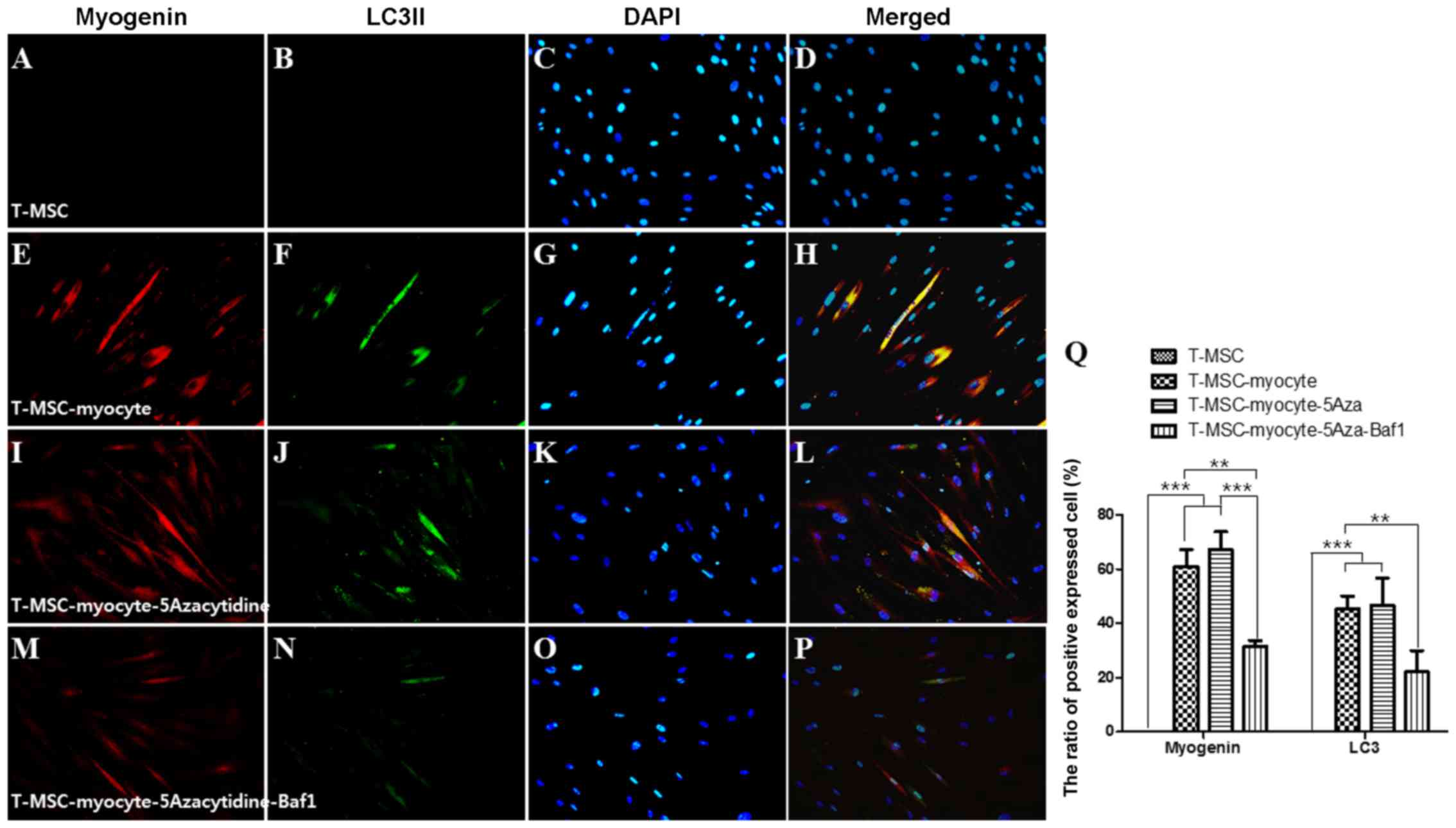
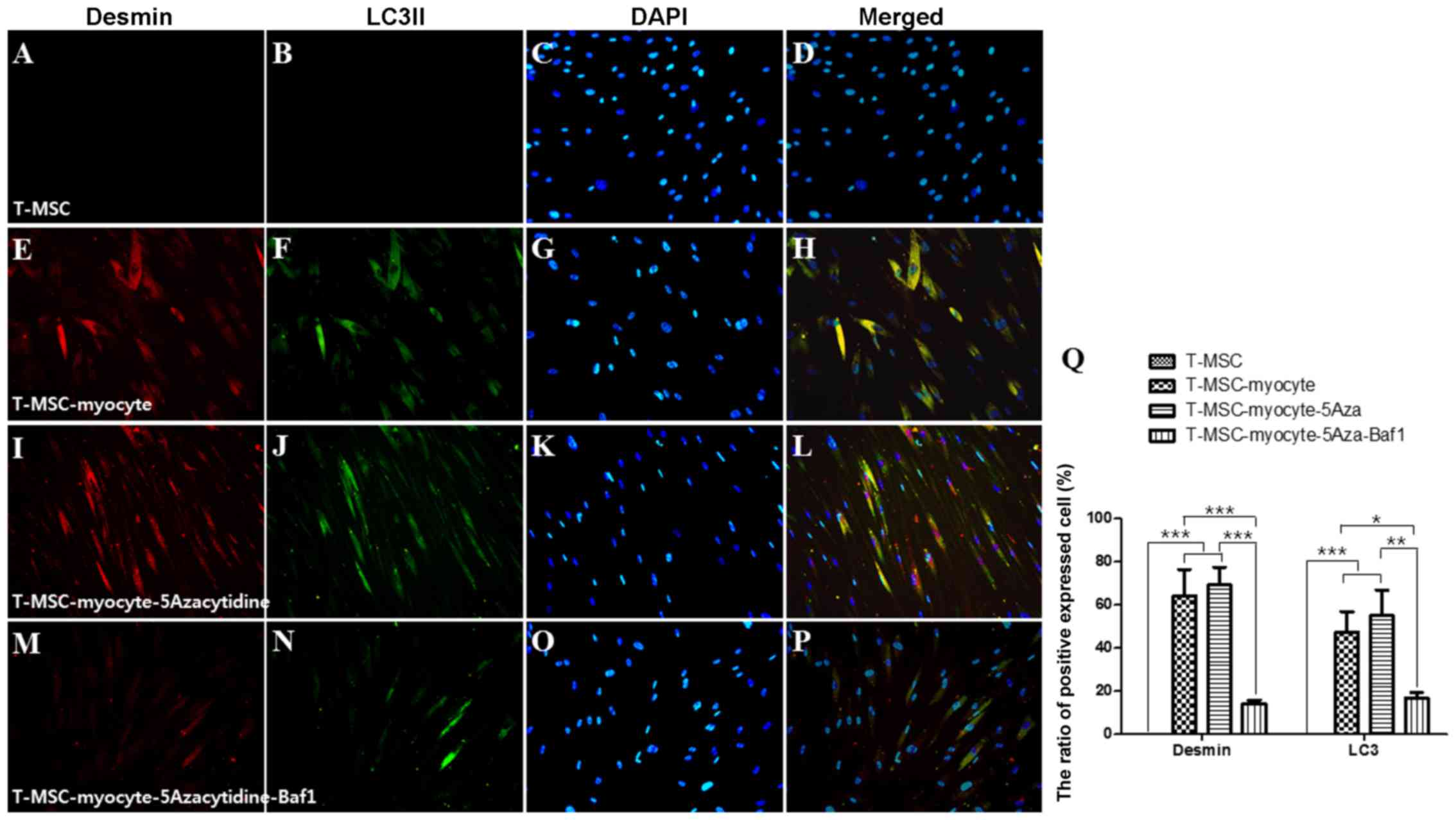
|
1
|
Ryu KH, Cho KA, Park HS, Kim JY, Woo SY,
Jo I, Choi YH, Park YM, Jung SC, Chung SM, et al: Tonsil-derived
mesenchymal stromal cells: Evaluation of biologic, immunologic and
genetic factors for successful banking. Cytotherapy. 14:1193–1202.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Park S, Choi Y, Jung N, Yu Y, Ryu KH, Kim
HS, Jo I, Choi BO and Jung SC: Myogenic differentiation potential
of human tonsil-derived mesenchymal stem cells and their potential
for use to promote skeletal muscle regeneration. Int J Mol Med.
37:1209–1220. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dezawa M, Ishikawa H, Itokazu Y, Yoshihara
T, Hoshino M, Takeda S, Ide C and Nabeshima Y: Bone marrow stromal
cells generate muscle cells and repair muscle degeneration.
Science. 309:314–317. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Di Rocco G, Iachininoto MG, Tritarelli A,
Straino S, Zacheo A, Germani A, Crea F and Capogrossi MC: Myogenic
potential of adipose-tissue-derived cells. J Cell Sci.
119:2945–2952. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim JA, Shon YH, Lim JO, Yoo JJ, Shin HI
and Park EK: MYOD mediates skeletal myogenic differentiation of
human amniotic fluid stem cells and regeneration of muscle injury.
Stem Cell Res Ther. 4:1472013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nunes VA, Cavaçana N, Canovas M, Strauss
BE and Zatz M: Stem cells from umbilical cord blood differentiate
into myotubes and express dystrophin in vitro only after exposure
to in vivo muscle environment. Biol Cell. 99:185–196. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Park S, Kim E, Koh SE, Maeng S, Lee WD,
Lim J, Shim I and Lee YJ: Dopaminergic differentiation of neural
progenitors derived from placental mesenchymal stem cells in the
brains of Parkinson's disease model rats and alleviation of
asymmetric rotational behavior. Brain Res. 1466:158–166. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kerkis I, Kerkis A, Dozortsev D,
Stukart-Parsons GC, Gomes Massironi SM, Pereira LV, Caplan AI and
Cerruti HF: Isolation and characterization of a population of
immature dental pulp stem cells expressing OCT-4 and other
embryonic stem cell markers. Cells Tissues Organs. 184:105–116.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Husmann I, Soulet L, Gautron J, Martelly I
and Barritault D: Growth factors in skeletal muscle regeneration.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 7:249–258. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang K, Wang C, Xiao F, Wang H and Wu Z:
JAK2/STAT2/STAT3 are required for myogenic differentiation. J Biol
Chem. 283:34029–34036. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Conboy IM and Rando TA: The regulation of
Notch signaling controls satellite cell activation and cell fate
determination in postnatal myogenesis. Dev Cell. 3:397–409. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fortini P, Ferretti C, Iorio E, Cagnin M,
Garribba L, Pietraforte D, Falchi M, Pascucci B, Baccarini S,
Morani F, et al: The fine tuning of metabolism, autophagy and
differentiation during in vitro myogenesis. Cell Death Dis.
7:e21682016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Maley MA, Fan Y, Beilharz MW and Grounds
MD: Intrinsic differences in MyoD and myogenin expression between
primary cultures of SJL/J and BALB/C skeletal muscle. Exp Cell Res.
211:99–107. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Miller KJ, Thaloor D, Matteson S and
Pavlath GK: Hepatocyte growth factor affects satellite cell
activation and differentiation in regenerating skeletal muscle. Am
J Physiol Cell Physiol. 278:C174–C181. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Heszele MF and Price SR: Insulin-like
growth factor I: The yin and yang of muscle atrophy. Endocrinology.
145:4803–4805. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nakanishi K, Dohmae N and Morishima N:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress increases myofiber formation in vitro.
FASEB J. 21:2994–3003. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Levine B and Klionsky DJ: Development by
self-digestion: Molecular mechanisms and biological functions of
autophagy. Dev Cell. 6:463–477. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nuschke A, Rodrigues M, Stolz DB, Chu CT,
Griffith L and Wells A: Human mesenchymal stem cells/multipotent
stromal cells consume accumulated autophagosomes early in
differentiation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 5:1402014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sin J, Andres AM, Taylor DJ, Weston T,
Hiraumi Y, Stotland A, Kim BJ, Huang C, Doran KS and Gottlieb RA:
Mitophagy is required for mitochondrial biogenesis and myogenic
differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts. Autophagy. 12:369–380. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yu Y, Park YS, Kim HS, Kim HY, Jin YM,
Jung SC, Ryu KH and Jo I: Characterization of long-term in vitro
culture-related alterations of human tonsil-derived mesenchymal
stem cells: Role for CCN1 in replicative senescence-associated
increase in osteogenic differentiation. J Anat. 225:510–518. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pestonjamasp KN, Pope RK, Wulfkuhle JD and
Luna EJ: Supervillin (p205): A novel membrane-associated,
F-actin-binding protein in the villin/gelsolin superfamily. J Cell
Biol. 139:1255–1269. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Morris NJ, Ross SA, Lane WS, Moestrup SK,
Petersen CM, Keller SR and Lienhard GE: Sortilin is the major
110-kDa protein in GLUT4 vesicles from adipocytes. J Biol Chem.
273:3582–3587. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hu H, Gao X, Sun Y, Zhou J, Yang M and Xu
Z: Alpha-actinin-2, a cytoskeletal protein, binds to angiogenin.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 329:661–667. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huett A, Ng A, Cao Z, Kuballa P, Komatsu
M, Daly MJ, Podolsky DK and Xavier RJ: A novel hybrid yeast-human
network analysis reveals an essential role for FNBP1L in
antibacterial autophagy. J Immunol. 182:4917–4930. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Marquez RT and Xu L: Bcl-2:Beclin 1
complex: Multiple, mechanisms regulating autophagy/apoptosis toggle
switch. Am J Cancer Res. 2:214–221. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nakatogawa H, Suzuki K, Kamada Y and
Ohsumi Y: Dynamics and diversity in autophagy mechanisms: Lessons
from yeast. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 10:458–467. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Moran JL, Li Y, Hill AA, Mounts WM and
Miller CP: Gene expression changes during mouse skeletal myoblast
differentiation revealed by transcriptional profiling. Physiol
Genomics. 10:103–111. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Osses N and Brandan E: ECM is required for
skeletal muscle differentiation independently of muscle regulatory
factor expression. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 282:C383–C394. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hinz B, Phan SH, Thannickal VJ, Galli A,
Bochaton-Piallat ML and Gabbiani G: The myofibroblast: One
function, multiple origins. Am J Pathol. 170:1807–1816. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Oh SW, Pope RK, Smith KP, Crowley JL, Nebl
T, Lawrence JB and Luna EJ: Archvillin, a muscle-specific isoform
of supervillin, is an early expressed component of the costameric
membrane skeleton. J Cell Sci. 116:2261–2275. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ariga M, Nedachi T, Katagiri H and Kanzaki
M: Functional role of sortilin in myogenesis and development of
insulin-responsive glucose transport system in C2C12 myocytes. J
Biol Chem. 283:10208–10220. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kostin S, Hein S, Arnon E, Scholz D and
Schaper J: The cytoskeleton and related proteins in the human
failing heart. Heart Fail Rev. 5:271–280. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Sakoh-Nakatogawa M, Matoba K, Asai E,
Kirisako H, Ishii J, Noda NN, Inagaki F, Nakatogawa H and Ohsumi Y:
Atg12-Atg5 conjugate enhances E2 activity of Atg3 by rearranging
its catalytic site. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 20:433–439. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Neel BA, Lin Y and Pessin JE: Skeletal
muscle autophagy: A new metabolic regulator. Trends Endocrinol
Metab. 24:635–643. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wakitani S, Saito T and Caplan AI:
Myogenic cells derived from rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
exposed to 5-azacytidine. Muscle Nerve. 18:1417–1426. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zheng JK, Wang Y, Karandikar A, Wang Q,
Gai H, Liu AL, Peng C and Sheng HZ: Skeletal myogenesis by human
embryonic stem cells. Cell Res. 16:713–722. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mizushima N, Ohsumi Y and Yoshimori T:
Autophagosome formation in mammalian cells. Cell Struct Funct.
27:421–429. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Jackson MJ: Reactive oxygen species and
redox-regulation of skeletal muscle adaptations to exercise. Philos
Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 360:2285–2291. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Malicdan MC, Noguchi S, Nonaka I, Saftig P
and Nishino I: Lysosomal myopathies: An excessive build-up in
autophagosomes is too much to handle. Neuromuscul Disord.
18:521–529. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|