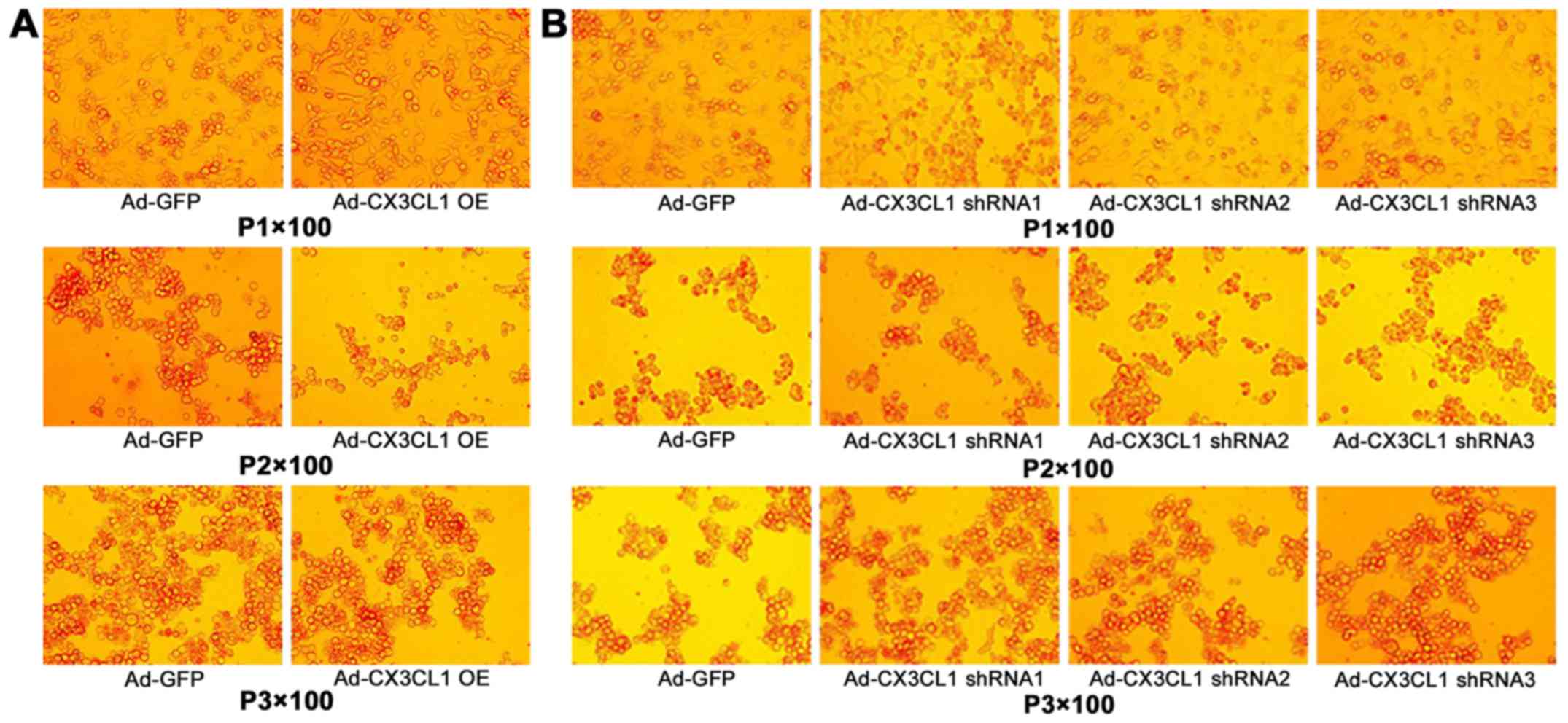
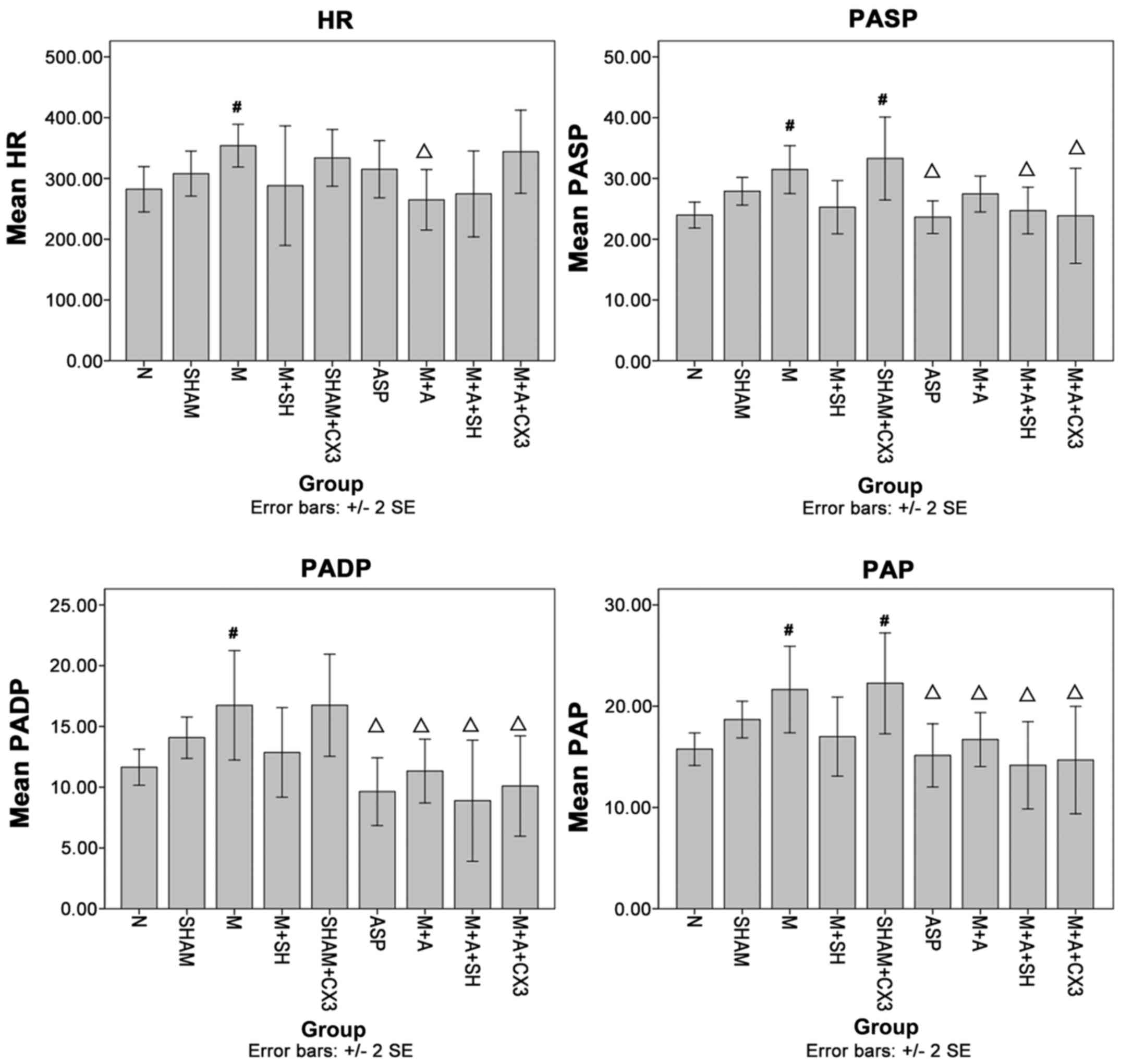
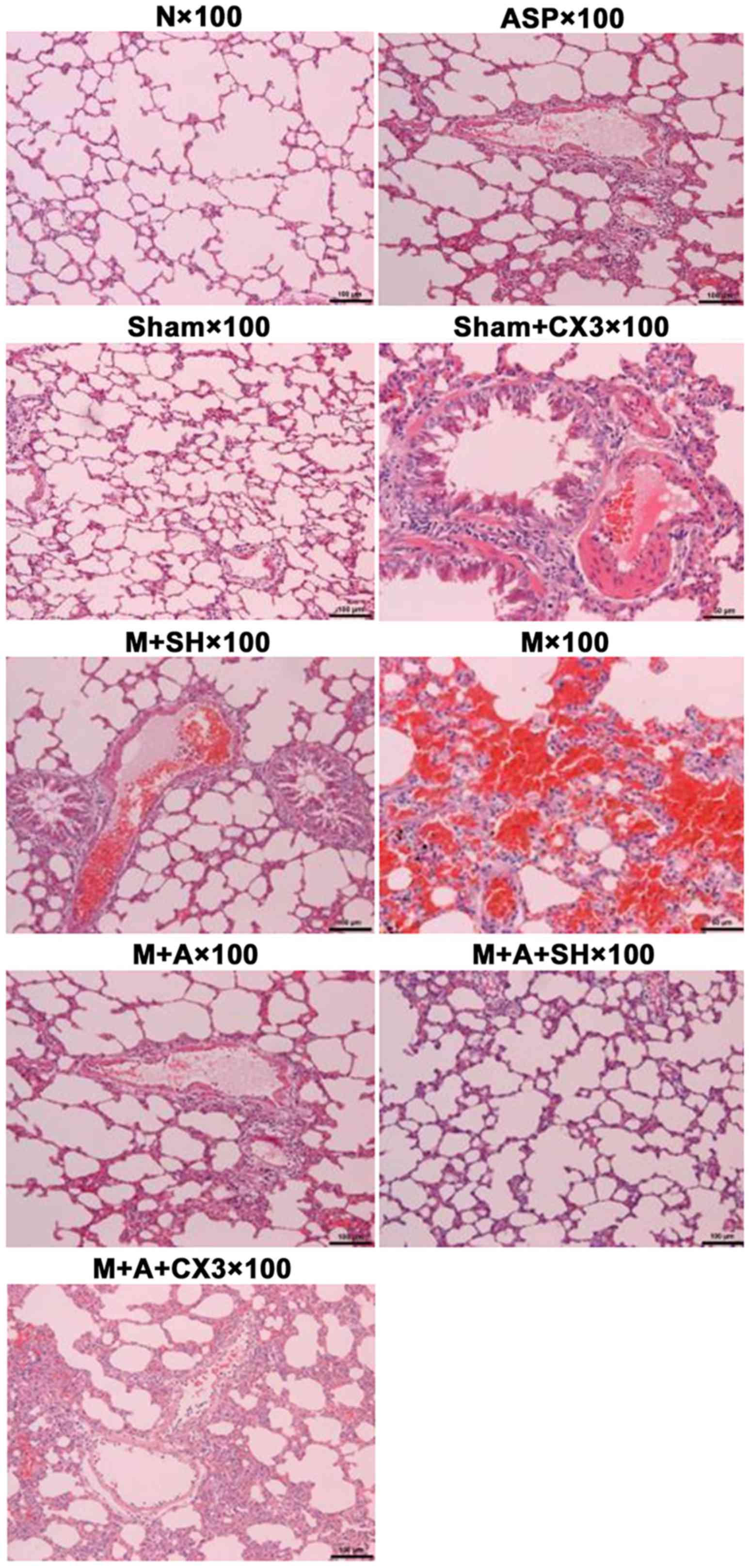
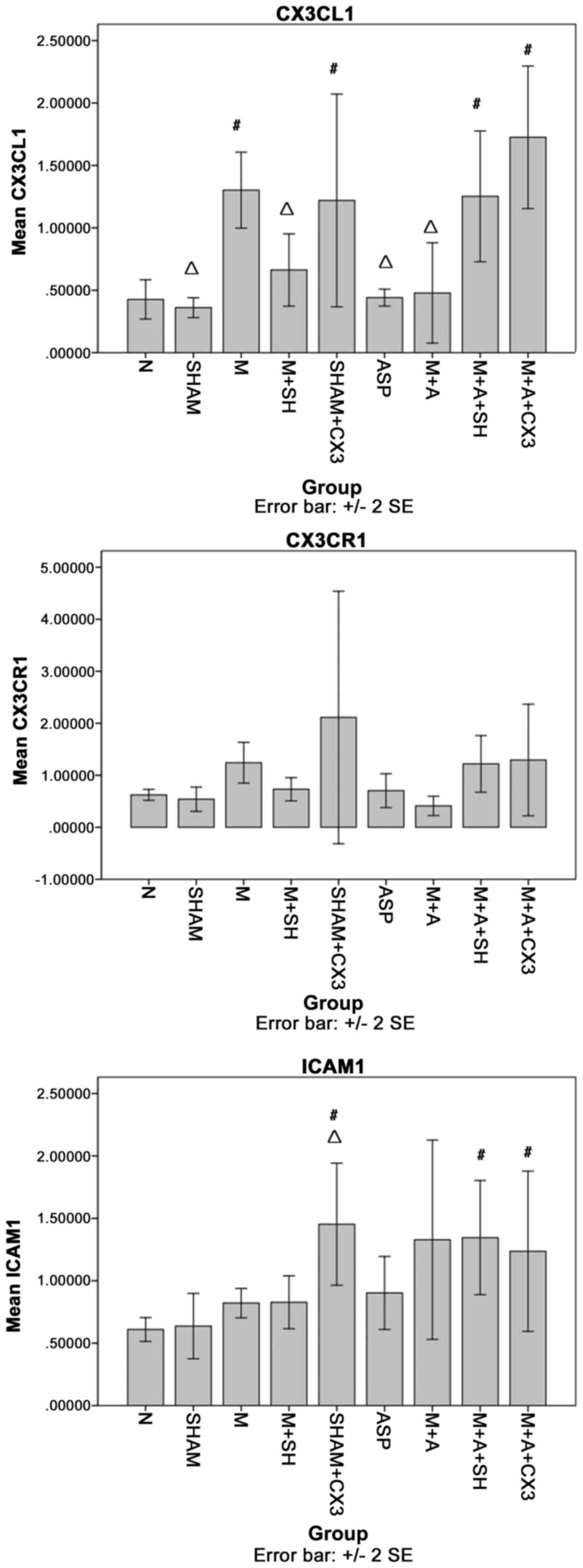
|
1
|
Geerts WH, Bergqvist D, Pineo GF, Heit JA,
Samama CM, Lassen MR and Colwell CW: Prevention of venous
thromboembolism: American college of chest physicians
evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (8th edition). Chest.
133(Suppl 6): 381S–453S. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cohen AT, Agnelli G, Anderson FA, Arcelus
JI, Bergqvist D, Brecht JG, Greer IA, Heit JA, Hutchinson JL,
Kakkar AK, et al VTE Impact Assessment Group in Europe (VITAE):
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) in Europe: The number of VTE events
and associated morbidity and mortality. Thromb Haemost. 98:756–764.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang Y, Liang L, Zhai Z, He H, Xie W, Peng
X and Wang C; Investigators for National Cooperative Project for
Prevention and Treatment of PTE-DVT: Pulmonary embolism incidence
and fatality trends in chinese hospitals from 1997 to 2008: A
multicenter registration study. PLoS One. 6:e268612011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang L, Wu J, Zhang W, Zhi Y, Wu Y, Jiang
R and Yang R: Effects of aspirin on the ERK and PI3K/Akt signaling
pathways in rats with acute pulmonary embolism. Mol Med Rep.
8:1465–1471. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang LC, Jiang RL, Zhang W, Wei LL and
Yang RH: Effects of aspirin on the expression of nuclear factor-κB
in a rat model of acute pulmonary embolism. World J Emerg Med.
5:229–233. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang LC, Wu JN, Xia GL, Mao W, Ying RB,
Huang LQ and Jiang RL: Effect of aspirin on fractalkine in rats
with pulmonary embolism. Trop J Pharm Res. 13:753–760. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Jiang R, Wei L, Zhu M, Wu J and Wang L:
Aspirin inhibits LPS-induced expression of PI3K/Akt, ERK, NF-κB,
CX3CL1, and MMPs in human bronchial epithelial cells. Inflammation.
39:643–650. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Konstantinides S, Torbicki A, Agnelli G,
Danchin N, Fitzmaurice D, Galiè N, Gibbs J, Huisman M, Humbert M,
Kucher N, et al; SEC Working Group for the ESC 2014 Guidelines on
the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism; Expert
Reviewers for the ESC 2014 Guidelines on the Diagnosis and
Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism. SEC Clinical Practice
Guidelines Committee: Comments on the 2014 ESC Guidelines on the
diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Rev Esp
Cardiol (Engl Ed). 68:10–16. 2015.
|
|
9
|
Schmeck J, Koch T, Patt B, Heller A,
Neuhof H and van Ackern K: The role of endothelin-1 as a mediator
of the pressure response after air embolism in blood perfused
lungs. Intensive Care Med. 24:605–611. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bazan JF, Bacon KB, Hardiman G, Wang W,
Soo K, Rossi D, Greaves DR, Zlotnik A and Schall TJ: A new class of
membrane-bound chemokine with a CX3C motif. Nature. 385:640–644.
1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Todorova D, Sabatier F, Doria E, Lyonnet
L, Vacher Coponat H, Robert S, Despoix N, Legris T, Moal V, Loundou
A, et al: Fractalkine expression induces endothelial progenitor
cell lysis by natural killer cells. PLoS One. 6:e266632011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Matsumiya T, Ota K, Imaizumi T, Yoshida H,
Kimura H and Satoh K: Characterization of synergistic induction of
CX3CL1/fractalkine by TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma in vascular
endothelial cells: An essential role for TNF-alpha in
post-transcriptional regulation of CX3CL1. J Immunol.
184:4205–4214. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Szukiewicz D, Kochanowski J, Mittal TK,
Pyzlak M, Szewczyk G and Cendrowski K: CX3CL1 (fractalkine) and
TNFα production by perfused human placental lobules under normoxic
and hypoxic conditions in vitro: The importance of CX3CR1
signaling. Inflamm Res. 63:179–189. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Apostolakis S and Spandidos D: Chemokines
and atherosclerosis: Focus on the CX3CL1/CX3CR1 pathway. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 34:1251–1256. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ars C, Thurion P, Delos M, Sibille Y and
Pilette C: Small airway obstruction in severe pulmonary arterial
hypertension correlates with increased airway CD8+
T-cells and fractalkine expression. Eur Respir J. 34:1494–1496.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ostrowski RP, Jadhav V, Chen W and Zhang
JH: Reduced matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity and cell death
after global ischemia in the brain preconditioned with hyperbaric
oxygen. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien). 106:47–49. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang C, Zhai Z, Yang Y, Cheng Z, Ying K,
Liang L, Dai H, Huang K, Lu W, et al: Inverse relationship of
bleeding risk with clot burden during pulmonary embolism treatment
with LMW heparin. Clin Respir J. 10:596–605. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Bhattacharyya S, Ghosh S and Sil PC:
Amelioration of aspirin induced oxidative impairment and apoptotic
cell death by a novel antioxidant protein molecule isolated from
the herb Phyllanthus niruri. PLoS One. 9:e890262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yamamoto Y and Gaynor RB: Therapeutic
potential of inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway in the treatment
of inflammation and cancer. J Clin Invest. 107:135–142. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Szukiewicz D, Wojciechowska M, Bilska A,
Stangret A, Szewczyk G, Mittal TK, Watroba M and Kochanowski J:
Aspirin action in endothelial cells: Different patterns of response
between chemokine CX3CL1/CX3CR1 and TNF-α/TNFR1 signaling pathways.
Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 29:219–229. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guo Y, Apostalakis S, Blann AD and Lip GY:
Plasma CX3CL1 levels and long term outcomes of patients with atrial
fibrillation: The West Birmingham Atrial Fibrillation Project.
Cerebrovasc Dis. 38:204–211. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ogonda L, Hill J, Doran E, Dennison J,
Stevenson M and Beverland D: Aspirin for thromboprophylaxis after
primary lower limb arthroplasty: Early thromboembolic events and 90
day mortality in 11,459 patients. Bone Joint J. 98-B:341–348. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Braithwaite I, Dunbar L, Eathorne A,
Weatherall M and Beasley R: Venous thromboembolism rates in
patients with lower limb immobilization after Achilles tendon
injury are unchanged after the introduction of prophylactic
aspirin: Audit. J Thromb Haemost. 14:331–335. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kaye ID, Patel DN, Strauss EJ, Alaia MJ,
Garofolo G, Martinez A and Jazrawi LM: Prevention of venous
thromboembolism after arthroscopic knee surgery in a low-risk
population with the use of aspirin. A randomized trial. Bull Hosp
Jt Dis (2013). 73:243–248. 2015.
|