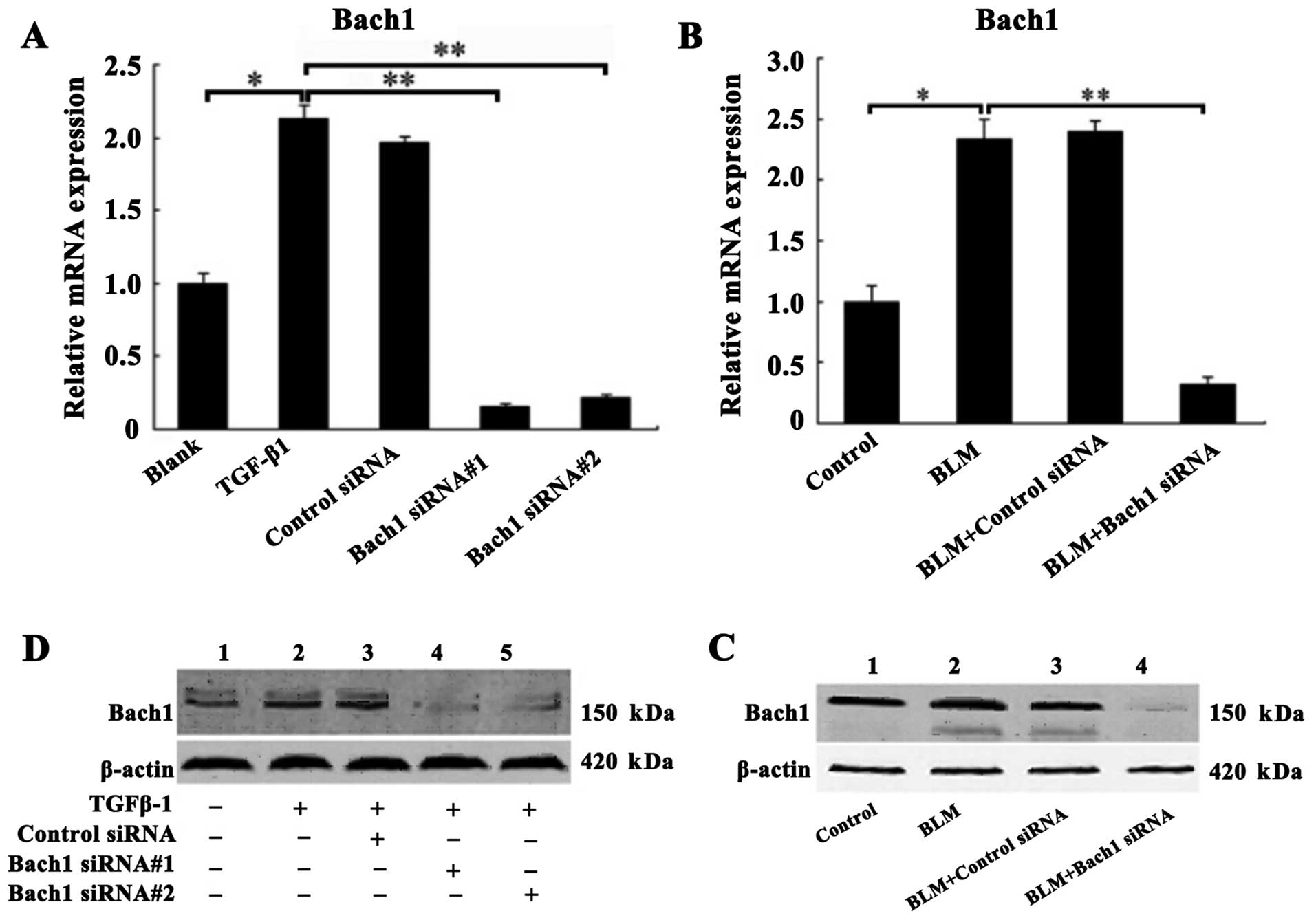
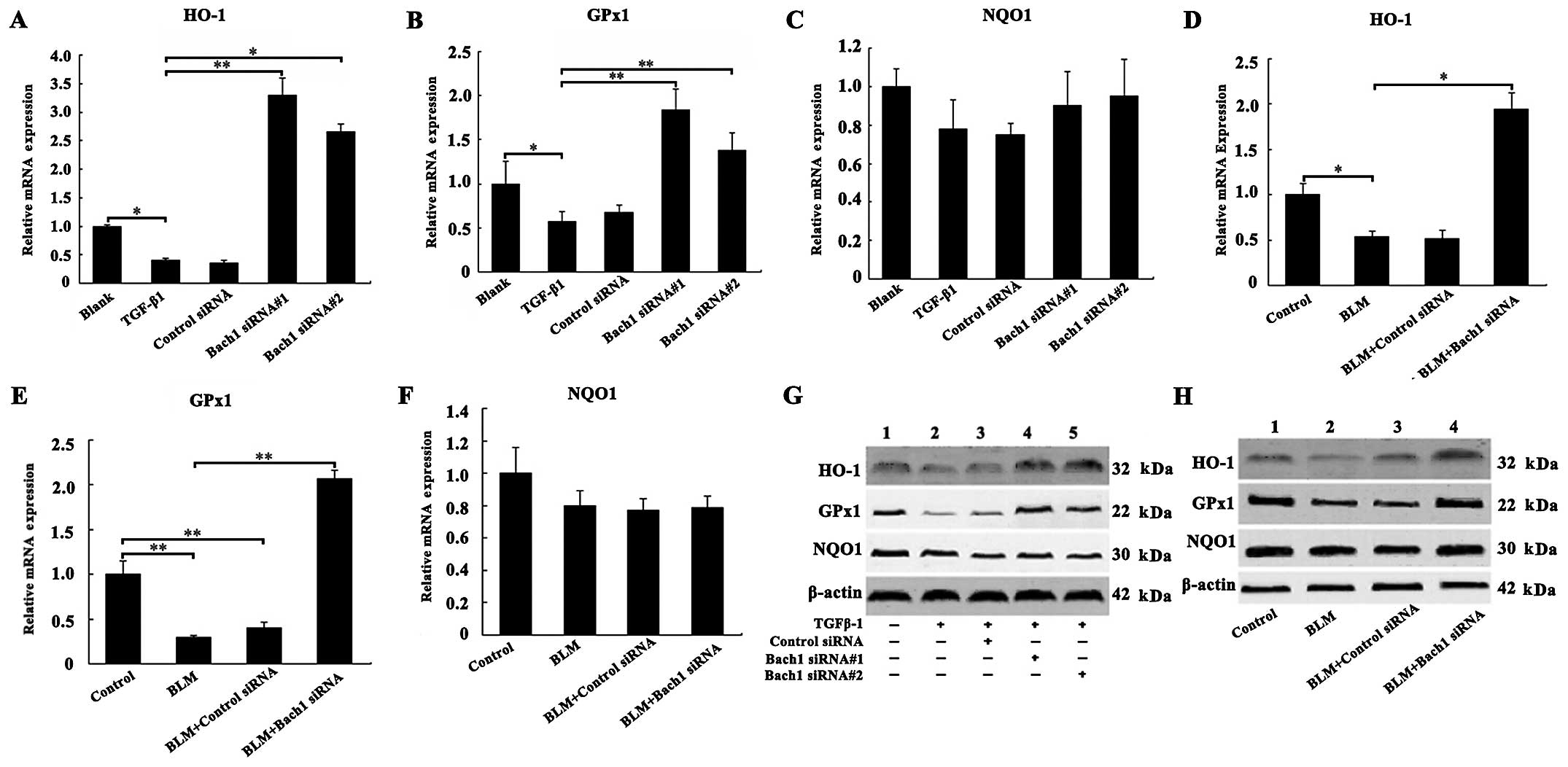
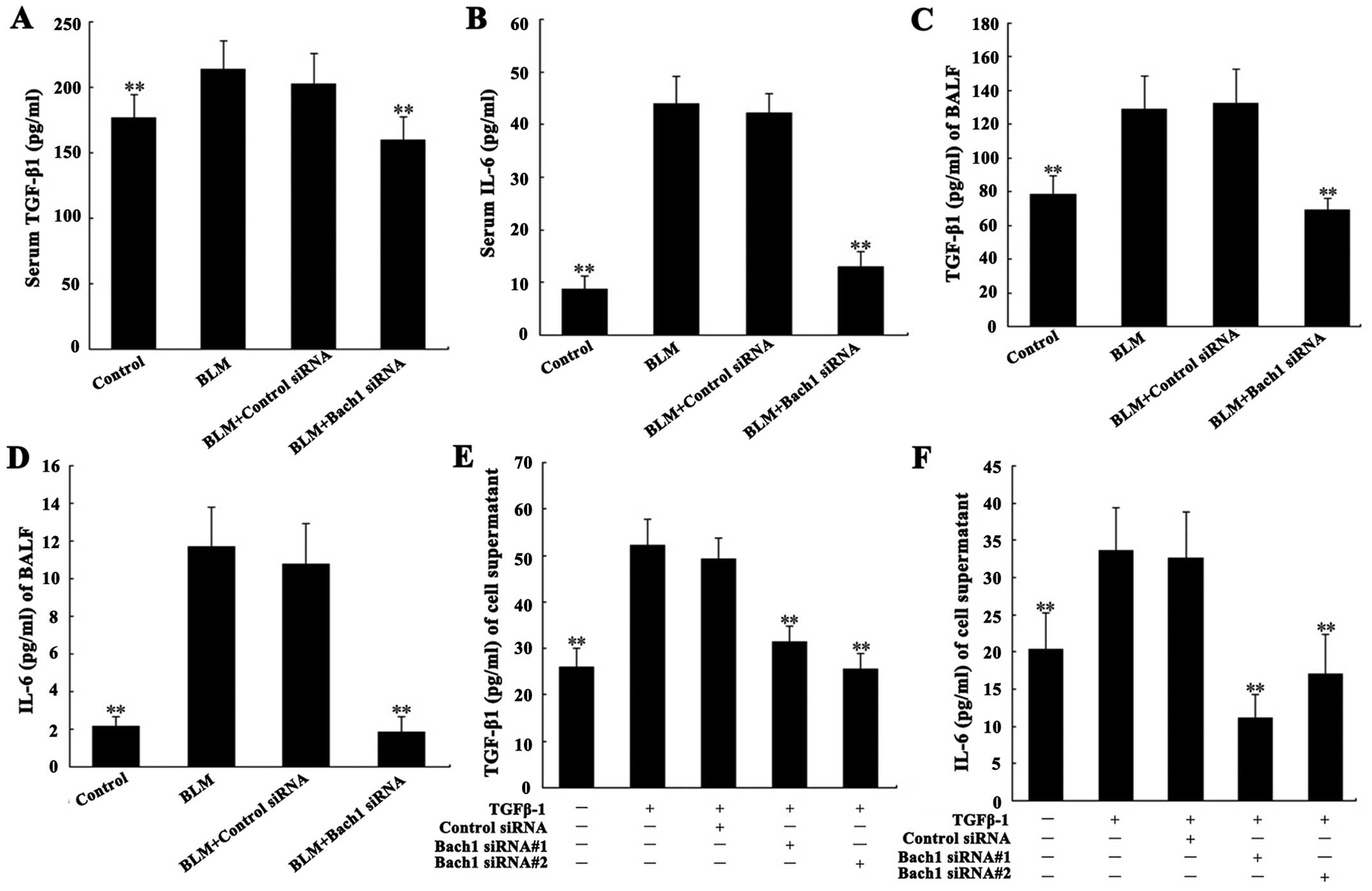
|
1
|
Gross TJ and Hunninghake GW: Idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 345:517–525. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kliment CR, Englert JM, Gochuico BR, Yu G,
Kaminski N, Rosas I and Oury TD: Oxidative stress alters syndecan-1
distribution in lungs with pulmonary fibrosis. J Biol Chem.
284:3537–3545. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Kaya V, Yazkan R, Yıldırım M, Doğuç DK,
Süren D, Bozkurt KK, Yüksel Ö, Demırpence Ö, Şen CA and Yalçın AY:
The relation of radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis with stress
and the efficiency of antioxidant treatment: an experimental study.
Med Sci Monit. 20:290–296. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Matsuzawa Y, Kawashima T, Kuwabara R,
Hayakawa S, Irie T, Yoshida T, Rikitake H, Wakabayashi T, Okada N,
Kawashima K, et al: Change in serum marker of oxidative stress in
the progression of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Pulm Pharmacol
Ther. 32:1–6. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Teixeira KC, Soares FS, Rocha LG, Silveira
PC, Silva LA, Valença SS, Dal Pizzol F, Streck EL and Pinho RA:
Attenuation of bleomycin-induced lung injury and oxidative stress
by N-acetylcysteine plus deferoxamine. Pulm Pharmacol Ther.
21:309–316. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Serrano-Mollar A, Closa D, Prats N, Blesa
S, Martinez-Losa M, Cortijo J, Estrela JM, Morcillo EJ and Bulbena
O: In vivo antioxidant treatment protects against bleomycin-induced
lung damage in rats. Br J Pharmacol. 138:1037–1048. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ishikawa M, Numazawa S and Yoshida T:
Redox regulation of the transcriptional repressor Bach1. Free
Radical Biol Med. 38:1344–1352. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Jyrkkänen HK, Kuosmanen S, Heinäniemi M,
Laitinen H, Kansanen E, Mella-Aho E, Leinonen H, Ylä-Herttuala S
and Levonen AL: Novel insights into the regulation of
antioxidant-response-element-mediated gene expression by
electrophiles: induction of the transcriptional repressor BACH1 by
Nrf2. Biochem J. 440:167–174. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Igarashi K and Sun J: The heme-Bach1
pathway in the regulation of oxidative stress response and
erythroid differentiation. Antioxid Redox Signal. 8:107–118. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Itoh K, Tong KI and Yamamoto M: Molecular
mechanism activating Nrf2-Keap1 pathway in regulation of adaptive
response to electrophiles. Free Radic Biol Med. 36:1208–1213. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Giudice A, Arra C and Turco MC: Review of
molecular mechanisms involved in the activation of the Nrf2-ARE
signaling pathway by chemopreventive agents. Methods Mol Biol.
647:37–74. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zucker SN, Fink EE, Bagati A, Mannava S,
Bianchi-Smiraglia A, Bogner PN, Wawrzyniak JA, Foley C, Leonova KI,
Grimm MJ, et al: Nrf2 amplifies oxidative stress via induction of
Klf9. Mol Cell. 53:916–928. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cho HY, Reddy SP and Kleeberger SR: Nrf2
defends the lung from oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal.
8:76–87. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kikuchi N, Ishii Y, Morishima Y, Yageta Y,
Haraguchi N, Itoh K, Yamamoto M and Hizawa N: Nrf2 protects against
pulmonary fibrosis by regulating the lung oxidant level and Th1/Th2
balance. Respir Res. 11:312010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cho HY, Reddy SP, Yamamoto M and
Kleeberger SR: The transcription factor NRF2 protects against
pulmonary fibrosis. FASEB J. 18:1258–1260. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tsuburai T, Suzuki M, Nagashima Y, Suzuki
S, Inoue S, Hasiba T, Ueda A, Ikehara K, Matsuse T and Ishigatsubo
Y: Adenovirus-mediated transfer and overexpression of heme
oxygenase 1 cDNA in lung prevents bleomycin-induced pulmonary
fibrosis via a Fas-Fas ligand-independent pathway. Hum Gene Ther.
13:1945–1960. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Santos-Silva MA, Pires KM, Trajano ET,
Martins V, Nesi RT, Benjamin CF, Caetano MS, Sternberg C, Machado
MN, Zin WA, et al: Redox imbalance and pulmonary function in
bleomycin-induced fibrosis in C57BL/6, DBA/2, and BALB/c mice.
Toxicol Pathol. 40:731–741. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moeller A, Ask K, Warburton D, Gauldie J
and Kolb M: The bleomycin animal model: a useful tool to
investigate treatment options for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis?
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 40:362–382. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Moore BB and Hogaboam CM: Murine models of
pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
294:L152–L160. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
B Moore B, Lawson WE, Oury TD, Sisson TH,
Raghavendran K and Hogaboam CM: Animal models of fibrotic lung
disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 49:167–179. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yoshida M, Sakuma J, Hayashi S, Abe K,
Saito I, Harada S, Sakatani M, Yamamoto S, Matsumoto N and Kaneda
Y: A histologically distinctive interstitial pneumonia induced by
overexpression of the interleukin 6, transforming growth factor
beta 1, or platelet-derived growth factor B gene. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 92:9570–9574. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Selman M and Pardo A: Role of epithelial
cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: from innocent targets to
serial killers. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 3:364–372. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Choe JY, Jung HJ, Park KY, Kum YS, Song
GG, Hyun DS, Park SH and Kim SK: Anti-fibrotic effect of
thalidomide through inhibiting TGF-beta-induced ERK1/2 pathways in
bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice. Inflamm Res. 59:177–188.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Xu YD, Hua J, Mui A, O'Connor R,
Grotendorst G and Khalil N: Release of biologically active
TGF-beta1 by alveolar epithelial cells results in pulmonary
fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 285:L527–L539. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee CM, Park JW, Cho WK, Zhou Y, Han B,
Yoon PO, Chae J, Elias JA and Lee CG: Modifiers of TGF-β1 effector
function as novel therapeutic targets of pulmonary fibrosis. Korean
J Intern Med. 29:281–290. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pecot CV, Calin GA, Coleman RL,
Lopez-Berestein G and Sood AK: RNA interference in the clinic:
challenges and future directions. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:59–67. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Zhao Y, Li H, Wu R, Li S, Wang P, Wang H,
Wang J and Zhou J: Antitumor effects of oncolytic
adenovirus-carrying siRNA targeting potential oncogene EphA3. PLoS
One. 10:e01267262015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Szapiel SV, Elson NA, Fulmer JD,
Hunninghake GW and Crystal RG: Bleomycin-induced interstitial
pulmonary disease in the nude, athymic mouse. Am Rev Respir Dis.
120:893–899. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ashcroft T, Simpson JM and Timbrell V:
Simple method of estimating severity of pulmonary fibrosis on a
numerical scale. J Clin Pathol. 41:467–470. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kinnula VL and Myllärniemi M:
Oxidant-antioxidant imbalance as a potential contributor to the
progression of human pulmonary fibrosis. Antioxid Redox Signal.
10:727–738. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Andersson-Sjöland A, Karlsson JC and
Rydell-Törmänen K: ROS-induced endothelial stress contributes to
pulmonary fibrosis through pericytes and Wnt signaling. Lab Invest.
96:206–217. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kinnula VL, Fattman CL, Tan RJ and Oury
TD: Oxidative stress in pulmonary fibrosis: a possible role for
redox modulatory therapy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 172:417–422.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dhakshinamoorthy S, Jain AK, Bloom DA and
Jaiswal AK: Bach1 competes with Nrf2 leading to negative regulation
of the antioxidant response element (ARE)-mediated NAD(P)H:quinone
oxidoreductase 1 gene expression and induction in response to
antioxidants. J Biol Chem. 280:16891–16900. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Warnatz HJ, Schmidt D, Manke T, Piccini I,
Sultan M, Borodina T, Balzereit D, Wruck W, Soldatov A, Vingron M,
et al: The BTB and CNC homology 1 (BACH1) target genes are involved
in the oxidative stress response and in control of the cell cycle.
J Biol Chem. 286:23521–23532. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hinz B, Phan SH, Thannickal VJ, Galli A,
Bochaton-Piallat ML and Gabbiani G: The myofibroblast: one
function, multiple origins. Am J Pathol. 170:1807–1816. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim S, Lim JH and Woo CH: ERK5
inhibition ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis via regulating
Smad5 acetylation. Am J Pathol. 183:1758–1768. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wu H, Li Y, Wang Y, Xu D, Li C, Liu M, Sun
X and Li Z: Tanshinone IIA attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary
fibrosis via modulating angiotensin-converting enzyme
2/angiotensin-(1–7) axis in rats. Int J Med Sci. 11:578–586. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
McManus MT and Sharp PA: Gene silencing in
mammals by small interfering RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 3:737–747. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Walters DM, Cho HY and Kleeberger SR:
Oxidative stress and antioxidants in the pathogenesis of pulmonary
fibrosis: a potential role for Nrf2. Antioxid Redox Signal.
10:321–332. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Koo HC, Davis JM, Li Y, Hatzis D, Opsimos
H, Pollack S, Strayer MS, Ballard PL and Kazzaz JA: Effects of
transgene expression of superoxide dismutase and glutathione
peroxidase on pulmonary epithelial cell growth in hyperoxia. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 288:L718–L726. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Reddy NM, Kleeberger SR, Cho HY, Yamamoto
M, Kensler TW, Biswal S and Reddy SP: Deficiency in Nrf2-GSH
signaling impairs type II cell growth and enhances sensitivity to
oxidants. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 37:3–8. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Holtzclaw WD, Dinkova-Kostova AT and
Talalay P: Protection against electrophile and oxidative stress by
induction of phase 2 genes: the quest for the elusive sensor that
responds to inducers. Adv Enzyme Regul. 44:335–367. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ni S, Wang D, Qiu X, Pang L, Song Z and
Guo K: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protect against
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rat by activating Nrf2
signaling. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:7752–7761. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Artaud-Macari E, Goven D, Brayer S, Hamimi
A, Besnard V, Marchal-Somme J, Ali ZE, Crestani B, Kerdine-Römer S,
Boutten A and Bonay M: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
nuclear translocation induces myofibroblastic dedifferentiation in
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 18:66–79.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ryter SW, Alam J and Choi AM: Heme
oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide: from basic science to therapeutic
applications. Physiol Rev. 86:583–650. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Reichard JF, Sartor MA and Puga A: BACH1
is a specific repressor of HMOX1 that is inactivated by arsenite. J
Biol Chem. 283:22363–22370. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
MacLeod AK, McMahon M, Plummer SM, Higgins
LG, Penning TM, Igarashi K and Hayes JD: Characterization of the
cancer chemopreventive NRF2-dependent gene battery in human
keratinocytes: demonstration that the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway, and not
the BACH1-NRF2 pathway, controls cytoprotection against
electrophiles as well as redox-cycling compounds. Carcinogenesis.
30:1571–1580. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cui K, Kou JQ, Gu JH, Han R, Wang G, Zhen
X and Qin ZH: Naja naja atra venom ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis
by inhibiting inflammatory response and oxidative stress. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 14:4612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yao R, Cao Y, He YR, Lau WB, Zeng Z and
Liang ZA: Adiponectin attenuates lung fibroblasts activation and
pulmonary fibrosis induced by paraquat. PLoS One. 10:e01251692015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|