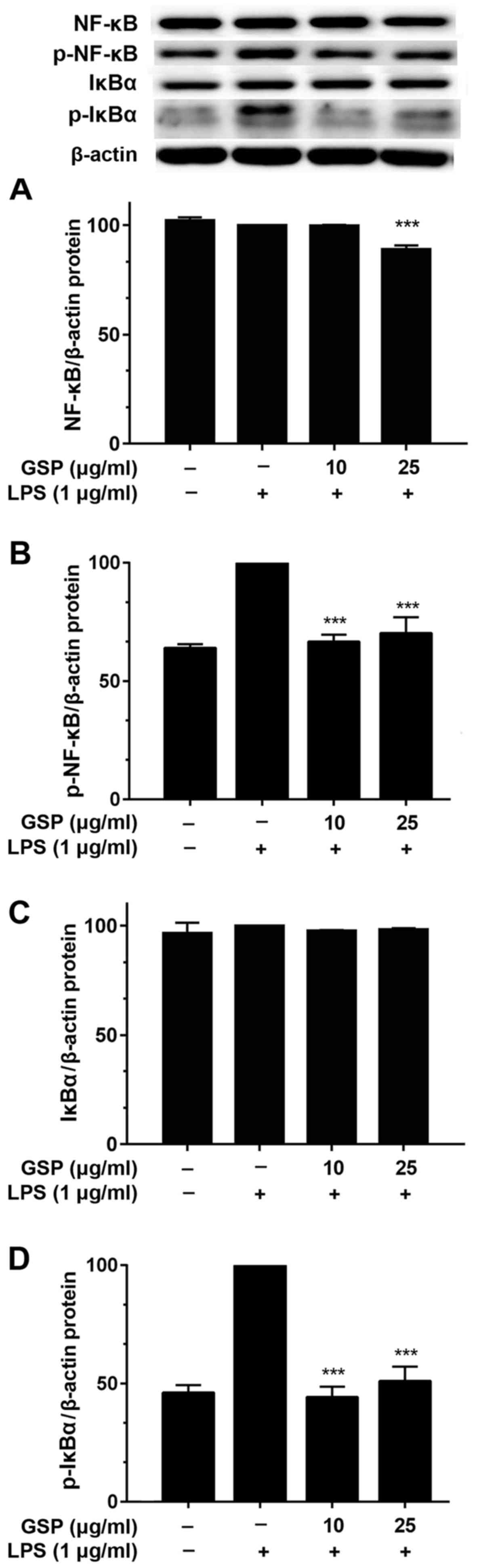
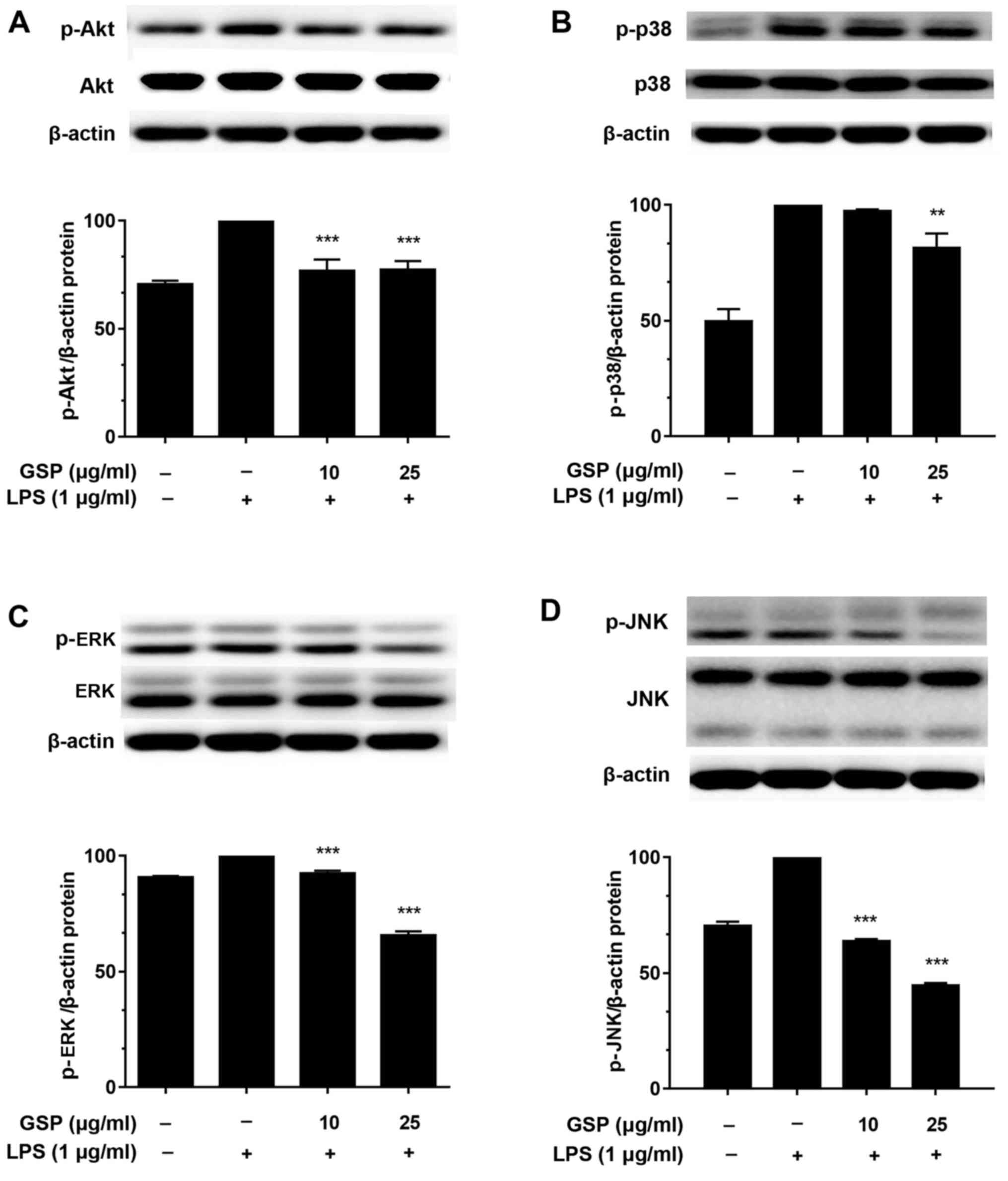
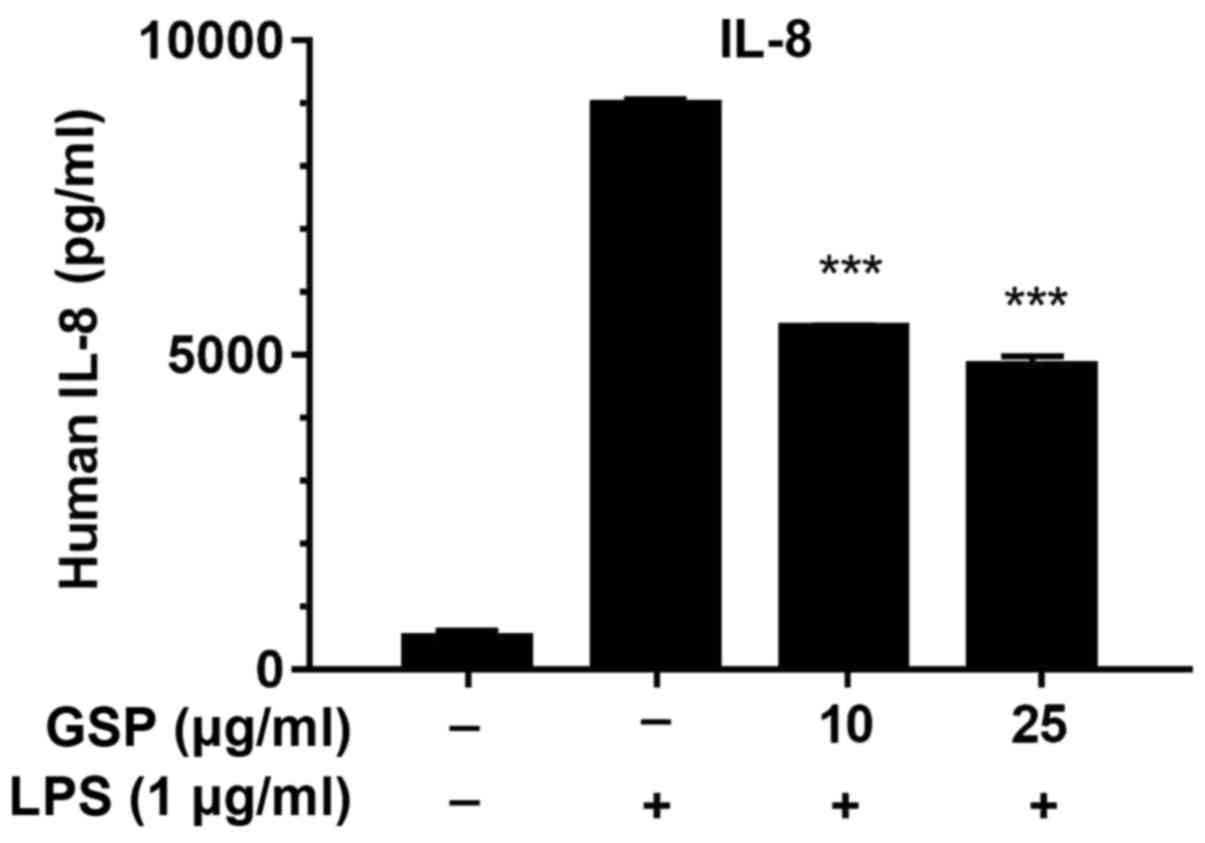
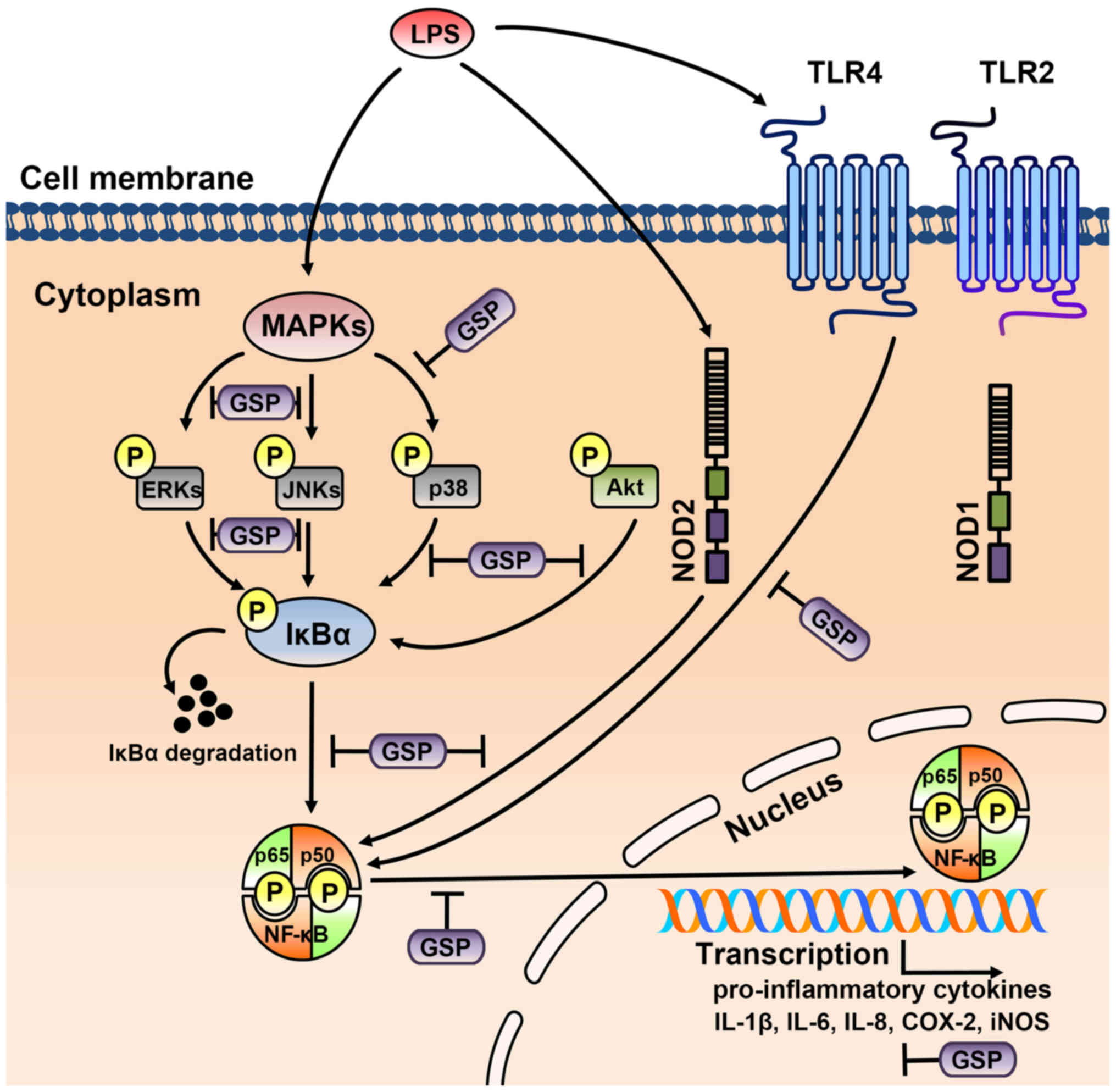
|
1
|
Bagchi D, Bagchi M, Stohs SJ, Das DK, Ray
SD, Kuszynski CA, Joshi SS and Pruess HG: Free radicals and grape
seed proanthocyanidin extract: Importance in human health and
disease prevention. Toxicology. 148:187–197. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Murphy KJ, Chronopoulos AK, Singh I,
Francis MA, Moriarty H, Pike MJ, Turner AH, Mann NJ and Sinclair
AJ: Dietary flavanols and procyanidin oligomers from cocoa
(Theobroma cacao) inhibit platelet function. Am J Clin Nutr.
77:1466–1473. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Steinberg FM, Bearden MM and Keen CL:
Cocoa and chocolate flavonoids: Implications for cardiovascular
health. J Am Diet Assoc. 103:215–223. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Maffei Facinó R, Carini M, Aldini G, Berti
F, Rossoni G, Bombardelli E and Morazzoni P: Procyanidines from
Vitis vinifera seeds protect rabbit heart from ischemia/reperfusion
injury: Antioxidant intervention and/or iron and copper
sequestering ability. Planta Med. 62:495–502. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
De Bruyne T, Pieters L, Witvrouw M, De
Clercq E, Vanden Berghe D and Vlietinck AJ: Biological evaluation
of proanthocyanidin dimers and related polyphenols. J Nat Prod.
62:954–958. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ye X, Krohn RL, Liu W, Joshi SS, Kuszynski
CA, McGinn TR, Bagchi M, Preuss HG, Stohs SJ and Bagchi D: The
cytotoxic effects of a novel IH636 grape seed proanthocyanidin
extract on cultured human cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem.
196:99–108. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li WG, Zhang XY, Wu YJ and Tian X:
Anti-inflammatory effect and mechanism of proanthocyanidins from
grape seeds. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 22:1117–1120. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ray S, Bagchi D, Lim PM, Bagchi M, Gross
SM, Kothari SC, Preuss HG and Stohs SJ: Acute and long-term safety
evaluation of a novel IH636 grape seed proanthocyanidin extract.
Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol. 109:165–197. 2001.
|
|
9
|
Seki E and Schwabe RF: Hepatic
inflammation and fibrosis: Functional links and key pathways.
Hepatology. 61:1066–1079. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Iredale JP: Hepatic stellate cell behavior
during resolution of liver injury. Semin Liver Dis. 21:427–436.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang BB, Cheng JY, Gao HH, Zhang Y, Chen
ZN and Bian H: Hepatic stellate cells in
inflammation-fibrosis-carcinoma axis. Anat Rec (Hoboken).
293:1492–1496. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Xu L, Hui AY, Albanis E, Arthur MJ,
O'Byrne SM, Blaner WS, Mukherjee P, Friedman SL and Eng FJ: Human
hepatic stellate cell lines, LX-1 and LX-2: New tools for analysis
of hepatic fibrosis. Gut. 54:142–151. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Henderson NC and Iredale JP: Liver
fibrosis: Cellular mechanisms of progression and resolution. Clin
Sci (Lond). 112:265–280. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yi HS and Jeong WI: Interaction of hepatic
stellate cells with diverse types of immune cells: Foe or friend? J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 28(Suppl 1): 99–104. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fallowfield JA: Therapeutic targets in
liver fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
300:G709–G715. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Duval F, Moreno-Cuevas JE, González-Garza
MT, Maldonado-Bernal C and Cruz-Vega DE: Liver fibrosis and
mechanisms of the protective action of medicinal plants targeting
inflammation and the immune response. Int J Inflamm.
2015:9434972015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Moon JE, Kim DM and Kim JY:
Anti-inflammatory effect of Rhus verniciflua stokes extract in the
murine macrophage cell line, Raw264.7. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem.
58:481–486. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Piccinini AM and Midwood KS: DAMPening
inflammation by modulating TLR signaling. Mediators Inflamm.
21:20102010.
|
|
19
|
Gabetta B, Fuzzati N, Griffini A, Lolla E,
Pace R, Ruffilli T and Peterlongo F: Characterization of
proanthocyanidins from grape seeds. Fitoterapia. 71:162–175. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mosmann T: Rapid colorimetric assay for
cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and
cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 65:55–63. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Seki E, De Minicis S, Osterreicher CH,
Kluwe J, Osawa Y, Brenner DA and Schwabe RF: TLR4 enhances TGF-beta
signaling and hepatic fibrosis. Nat Med. 13:1324–1332. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hambleton J, Weinstein SL, Lem L and
DeFranco AL: Activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in bacterial
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
93:2774–2778. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hellerbrand C, Wang SC, Tsukamoto H,
Brenner DA and Rippe RA: Expression of intracellular adhesion
molecule 1 by activated hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology.
24:670–676. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kayano K and Okita K: Does IL-6 regulate
liver fibrosis/cirrhosis directly and indirectly? J Gastroenterol.
35:250–251. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Czaja MJ, Geerts A, Xu J, Schmiedeberg P
and Ju Y: Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) expression
occurs in toxic rat liver injury and human liver disease. J Leukoc
Biol. 55:120–126. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Maher JJ, Lozier JS and Scott MK: Rat
hepatic stellate cells produce cytokine-induced neutrophil
chemoattractant in culture and in vivo. Am J Physiol.
275:G847–G853. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Reitamo S, Remitz A, Tamai K and Uitto J:
Interleukin-10 modulates type I collagen and matrix metalloprotease
gene expression in cultured human skin fibroblasts. J Clin Invest.
94:2489–2492. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Underhill DM and Ozinsky A: Toll-like
receptors: Key mediators of microbe detection. Curr Opin Immunol.
14:103–110. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Inohara N and Nuñez G: NODs: Intracellular
proteins involved in inflammation and apoptosis. Nat Rev Immunol.
3:371–382. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee MS and Kim YJ: Signaling pathways
downstream of pattern-recognition receptors and their cross talk.
Annu Rev Biochem. 76:447–480. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Surh YJ, Chun KS, Cha HH, Han SS, Keum YS,
Park KK and Lee SS: Molecular mechanisms underlying chemopreventive
activities of anti-inflammatory phytochemicals: Down-regulation of
COX-2 and iNOS through suppression of NF-kappa B activation. Mutat
Res. 480–481:243–268. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Uto T, Suangkaew N, Morinaga O, Kariyazono
H, Oiso S and Shoyama Y: Eriobotryae folium extract suppresses
LPS-induced iNOS and COX-2 expression by inhibition of NF-kappaB
and MAPK activation in murine macrophages. Am J Chin Med.
38:985–994. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Schabbauer G, Tencati M, Pedersen B,
Pawlinski R and Mackman N: PI3K-Akt pathway suppresses coagulation
and inflammation in endotoxemic mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 24:1963–1969. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|