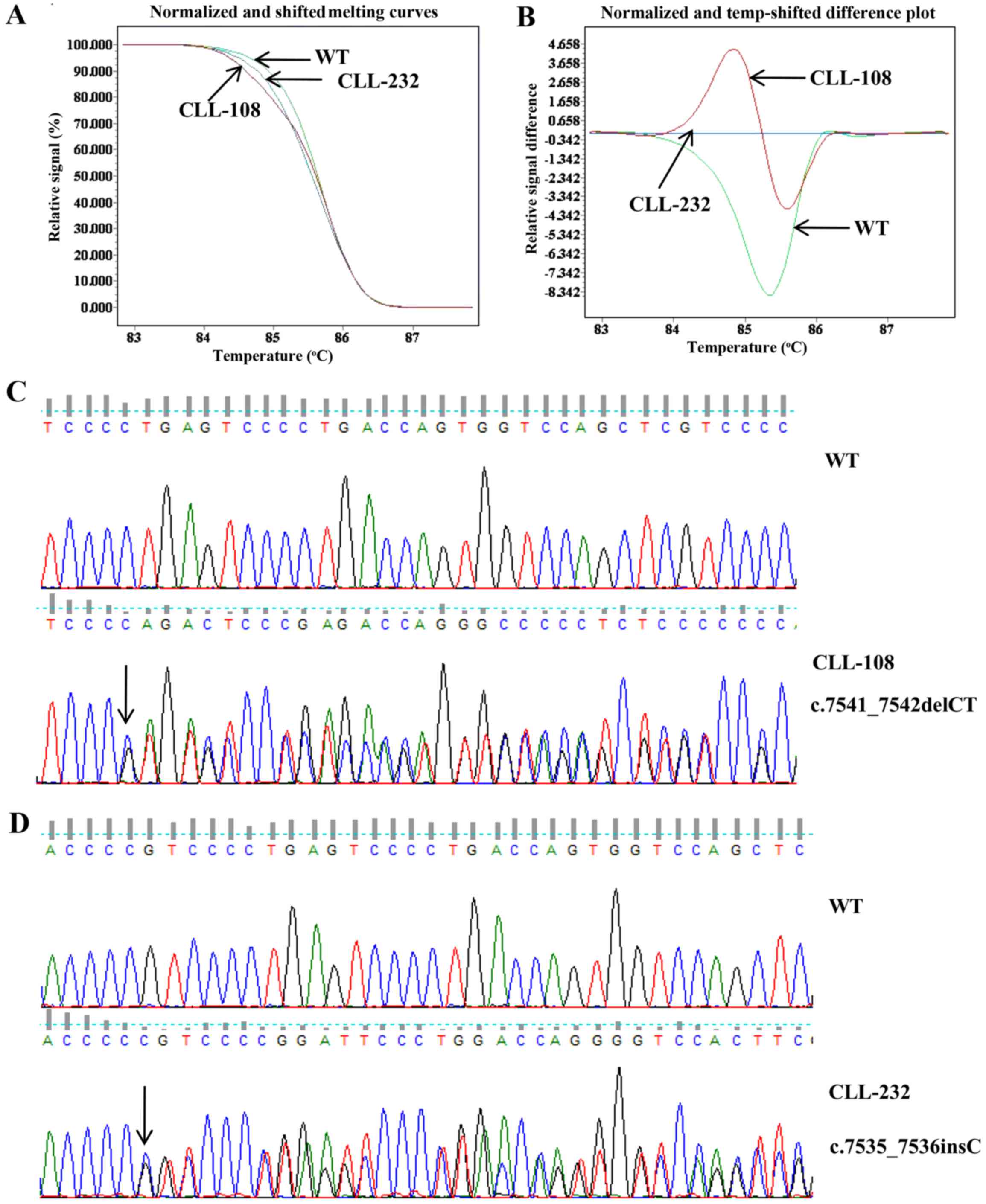
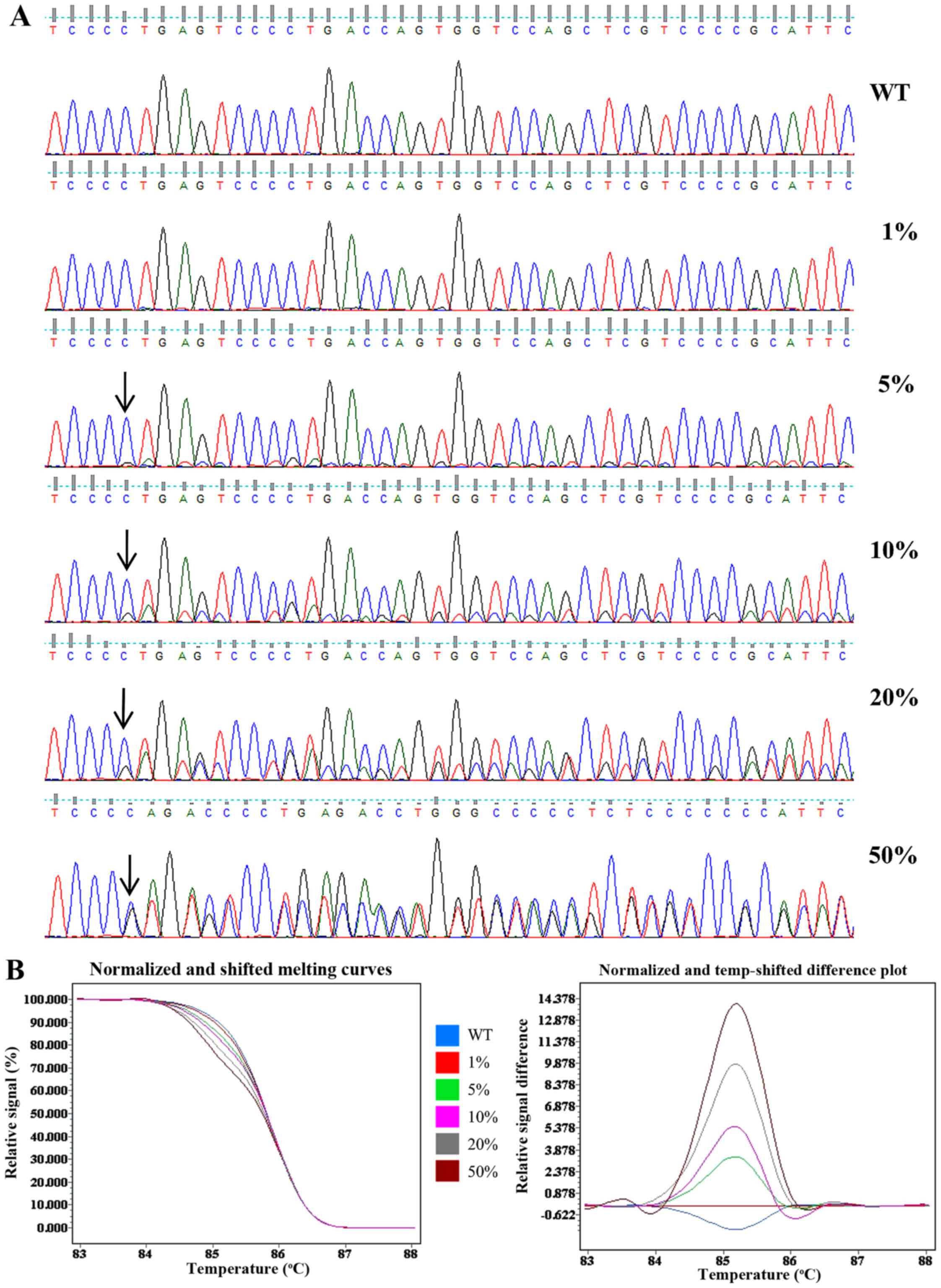
|
1
|
Zenz T, Mertens D, Küppers R, Döhner H and
Stilgenbauer S: From pathogenesis to treatment of chronic
lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:37–50. 2010.
|
|
2
|
Gaidano G, Foà R and Dalla-Favera R:
Molecular pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin
Invest. 122:3432–3438. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chiorazzi N, Rai KR and Ferrarini M:
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 352:804–815. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tam CS and Keating MJ: Chemoimmunotherapy
of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 7:521–532.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Puente XS, Pinyol M, Quesada V, Conde L,
Ordóñez GR, Villamor N, Escaramis G, Jares P, Beà S, González-Díaz
M, et al: Whole-genome sequencing identifies recurrent mutations in
chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nature. 475:101–105. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rossi D, Fangazio M, Rasi S, Vaisitti T,
Monti S, Cresta S, Chiaretti S, Del Giudice I, Fabbri G, Bruscaggin
A, et al: Disruption of BIRC3 associates with fludarabine
chemore-fractoriness in TP53 wild-type chronic lymphocytic
leukemia. Blood. 119:2854–2862. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Blaumueller CM, Qi H, Zagouras P and
Artavanis-Tsakonas S: Intracellular cleavage of Notch leads to a
heterodimeric receptor on the plasma membrane. Cell. 90:281–291.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yuan JS, Kousis PC, Suliman S, Visan I and
Guidos CJ: Functions of notch signaling in the immune system:
Consensus and controversies. Annu Rev Immunol. 28:343–365. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lobry C, Oh P and Aifantis I: Oncogenic
and tumor suppressor functions of Notch in cancer: It's NOTCH what
you think. J Exp Med. 208:1931–1935. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lobry C, Oh P, Mansour MR, Look AT and
Aifantis I: Notch signaling: Switching an oncogene to a tumor
suppressor. Blood. 123:2451–2459. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rosati E, Sabatini R, Rampino G, Tabilio
A, Di Ianni M, Fettucciari K, Bartoli A, Coaccioli S, Screpanti I
and Marconi P: Constitutively activated Notch signaling is involved
in survival and apoptosis resistance of B-CLL cells. Blood.
113:856–865. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Arruga F, Gizdic B, Serra S, Vaisitti T,
Ciardullo C, Coscia M, Laurenti L, D'Arena G, Jaksic O, Inghirami
G, et al: Functional impact of NOTCH1 mutations in chronic
lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 28:1060–1070. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Fabbri G, Rasi S, Rossi D, Trifonov V,
Khiabanian H, Ma J, Grunn A, Fangazio M, Capello D, Monti S, et al:
Analysis of the chronic lymphocytic leukemia coding genome: Role of
NOTCH1 mutational activation. J Exp Med. 208:1389–1401. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rossi D, Rasi S, Fabbri G, Spina V,
Fangazio M, Forconi F, Marasca R, Laurenti L, Bruscaggin A, Cerri
M, et al: Mutations of NOTCH1 are an independent predictor of
survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 119:521–529. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Weissmann S, Roller A, Jeromin S,
Hernández M, Abáigar M, Hernández-Rivas JM, Grossmann V, Haferlach
C, Kern W, Haferlach T, et al: Prognostic impact and landscape of
NOTCH1 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): A study on
852 patients. Leukemia. 27:2393–2396. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
López-Guerra M, Xargay-Torrent S, Rosich
L, Montraveta A, Roldán J, Matas-Céspedes A, Villamor N, Aymerich
M, López-Otín C, Pérez-Galán P, et al: The γ-secretase inhibitor
PF-03084014 combined with fludarabine antagonizes migration,
invasion and angiogenesis in NOTCH1-mutated CLL cells. Leukemia.
29:96–106. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Osipo C, Golde TE, Osborne BA and Miele
LA: Off the beaten pathway: The complex cross talk between Notch
and NF-kappaB. Lab Invest. 11–17. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Di Ianni M, Baldoni S, Rosati E, Ciurnelli
R, Cavalli L, Martelli MF, Marconi P, Screpanti I and Falzetti F: A
new genetic lesion in B-CLL: A NOTCH1 PEST domain mutation. Br J
Haematol. 146:689–691. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sportoletti P, Baldoni S, Cavalli L, Del
Papa B, Bonifacio E, Ciurnelli R, Bell AS, Di Tommaso A, Rosati E,
Crescenzi B, et al: NOTCH1 PEST domain mutation is an adverse
prognostic factor in B-CLL. Br J Haematol. 151:404–406. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sportoletti P, Baldoni S, Del Papa B,
Aureli P, Dorillo E, Ruggeri L, Plebani S, Amico V, Di Tommaso A,
Rosati E, et al: A revised NOTCH1 mutation frequency still impacts
survival while the allele burden predicts early progression in
chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 28:436–439. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Stilgenbauer S, Schnaiter A, Paschka P,
Zenz T, Rossi M, Döhner K, Bühler A, Böttcher S, Ritgen M, Kneba M,
et al: Gene mutations and treatment outcome in chronic lymphocytic
leukemia: Results from the CLL8 trial. Blood. 123:3247–3254. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Oscier DG, Rose-Zerilli MJ, Winkelmann N,
Gonzalez de Castro D, Gomez B, Forster J, Parker H, Parker A,
Gardiner A, Collins A, et al: The clinical significance of NOTCH1
and SF3B1 mutations in the UK LRF CLL4 trial. Blood. 121:468–475.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Puente XS, Beà S, Valdés-Mas R, Villamor
N, Gutiérrez-Abril J, Martín-Subero JI, Munar M, Rubio-Pérez C,
Jares P, Aymerich M, et al: Non-coding recurrent mutations in
chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nature. 526:519–524. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gundry CN, Vandersteen JG, Reed GH, Pryor
RJ, Chen J and Wittwer CT: Amplicon melting analysis with labeled
primers: A closed-tube method for differentiating homozygotes and
hetero-zygotes. Clin Chem. 49:396–406. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Reed GH, Kent JO and Wittwer CT:
High-resolution DNA melting analysis for simple and efficient
molecular diagnostics. Pharmacogenomics. 8:597–608. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Taylor CF: Mutation scanning using
high-resolution melting. Biochem Soc Trans. 37:433–437. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liew M, Pryor R, Palais R, Meadows C,
Erali M, Lyon E and Wittwer C: Genotyping of single-nucleotide
polymorphisms by high-resolution melting of small amplicons. Clin
Chem. 50:1156–1164. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Reed GH and Wittwer CT: Sensitivity and
specificity of single-nucleotide polymorphism scanning by
high-resolution melting analysis. Clin Chem. 50:1748–1754. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Graham R, Liew M, Meadows C, Lyon E and
Wittwer CT: Distinguishing different DNA heterozygotes by
high-resolution melting. Clin Chem. 51:1295–1298. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Herrmann MG, Durtschi JD, Bromley LK,
Wittwer CT and Voelkerding KV: Amplicon DNA melting analysis for
mutation scanning and genotyping: Cross-platform comparison of
instruments and dyes. Clin Chem. 52:494–503. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Montgomery J, Wittwer CT, Palais R and
Zhou L: Simultaneous mutation scanning and genotyping by
high-resolution DNA melting analysis. Nat Protoc. 2:59–66. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wei P, Walls M, Qiu M, Ding R, Denlinger
RH, Wong A, Tsaparikos K, Jani JP, Hosea N, Sands M, et al:
Evaluation of selective gamma-secretase inhibitor PF-03084014 for
its antitumor efficacy and gastrointestinal safety to guide optimal
clinical trial design. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:1618–1628. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu Y, Cain-Hom C, Choy L, Hagenbeek TJ, de
Leon GP, Chen Y, Finkle D, Venook R, Wu X, Ridgway J, et al:
Therapeutic antibody targeting of individual Notch receptors.
Nature. 464:1052–1057. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schmidt U, Hulkkonen J and Naue J:
Detection of a G>C single nucleotide polymorphism within a
repetitive DNA sequence by high-resolution DNA melting. Int J Legal
Med. Mar 14–2016.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hong Y, Pandey MK, Liu Y, Chen X, Liu H,
Varshney RK, Liang X and Huang S: Identification and evaluation of
single-nucleotide polymorphisms in allotetraploid peanut (Arachis
hypogaea L.) based on amplicon sequencing combined with high
resolution melting (HRM) analysis. Front Plant Sci. 6:10682015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
de Juan I, Esteban E, Palanca S, Barragán
E and Bolufer P: High-resolution melting analysis for rapid
screening of BRCA1 and BRCA2 Spanish mutations. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 115:405–414. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Er TK and Chang JG: High-resolution
melting: Applications in genetic disorders. Clin Chim Acta.
414:197–201. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xia Y, Fan L, Wang L, Gale RP, Wang M,
Tian T, Wu W, Yu L, Chen YY, Xu W, et al: Frequencies of SF3B1,
NOTCH1, MYD88, BIRC3 and IGHV mutations and TP53 disruptions in
Chinese with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Disparities with
Europeans. Oncotarget. 6:5426–5434. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shedden K, Li Y, Ouillette P and Malek SN:
Characteristics of chronic lymphocytic leukemia with somatically
acquired mutations in NOTCH1 exon 34. Leukemia. 26:1108–1110. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Balatti V, Bottoni A, Palamarchuk A, Alder
H, Rassenti LZ, Kipps TJ, Pekarsky Y and Croce CM: NOTCH1 mutations
in CLL associated with trisomy 12. Blood. 119:329–331. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Del Giudice I, Rossi D, Chiaretti S,
Marinelli M, Tavolaro S, Gabrielli S, Laurenti L, Marasca R, Rasi
S, Fangazio M, et al: NOTCH1 mutations in +12 chronic lymphocytic
leukemia (CLL) confer an unfavorable prognosis, induce a
distinctive transcriptional profiling and refine the intermediate
prognosis of +12 CLL. Haematologica. 97:437–441. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
42
|
Villamor N, Conde L, Martínez-Trillos A,
Cazorla M, Navarro A, Beà S, López C, Colomer D, Pinyol M, Aymerich
M, et al: NOTCH1 mutations identify a genetic subgroup of chronic
lymphocytic leukemia patients with high risk of transformation and
poor outcome. Leukemia. 27:1100–1106. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Do H, Krypuy M, Mitchell PL, Fox SB and
Dobrovic A: High resolution melting analysis for rapid and
sensitive EGFR and KRAS mutation detection in formalin fixed
paraffin embedded biopsies. BMC Cancer. 8:1422008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Marino M, Monzani ML, Brigante G, Cioni K,
Madeo B, Santi D, Maiorana A, Bettelli S, Moriondo V, Pignatti E,
et al: High-resolution melting is a sensitive, cost-effective,
time-saving technique for BRAF V600E detection in thyroid FNAB
washing liquid: A prospective cohort study. Eur Thyroid J. 4:73–81.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wright GM, Do H, Weiss J, Alam NZ, Rathi
V, Walkiewicz M, John T, Russell PA and Dobrovic A: Mapping of
actionable mutations to histological subtype domains in lung
adenocarcinoma: Implications for precision medicine. Oncotarget.
5:2107–2115. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
El Khachibi M, Diakite B, Hamzi K, Badou
A, Senhaji MA, Bakhchane A, Jouhadi H, Barakat A, Benider A and
Nadifi S: Screening of exon 11 of BRCA1 gene using the high
resolution melting approach for diagnosis in Moroccan breast cancer
patients. BMC Cancer. 15:812015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang J, Ren X, Bai X, Zhang T, Wang Y, Li
K and Li G: Identification of gene mutation in patients with
osteogenesis imperfecta using high resolution melting analysis. Sci
Rep. 5:134682015. View Article : Google Scholar
|