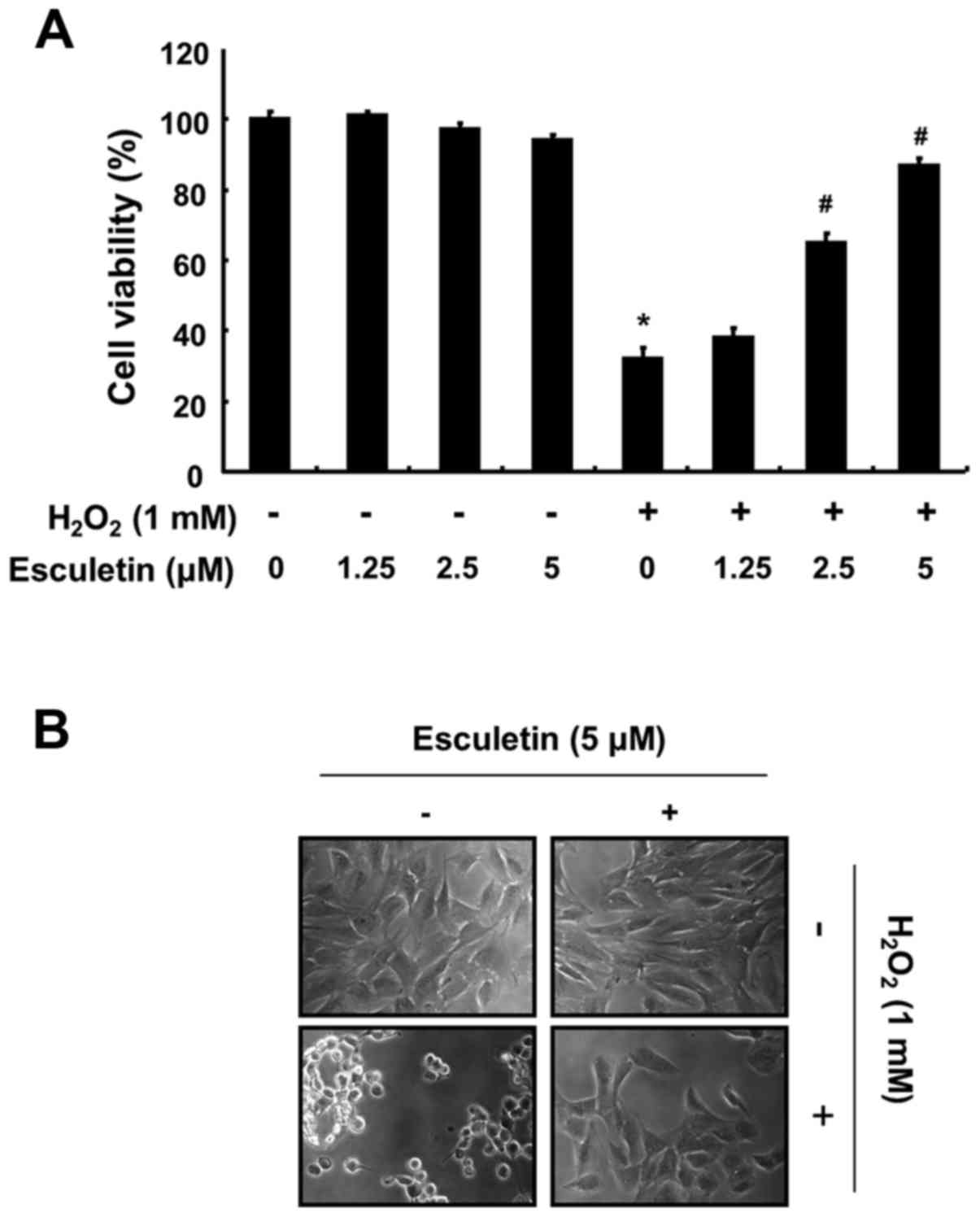
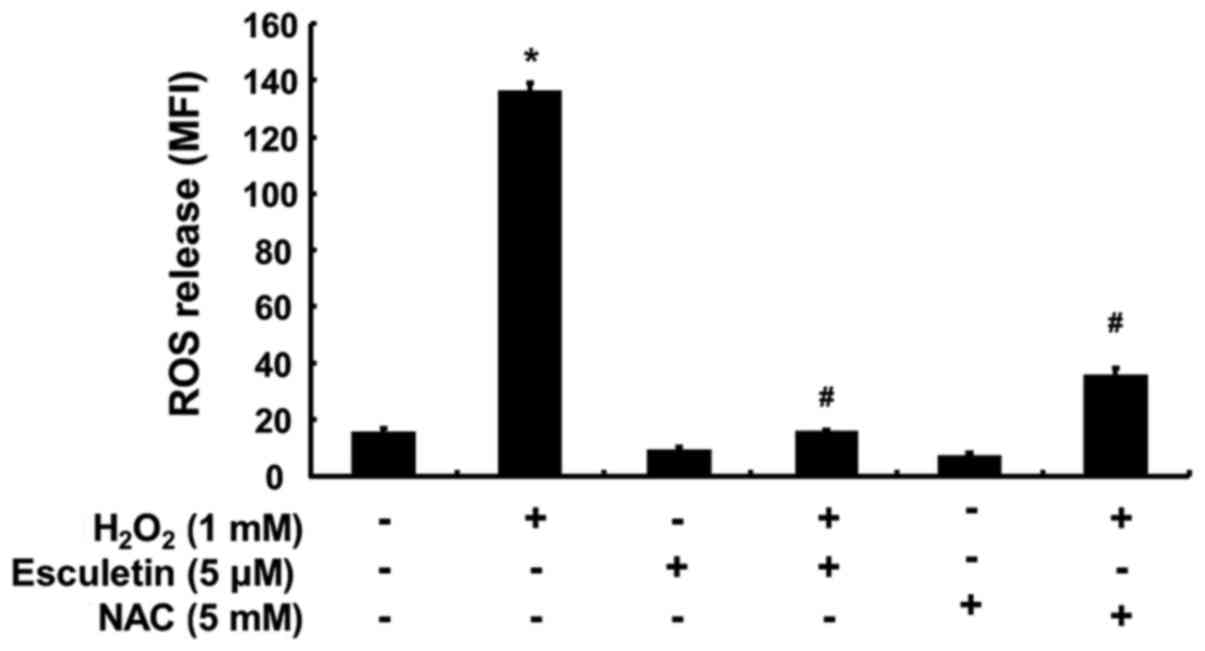
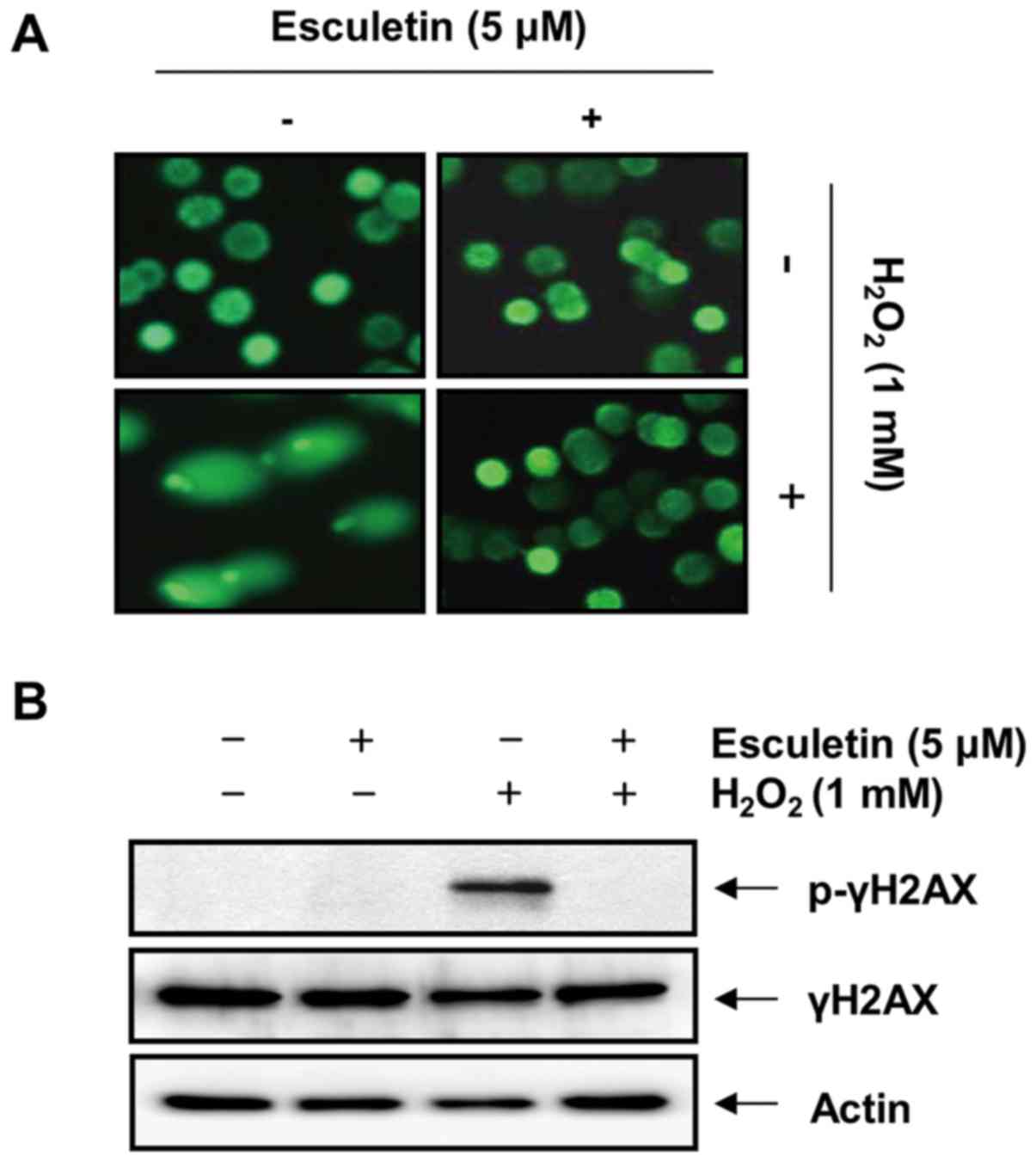
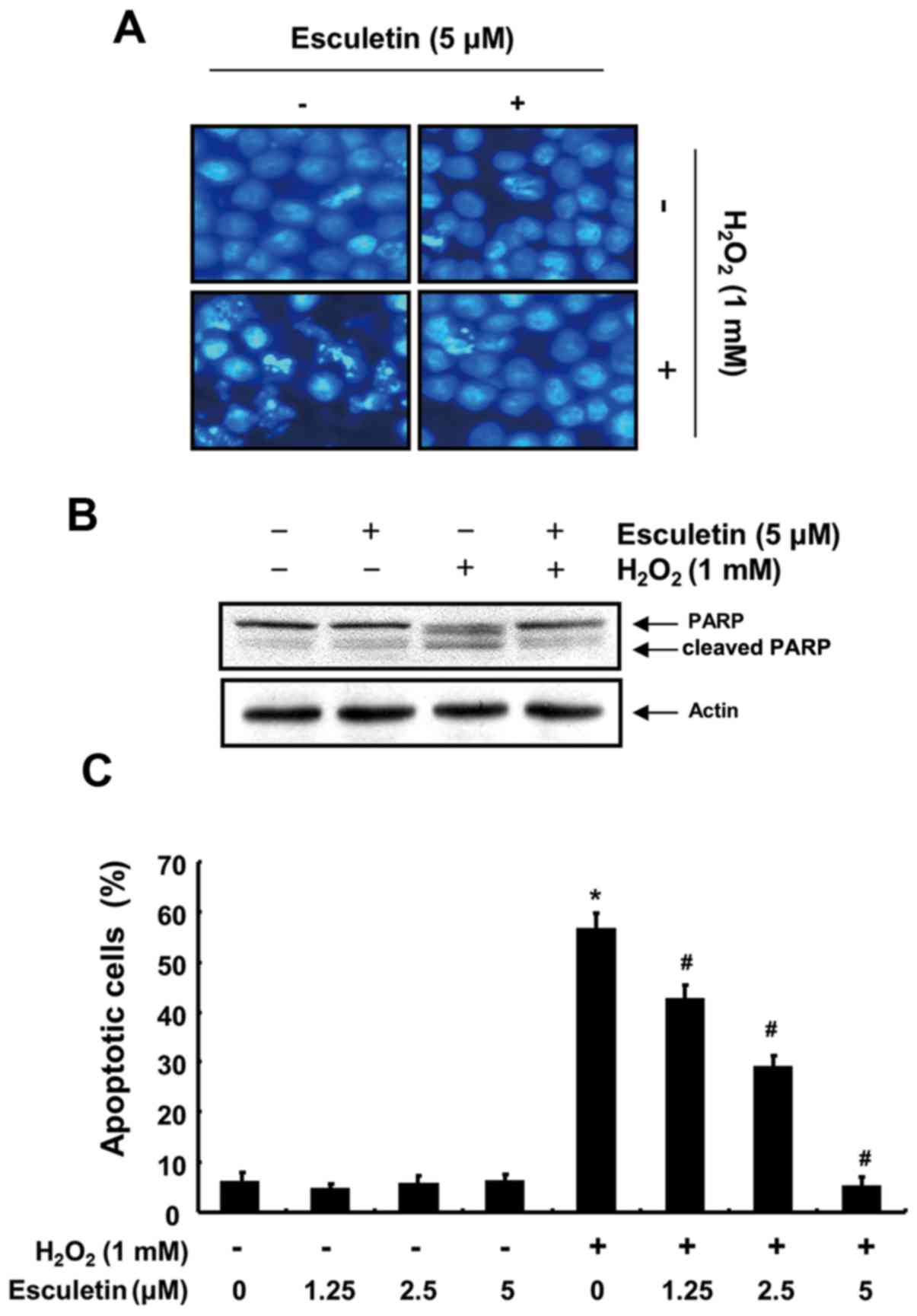
|
1
|
Lyakhovich A and Graifer D:
Mitochondria-mediated oxidative stress: Old target for new drugs.
Curr Med Chem. 22:3040–3053. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ermakov AV, Konkova MS, Kostyuk SV,
Izevskaya VL, Baranova A and Veiko NN: Oxidized extracellular DNA
as a stress signal in human cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2013:6497472013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dai DF, Chiao YA, Marcinek DJ, Szeto HH
and Rabinovitch PS: Mitochondrial oxidative stress in aging and
healthspan. Longev Healthspan. 3:62014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brieger K, Schiavone S, Miller FJ Jr and
Krause KH: Reactive oxygen species: From health to disease. Swiss
Med Wkly. 142:w136592012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mena S, Ortega A and Estrela JM: Oxidative
stress in environmental-induced carcinogenesis. Mutat Res.
674:36–44. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Rajendran P, Nandakumar N, Rengarajan T,
Palaniswami R, Gnanadhas EN, Lakshminarasaiah U, Gopas J and
Nishigaki I: Antioxidants and human diseases. Clin Chim Acta.
436:332–347. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang HY and Lee TH: Antioxidant enzymes as
redox-based biomarkers: A brief review. BMB Rep. 48:200–208. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Silva-Palacios A, Königsberg M and Zazueta
C: Nrf2 signaling and redox homeostasis in the aging heart: A
potential target to prevent cardiovascular diseases? Ageing Res
Rev. 26:81–95. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huang Y, Li W, Su ZY and Kong AN: The
complexity of the Nrf2 pathway: Beyond the antioxidant response. J
Nutr Biochem. 26:1401–1413. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gan L and Johnson JA: Oxidative damage and
the Nrf2-ARE pathway in neurodegenerative diseases. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1842:1208–1218. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Suzuki T and Yamamoto M: Molecular basis
of the Keap1-Nrf2 system. Free Radic Biol Med. 88:93–100. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
O'Connell MA and Hayes JD: The Keap1/Nrf2
pathway in health and disease: From the bench to the clinic.
Biochem Soc Trans. 43:687–689. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jaramillo MC and Zhang DD: The emerging
role of the Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway in cancer. Genes Dev.
27:2179–2191. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Murakami S and Motohashi H: Roles of Nrf2
in cell proliferation and differentiation. Free Radic Biol Med.
88:168–178. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stefanson AL and Bakovic M: Dietary
regulation of Keap1/Nrf2/ARE pathway: Focus on plant-derived
compounds and trace minerals. Nutrients. 6:3777–3801. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mancuso C and Barone E: The heme
oxygenase/biliverdin reductase pathway in drug research and
development. Curr Drug Metab. 10:579–594. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wegiel B, Nemeth Z, Correa-Costa M, Bulmer
AC and Otterbein LE: Heme oxygenase-1: A metabolic Nike. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 20:1709–1722. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Baulig A, Garlatti M, Bonvallot V,
Marchand A, Barouki R, Marano F and Baeza-Squiban A: Involvement of
reactive oxygen species in the metabolic pathways triggered by
diesel exhaust particles in human airway epithelial cells. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 285:L671–L679. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Piao MS, Choi JY, Lee DH, Yun SJ, Lee JB
and Lee SC: Differentiation-dependent expression of NADP(H):quinone
oxidoreductase-1 via NF-E2 related factor-2 activation in human
epidermal keratinocytes. J Dermatol Sci. 62:147–153. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fylaktakidou KC, Hadjipavlou-Litina DJ,
Litinas KE and Nicolaides DN: Natural and synthetic coumarin
derivatives with anti-inflammatory/antioxidant activities. Curr
Pharm Des. 10:3813–3833. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lacy A and O'Kennedy R: Studies on
coumarins and coumarin-related compounds to determine their
therapeutic role in the treatment of cancer. Curr Pharm Des.
10:3797–3811. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chang WS, Lin CC, Chuang SC and Chiang HC:
Superoxide anion scavenging effect of coumarins. Am J Chin Med.
24:11–17. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hu J, Zhu Q, Bai S and Jia Z: New
eudesmane sesquiterpene and other constituents from Artemisia
mongolica. Planta Med. 62:477–478. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
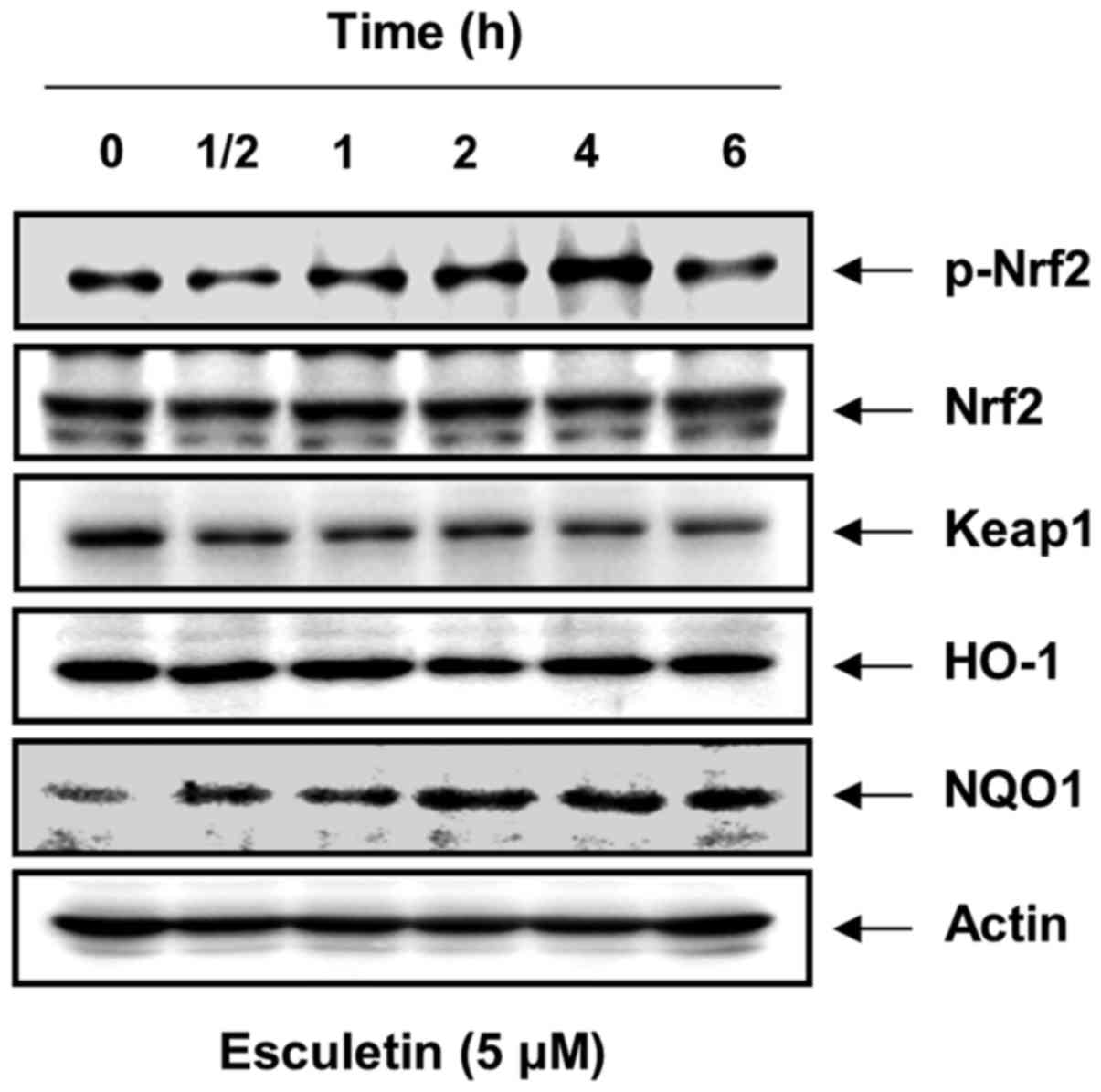
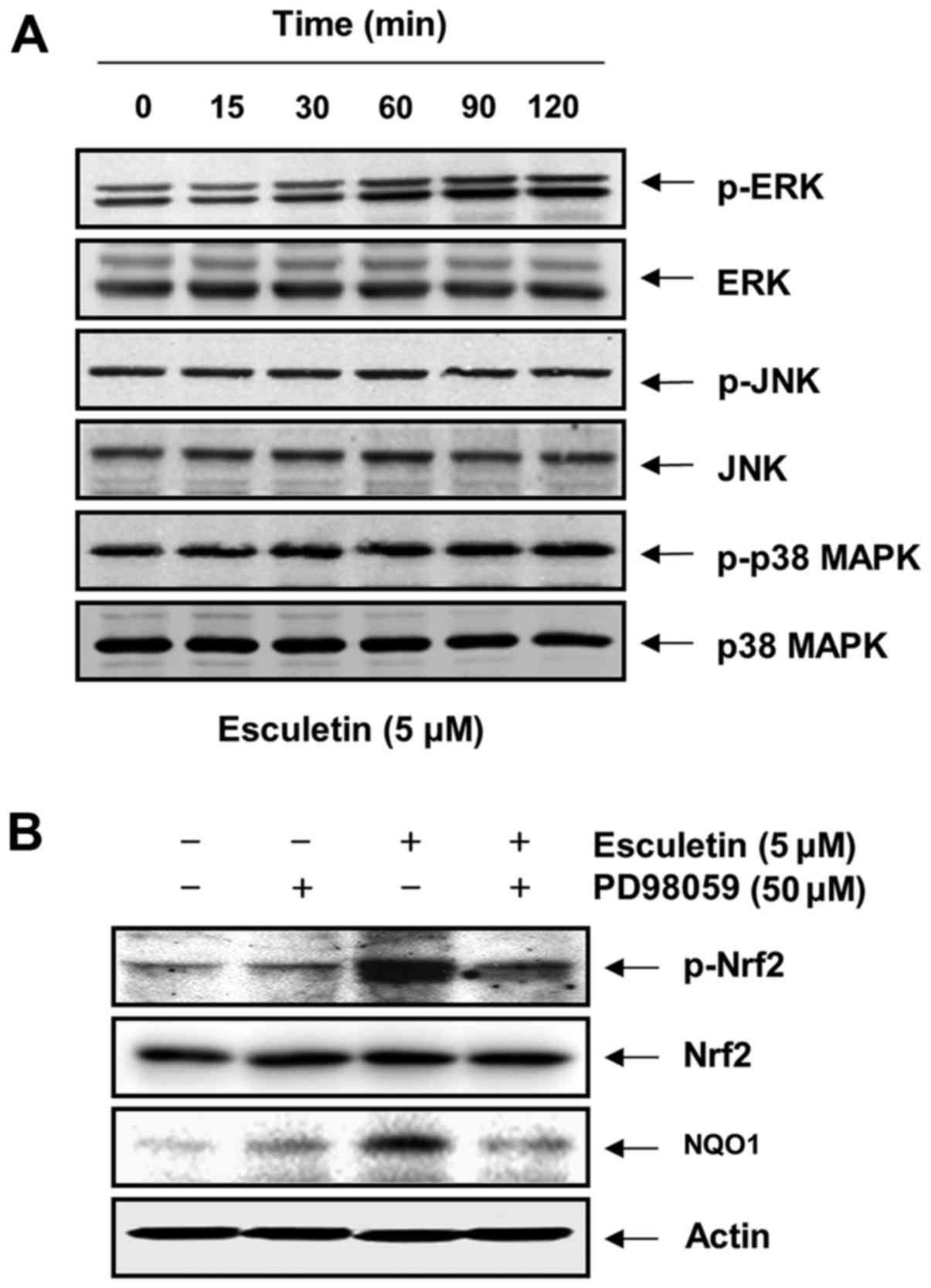
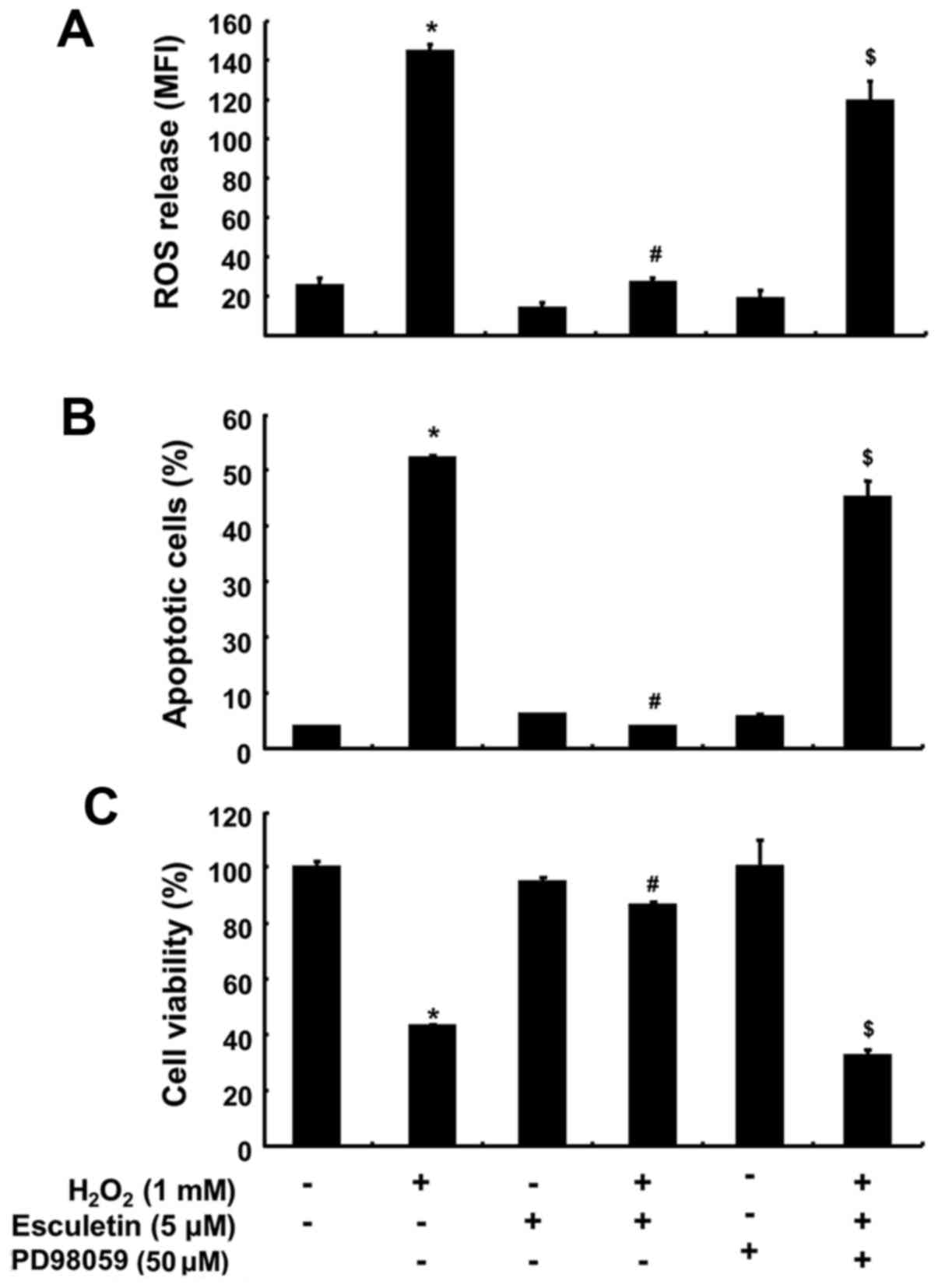
Subramaniam SR and Ellis EM:
Esculetin-induced protection of human hepatoma HepG2 cells against
hydrogen peroxide is associated with the Nrf2-dependent induction
of the NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1 gene. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 250:130–136. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lee CR, Shin EJ, Kim HC, Choi YS, Shin T
and Wie MB: Esculetin inhibits N-methyl-D-aspartate neurotoxicity
via glutathione preservation in primary cortical cultures. Lab Anim
Res. 27:259–263. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Park SL, Won SY, Song JH, Lee SY, Kim WJ
and Moon SK: Esculetin inhibits VEGF-induced angiogenesis both in
vitro and in vivo. Am J Chin Med. 44:61–76. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu L, Nang C, Luo F, Pan H, Zhang K, Liu
J, Zhou R, Gao J, Chang X, He H, et al: Esculetin attenuates
lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced neuroinflammatory processes and
depressive-like behavior in mice. Physiol Behav. 163:184–192. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hong SH, Jeong HK, Han MH, Park C and Choi
YH: Esculetin suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory
mediators and cytokines by inhibiting nuclear factor-κB
translocation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Mol Med Rep. 10:3241–3246.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jeon YJ, Cho JH, Lee SY, Choi YH, Park H,
Jung S, Shim JH and Chae JI: Esculetin induces apoptosis through
EGFR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and nucleophosmin relocalization. J
Cell Biochem. 117:1210–1221. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lee SY, Lim TG, Chen H, Jung SK, Lee HJ,
Lee MH, Kim DJ, Shin A, Lee KW, Bode AM, et al: Esculetin
suppresses proliferation of human colon cancer cells by directly
targeting β-catenin. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 6:1356–1364. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Park C, Jin CY, Kim GY, Choi IW, Kwon TK,
Choi BT, Lee SJ, Lee WH and Choi YH: Induction of apoptosis by
esculetin in human leukemia U937 cells through activation of JNK
and ERK. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 227:219–228. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Park C, Jin CY, Kwon HJ, Hwang HJ, Kim GY,
Choi IW, Kwon TK, Kim BW, Kim WJ and Choi YH: Induction of
apoptosis by esculetin in human leukemia U937 cells: Roles of Bcl-2
and extracellular-regulated kinase signaling. Toxicol In Vitro.
24:486–494. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Sulakhiya K, Keshavlal GP, Bezbaruah BB,
Dwivedi S, Gurjar SS, Munde N, Jangra A, Lahkar M and Gogoi R:
Lipopolysaccharide induced anxiety- and depressive-like behaviour
in mice are prevented by chronic pre-treatment of esculetin.
Neurosci Lett. 611:106–111. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kim JH, Jeong MS, Kim DY, Her S and Wie
MB: Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce lipoxygenase-mediated apoptosis
and necrosis in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Neurochem Int.
90:204–214. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Prabakaran D and Ashokkumar N: Protective
effect of esculetin on hyperglycemia-mediated oxidative damage in
the hepatic and renal tissues of experimental diabetic rats.
Biochimie. 95:366–373. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Hong SH, Sim MJ and Kim YC:
Melanogenesis-promoting effects of Rhynchosia nulubilis and
Rhynchosia volubilis ethanol extracts in melan-a cells. Toxicol
Res. 32:141–147. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gunasekarana V, Raj GV and Chand P: A
comprehensive review on clinical applications of comet assay. J
Clin Diagn Res. 9:GE01–GE05. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhao X, Sun P, Qian Y and Suo H: D.
candidum has in vitro anticancer effects in HCT-116 cancer cells
and exerts in vivo anti-metastatic effects in mice. Nutr Res Pract.
8:487–493. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kwon T, Rho JK, Lee JC, Park YH, Shin HJ,
Cho S, Kang YK, Kim Y, Yoon DY and Yu DY: An important role for
peroxiredoxin II in survival of A549 lung cancer cells resistant to
gefitinib. Exp Mol Med. 47:e1652015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rogakou EP, Pilch DR, Orr AH, Ivanova VS
and Bonner WM: DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX
phosphorylation on serine 139. J Biol Chem. 273:5858–5868. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Venugopal R and Jaiswal AK: Nrf1 and Nrf2
positively and c-Fos and Fra1 negatively regulate the human
antioxidant response element-mediated expression of NAD(P)H:quinone
oxidoreductase1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:14960–14965. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kweon MH, Adhami VM, Lee JS and Mukhtar H:
Constitutive overexpression of Nrf2-dependent heme oxygenase-1 in
A549 cells contributes to resistance to apoptosis induced by
epigallocatechin 3-gallate. J Biol Chem. 281:33761–33772. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Surh YJ, Kundu JK and Na HK: Nrf2 as a
master redox switch in turning on the cellular signaling involved
in the induction of cytoprotective genes by some chemopreventive
phytochemicals. Planta Med. 74:1526–1539. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|