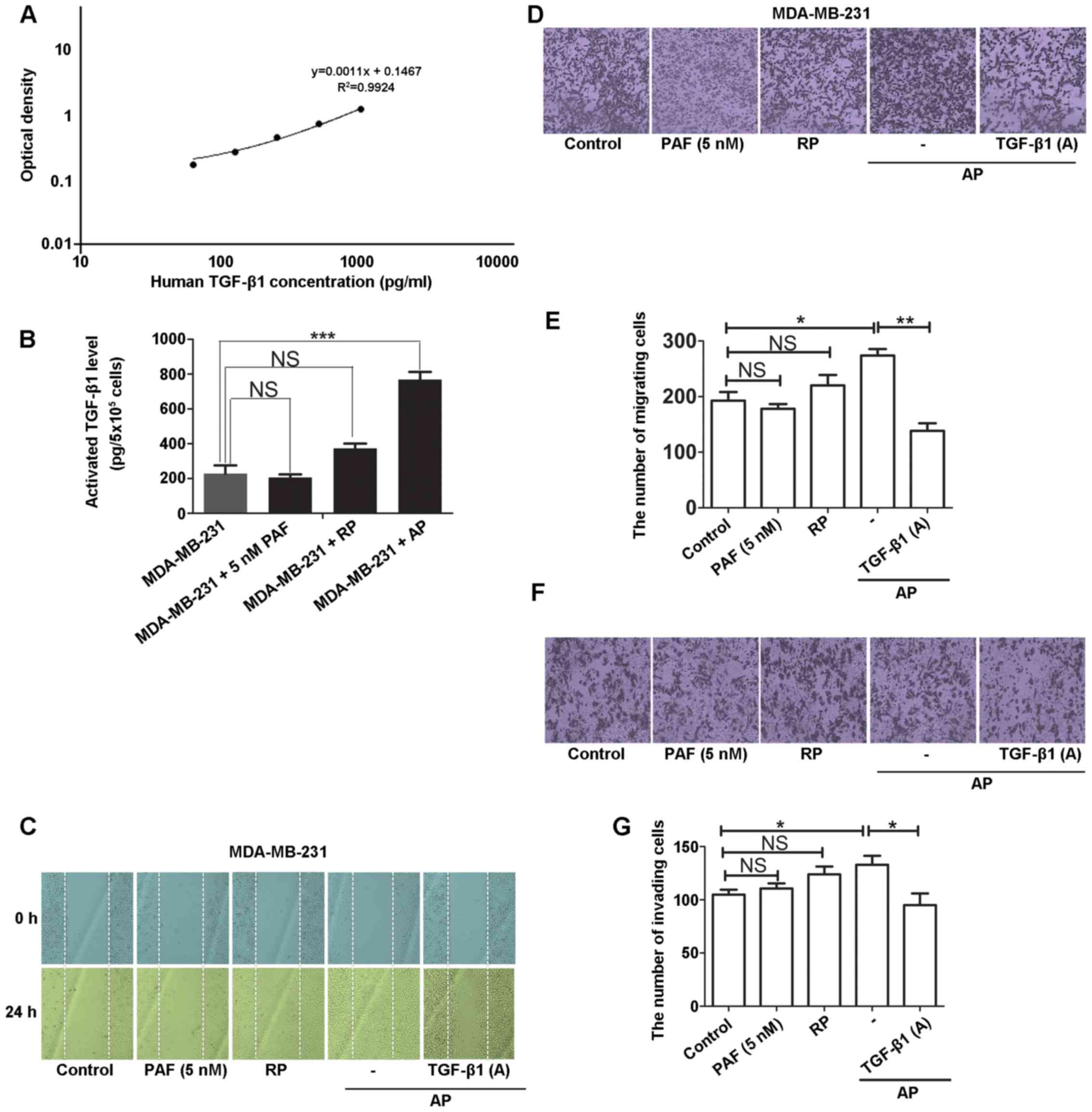
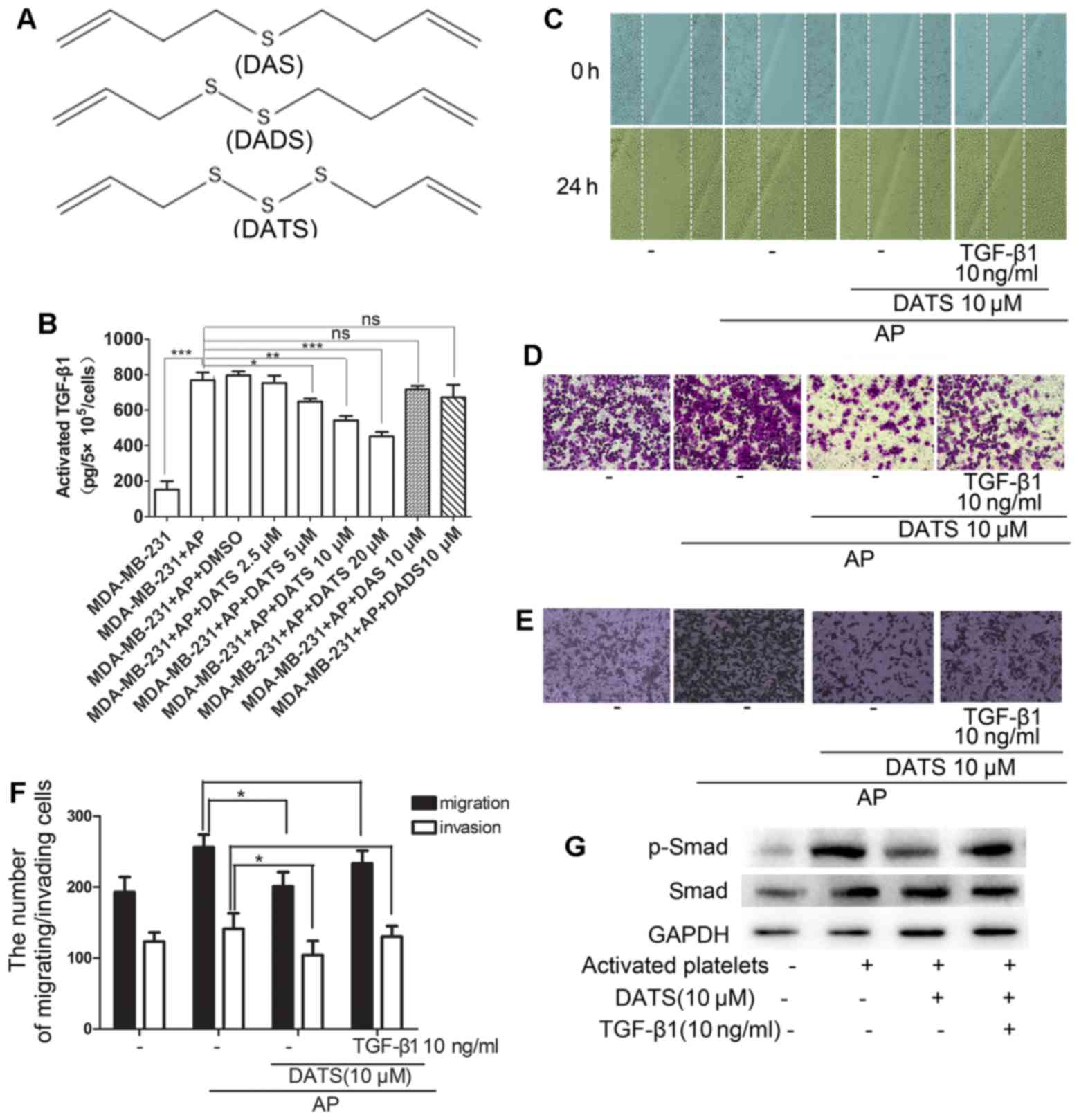
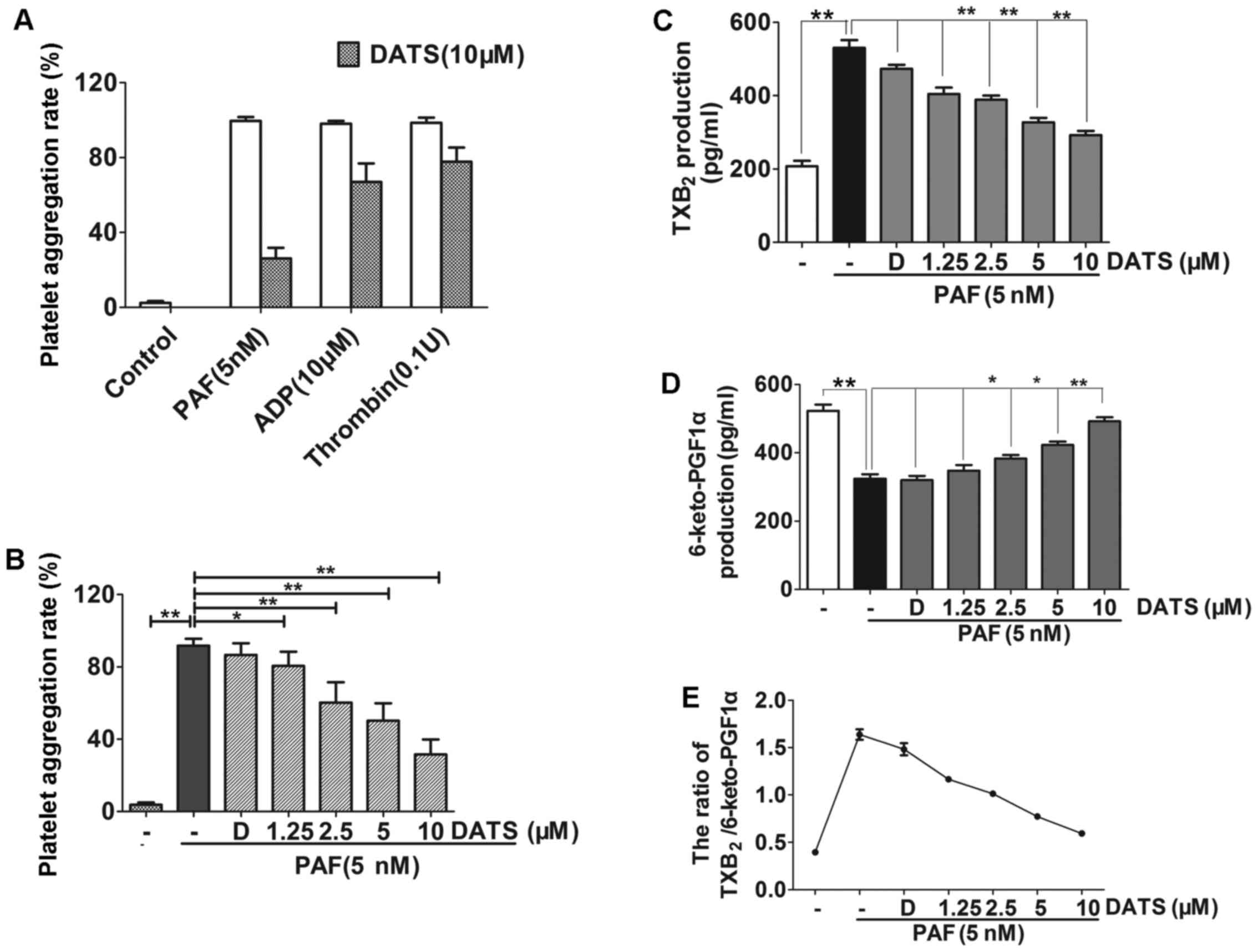
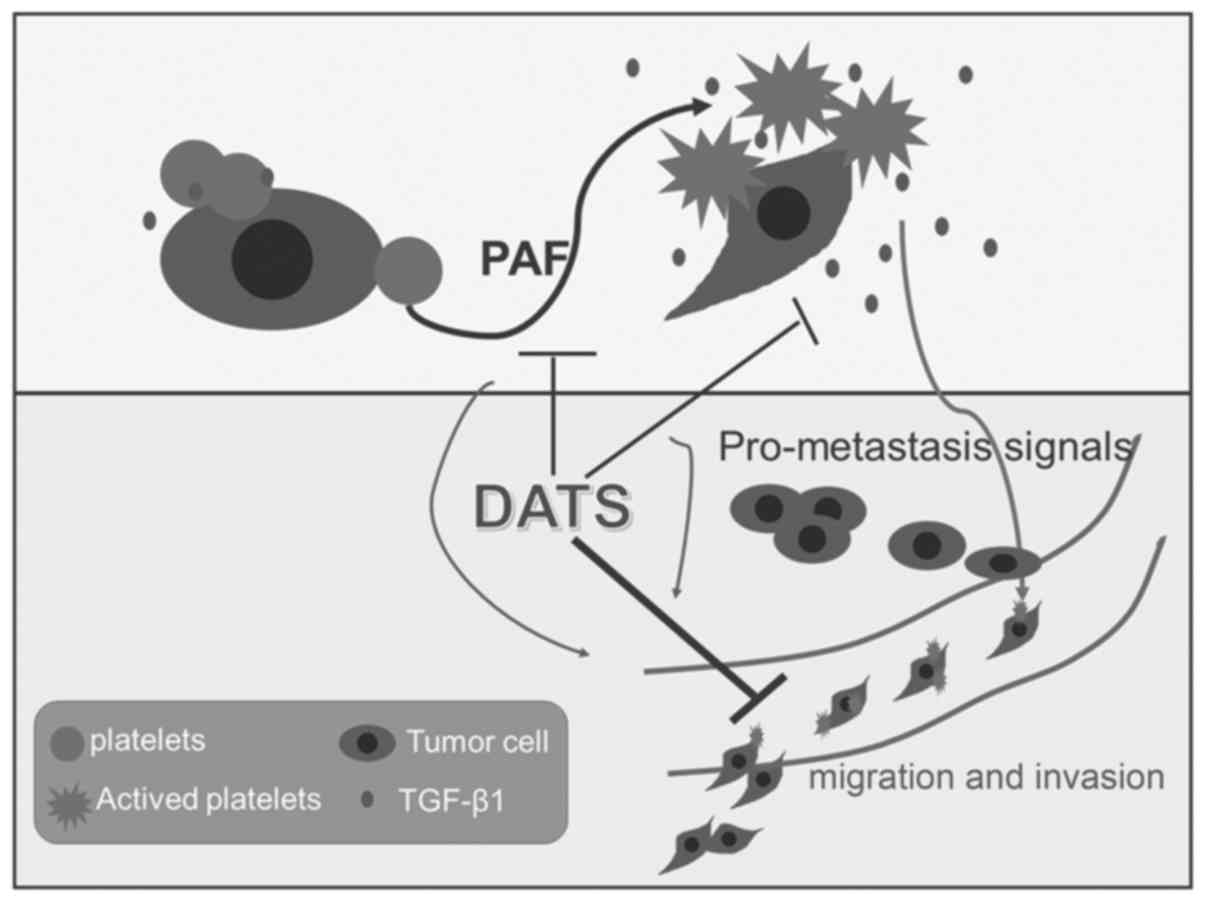
|
1
|
Zhang XH: Why cancer cells metastasize?
Med Hypotheses. 80:669–671. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Labelle M and Hynes RO: The initial hours
of metastasis: the importance of cooperative host-tumor cell
interactions during hematogenous dissemination. Cancer Discov.
2:1091–1099. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mezouar S, Mege D, Darbousset R, Farge D,
Debourdeau P, Dignat-George F, Panicot-Dubois L and Dubois C:
Involvement of platelet-derived microparticles in tumor progression
and thrombosis. Semin Oncol. 41:346–358. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stravodimou A and Voutsadakis IA:
Pretreatment thrombocytosis as a prognostic factor in metastatic
breast cancer. Int J Breast Cancer. 2013:2895632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang PL, Cheng YB and Kuerban G: The
clinical characteristic differences between thrombosis-related
edema and lymphedema following radiotherapy or chemoradiotherapy
for patients with cervical cancer. J Radiat Res (Tokyo).
53:125–129. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Holmes CE, Levis JE and Ornstein DL:
Activated platelets enhance ovarian cancer cell invasion in a
cellular model of metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis. 26:653–661.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhu JF, Cai L, Zhang XW, Wen YS, Su XD,
Rong TH and Zhang LJ: High plasma fibrinogen concentration and
platelet count unfavorably impact survival in non-small cell lung
cancer patients with brain metastases. Chin J Cancer. 33:96–104.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Gupta GP and Massagué J: Platelets and
metastasis revisited: a novel fatty link. J Clin Invest.
114:1691–1693. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Smith AL, Robin TP and Ford HL: Molecular
pathways: targeting the TGF-β pathway for cancer therapy. Clin
Cancer Res. 18:4514–4521. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Perera M, Tsang CS, Distel RJ, Lacy JN,
Ohno-Machado L, Ricchiuti V, Samaranayake LP, Smejkal GB, Smith MG,
Trachtenberg AJ, et al: TGF-beta1 interactome: metastasis and
beyond. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 7:217–229. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ma J, Gao HM, Hua X, Lu ZY and Gao HC:
Role of TGF-β1 in human colorectal cancer and effects after
cantharidinate intervention. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:4045–4048.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hyytiäinen M, Penttinen C and Keski-Oja J:
Latent TGF-beta binding proteins: extracellular matrix association
and roles in TGF-beta activation. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci.
41:233–264. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Meindl-Beinker NM, Matsuzaki K and Dooley
S: TGF-β signaling in onset and progression of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Dig Dis. 30:514–523. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bakkebø M, Huse K, Hilden VI, Smeland EB
and Oksvold MP: TGF-β-induced growth inhibition in B-cell lymphoma
correlates with Smad1/5 signalling and constitutively active p38
MAPK. BMC Immunol. 11:572010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Binker MG, Binker-Cosen AA, Gaisano HY, de
Cosen RH and Cosen-Binker LI: TGF-β1 increases invasiveness of
SW1990 cells through Rac1/ROS/NF-κB/IL-6/MMP-2. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 405:140–145. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Morita T, Mayanagi T and Sobue K: Dual
roles of myocardin-related transcription factors in epithelial
mesenchymal transition via slug induction and actin remodeling. J
Cell Biol. 179:1027–1042. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wilkins-Port CE, Higgins SP, Higgins CE,
Kobori-Hotchkiss I and Higgins PJ: Complex regulation of the
pericellular proteolytic microenvironment during tumor progression
and wound repair: functional interactions between the serine
protease and matrix metalloproteinase cascades. Biochem Res Int.
2012:4543682012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hawinkels LJ, Verspaget HW, van der
Reijden JJ, van der Zon JM, Verheijen JH, Hommes DW, Lamers CB and
Sier CF: Active TGF-beta1 correlates with myofibroblasts and
malignancy in the colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence. Cancer
Sci. 100:663–670. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Donovan MJ and Cordon-Cardo C: Genomic
analysis in active surveillance: predicting high-risk disease using
tissue biomarkers. Curr Opin Urol. 24:303–310. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Joseph JV, Balasubramaniyan V, Walenkamp A
and Kruyt FA: TGF-β as a therapeutic target in high grade gliomas -
promises and challenges. Biochem Pharmacol. 85:478–485. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Han H, Cao FL, Wang BZ, Mu XR, Li GY and
Wang XW: Expression of angiogenesis regulatory proteins and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition factors in platelets of the
breast cancer patients. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014:8782092014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pak KH, Kim DH, Kim H, Lee do H and Cheong
JH: Differences in TGF-β1 signaling and clinicopathologic
characteristics of histologic subtypes of gastric cancer. BMC
Cancer. 16:602016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Surh YJ and Ferguson LR: Dietary and
medicinal antimutagens and anticarcinogens: molecular mechanisms
and chemopreventive potential - highlights of a symposium. Mutat
Res. 523–524:1–8. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Mousa SA: Antithrombotic effects of
naturally derived products on coagulation and platelet function.
Methods Mol Biol. 663:229–240. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chan KC, Yin MC and Chao WJ: Effect of
diallyl trisulfide-rich garlic oil on blood coagulation and plasma
activity of anticoagulation factors in rats. Food Chem Toxicol.
45:502–507. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Khatua TN, Adela R and Banerjee SK: Garlic
and cardioprotection: insights into the molecular mechanisms. Can J
Physiol Pharmacol. 91:448–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Allison GL, Lowe GM and Rahman K: Aged
garlic extract and its constituents inhibit platelet aggregation
through multiple mechanisms. J Nutr. 136(Suppl 3): 782S–788S.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rahman K and Billington D: Dietary
supplementation with aged garlic extract inhibits ADP-induced
platelet aggregation in humans. J Nutr. 130:2662–2665.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Trio PZ, You S, He X, He J, Sakao K and
Hou DX: Chemo-preventive functions and molecular mechanisms of
garlic organosulfur compounds. Food Funct. 5:833–844. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chandra-Kuntal K, Lee J and Singh SV:
Critical role for reactive oxygen species in apoptosis induction
and cell migration inhibition by diallyl trisulfide, a cancer
chemopreventive component of garlic. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
138:69–79. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li Y, Zhang J, Zhang L, Si M, Yin H and Li
J: Diallyl trisulfide inhibits proliferation, invasion and
angiogenesis of osteosarcoma cells by switching on suppressor
microRNAs and inactivating of Notch-1 signaling. Carcinogenesis.
34:1601–1610. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lai KC, Hsu SC, Kuo CL, Yang JS, Ma CY, Lu
HF, Tang NY, Hsia TC, Ho HC and Chung JG: Diallyl sulfide, diallyl
disulfide, and diallyl trisulfide inhibit migration and invasion in
human colon cancer colo 205 cells through the inhibition of matrix
metalloproteinase-2, -7, and -9 expressions. Environ Toxicol.
28:479–488. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Singh SV, Powolny AA, Stan SD, Xiao D,
Arlotti JA, Warin R, Hahm ER, Marynowski SW, Bommareddy A, Potter
DM and Dhir R: Garlic constituent diallyl trisulfide prevents
development of poorly differentiated prostate cancer and pulmonary
metastasis multiplicity in TRAMP mice. Cancer Res. 68:9503–9511.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xiao D, Herman-Antosiewicz A, Antosiewicz
J, Xiao H, Brisson M, Lazo JS and Singh SV: Diallyl
trisulfide-induced G(2)-M phase cell cycle arrest in human prostate
cancer cells is caused by reactive oxygen species-dependent
destruction and hyperphosphorylation of Cdc 25 C. Oncogene.
24:6256–6268. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shankar S, Chen Q, Ganapathy S, Singh KP
and Srivastava RK: Diallyl trisulfide increases the effectiveness
of TRAIL and inhibits prostate cancer growth in an orthotopic
model: molecular mechanisms. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:2328–2338. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Powolny AA and Singh SV: Multitargeted
prevention and therapy of cancer by diallyl trisulfide and related
Allium vegetable-derived organosulfur compounds. Cancer Lett.
269:305–314. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ng KT, Guo DY, Cheng Q, Geng W, Ling CC,
Li CX, Liu XB, Ma YY, Lo CM, Poon RT, et al: A garlic derivative,
S-allylcysteine (SAC), suppresses proliferation and metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e316552012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Belloc C, Lu H, Soria C, Fridman R,
Legrand Y and Menashi S: The effect of platelets on invasiveness
and protease production of human mammary tumor cells. Int J Cancer.
60:413–417. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nierodzik ML, Plotkin A, Kajumo F and
Karpatkin S: Thrombin stimulates tumor-platelet adhesion in vitro
and metastasis in vivo. J Clin Invest. 87:229–236. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jurasz P, Alonso-Escolano D and Radomski
MW: Platele-cancer interactions: mechanisms and pharmacology of
tumour cell-induced platelet aggregation. Br J Pharmacol.
143:819–826. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Qian YF and Wang XJ: Effects of
blood-activating and stasis-resolving drugs on tumor formation and
metastasis. J Tradit Chin Med. 29:301–310. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Gil-Bernabé AM, Ferjancic S, Tlalka M,
Zhao L, Allen PD, Im JH, Watson K, Hill SA, Amirkhosravi A, Francis
JL, et al: Recruitment of monocytes/macrophages by tissue
factor-mediated coagulation is essential for metastatic cell
survival and premetastatic niche establishment in mice. Blood.
119:3164–3175. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Im JH, Fu W, Wang H, Bhatia SK, Hammer DA,
Kowalska MA and Muschel RJ: Coagulation facilitates tumor cell
spreading in the pulmonary vasculature during early metastatic
colony formation. Cancer Res. 64:8613–8619. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
McEachron TA, Pawlinski R, Richards KL,
Church FC and Mackman N: Protease-activated receptors mediate
crosstalk between coagulation and fibrinolysis. Blood.
116:5037–5044. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Battinelli EM, Markens BA and Italiano JE
Jr: Release of angiogenesis regulatory proteins from platelet alpha
granules: modulation of physiologic and pathologic angiogenesis.
Blood. 118:1359–1369. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hara T, Shimizu K, Ogawa F, Yanaba K,
Iwata Y, Muroi E, Takenaka M, Komura K, Hasegawa M, Fujimoto M, et
al: Platelets control leukocyte recruitment in a murine model of
cutaneous arthus reaction. Am J Pathol. 176:259–269. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
47
|
Xu L, Tong R, Cochran DM and Jain RK:
Blocking platelet-derived growth factor-D/platelet-derived growth
factor receptor beta signaling inhibits human renal cell carcinoma
progression in an orthotopic mouse model. Cancer Res. 65:5711–5719.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fleischauer AT and Arab L: Garlic and
cancer: a critical review of the epidemiologic literature. J Nutr.
131:1032S–1040S. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ginter E and Simko V: Garlic (Allium
sativum L.) and cardiovascular diseases. Bratisl Lek Listy.
111:452–456. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Allison GL, Lowe GM and Rahman K: Aged
garlic extract inhibits platelet activation by increasing
intracellular cAMP and reducing the interaction of GPIIb/IIIa
receptor with fibrinogen. Life Sci. 91:1275–1280. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li W, Tian H, Li L, Li S, Yue W, Chen Z,
Qi L, Hu W, Zhu Y, Hao B, et al: Diallyl trisulfide induces
apoptosis and inhibits proliferation of A549 cells in vitro and in
vivo. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 44:577–583. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Watanabe K, Hosono T, Watanabe K,
Hosono-Fukao T, Ariga T and Seki T: Diallyl trisulfide induces
apoptosis in Jurkat cells by the modification of cysteine residues
in thioredoxin. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 78:1418–1420. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ma HB, Huang S, Yin XR, Zhang Y and Di ZL:
Apoptotic pathway induced by diallyl trisulfide in pancreatic
cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol. 20:193–203. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Sakamoto K, Lawson LD and Milner JA: Allyl
sulfides from garlic suppress the in vitro proliferation of human
A549 lung tumor cells. Nutr Cancer. 29:152–156. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Li J, Liu W, Zhao K, Zhang Y, Li X, Yang
Q, Li Z and Li J: Diallyl trisulfide reverses drug resistance and
lowers the ratio of CD133+ cells in conjunction with
methotrexate in a human osteosarcoma drug-resistant cell subline.
Mol Med Rep. 2:245–252. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Tsai CY, Wang CC, Lai TY, Tsu HN, Wang CH,
Liang HY and Kuo WW: Antioxidant effects of diallyl trisulfide on
high glucose-induced apoptosis are mediated by the
PI3K/Akt-dependent activation of Nrf2 in cardiomyocytes. Int J
Cardiol. 168:1286–1297. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|