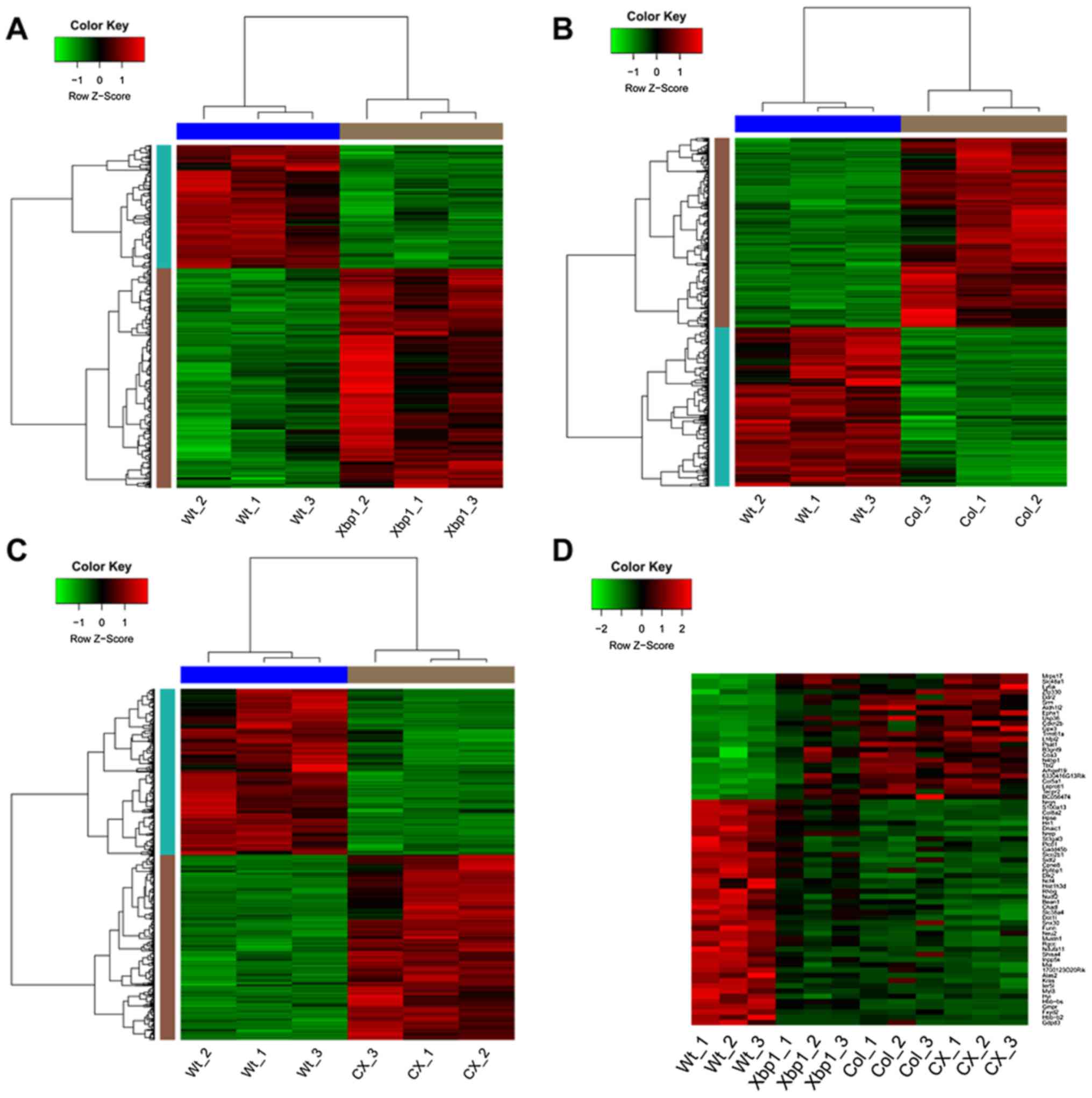
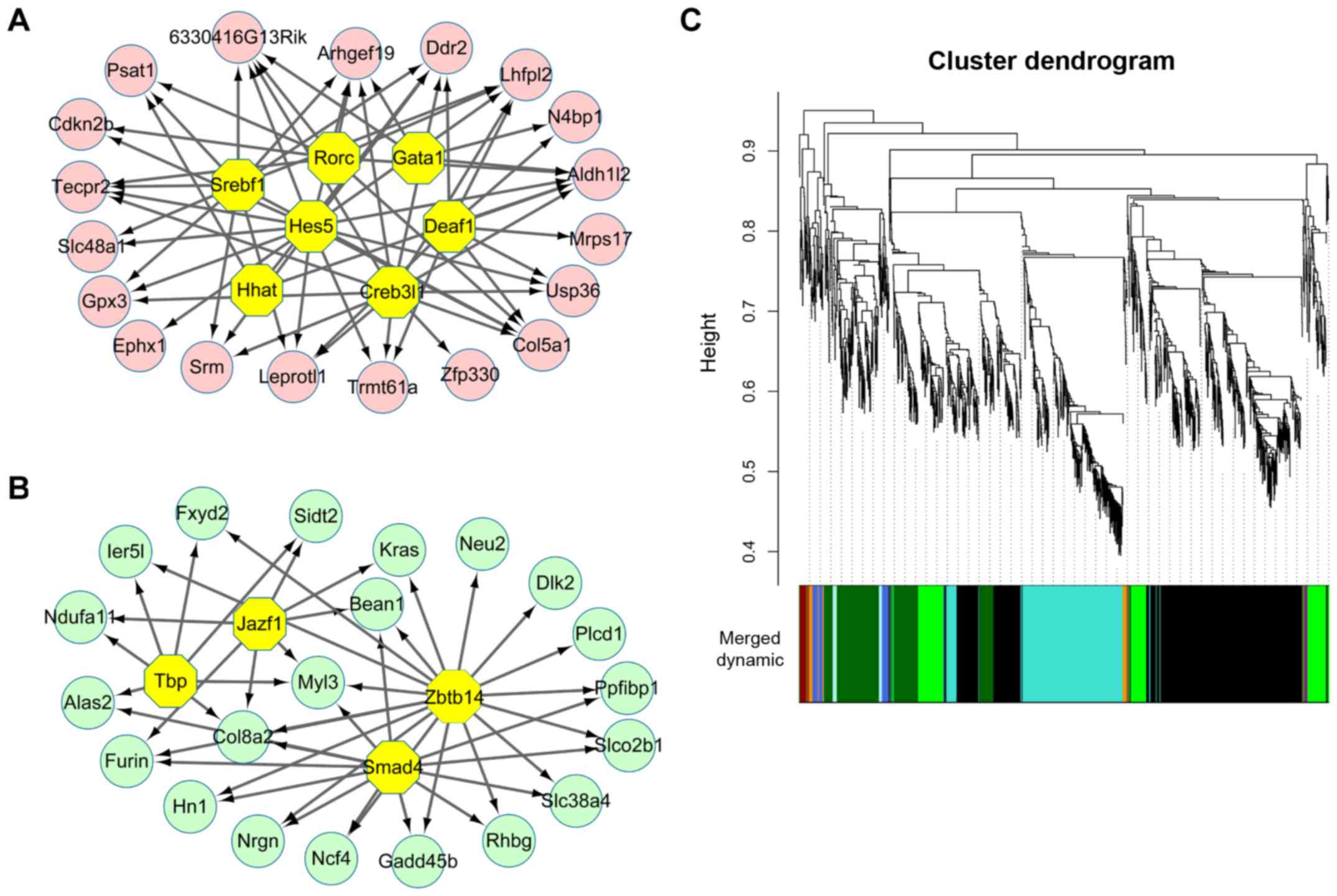
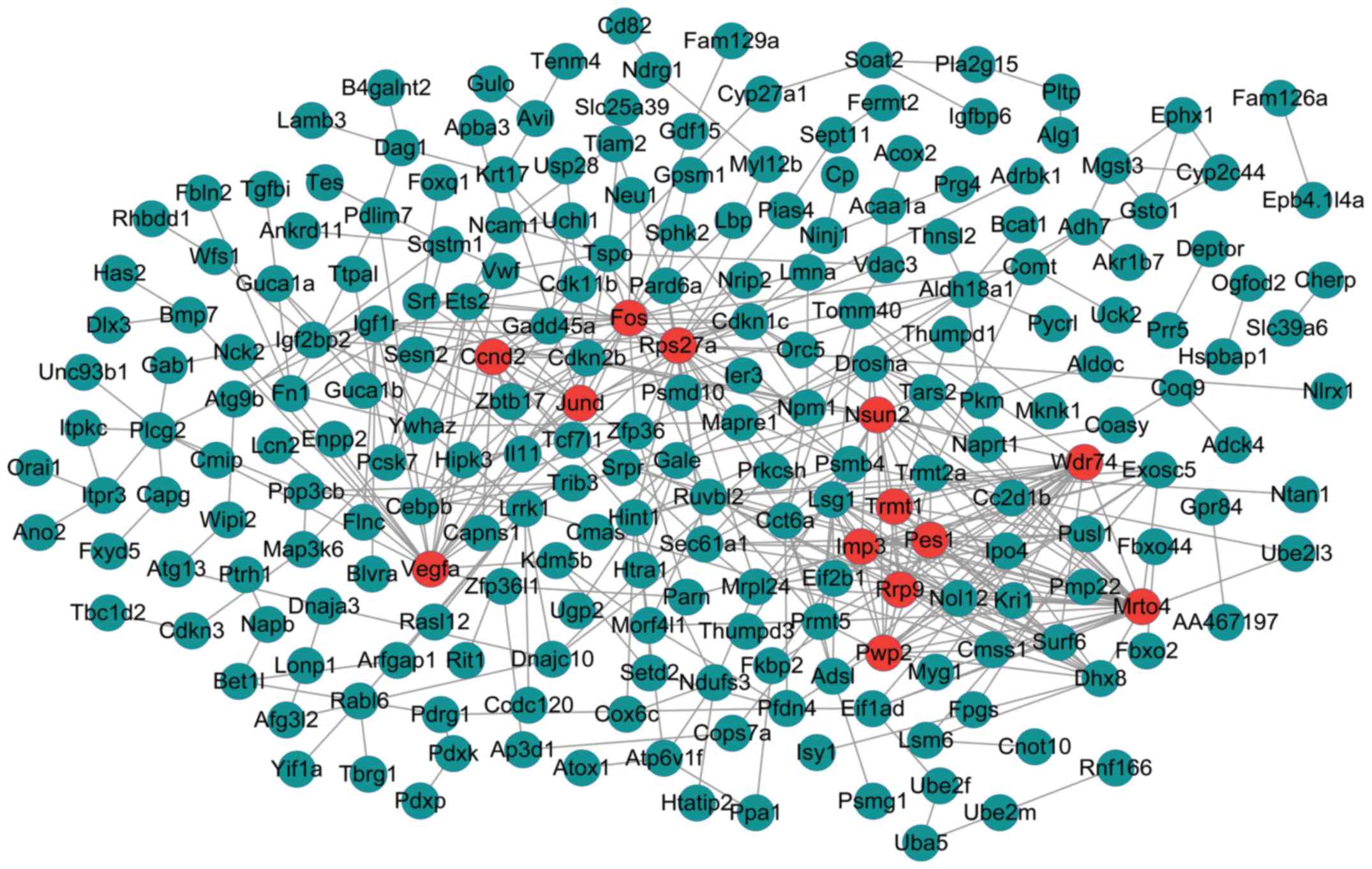
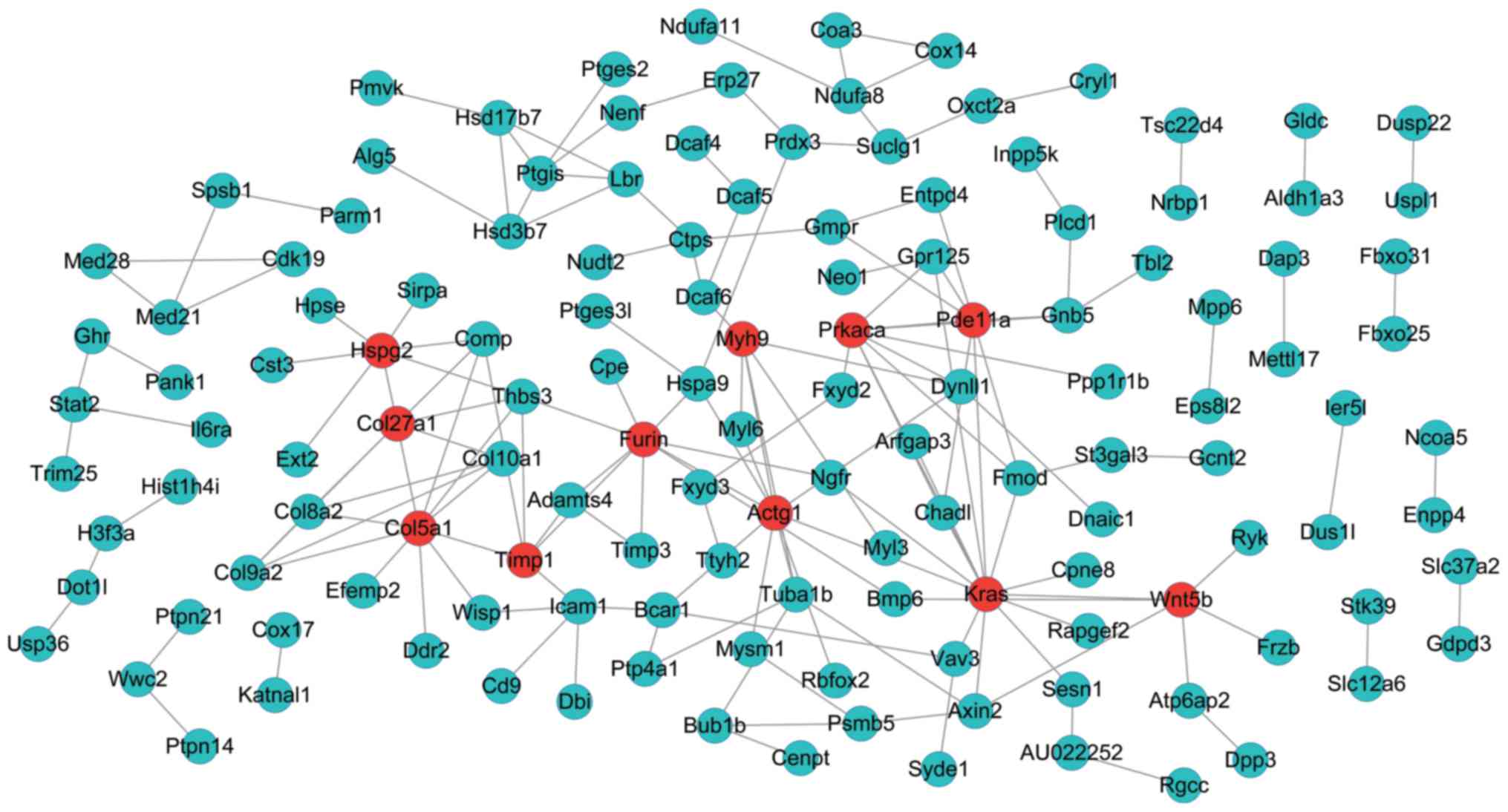
|
1
|
Park H, Hong S, Cho SI, Cho TJ, Choi IH,
Jin DK, Sohn YB, Park SW, Cho HH, Cheon JE, et al: Case of mild
Schmid-type metaphyseal chondrodysplasia with novel sequence
variation involving an unusual mutational site of the COL10A1 gene.
Eur J Med Genet. 58:175–179. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bateman JF, Freddi S, Nattrass G and
Savarirayan R: Tissue-specific RNA surveillance? Nonsense-mediated
mRNA decay causes collagen X haploinsufficiency in Schmid
metaphyseal chondrodysplasia cartilage. Hum Mol Genet. 12:217–225.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Patterson SE and Dealy CN: Mechanisms and
models of endoplasmic reticulum stress in chondrodysplasia. Dev
Dyn. 243:875–893. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bogin O, Kvansakul M, Rom E, Singer J,
Yayon A and Hohenester E: Insight into Schmid metaphyseal
chondrodysplasia from the crystal structure of the collagen X NC1
domain trimer. Structure. 10:165–173. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Woelfle JV, Brenner RE, Zabel B, Reichel H
and Nelitz M: Schmid-type metaphyseal chondrodysplasia as the
result of a collagen type X defect due to a novel COL10A1 nonsense
mutation: A case report of a novel COL10A1 mutation. J Orthop Sci.
16:245–249. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Warman ML, Cormier-Daire V, Hall C, Krakow
D, Lachman R, LeMerrer M, Mortier G, Mundlos S, Nishimura G, Rimoin
DL, et al: Nosology and classification of genetic skeletal
disorders: 2010 revision. Am J Med Genet A. 155A:943–968. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Arnold WV and Fertala A: Skeletal diseases
caused by mutations that affect collagen structure and function.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 45:1556–1567. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hetz C: The unfolded protein response:
Controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 13:89–102. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rajpar MH, McDermott B, Kung L, Eardley R,
Knowles L, Heeran M, Thornton DJ, Wilson R, Bateman JF and Poulsom
R: Targeted induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress induces
cartilage pathology. PLoS Genet. 5:e10006912009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yoshida H, Matsui T, Yamamoto A, Okada T
and Mori K: XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in
response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription
factor. Cell. 107:881–891. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Cameron TL, Bell KM, Gresshoff IL,
Sampurno L, Mullan L, Ermann J, Glimcher LH, Boot-Handford RP and
Bateman JF: XBP1-Independent UPR Pathways Suppress C/EBP-β Mediated
Chondrocyte Differentiation in ER-Stress Related Skeletal Disease.
PLoS Genet. 11:e10055052015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bolstad BM: preprocessCore: A collection
of pre-processing functions. R package version 1. 2013, http://www.bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/preprocessCore.html.
Accessed March 27, 2013.
|
|
13
|
Gardeux V, Arslan AD, Achour I, Ho TT,
Beck WT and Lussier YA: Concordance of deregulated mechanisms
unveiled in underpowered experiments: TBP1 knockdown case study.
BMC Med Genomics. 7(Suppl 1): S12014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Hoeksema MA, Scicluna BP, Boshuizen MC,
van der Velden S, Neele AE, Van den Bossche J, Matlung HL, van den
Berg TK, Goossens P and de Winther MP: IFN-γ priming of macrophages
represses a part of the inflammatory program and attenuates
neutrophil recruitment. J Immunol. 194:3909–3916. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Warnes GR, Bolker B, Bonebakker L,
Gentleman R, Huber W, Liaw A, Lumley T, Maechler M, Magnusson A and
Moeller S: gplots: Various R programming tools for plotting data. R
package version 2.12.1. 2013, http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/gplots/index.html.
|
|
17
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:32003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Mao X, Cai T, Olyarchuk JG and Wei L:
Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the
KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics.
21:3787–3793. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Janky R, Verfaillie A, Imrichová H, Van de
Sande B, Standaert L, Christiaens V, Hulselmans G, Herten K, Naval
Sanchez M and Potier D: iRegulon: from a gene list to a gene
regulatory network using large motif and track collections. PLoS
Comput Biol. 10:e10037312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang P-L
and Ideker T: Cytoscape 2.8: New features for data integration and
network visualization. Bioinformatics. 27:431–432. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Langfelder P and Horvath S: WGCNA: An R
package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC
Bioinformatics. 9:5592008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering
C, et al: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks, with
increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Kuhn M,
Simonovic M, Roth A, Minguez P, Doerks T, Stark M, Muller J, Bork
P, et al: The STRING database in 2011: Functional interaction
networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39:D561–D568. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Spinelli L, Gambette P, Chapple CE,
Robisson B, Baudot A, Garreta H, Tichit L, Guénoche A and Brun C:
Clust&See: A Cytoscape plugin for the identification,
visualization and manipulation of network clusters. Biosystems.
113:91–95. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vakiani E and Solit DB: KRAS and BRAF:
Drug targets and predictive biomarkers. J Pathol. 223:219–229.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Bryant KL, Mancias JD, Kimmelman AC and
Der CJ: KRAS: Feeding pancreatic cancer proliferation. Trends
Biochem Sci. 39:91–100. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chan D, Ho MS and Cheah KS: Aberrant
signal peptide cleavage of collagen X in Schmid metaphyseal
chondrodysplasia. Implications for the molecular basis of the
disease. J Biol Chem. 276:7992–7997. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Raleigh SM, van der Merwe L, Ribbans WJ,
Smith RK, Schwellnus MP and Collins M: Variants within the MMP3
gene are associated with Achilles tendinopathy: Possible
interaction with the COL5A1 gene. Br J Sports Med. 43:514–520.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kahai S, Vary CP, Gao Y and Seth A:
Collagen, type V, α1 (COL5A1) is regulated by TGF-β in osteoblasts.
Matrix Biol. 23:445–455. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dubois CM, Blanchette F, Laprise MH, Leduc
R, Grondin F and Seidah NG: Evidence that furin is an authentic
transforming growth factor-β1-converting enzyme. Am J Pathol.
158:305–316. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang M, Wang X, Zhang L, Yu C, Zhang B,
Cole W, Cavey G, Davidson P and Gibson G: Demonstration of the
interaction of transforming growth factor beta 2 and type X
collagen using a modified tandem affinity purification tag. J
Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 875:493–501. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|