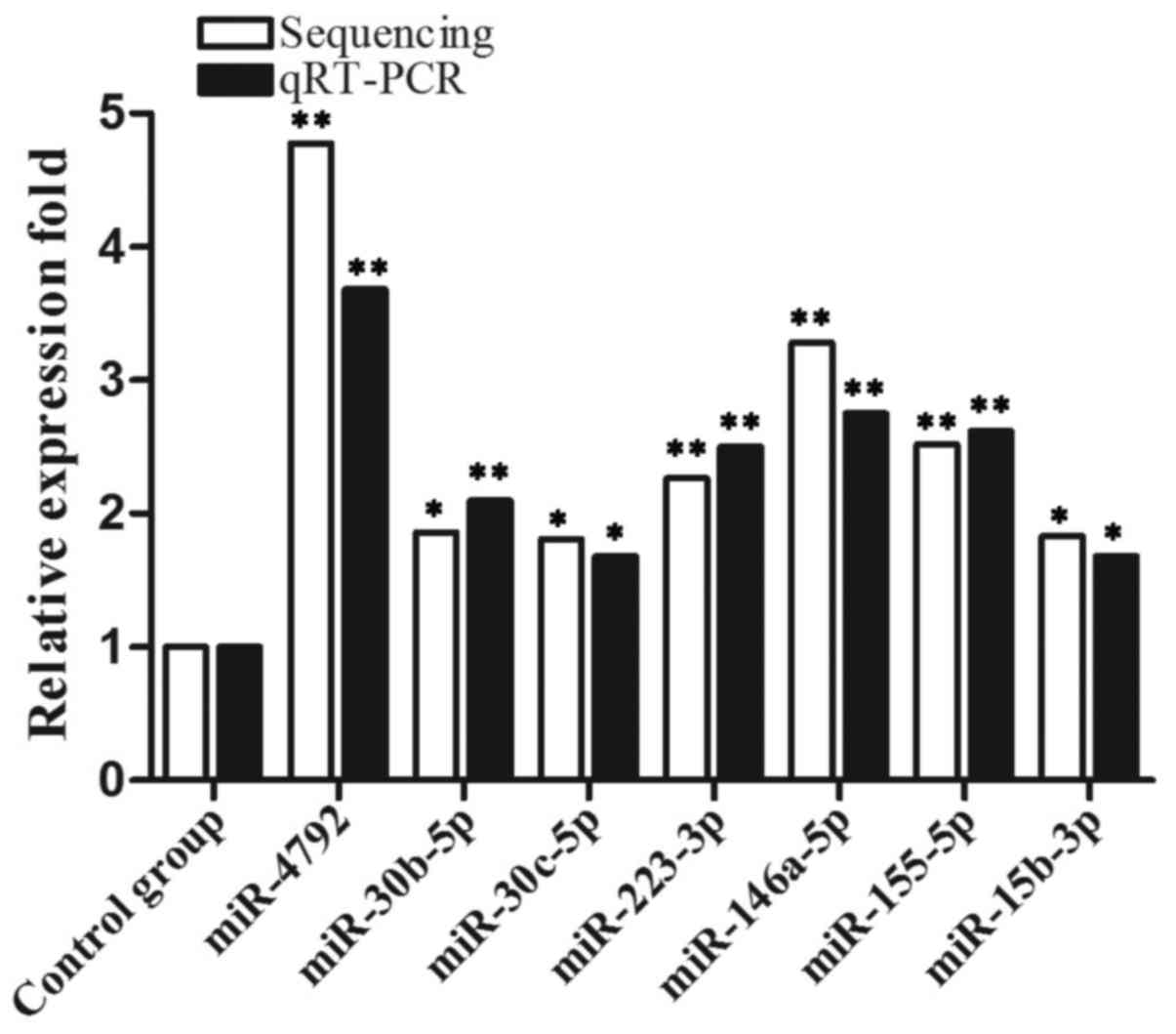
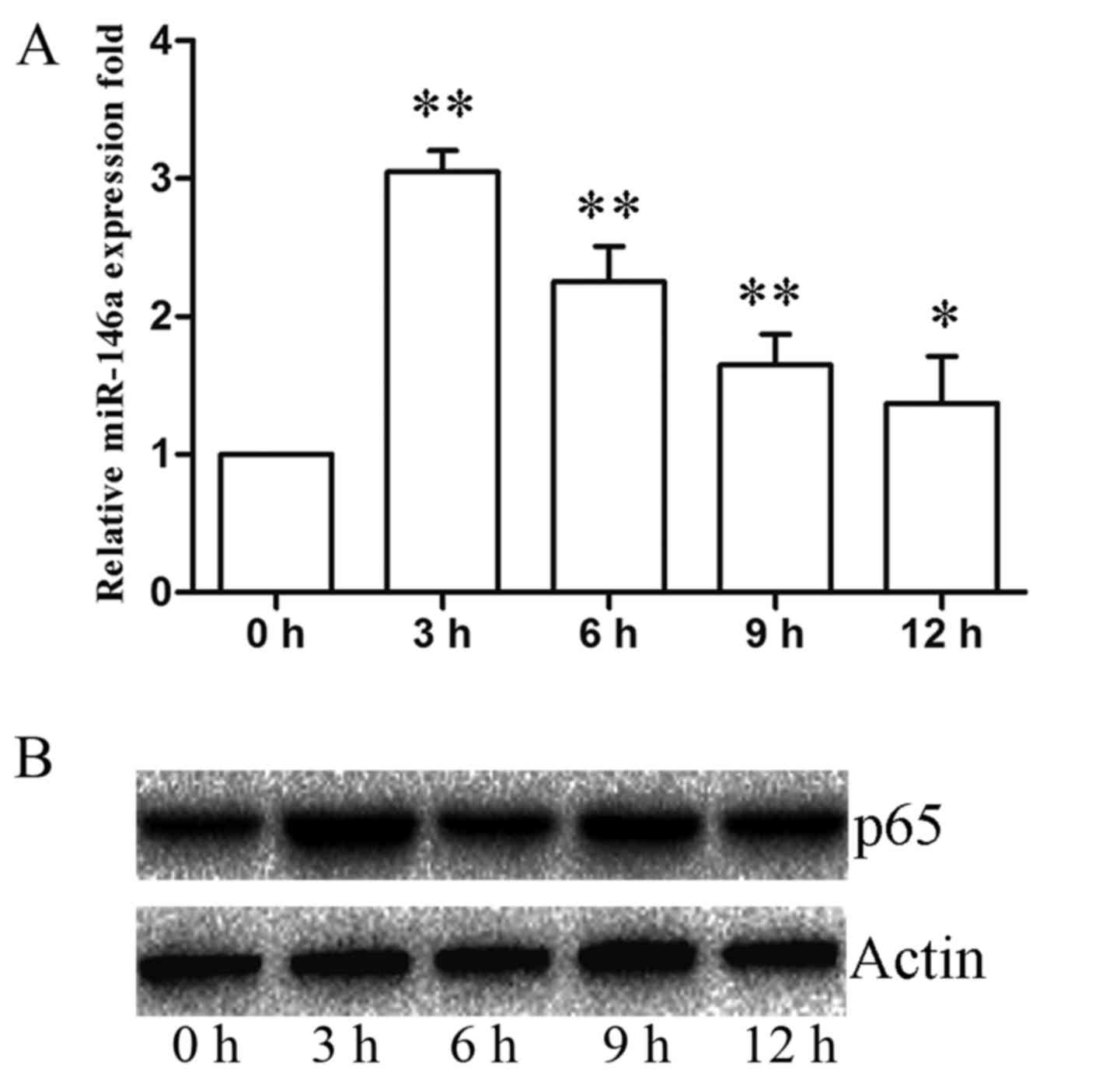
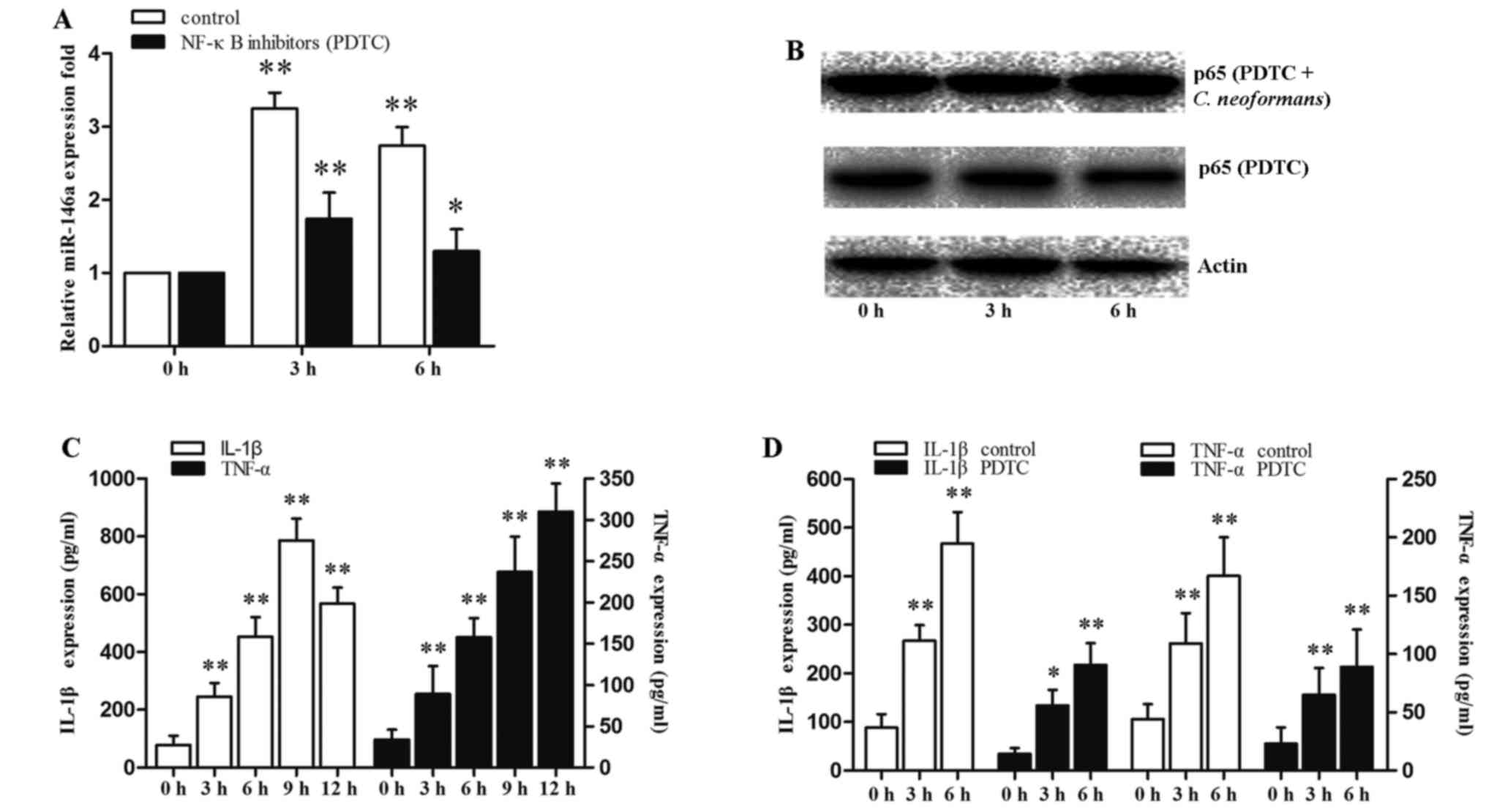
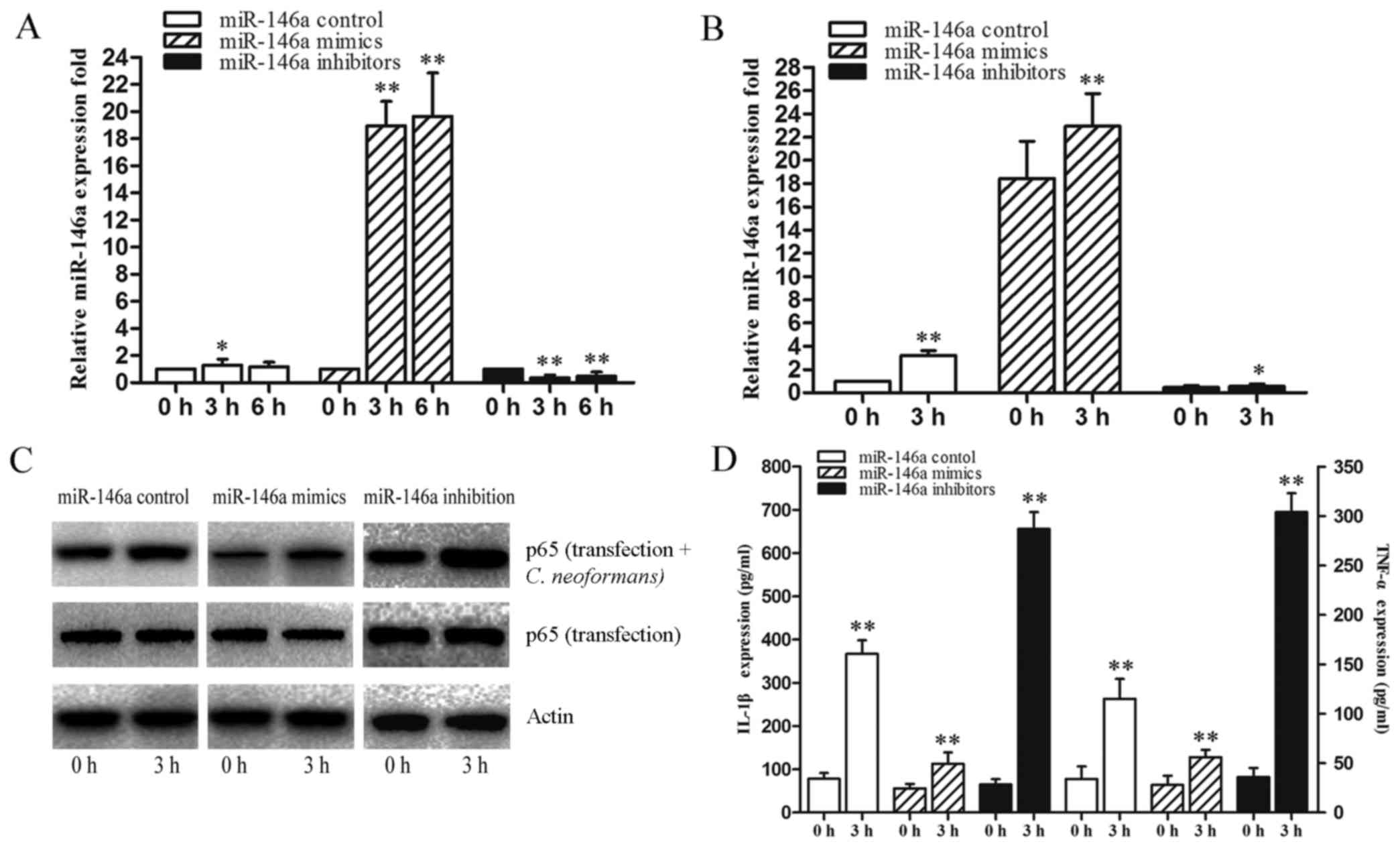
|
1
|
Chayakulkeeree M and Perfect JR:
Cryptococcosis. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 20:507–544. v–vi. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wu SX, Guo NR, Li XF, Liao WQ, Chen M,
Zhang QQ, Li CY, Li RY, Bulmer GS, Li DM, et al: Human pathogenic
fungi in China - emerging trends from ongoing national survey for
1986, 1996, and 2006. Mycopathologia. 171:387–393. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hajjeh RA, Conn LA, Stephens DS, Baughman
W, Hamill R, Graviss E, Pappas PG, Thomas C, Reingold A, Rothrock
G, et al Cryptococcal Active Surveillance Group: Cryptococcosis:
Population-based multistate active surveillance and risk factors in
human immunodeficiency virus-infected persons. J Infect Dis.
179:449–454. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen SST, Nimmo G, Speed B, Currie B,
Ellis D, Marriott D, Pfeiffer T, Parr D and Byth K: Epidemiology
and host- and varietydependent characteristics of infection due to
Cryptococcus neoformans in Australia and New Zealand. Australasian
Cryptococcal Study Group Clin Infect Dis. 31:92000.
|
|
5
|
Mihara T, Izumikawa K, Kakeya H,
Ngamskulrungroj P, Umeyama T, Takazono T, Tashiro M, Nakamura S,
Imamura Y, Miyazaki T, et al: Multilocus sequence typing of
Cryptococcus neoformans in non-HIV associated cryptococcosis in
Nagasaki, Japan. Med Mycol. 51:252–260. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Saijo T, Chen J, Chen SC, Rosen LB, Yi J,
Sorrell TC, Bennett JE, Holland SM, Browne SK and Kwon-Chung KJ:
Anti-granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor
autoantibodies are a risk factor for central nervous system
infection by Cryptococcus gattii in otherwise immunocompetent
patients. MBio. 5:e00912–e00914. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lawrence T and Natoli G: Transcriptional
regulation of macrophage polarization: Enabling diversity with
identity. Nat Rev Immunol. 11:750–761. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mosser DM and Edwards JP: Exploring the
full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:958–969.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Martinez FO, Helming L and Gordon S:
Alternative activation of macrophages: An immunologic functional
perspective. Annu Rev Immunol. 27:451–483. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Murray PJ and Wynn TA: Protective and
pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat Rev Immunol.
11:723–737. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Taylor PR, Martinez-Pomares L, Stacey M,
Lin HH, Brown GD and Gordon S: Macrophage receptors and immune
recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 23:901–944. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kawai T and Akira S: The role of
pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on
Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol. 11:373–384. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kawai T and Akira S: Toll-like receptors
and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and
immunity. Immunity. 34:637–650. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiménez-Dalmaroni MJ, Radcliffe CM, Harvey
DJ, Wormald MR, Verdino P, Ainge GD, Larsen DS, Painter GF,
Ulevitch R, Beutler B, et al: Soluble human TLR2 ectodomain binds
diacylglycerol from microbial lipopeptides and glycolipids. Innate
Immun. 21:175–193. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Nakamura K, Miyagi K, Koguchi Y, Kinjo Y,
Uezu K, Kinjo T, Akamine M, Fujita J, Kawamura I, Mitsuyama M, et
al: Limited contribution of Toll-like receptor 2 and 4 to the host
response to a fungal infectious pathogen, Cryptococcus neoformans.
FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 47:148–154. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yauch LE, Mansour MK, Shoham S, Rottman JB
and Levitz SM: Involvement of CD14, toll-like receptors 2 and 4,
and MyD88 in the host response to the fungal pathogen Cryptococcus
neoformans in vivo. Infect Immun. 72:5373–5382. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Akira S, Uematsu S and Takeuchi O:
Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 124:783–801. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Selbach M, Schwanhäusser B, Thierfelder N,
Fang Z, Khanin R and Rajewsky N: Widespread changes in protein
synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature. 455:58–63. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Ebert MS and Sharp PA: Roles for microRNAs
in conferring robustness to biological processes. Cell.
149:515–524. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang C and Wei W: The miRNA expression
profile of the uveal melanoma. Sci China Life Sci. 54:351–358.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Baltimore D, Boldin MP, O'Connell RM, Rao
DS and Taganov KD: MicroRNAs: New regulators of immune cell
development and function. Nat Immunol. 9:839–845. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lodish HF, Zhou B, Liu G and Chen CZ:
Micromanagement of the immune system by microRNAs. Nat Rev Immunol.
8:120–130. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Case SR, Martin RJ, Jiang D, Minor MN and
Chu HW: MicroRNA-21 inhibits toll-like receptor 2 agonist-induced
lung inflammation in mice. Exp Lung Res. 37:500–508. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Monk CE, Hutvagner G and Arthur JS:
Regulation of miRNA transcription in macrophages in response to
Candida albicans. PLoS One. 5:e136692010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Gantier MP: New perspectives in MicroRNA
regulation of innate immunity. J Interferon Cytokine Res.
30:283–289. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ and
Baltimore D: NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an
inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune
responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:12481–12486. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, Zhou Z, Lee
DH, Nguyen JT, Barbisin M, Xu NL, Mahuvakar VR, Andersen MR, et al:
Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic
Acids Res. 33:e1792005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bhaumik D, Scott GK, Schokrpur S, Patil
CK, Campisi J and Benz CC: Expression of microRNA-146 suppresses
NF-kappaB activity with reduction of metastatic potential in breast
cancer cells. Oncogene. 27:5643–5647. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nahid MA, Pauley KM, Satoh M and Chan EK:
miR-146a is critical for endotoxin-induced tolerance: IMPLICATION
IN INNATE IMMUNITY. J Biol Chem. 284:34590–34599. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hardison SE and Brown GD: C-type lectin
receptors orchestrate antifungal immunity. Nat Immunol. 13:817–822.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Feriotti C, Loures FV, Frank de Araujo E,
da Costa TA and Calich VL: Mannosyl-recognizing receptors induce an
M1-like phenotype in macrophages of susceptible mice but an M2-like
phenotype in mice resistant to a fungal infection. PLoS One.
8:e548452013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hou J, Wang P, Lin L, Liu X, Ma F, An H,
Wang Z and Cao X: MicroRNA-146a feedback inhibits RIG-I-dependent
Type I IFN production in macrophages by targeting TRAF6, IRAK1, and
IRAK2. J Immunol. 183:2150–2158. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang P, Hou J, Lin L, Wang C, Liu X, Li D,
Ma F, Wang Z and Cao X: Inducible microRNA-155 feedback promotes
type I IFN signaling in antiviral innate immunity by targeting
suppressor of cytokine signaling 1. J Immunol. 185:6226–6233. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tili E, Michaille JJ, Cimino A, Costinean
S, Dumitru CD, Adair B, Fabbri M, Alder H, Liu CG, Calin GA, et al:
Modulation of miR-155 and miR-125b levels following
lipopolysaccharide/TNF-alpha stimulation and their possible roles
in regulating the response to endotoxin shock. J Immunol.
179:5082–5089. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jazdzewski K, Liyanarachchi S, Swierniak
M, Pachucki J, Ringel MD, Jarzab B and de la Chapelle A:
Polymorphic mature microRNAs from passenger strand of pre-miR-146a
contribute to thyroid cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:1502–1505. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pauley KM, Satoh M, Chan AL, Bubb MR,
Reeves WH and Chan EK: Upregulated miR-146a expression in
peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis
patients. Arthritis Res Ther. 10:R1012008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yamasaki K, Nakasa T, Miyaki S, Ishikawa
M, Deie M, Adachi N, Yasunaga Y, Asahara H and Ochi M: Expression
of MicroRNA-146a in osteoarthritis cartilage. Arthritis Rheum.
60:1035–1041. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tang Y, Luo X, Cui H, Ni X, Yuan M, Guo Y,
Huang X, Zhou H, de Vries N, Tak PP, et al: MicroRNA-146A
contributes to abnormal activation of the type I interferon pathway
in human lupus by targeting the key signaling proteins. Arthritis
Rheum. 60:1065–1075. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wu S, He L, Li Y, Wang T, Feng L, Jiang L,
Zhang P and Huang X: miR-146a facilitates replication of dengue
virus by dampening interferon induction by targeting TRAF6. J
Infect. 67:329–341. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Takeda K and Akira S: TLR signaling
pathways. Semin Immunol. 16:3–9. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Seki E and Brenner DA: Toll-like receptors
and adaptor molecules in liver disease: Update. Hepatology.
48:322–335. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhao JL, Rao DS, Boldin MP, Taganov KD,
O'Connell RM and Baltimore D: NF-kappaB dysregulation in
microRNA-146a-deficient mice drives the development of myeloid
malignancies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:9184–9189. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yang K, He YS, Wang XQ, Lu L, Chen QJ, Liu
J, Sun Z and Shen WF: MiR-146a inhibits oxidized low-density
lipoprotein-induced lipid accumulation and inflammatory response
via targeting toll-like receptor 4. FEBS Lett. 585:854–860. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mei J, Bachoo R and Zhang CL:
MicroRNA-146a inhibits glioma development by targeting Notch1. Mol
Cell Biol. 31:3584–3592. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Takeda K: Evolution and integration of
innate immune recognition systems: The Toll-like receptors. J
Endotoxin Res. 11:51–55. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li L, Cousart S, Hu J and McCall CE:
Characterization of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase in
normal and endotoxin-tolerant cells. J Biol Chem. 275:23340–23345.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Boone DL, Turer EE, Lee EG, Ahmad RC,
Wheeler MT, Tsui C, Hurley P, Chien M, Chai S, Hitotsumatsu O, et
al: The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 is required for termination
of Toll-like receptor responses. Nat Immunol. 5:1052–1060. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Nahid MA, Satoh M and Chan EK: Mechanistic
role of microRNA-146a in endotoxin-induced differential
cross-regulation of TLR signaling. J Immunol. 186:1723–1734. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|