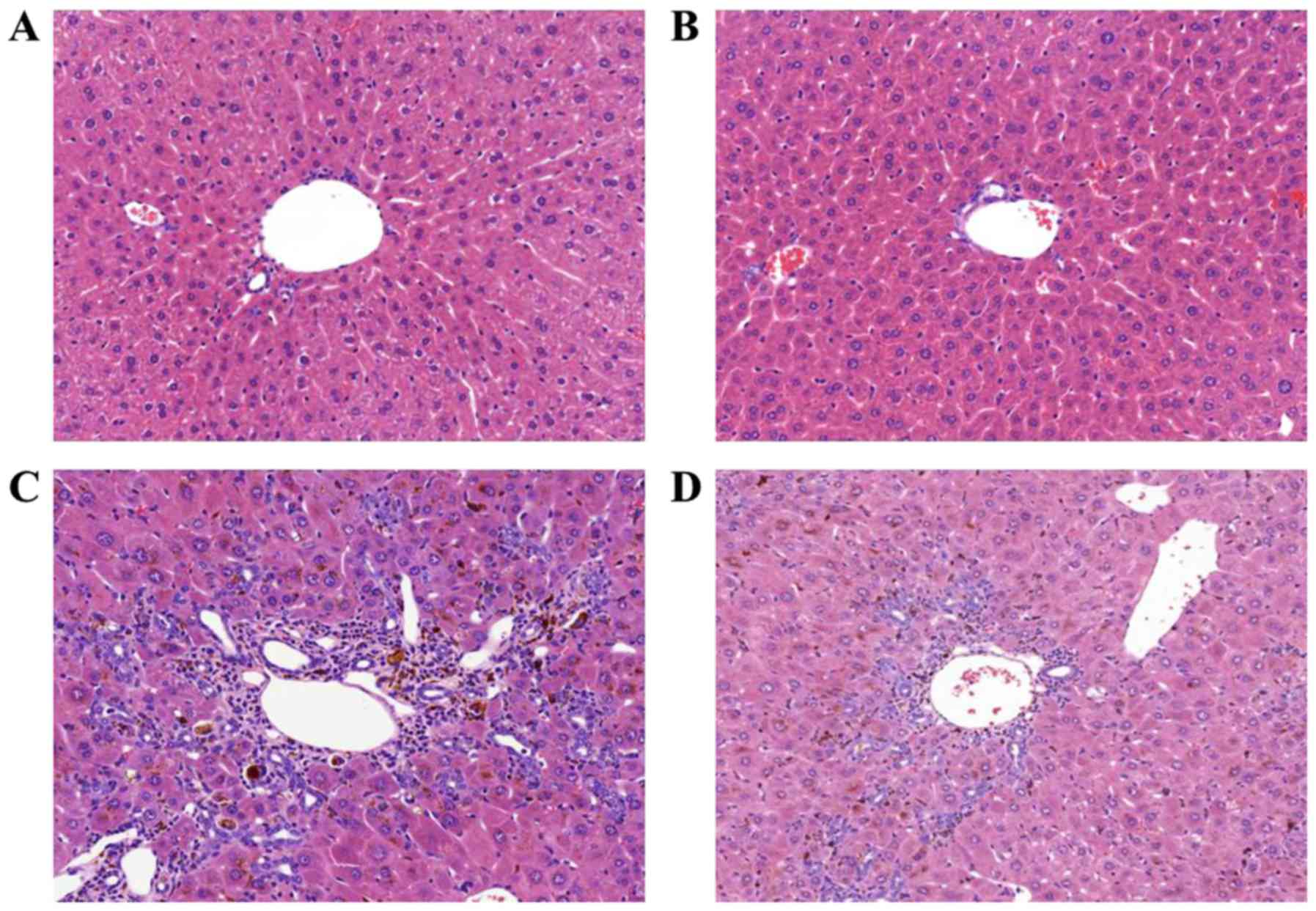
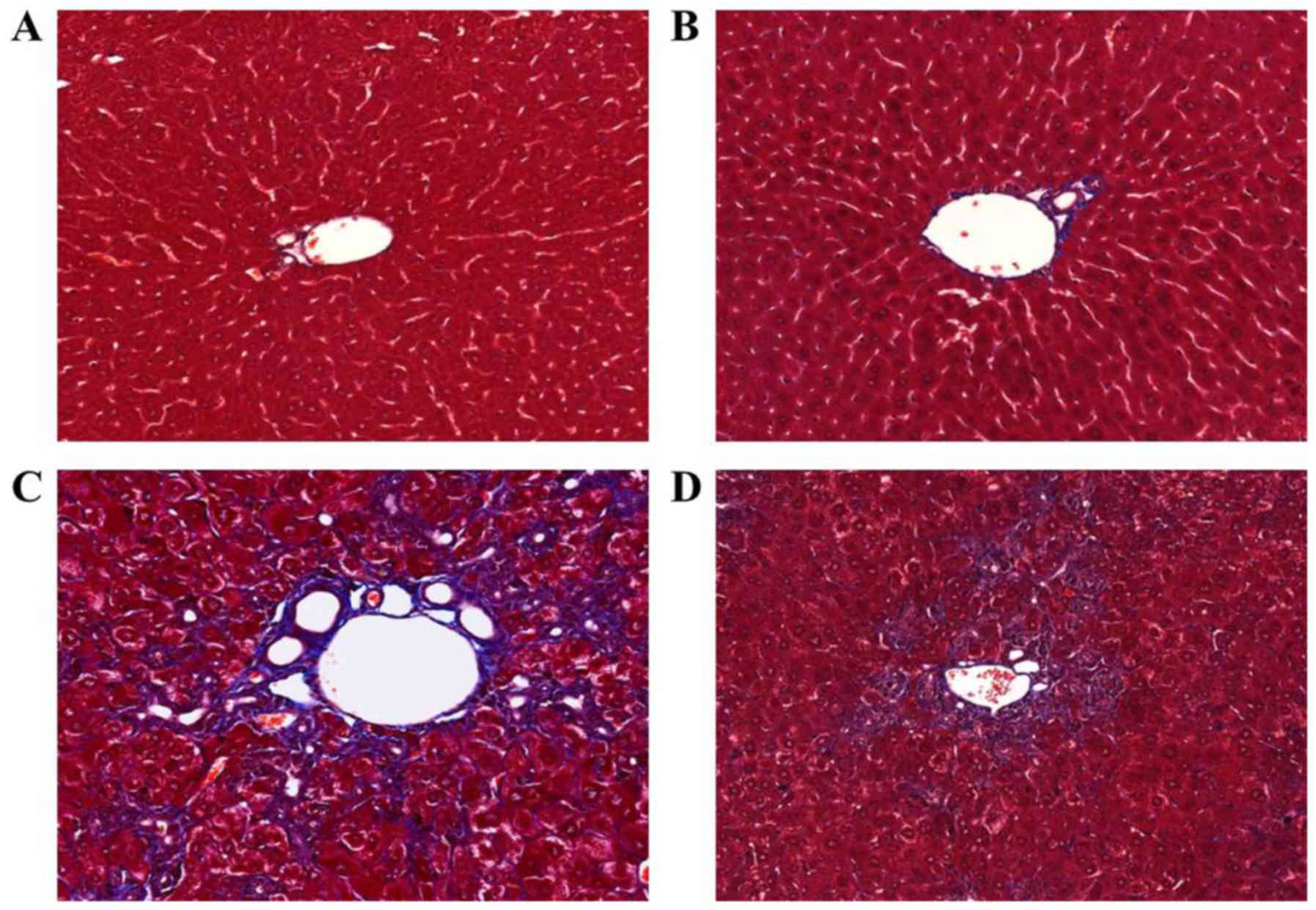
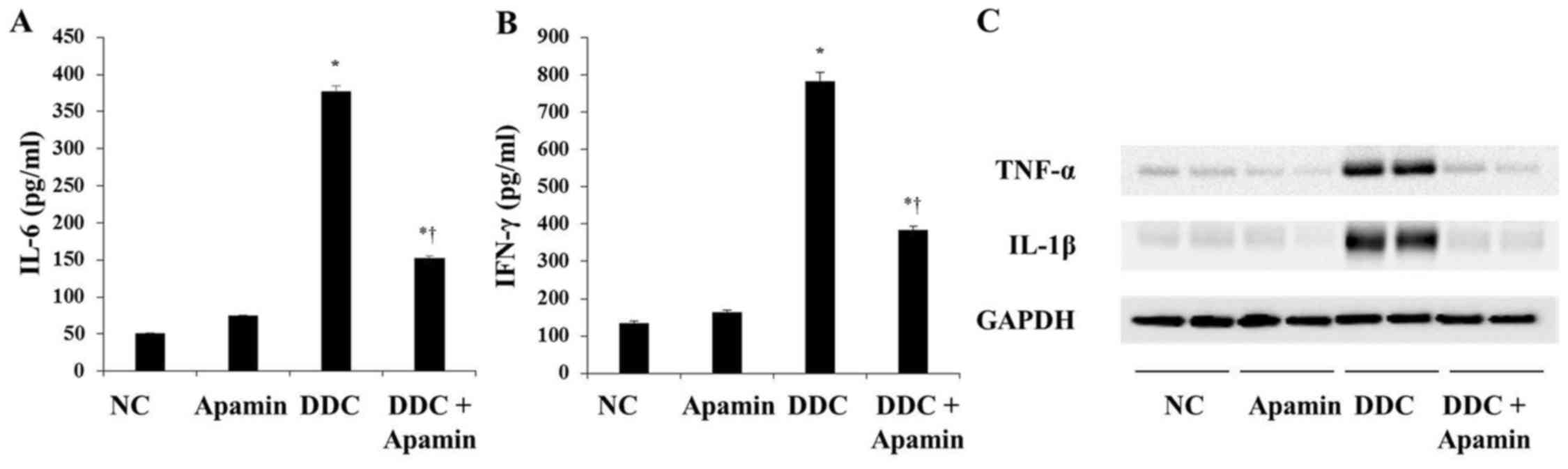
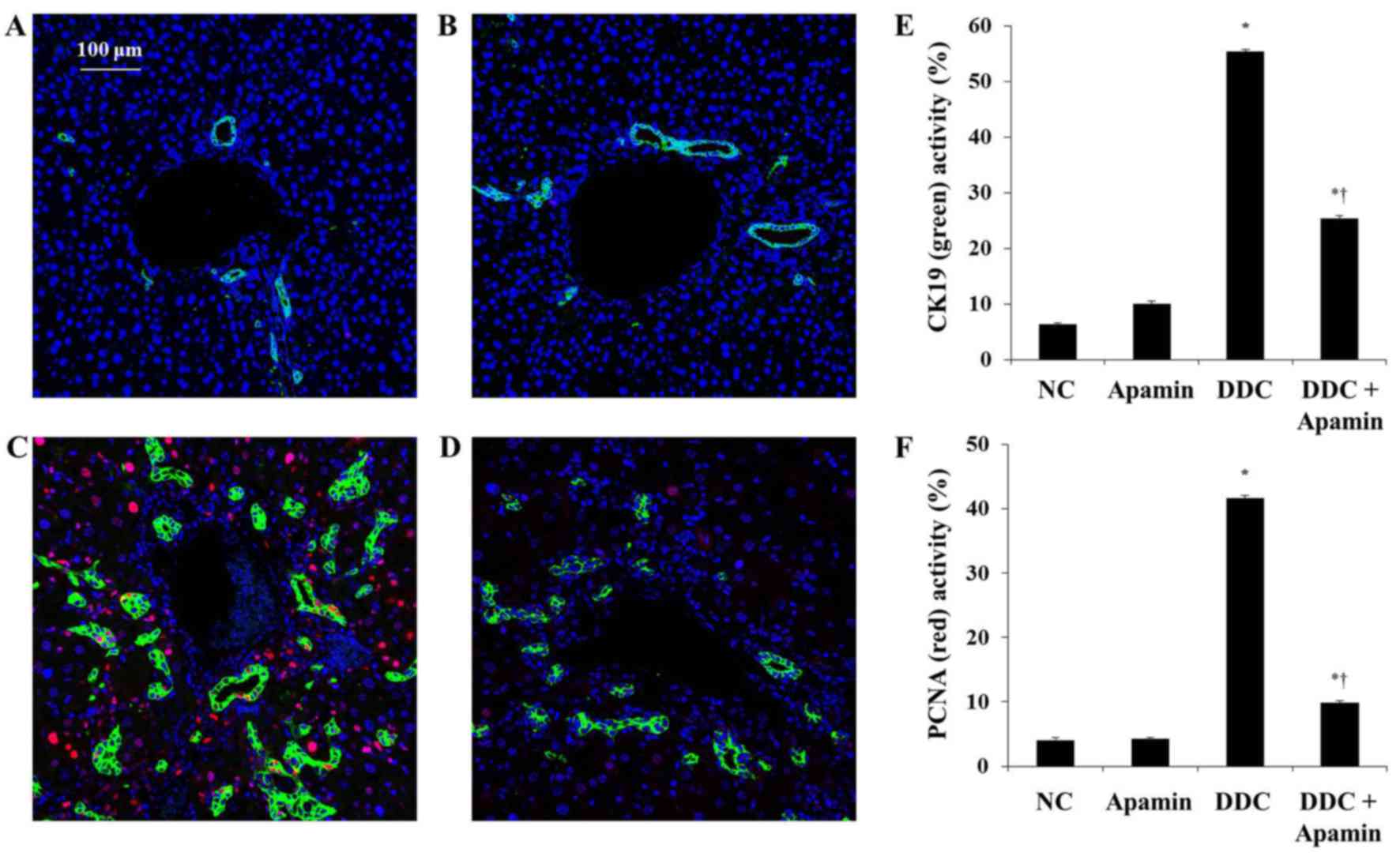
|
1
|
Friedman SL: Mechanisms of hepatic
fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology. 134:1655–1669. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gonzalez-Sanchez E, Firrincieli D, Housset
C and Chignard N: Nuclear receptors in acute and chronic
cholestasis. Dig Dis. 33:357–366. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zollner G, Marschall HU, Wagner M and
Trauner M: Role of nuclear receptors in the adaptive response to
bile acids and cholestasis: Pathogenetic and therapeutic
considerations. Mol Pharm. 3:231–251. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Glaser SS, Gaudio E, Miller T, Alvaro D
and Alpini G: Cholangiocyte proliferation and liver fibrosis.
Expert Rev Mol Med. 11:e72009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lindor KD, Gershwin ME, Poupon R, Kaplan
M, Bergasa V and Heathcote EJ; American Association for Study of
Liver Diseases: Primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology. 50:291–308.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Glaser SS, Onori P, Wise C, Yang F,
Marzioni M, Alvaro D, Franchitto A, Mancinelli R, Alpini G, Munshi
MK, et al: Recent advances in the regulation of cholangiocyte
proliferation and function during extrahepatic cholestasis. Dig
Liver Dis. 42:245–252. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Matsumoto K, Fujii H, Michalopoulos G,
Fung JJ and Demetris AJ: Human biliary epithelial cells secrete and
respond to cytokines and hepatocyte growth factors in vitro:
Interleukin-6, hepatocyte growth factor and epidermal growth factor
promote DNA synthesis in vitro. Hepatology. 20:376–382. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Popov Y and Schuppan D: Targeting liver
fibrosis: Strategies for development and validation of antifibrotic
therapies. Hepatology. 50:1294–1306. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Friedman SL: Molecular regulation of
hepatic fibrosis, an integrated cellular response to tissue injury.
J Biol Chem. 275:2247–2250. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Moreno M and Giralt E: Three valuable
peptides from bee and wasp venoms for therapeutic and
biotechnological use: Melittin, apamin and mastoparan. Toxins
(Basel). 7:1126–1150. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Mourre C, Fournier C and Soumireu-Mourat
B: Apamin, a blocker of the calcium-activated potassium channel,
induces neurodegeneration of Purkinje cells exclusively. Brain Res.
778:405–408. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Feranchak AP, Doctor RB, Troetsch M,
Brookman K, Johnson SM and Fitz JG: Calcium-dependent regulation of
secretion in biliary epithelial cells: The role of apamin-sensitive
SK channels. Gastroenterology. 127:903–913. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee WR, Kim KH, An HJ, Kim JY, Lee SJ, Han
SM, Pak SC and Park KK: Apamin inhibits hepatic fibrosis through
suppression of transforming growth factor β1-induced hepatocyte
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
450:195–201. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim SJ, Park JH, Kim KH, Lee WR, An HJ,
Min BK, Han SM, Kim KS and Park KK: Apamin inhibits THP-1-derived
macrophage apoptosis via mitochondria-related apoptotic pathway.
Exp Mol Pathol. 93:129–134. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim KH, Sung HJ, Lee WR, An HJ, Kim JY,
Pak SC, Han SM and Park KK: Effects of melittin treatment in
cholangitis and biliary fibrosis in a model of xenobiotic-induced
cholestasis in mice. Toxins (Basel). 7:3372–3387. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kim JY, Kim KH, Lee WR, An HJ, Lee SJ, Han
SM, Lee KG, Park YY, Kim KS, Lee YS, et al: Apamin inhibits
PDGF-BB-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and
migration through suppressions of activated Akt and Erk signaling
pathway. Vascul Pharmacol. 70:8–14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Baghdasaryan A, Fuchs CD, Österreicher CH,
Lemberger UJ, Halilbasic E, Påhlman I, Graffner H, Krones E,
Fickert P, Wahlström A, et al: Inhibition of intestinal bile acid
absorption improves cholestatic liver and bile duct injury in a
mouse model of sclerosing cholangitis. J Hepatol. 64:674–681. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Pollheimer MJ, Fickert P and Stieger B:
Chronic cholestatic liver diseases: Clues from histopathology for
pathogenesis. Mol Aspects Med. 37:35–56. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yongping M, Zhang X, Xuewei L, Fan W, Chen
J, Zhang H, Chen G, Liu C and Liu P: Astragaloside prevents
BDL-induced liver fibrosis through inhibition of notch signaling
activation. J Ethnopharmacol. 169:200–209. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang JW, Hien TT, Lim SC, Jun DW, Choi HS,
Yoon JH, Cho IJ and Kang KW: Pin1 induction in the fibrotic liver
and its roles in TGF-β1 expression and Smad2/3 phosphorylation. J
Hepatol. 60:1235–1241. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim SJ, Park JH, Kim KH, Lee WR, Chang YC,
Park KK, Lee KG, Han SM, Yeo JH and Pak SC: Bee venom inhibits
hepatic fibrosis through suppression of pro-fibrogenic cytokine
expression. Am J Chin Med. 38:921–935. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee WR, Pak SC and Park KK: The protective
effect of bee venom on fibrosis causing inflammatory diseases.
Toxins (Basel). 7:4758–4772. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lee WR, Park JH, Kim KH, Park YY, Han SM
and Park KK: Protective effects of melittin on transforming growth
factor-β1 injury to hepatocytes via anti-apoptotic mechanism.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 256:209–215. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Park JH, Kum YS, Lee TI, Kim SJ, Lee WR,
Kim BI, Kim HS, Kim KH and Park KK: Melittin attenuates liver
injury in thioacetamide-treated mice through modulating
inflammation and fibrogenesis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
236:1306–1313. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Son DJ, Lee JW, Lee YH, Song HS, Lee CK
and Hong JT: Therapeutic application of anti-arthritis,
pain-releasing, and anti-cancer effects of bee venom and its
constituent compounds. Pharmacol Ther. 115:246–270. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dutta AK, Khimji AK, Sathe M, Kresge C,
Parameswara V, Esser V, Rockey DC and Feranchak AP: Identification
and functional characterization of the intermediate-conductance
Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channel (IK-1) in biliary epithelium. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 297:G1009–G1018. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Tabibian JH, Masyuk AI, Masyuk TV, O'Hara
SP and LaRusso NF: Physiology of cholangiocytes. Compr Physiol.
3:541–565. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fickert P, Stöger U, Fuchsbichler A,
Moustafa T, Marschall HU, Weiglein AH, Tsybrovskyy O, Jaeschke H,
Zatloukal K, Denk H, et al: A new xenobiotic-induced mouse model of
sclerosing cholangitis and biliary fibrosis. Am J Pathol.
171:525–536. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen Y, Guldiken N, Spurny M, Mohammed HH,
Haybaeck J, Pollheimer MJ, Fickert P, Gassler N, Jeon MK, Trautwein
C, et al: Loss of keratin 19 favours the development of cholestatic
liver disease through decreased ductular reaction. J Pathol.
237:343–354. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Leask A and Abraham DJ: TGF-beta signaling
and the fibrotic response. FASEB J. 18:816–827. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Flanders KC: Smad3 as a mediator of the
fibrotic response. Int J Exp Pathol. 85:47–64. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Inagaki Y and Okazaki I: Emerging insights
into Transforming growth factor beta Smad signal in hepatic
fibrogenesis. Gut. 56:284–292. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|