|
1
|
Adeoye O, Hornung R, Khatri P and
Kleindorfer D: Recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator use
for ischemic stroke in the United States: A doubling of treatment
rates over the course of 5 years. Stroke. 42:1952–1955. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Manzanero S, Santro T and Arumugam TV:
Neuronal oxidative stress in acute ischemic stroke: Sources and
contribution to cell injury. Neurochem Int. 62:712–718. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sierra C, Coca A and Schiffrin EL:
Vascular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of stroke. Curr Hypertens
Rep. 13:200–207. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xin Q, Ji B, Cheng B, Wang C, Liu H, Chen
X, Chen J and Bai B: Endoplasmic reticulum stress in cerebral
ischemia. Neurochem Int. 68:18–27. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
DeGracia DJ and Montie HL: Cerebral
ischemia and the unfolded protein response. J Neurochem. 91:1–8.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang CH, Lee WJ, Ghanta VK, Wang WT, Cheng
SY and Hsueh CM: Molecules involve in the self-protection of
neurons against glucose-oxygen-serum deprivation (GOSD)-induced
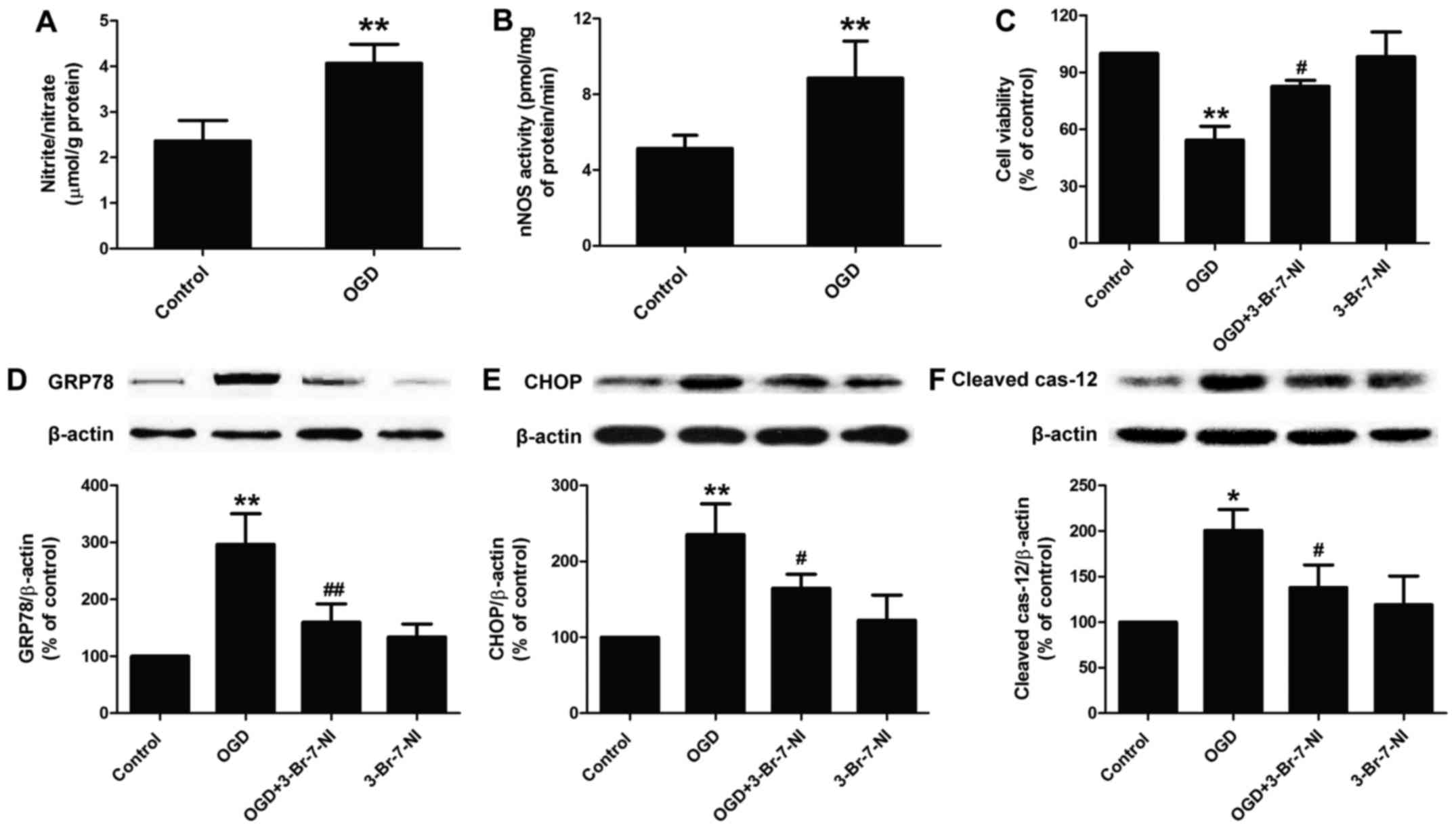
cell damage. Brain Res Bull. 79:169–176. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vincent SR: Nitric oxide: A radical
neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol.
42:129–160. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Garthwaite J, Charles SL and
Chess-Williams R: Endothelium-derived relaxing factor release on
activation of NMDA receptors suggests role as intercellular
messenger in the brain. Nature. 336:385–388. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qi SH, Hao LY, Yue J, Zong YY and Zhang
GY: Exogenous nitric oxide negatively regulates the S-nitrosylation
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation during cerebral
ischaemia and reperfusion. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 39:284–297.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Liu H, Li J, Zhao F, Wang H, Qu Y and Mu
D: Nitric oxide synthase in hypoxic or ischemic brain injury. Rev
Neurosci. 26:105–117. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Brown GC: Nitric oxide and neuronal death.
Nitric Oxide. 23:153–165. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tzatsos A and Tsichlis PN: Energy
depletion inhibits phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling and
induces apoptosis via AMP-activated protein kinase-dependent
phosphorylation of IRS-1 at Ser-794. J Biol Chem. 282:18069–18082.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li J and McCullough LD: Effects of
AMP-activated protein kinase in cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood
Flow Metab. 30:480–492. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Hardie DG and Frenguelli BG: A neural
protection racket: AMPK and the GABA(B) receptor. Neuron.
53:159–162. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Culmsee C, Monnig J, Kemp BE and Mattson
MP: AMP-activated protein kinase is highly expressed in neurons in
the developing rat brain and promotes neuronal survival following
glucose deprivation. J Mol Neurosci. 17:45–58. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kuramoto N, Wilkins ME, Fairfax BP,
Revilla-Sanchez R, Terunuma M, Tamaki K, Iemata M, Warren N, Couve
A, Calver A, et al: Phospho-dependent functional modulation of
GABA(B) receptors by the metabolic sensor AMP-dependent protein
kinase. Neuron. 53:233–247. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
McCullough LD, Zeng Z, Li H, Landree LE,
McFadden J and Ronnett GV: Pharmacological inhibition of
AMP-activated protein kinase provides neuroprotection in stroke. J
Biol Chem. 280:20493–20502. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Heales SJ, Bolaños JP, Stewart VC, Brookes
PS, Land JM and Clark JB: Nitric oxide, mitochondria and
neurological disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1410:215–228. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Stein A and Bailey SM: Redox biology of
hydrogen sulfide: Implications for physiology, pathophysiology, and
pharmacology. Redox Biol. 1:32–39. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang X and Bian JS: Hydrogen sulfide: A
neuromodulator and neuroprotectant in the central nervous system.
ACS Chem Neurosci. 5:876–883. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gheibi S, Aboutaleb N, Khaksari M,
Kalalian-Moghaddam H, Vakili A, Asadi Y, Mehrjerdi FZ and Gheibi A:
Hydrogen sulfide protects the brain against ischemic reperfusion
injury in a transient model of focal cerebral ischemia. J Mol
Neurosci. 54:264–270. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yin J, Tu C, Zhao J, Ou D, Chen G, Liu Y
and Xiao X: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide protects against global
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via its anti-oxidative,
anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects in rats. Brain Res.
1491:188–196. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Xie L, Tiong CX and Bian JS: Hydrogen
sulfide protects SH-SY5Y cells against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
303:C81–C91. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wei HJ, Xu JH, Li MH, Tang JP, Zou W,
Zhang P, Wang L, Wang CY and Tang XQ: Hydrogen sulfide inhibits
homocysteine-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and neuronal
apoptosis in rat hippocampus via upregulation of the BDNF-TrkB
pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 35:707–715. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yin W, Lan L, Huang Z, Ji J, Fang J, Wang
X, Ji H, Peng S, Xu J and Zhang Y: Discovery of a ring-opened
derivative of 3-n-butylphthalide bearing NO/H2S-donating
moieties as a potential anti-ischemic stroke agent. Eur J Med Chem.
115:369–380. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Morikawa T, Kajimura M, Nakamura T,
Hishiki T, Nakanishi T, Yukutake Y, Nagahata Y, Ishikawa M, Hattori
K, Takenouchi T, et al: Hypoxic regulation of the cerebral
microcirculation is mediated by a carbon monoxide-sensitive
hydrogen sulfide pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:1293–1298.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Taoka S and Banerjee R: Characterization
of NO binding to human cystathionine beta-synthase: Possible
implications of the effects of CO and NO binding to the human
enzyme. J Inorg Biochem. 87:245–251. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhao W, Zhang J, Lu Y and Wang R: The
vasorelaxant effect of H(2)S as a novel endogenous gaseous K(ATP)
channel opener. EMBO J. 20:6008–6016. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu HT and Mu DZ: Inducible nitric oxide
synthase and brain hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Zhongguo Dang dai
er ke za zhi. 16:962–967. 2014.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Moskowitz MA, Lo EH and Iadecola C: The
science of stroke: Mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron.
67:181–198. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bai X, Liu S, Yuan L, Xie Y, Li T, Wang L,
Wang X, Zhang T, Qin S, Song G, et al: Hydrogen-rich saline
mediates neuroprotection through the regulation of endoplasmic
reticulum stress and autophagy under hypoxia-ischemia neonatal
brain injury in mice. Brain Res. 1646:410–417. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cao G, Zhou H, Jiang N, Han Y, Hu Y, Zhang
Y, Qi J, Kou J and Yu B: YiQiFuMai powder injection ameliorates
cerebral ischemia by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum
stress-mediated neuronal apoptosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016:54932792016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Osada N, Kosuge Y, Ishige K and Ito Y:
Characterization of neuronal and astroglial responses to ER stress
in the hippocampal CA1 area in mice following transient forebrain
ischemia. Neurochem Int. 57:1–7. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Herrmann AG, Deighton RF, Le Bihan T,
McCulloch MC, Searcy JL, Kerr LE and McCulloch J: Adaptive changes
in the neuronal proteome: Mitochondrial energy production,
endoplasmic reticulum stress, and ribosomal dysfunction in the
cellular response to metabolic stress. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
33:673–683. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Edelman GM and Gally JA: Nitric oxide:
Linking space and time in the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
89:11651–11652. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lu Q, Harris VA, Rafikov R, Sun X, Kumar S
and Black SM: Nitric oxide induces hypoxia ischemic injury in the
neonatal brain via the disruption of neuronal iron metabolism.
Redox Biol. 6:112–121. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pei DS, Song YJ, Yu HM, Hu WW, Du Y and
Zhang GY: Exogenous nitric oxide negatively regulates c-Jun
N-terminal kinase activation via inhibiting endogenous NO-induced
S-nitrosylation during cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in rat
hippocampus. J Neurochem. 106:1952–1963. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang Z, Huang PL, Ma J, Meng W, Ayata C,
Fishman MC and Moskowitz MA: Enlarged infarcts in endothelial
nitric oxide synthase knockout mice are attenuated by
nitro-L-arginine. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 16:981–987. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Huang Z, Huang PL, Panahian N, Dalkara T,
Fishman MC and Moskowitz MA: Effects of cerebral ischemia in mice
deficient in neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Science.
265:1883–1885. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ferriero DM, Holtzman DM, Black SM and
Sheldon RA: Neonatal mice lacking neuronal nitric oxide synthase
are less vulnerable to hypoxic-ischemic injury. Neurobiol Dis.
3:64–71. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nowicki JP, Duval D, Poignet H and Scatton
B: Nitric oxide mediates neuronal death after focal cerebral
ischemia in the mouse. Eur J Pharmacol. 204:339–340. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mohammadi MT, Shid Moosavi SM and Dehghani
GA: Contribution of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity in
blood-brain barrier disruption and edema after acute
ischemia/reperfusion in aortic coarctation-induced hypertensive
rats. Iran Biomed J. 15:22–30. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nadjafi S, Ebrahimi SA and
Rahbar-Roshandel N: Effect of berberine on nitric oxide production
during oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion in OLN-93
oligodendrocytes. Pak J Biol Sci. 17:1185–1189. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Srinivasan K and Sharma SS:
3-Bromo-7-nitroindazole attenuates brain ischemic injury in
diabetic stroke via inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress
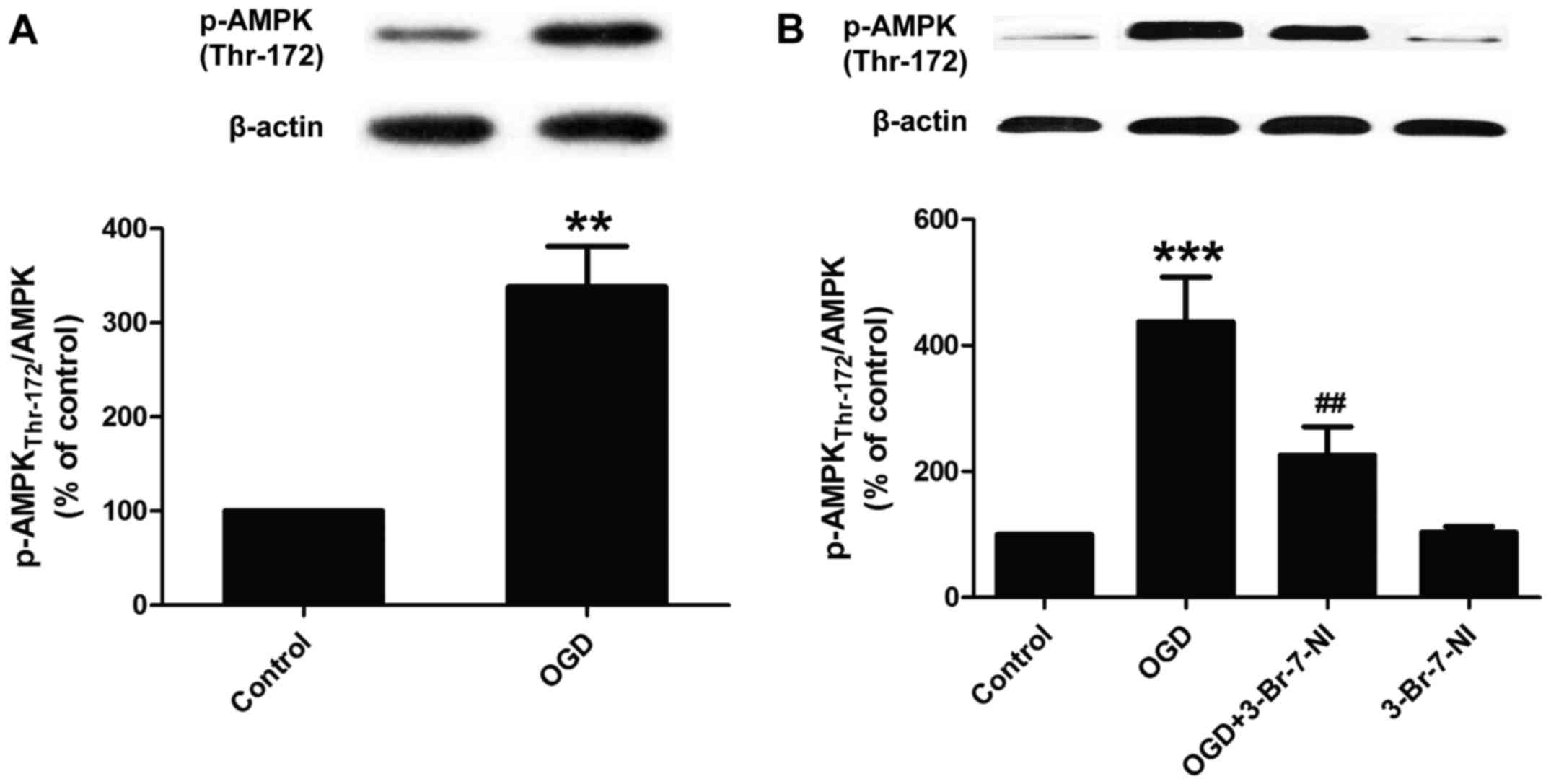
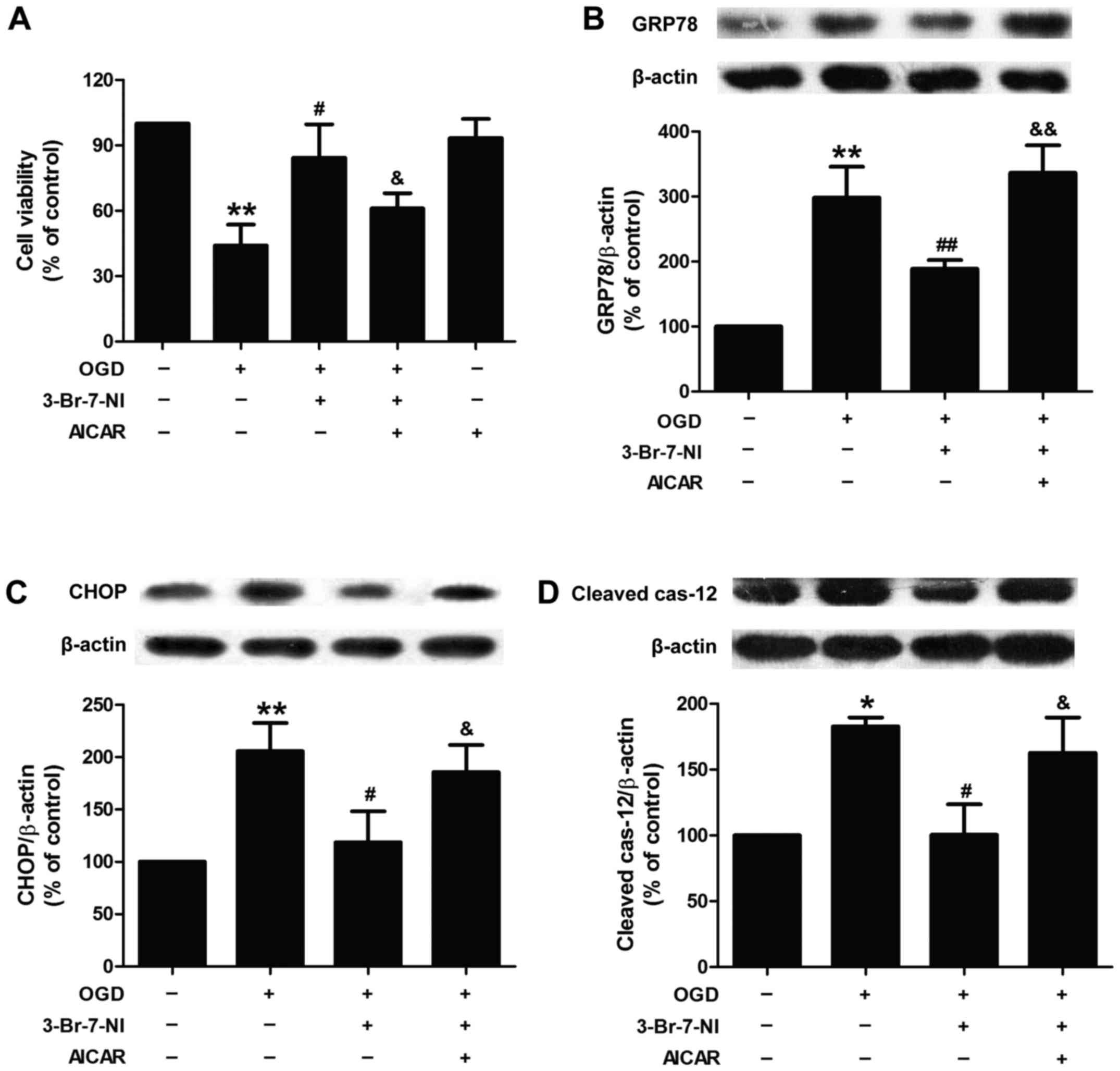
pathway involving CHOP. Life Sci. 90:154–160. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Gao G, Widmer J, Stapleton D, Teh T, Cox
T, Kemp BE and Witters LA: Catalytic subunits of the porcine and
rat 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase are members of the SNF1 protein
kinase family. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1266:73–82. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ramamurthy S and Ronnett GV: Developing a
head for energy sensing: AMP-activated protein kinase as a
multifunctional metabolic sensor in the brain. J Physiol.
574:85–93. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ji K, Xue L, Cheng J and Bai Y:
Preconditioning of H2S inha-lation protects against
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by induction of HSP70 through
PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway. Brain Res Bull. 121:68–74. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tan H, Zou W, Jiang J, Tian Y, Xiao Z, Bi
L, Zeng H and Tang X: Disturbance of hippocampal H2S
generation contributes to CUMS-induced depression-like behavior:
Involvement in endoplasmic reticulum stress of hippocampus. Acta
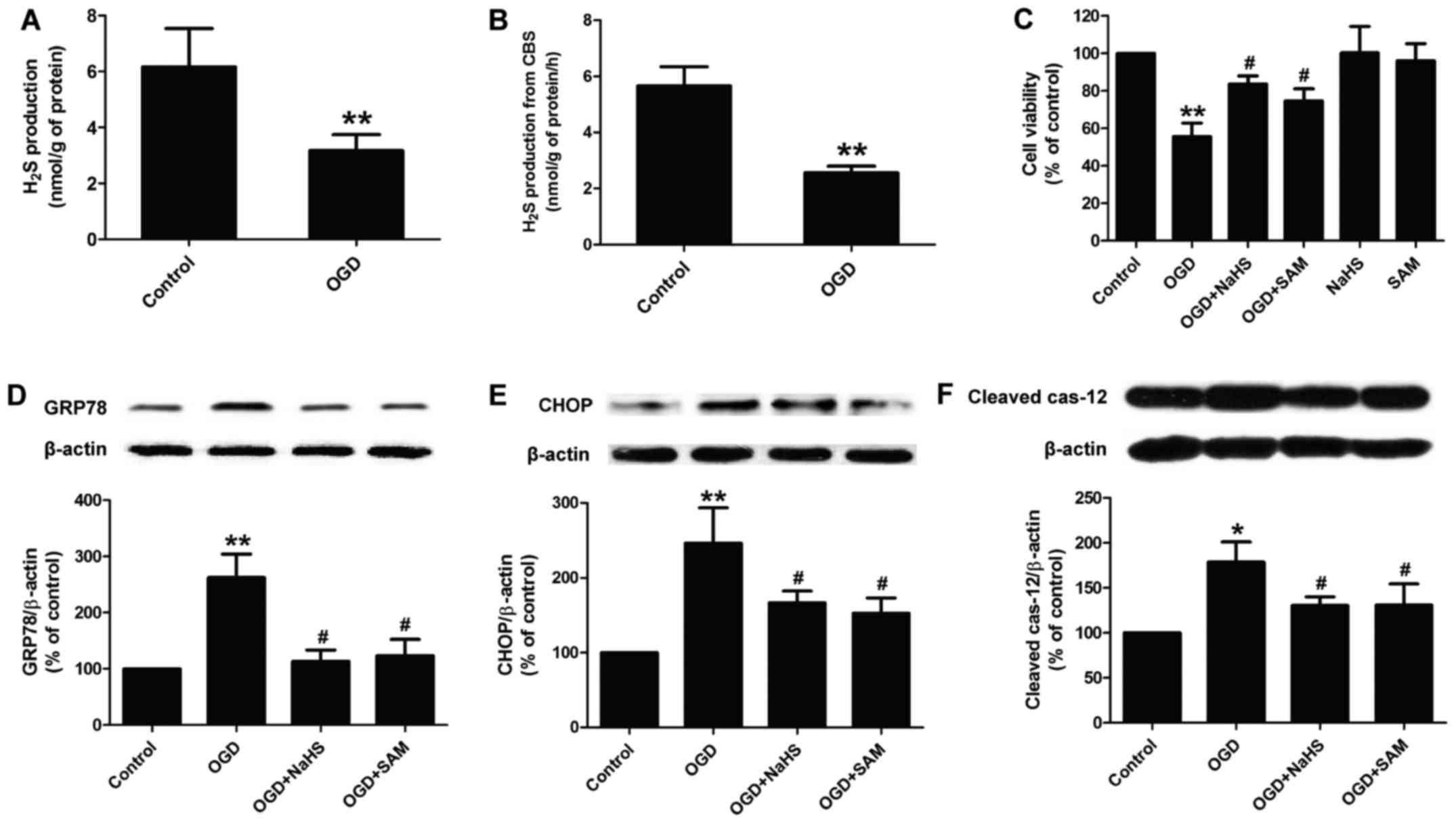
Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 47:285–291. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Shen Y, Shen Z, Miao L, Xin X, Lin S, Zhu
Y, Guo W and Zhu YZ: miRNA-30 family inhibition protects against
cardiac ischemic injury by regulating cystathionine-gamma-lyase
expression. Antioxid Redox Signal. 22:224–240. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
Chatzianastasiou A, Bibli SI, Andreadou I,
Efentakis P, Kaludercic N, Wood ME, Whiteman M, Di Lisa F, Daiber
A, Manolopoulos VG, et al: Cardioprotection by H2S
donors: Nitric oxide-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 358:431–440. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Duan XC, Liu SY, Guo R, Xiao L, Xue HM,
Guo Q, Jin S and Wu YM: Cystathionine-β-synthase gene transfer into
rostral ventrolateral medulla exacerbates hypertension via nitric
oxide in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Hypertens.
28:1106–1113. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Grossi L: Hydrogen sulfide induces nitric
oxide release from nitrite. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 19:6092–6094.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kubo S, Doe I, Kurokawa Y, Nishikawa H and
Kawabata A: Direct inhibition of endothelial nitric oxide synthase
by hydrogen sulfide: Contribution to dual modulation of vascular
tension. Toxicology. 232:138–146. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|