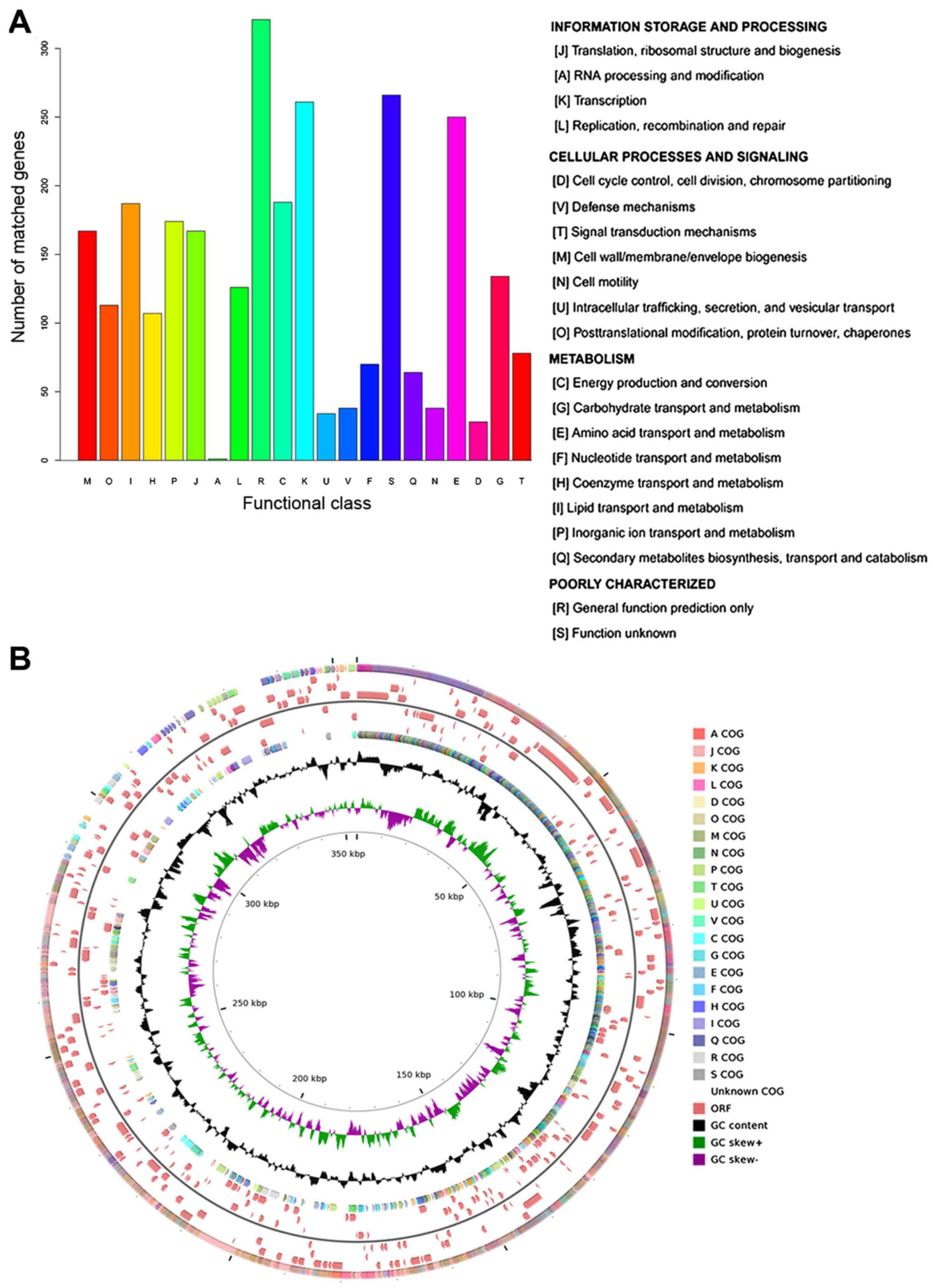
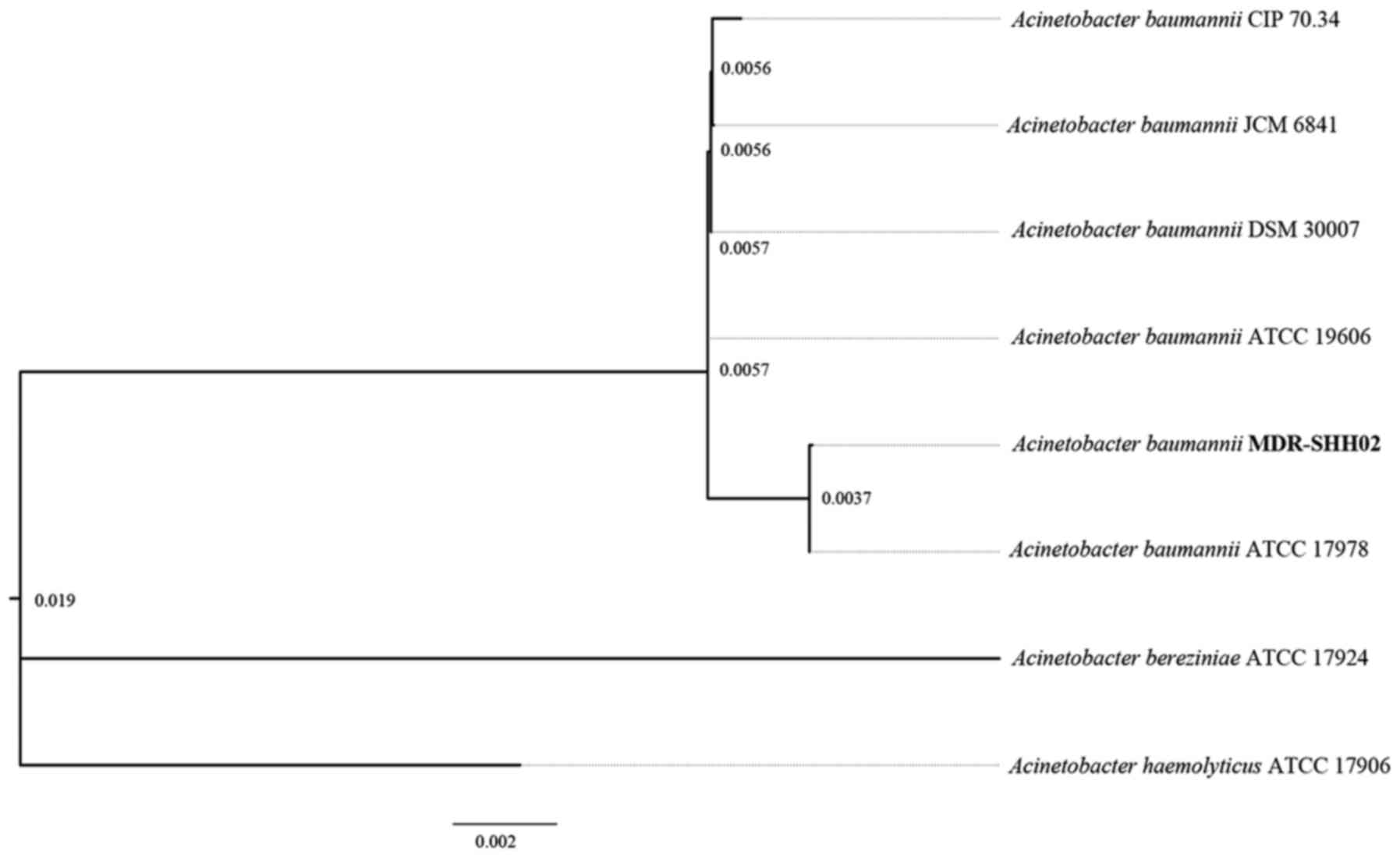
|
1
|
Lockhart SR, Abramson MA, Beekmann SE,
Gallagher G, Riedel S, Diekema DJ, Quinn JP and Doern GV:
Antimicrobial resistance among Gram-negative bacilli causing
infections in intensive care unit patients in the United States
between 1993 and 2004. J Clin Microbiol. 45:3352–3359. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Visca P, Seifert H and Towner KJ:
Acinetobacter infection - an emerging threat to human health. IUBMB
Life. 63:1048–1054. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mortensen BL and Skaar EP: Host-microbe
interactions that shape the pathogenesis of Acinetobacter baumannii
infection. Cell Microbiol. 14:1336–1344. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Higgins PG, Pérez-Llarena FJ, Zander E,
Fernández A, Bou G and Seifert H: OXA-235, a novel class D
β-lactamase involved in resistance to carbapenems in Acinetobacter
baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 57:2121–2126. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zander E, Nemec A, Seifert H and Higgins
PG: Association between β-lactamase-encoding bla DiversiLab
rep-PCR-based typing of Acinetobacter (OXA-51) variants and
baumannii isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 50:1900–1904. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Krizova L, Poirel L, Nordmann P and Nemec
A: TEM-1 β-lactamase as a source of resistance to sulbactam in
clinical strains of Acinetobacter baumannii. J Antimicrob
Chemother. 68:2786–2791. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fournier PE, Vallenet D, Barbe V, Audic S,
Ogata H, Poirel L, Richet H, Robert C, Mangenot S, Abergel C, et
al: Comparative genomics of multidrug resistance in Acinetobacter
baumannii. PLoS Genet. 2:e72006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ramírez MS, Vilacoba E, Stietz MS, Merkier
AK, Jeric P, Limansky AS, Márquez C, Bello H, Catalano M and
Centrón D: Spreading of AbaR-type genomic islands in multidrug
resistance Acinetobacter baumannii strains belonging to different
clonal complexes. Curr Microbiol. 67:9–14. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Šeputienė V, Povilonis J and Sužiedėlienė
E: Novel variants of AbaR resistance islands with a common backbone
in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates of European clone II.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 56:1969–1973. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Taitt CR, Leski T, Stockelman MG, Craft
DW, Zurawski DV, Kirkup BC and Vora GJ: Antimicrobial resistance
determinants in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates taken from
military treatment facilities. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
58:767–781. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Zhou H, Zhang T, Yu D, Pi B, Yang Q, Zhou
J, Hu S and Yu Y: Genomic analysis of the multidrug-resistant
Acinetobacter baumannii strain MDR-ZJ06 widely spread in China.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 55:4506–4512. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hornsey M, Loman N, Wareham DW, Ellington
MJ, Pallen MJ, Turton JF, Underwood A, Gaulton T, Thomas CP,
Doumith M, et al: Whole-genome comparison of two Acinetobacter
baumannii isolates from a single patient, where resistance
developed during tigecycline therapy. J Antimicrob Chemother.
66:1499–1503. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li H, Liu F, Zhang Y, Wang X, Zhao C, Chen
H, Zhang F, Zhu B, Hu Y and Wang H: Evolution of
carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii revealed through
whole-genome sequencing and comparative genomic analysis.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 59:1168–1176. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Atlas RM, Brown AE and Parks LC:
Laboratory Manual of Experimental Microbiology. Mosby; St. Louis,
MO: pp. 119–127. 1995
|
|
15
|
Watts JL: Performance Standards For
Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria
Isolated From Animals: Approved Standard. Clinical and Laboratory
Standards Institute; 2008
|
|
16
|
Bauer AW, Kirby WM, Sherris JC and Turck
M: Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk
method. Am J Clin Pathol. 45:493–496. 1966.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Delcher AL, Bratke KA, Powers EC and
Salzberg SL: Identifying bacterial genes and endosymbiont DNA with
Glimmer. Bioinformatics. 23:673–679. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schattner P, Brooks AN and Lowe TM: The
tRNAscan-SE, snoscan and snoGPS web servers for the detection of
tRNAs and snoRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 33(Web Server): W686–W689.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rødland EA,
Staerfeldt H-H, Rognes T and Ussery DW: RNAmmer: consistent and
rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res.
35:3100–3108. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tatusov RL, Fedorova ND, Jackson JD,
Jacobs AR, Kiryutin B, Koonin EV, Krylov DM, Mazumder R, Mekhedov
SL, Nikolskaya AN, et al: The COG database: an updated version
includes eukaryotes. BMC Bioinformatics. 4:412003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mount DW: Using the basic local alignment
search tool (BLAST). CSH Protoc. 2007:pdb. top172007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chenna R, Sugawara H, Koike T, Lopez R,
Gibson TJ, Higgins DG and Thompson JD: Multiple sequence alignment
with the Clustal series of programs. Nucleic Acids Res.
31:3497–3500. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yoon SH, Park Y-K, Lee S, Choi D, Oh TK,
Hur C-G and Kim JF: Towards pathogenomics: a web-based resource for
pathogenicity islands. Nucleic Acids Res. 35(Database): D395–D400.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Liu B and Pop M: ARDB - Antibiotic
Resistance Genes Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 37(Database):
D443–D447. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Pósfai G, Koob MD, Kirkpatrick HA and
Blattner FR: Versatile insertion plasmids for targeted genome
manipulations in bacteria: isolation, deletion, and rescue of the
pathogenicity island LEE of the Escherichia coli O157:H7 genome. J
Bacteriol. 179:4426–4428. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tauschek M, Strugnell RA and Robins-Browne
RM: Characterization and evidence of mobilization of the LEE
pathogenicity island of rabbit-specific strains of enteropathogenic
Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 44:1533–1550. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Harrison EM, Carter ME, Luck S, Ou H-Y, He
X, Deng Z, O'Callaghan C, Kadioglu A and Rajakumar K: Pathogenicity
islands PAPI-1 and PAPI-2 contribute individually and
synergistically to the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain
A14. Infect Immun. 78:1437–1446. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Towner KJ: Acinetobacter: an old friend,
but a new enemy. J Hosp Infect. 73:355–363. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ramirez MS and Tolmasky ME: Aminoglycoside
modifying enzymes. Drug Resist Updat. 13:151–171. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nemec A, Dolzani L, Brisse S, van den
Broek P and Dijkshoorn L: Diversity of aminoglycoside-resistance
genes and their association with class 1 integrons among strains of
pan-European Acinetobacter baumannii clones. J Med Microbiol.
53:1233–1240. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cho YJ, Moon DC, Jin JS, Choi CH, Lee YC
and Lee JC: Genetic basis of resistance to aminoglycosides in
Acinetobacter spp. and spread of armA in Acinetobacter baumannii
sequence group 1 in Korean hospitals. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis.
64:185–190. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ploy MC, Denis F, Courvalin P and Lambert
T: Molecular characterization of integrons in Acinetobacter
baumannii: description of a hybrid class 2 integron. Antimicrob
Agents Chemother. 44:2684–2688. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Waterman PE, McGann P, Snesrud E, Clifford
RJ, Kwak YI, Munoz-Urbizo IP, Tabora-Castellanos J, Milillo M,
Preston L, Aviles R, et al: Bacterial peritonitis due to
Acinetobacter baumannii sequence type 25 with plasmid-borne new
delhi metallo-β-lactamase in Honduras. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
57:4584–4586. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Akers KS, Chaney C, Barsoumian A, Beckius
M, Zera W, Yu X, Guymon C, Keen EF III, Robinson BJ, Mende K, et
al: Aminoglycoside resistance and susceptibility testing errors in
Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus complex. J Clin Microbiol.
48:1132–1138. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kostić T, Ellis M, Williams MR, Stedtfeld
TM, Kaneene JB, Stedtfeld RD and Hashsham SA: Thirty-minute
screening of antibiotic resistance genes in bacterial isolates with
minimal sample preparation in static self-dispensing 64 and 384
assay cards. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 99:7711–7722. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Hatosy SM and Martiny AC: The ocean as a
global reservoir of antibiotic resistance genes. Appl Environ
Microbiol. 81:7593–7599. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chang-Tai Z, Yang L, Zhong-Yi H,
Chang-Song Z, Yin-Ze K, Yong-Ping L and Chun-Lei D: High frequency
of integrons related to drug-resistance in clinical isolates of
Acinetobacter baumannii. Indian J Med Microbiol. 29:118–123. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Martí S, Fernández-Cuenca F, Pascual A,
Ribera A, Rodríguez-Baño J, Bou G, Miguel Cisneros J, Pachón J,
Martínez-Martínez L and Vila J; Grupo de Estudio de Infección
Hospitalaria (GEIH): Prevalence of the tetA and tetB genes as
mechanisms of resistance to tetracycline and minocycline in
Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates. Enferm Infecc Microbiol
Clin. 24:77–80. 2006.In Spanish. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Post V and Hall RM: AbaR5, a large
multiple-antibiotic resistance region found in Acinetobacter
baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 53:2667–2671. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Agersø Y and Petersen A: The tetracycline
resistance determinant Tet 39 and the sulphonamide resistance gene
sulII are common among resistant Acinetobacter spp. isolated from
integrated fish farms in Thailand. J Antimicrob Chemother.
59:23–27. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|