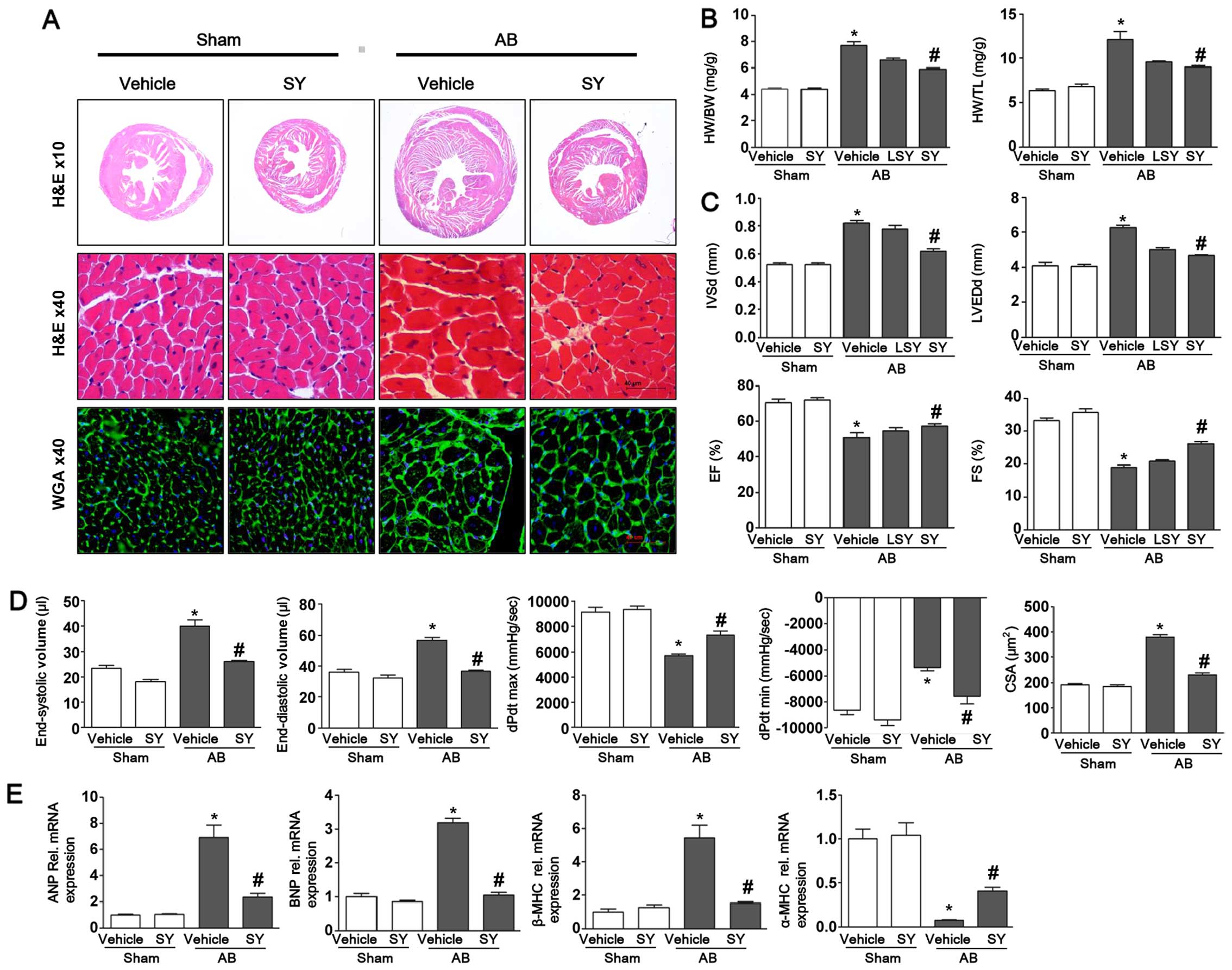
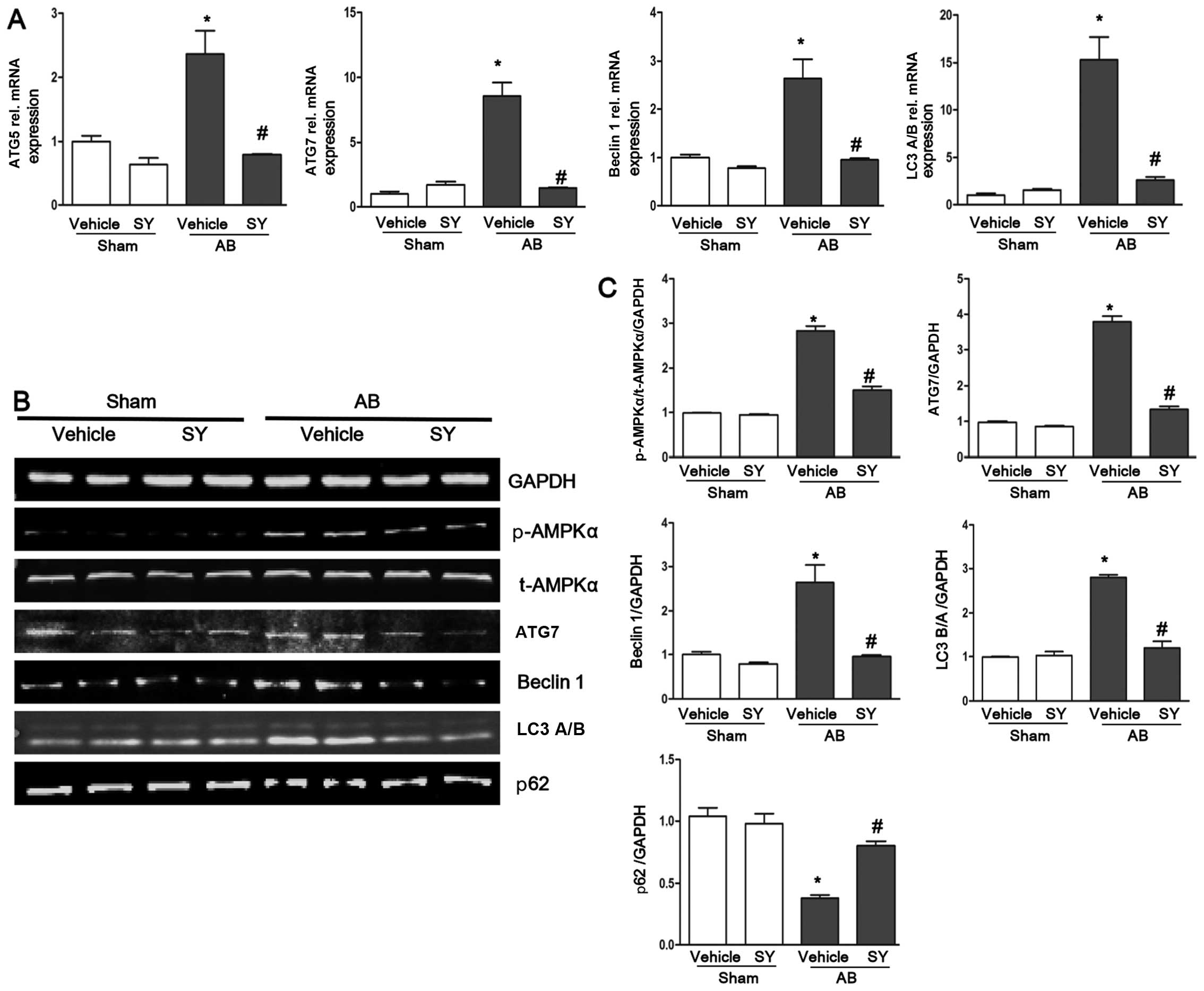
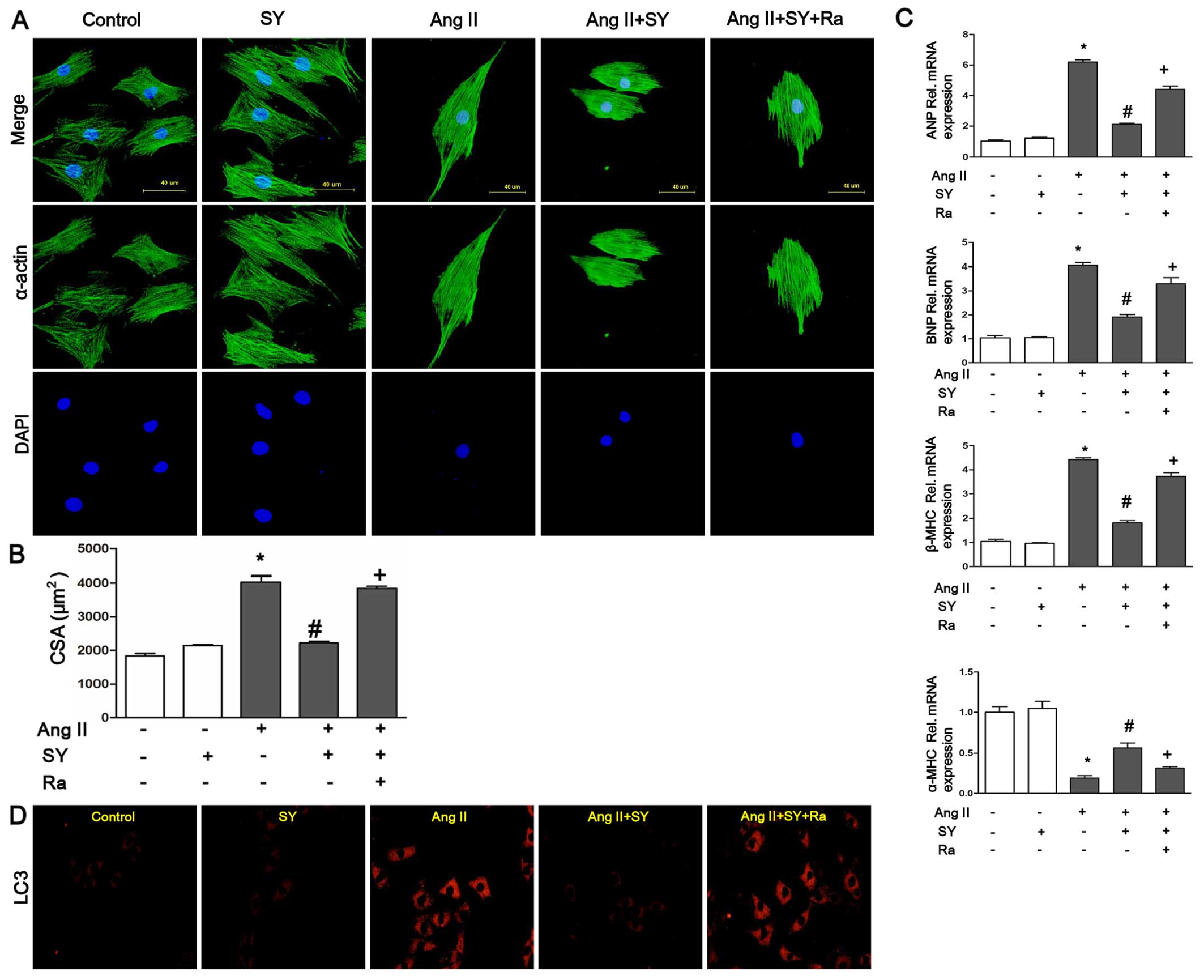
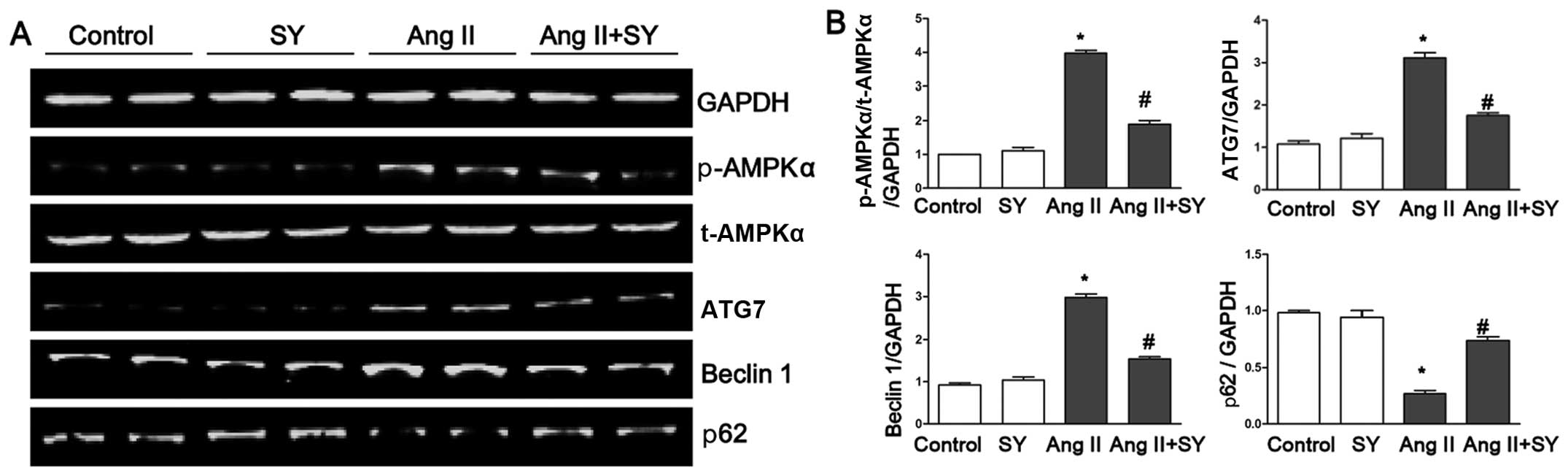
|
1
|
Wu QQ, Xu M, Yuan Y, Li FF, Yang Z, Liu Y,
Zhou MQ, Bian ZY, Deng W, Gao L, et al: Cathepsin B deficiency
attenuates cardiac remodeling in response to pressure overload via
TNF-α/ASK1/JNK pathway. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
308:H1143–H1154. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhou H, Guo H, Zong J, Dai J, Yuan Y, Bian
ZY and Tang QZ: ATF3 regulates multiple targets and may play a dual
role in cardiac hypertrophy and injury. Int J Cardiol. 174:838–839.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Deng W, Zong J, Wei L, Guo H, Cheng Z,
Zhang R, Lin Y and Tang Q: 3,3′-Diindolylmethane improves
myocardial energy metabolism imbalance induced by pressure overload
via AMPKα in mice. Int J Cardiol. 177:235–237. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bian Z, Dai J, Hiroyasu N, Guan H, Yuan Y,
Gan L, Zhou H, Zong J, Zhang Y, Li F, et al: Disruption of tumor
necrosis factor receptor associated factor 5 exacerbates pressure
overload cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis. J Cell Biochem.
115:349–358. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zong J, Wu QQ, Zhou H, Zhang JY, Yuan Y,
Bian ZY, Deng W, Dai J, Li FF, Xu M, et al: 3,3′-Diindolylmethane
attenuates cardiac H9c2 cell hypertrophy through 5′-adenosine
monophosphate-activated protein kinase-α. Mol Med Rep.
12:1247–1252. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou H, Yuan Y, Liu Y, Ni J, Deng W, Bian
ZY, Dai J and Tang QZ: Icariin protects H9c2 cardiomyocytes from
lipopoly-saccharide induced injury via inhibition of the reactive
oxygen species dependent c Jun N terminal kinases/nuclear factor-κB
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 11:4327–4332. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Deng W, Wang X, Xiao J, Chen K, Zhou H,
Shen D, Li H and Tang Q: Loss of regulator of G protein signaling 5
exacerbates obesity, hepatic steatosis, inflammation and insulin
resistance. PLoS One. 7:e302562012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zong J, Salim M, Zhou H, Bian ZY, Dai J,
Yuan Y, Deng W, Zhang JY, Zhang R, Wu QQ and Tang QZ: NOD2 deletion
promotes cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis induced by pressure
overload. Lab Invest. 93:1128–1136. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yussman MG, Toyokawa T, Odley A, Lynch RA,
Wu G, Colbert MC, Aronow BJ, Lorenz JN and Dorn GW II:
Mitochondrial death protein Nix is induced in cardiac hypertrophy
and triggers apoptotic cardiomyopathy. Nat Med. 8:725–730.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fernandes RO, Dreher GJ, Schenkel PC,
Fernandes TR, Ribeiro MF, Araujo AS and Belló-Klein A: Redox status
and pro-survival/pro-apoptotic protein expression in the early
cardiac hypertrophy induced by experimental hyperthyroidism. Cell
Biochem Funct. 29:617–623. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Adams JW, Sakata Y, Davis MG, Sah VP, Wang
Y, Liggett SB, Chien KR, Brown JH and Dorn GW II: Enhanced Galphaq
signaling: A common pathway mediates cardiac hypertrophy and
apoptotic heart failure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:10140–10145.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gong X, Zhang L, Jiang R, Wang CD, Yin XR
and Wan JY: Hepatoprotective effects of syringin on fulminant
hepatic failure induced by D-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide
in mice. J Appl Toxicol. 34:265–271. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Cui Y, Zhang Y and Liu G: Syringin may
exert sleep-potentiating effects through the NOS/NO pathway. Fundam
Clin Pharmacol. 29:178–184. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li Q, Sun LX, Xu L, Jia Y, Wang ZW, Shen
ZD and Bi KS: Determination and pharmacokinetic study of syringin
and chlorogenic acid in rat plasma after administration of Aidi
lyophilizer. Biomed Chromatogr. 20:1315–1320. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu KY, Wu YC, Liu IM, Yu WC and Cheng JT:
Release of acetylcholine by syringin, an active principle of
Eleutherococcus senticosus, to raise insulin secretion in Wistar
rats. Neurosci Lett. 434:195–199. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Niu HS, Hsu FL and Liu IM: Role of
sympathetic tone in the loss of syringin-induced plasma glucose
lowering action in conscious Wistar rats. Neurosci Lett.
445:113–116. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cho JY, Nam KH, Kim AR, Park J, Yoo ES,
Baik KU, Yu YH and Park MH: In-vitro and in-vivo immunomodulatory
effects of syringin. J Pharm Pharmacol. 53:1287–1294. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yan L, Vatner DE, Kim SJ, Ge H, Masurekar
M, Massover WH, Yang G, Matsui Y, Sadoshima J and Vatner SF:
Autophagy in chronically ischemic myocardium. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 102:13807–13812. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Godar RJ, Ma X, Liu H, Murphy JT,
Weinheimer CJ, Kovacs A, Crosby SD, Saftig P and Diwan A:
Repetitive stimulation of autophagy-lysosome machinery by
intermittent fasting preconditions the myocardium to
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Autophagy. 11:1537–1560. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Higashi K, Yamada Y, Minatoguchi S, Baba
S, Iwasa M, Kanamori H, Kawasaki M, Nishigaki K, Takemura G,
Kumazaki M, et al: MicroRNA-145 repairs infarcted myocardium by
accelerating cardiomyocyte autophagy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 309:H1813–H1826. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhu H, Tannous P, Johnstone JL, Kong Y,
Shelton JM, Richardson JA, Le V, Levine B, Rothermel BA and Hill
JA: Cardiac autophagy is a maladaptive response to hemodynamic
stress. J Clin Invest. 117:1782–1793. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li Z, Wang J and Yang X: Functions of
autophagy in pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Int J Biol Sci.
11:672–678. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu X, Hua Y, Nair S, Bucala R and Ren J:
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor deletion exacerbates
pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy through mitigating
autophagy. Hypertension. 63:490–499. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Tohda C, Ichimura M, Bai Y, Tanaka K, Zhu
S and Komatsu K: Inhibitory effects of Eleutherococcus senticosus
extracts on amyloid β(25–35)-induced neuritic atrophy and synaptic
loss. J Pharmacol Sci. 107:329–339. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ma B, Zhang Q, Liu Y, Li J, Xu Q, Li X,
Yang X, Yao D, Sun J, Cui G, et al: Simultaneous determination of
Eleutheroside B and Eleutheroside E in rat plasma by high
performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass
spectrometry and its application in a pharmacokinetic study. J
Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 917–918:84–92. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sergeeva IA and Christoffels VM:
Regulation of expression of atrial and brain natriuretic peptide,
biomarkers for heart development and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1832:2403–2413. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu Q, Xu-Cai YO, Chen S and Wang W: Corin:
New insights into the natriuretic peptide system. Kidney Int.
75:142–146. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Volpe M, Rubattu S and Burnett J Jr:
Natriuretic peptides in cardiovascular diseases: Current use and
perspectives. Eur Heart J. 35:419–425. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Zhang Y, Mi SL, Hu N, Doser TA, Sun A, Ge
J and Ren J: Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 accentuates
aging-induced cardiac remodeling and contractile dysfunction: Role
of AMPK, Sirt1, and mitochondrial function. Free Radic Biol Med.
71:208–220. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim M, Shen M, Ngoy S, Karamanlidis G,
Liao R and Tian R: AMPK isoform expression in the normal and
failing hearts. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 52:1066–1073. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Turdi S, Kandadi MR, Zhao J, Huff AF, Du M
and Ren J: Deficiency in AMP-activated protein kinase exaggerates
high fat diet-induced cardiac hypertrophy and contractile
dysfunction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 50:712–722. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Beauloye C, Bertrand L, Horman S and Hue
L: AMPK activation, a preventive therapeutic target in the
transition from cardiac injury to heart failure. Cardiovasc Res.
90:224–233. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dyck JR and Lopaschuk GD: AMPK alterations
in cardiac physiology and pathology: Enemy or ally? J Physiol.
574:95–112. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Meng R, Pei Z, Zhang A, Zhou Y, Cai X,
Chen B, Liu G, Mai W, Wei J and Dong Y: AMPK activation enhances
PPARα activity to inhibit cardiac hypertrophy via ERK1/2 MAPK
signaling pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. 511:1–7. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li Y, Chen C, Yao F, Su Q, Liu D, Xue R,
Dai G, Fang R, Zeng J, Chen Y, et al: AMPK inhibits cardiac
hypertrophy by promoting autophagy via mTORC1. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 558:79–86. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kudo N, Barr AJ, Barr RL, Desai S and
Lopaschuk GD: High rates of fatty acid oxidation during reperfusion
of ischemic hearts are associated with a decrease in malonyl-CoA
levels due to an increase in 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase
inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 270:17513–17520.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kudo N, Gillespie JG, Kung L, Witters LA,
Schulz R, Clanachan AS and Lopaschuk GD: Characterization of
5′AMP-activated protein kinase activity in the heart and its role
in inhibiting acetyl-CoA carboxylase during reperfusion following
ischemia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1301:67–75. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fassett JT, Hu X, Xu X, Lu Z, Zhang P,
Chen Y and Bache RJ: AMPK attenuates microtubule proliferation in
cardiac hypertrophy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
304:H749–H758. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhu J, Ning RB, Lin XY, Chai DJ, Xu CS,
Xie H, Zeng JZ and Lin JX: Retinoid X receptor agonists inhibit
hypertension-induced myocardial hypertrophy by modulating
LKB1/AMPK/p70S6K signaling pathway. Am J Hypertens. 27:1112–1124.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Davies JK, Wells DJ, Liu K, Whitrow HR,
Daniel TD, Grignani R, Lygate CA, Schneider JE, Noël G, Watkins H
and Carling D: Characterization of the role of gamma2 R531G
mutation in AMP-activated protein kinase in cardiac hypertrophy and
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
290:H1942–H1951. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Patel VV, Arad M, Moskowitz IP, Maguire
CT, Branco D, Seidman JG, Seidman CE and Berul CI:
Electrophysiologic characterization and postnatal development of
ventricular pre-excitation in a mouse model of cardiac hypertrophy
and Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 42:942–951.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Arad M, Moskowitz IP, Patel VV, Ahmad F,
Perez-Atayde AR, Sawyer DB, Walter M, Li GH, Burgon PG, Maguire CT,
et al: Transgenic mice overexpressing mutant PRKAG2 define the
cause of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome in glycogen storage
cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 107:2850–2856. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gollob MH, Green MS, Tang AS, Gollob T,
Karibe A, Ali Hassan AS, Ahmad F, Lozado R, Shah G, Fananapazir L,
et al: Identification of a gene responsible for familial
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. N Engl J Med. 344:1823–1831. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Capano M and Crompton M: Bax translocates
to mitochondria of heart cells during simulated ischaemia:
Involvement of AMP-activated and p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinases. Biochem J. 395:57–64. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
45
|
Russell RR III, Li J, Coven DL, Pypaert M,
Zechner C, Palmeri M, Giordano FJ, Mu J, Birnbaum MJ and Young LH:
AMP-activated protein kinase mediates ischemic glucose uptake and
prevents postischemic cardiac dysfunction, apoptosis, and injury. J
Clin Invest. 114:495–503. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nagata D and Hirata Y: The role of
AMP-activated protein kinase in the cardiovascular system.
Hypertens Res. 33:22–28. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Horman S, Beauloye C, Vanoverschelde JL
and Bertrand L: AMP-activated protein kinase in the control of
cardiac metabolism and remodeling. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 9:164–173.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xie S, Deng Y, Pan YY, Wang ZH, Ren J, Guo
XL, Yuan X, Shang J and Liu HG: Melatonin protects against chronic
intermittent hypoxia-induced cardiac hypertrophy by modulating
autophagy through the 5′ adenosine monophosphate-activated protein
kinase pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 464:975–981. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liu L, Wang C, Sun D, Jiang S, Li H, Zhang
W, Zhao Y, Xi Y, Shi S, Lu F, et al: Calhex231
ameliorates cardiac hypertrophy by inhibiting cellular autophagy in
vivo and in vitro. Cell Physiol Biochem. 36:1597–1612. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Liu B, Wu Z, Li Y, Ou C, Huang Z, Zhang J,
Liu P, Luo C and Chen M: Puerarin prevents cardiac hypertrophy
induced by pressure overload through activation of autophagy.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 464:908–915. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Mellor KM, Reichelt ME and Delbridge LM:
Autophagy anomalies in the diabetic myocardium. Autophagy.
7:1263–1267. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang X, Gibson ME, Li ZL, Zhu XY, Jordan
KL, Lerman A and Lerman LO: Autophagy portends the level of cardiac
hypertrophy in experimental hypertensive swine model. Am J
Hypertens. 29:81–89. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Yu P, Zhang Y, Li C, Li Y, Jiang S, Zhang
X, Ding Z, Tu F, Wu J, Gao X and Li L: Class III PI3K-mediated
prolonged activation of autophagy plays a critical role in the
transition of cardiac hypertrophy to heart failure. J Cell Mol Med.
19:1710–1719. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Oyabu J, Yamaguchi O, Hikoso S, Takeda T,
Oka T, Murakawa T, Yasui H, Ueda H, Nakayama H, Taneike M, et al:
Autophagy-mediated degradation is necessary for regression of
cardiac hypertrophy during ventricular unloading. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 441:787–792. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hariharan N, Ikeda Y, Hong C, Alcendor RR,
Usui S, Gao S, Maejima Y and Sadoshima J: Autophagy plays an
essential role in mediating regression of hypertrophy during
unloading of the heart. PLoS One. 8:e516322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Song L, Su M, Wang S, Zou Y, Wang X, Wang
Y, Cui H, Zhao P, Hui R and Wang J: MiR-451 is decreased in
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and regulates autophagy by targeting
TSC1. J Cell Mol Med. 18:2266–2274. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|