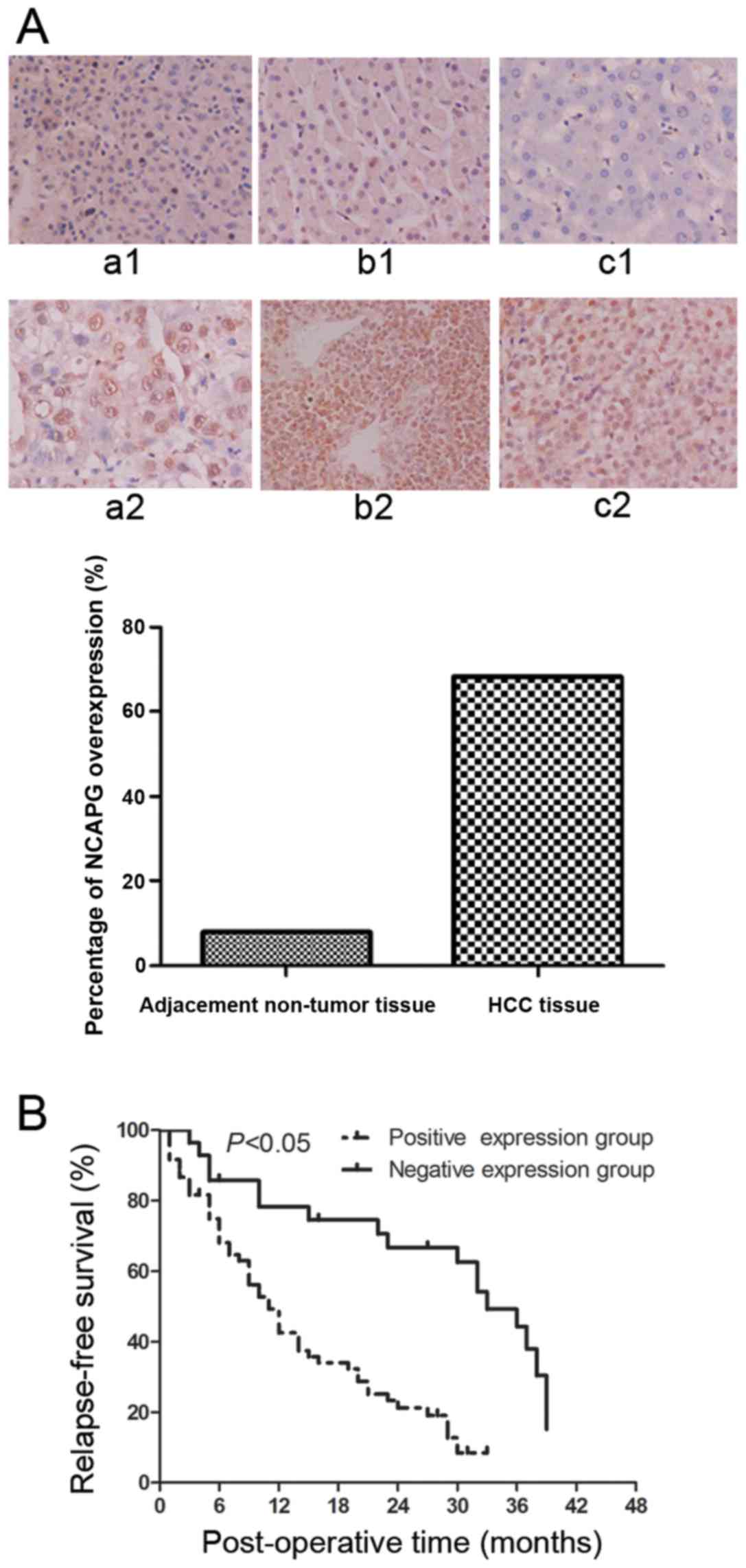
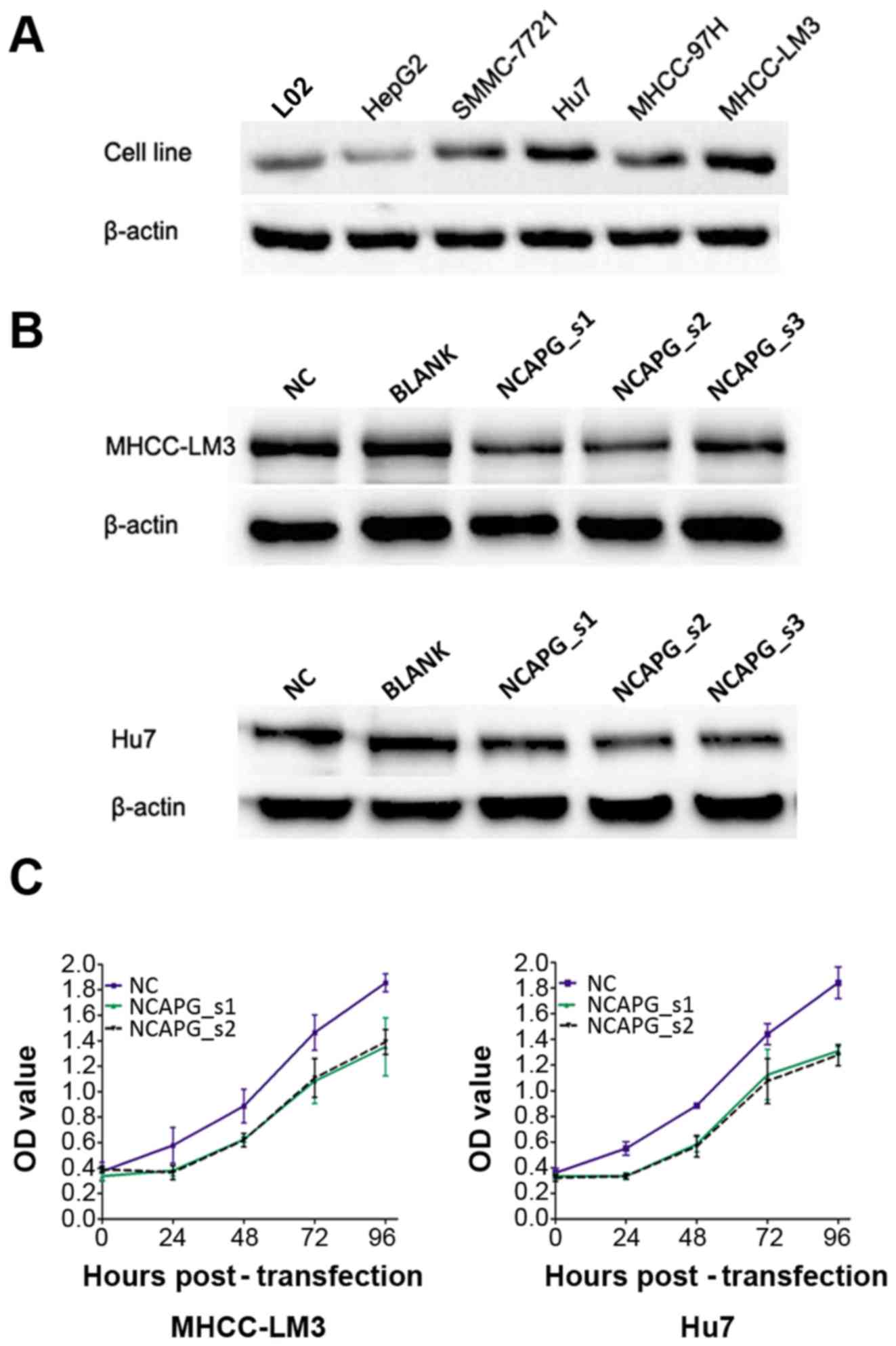
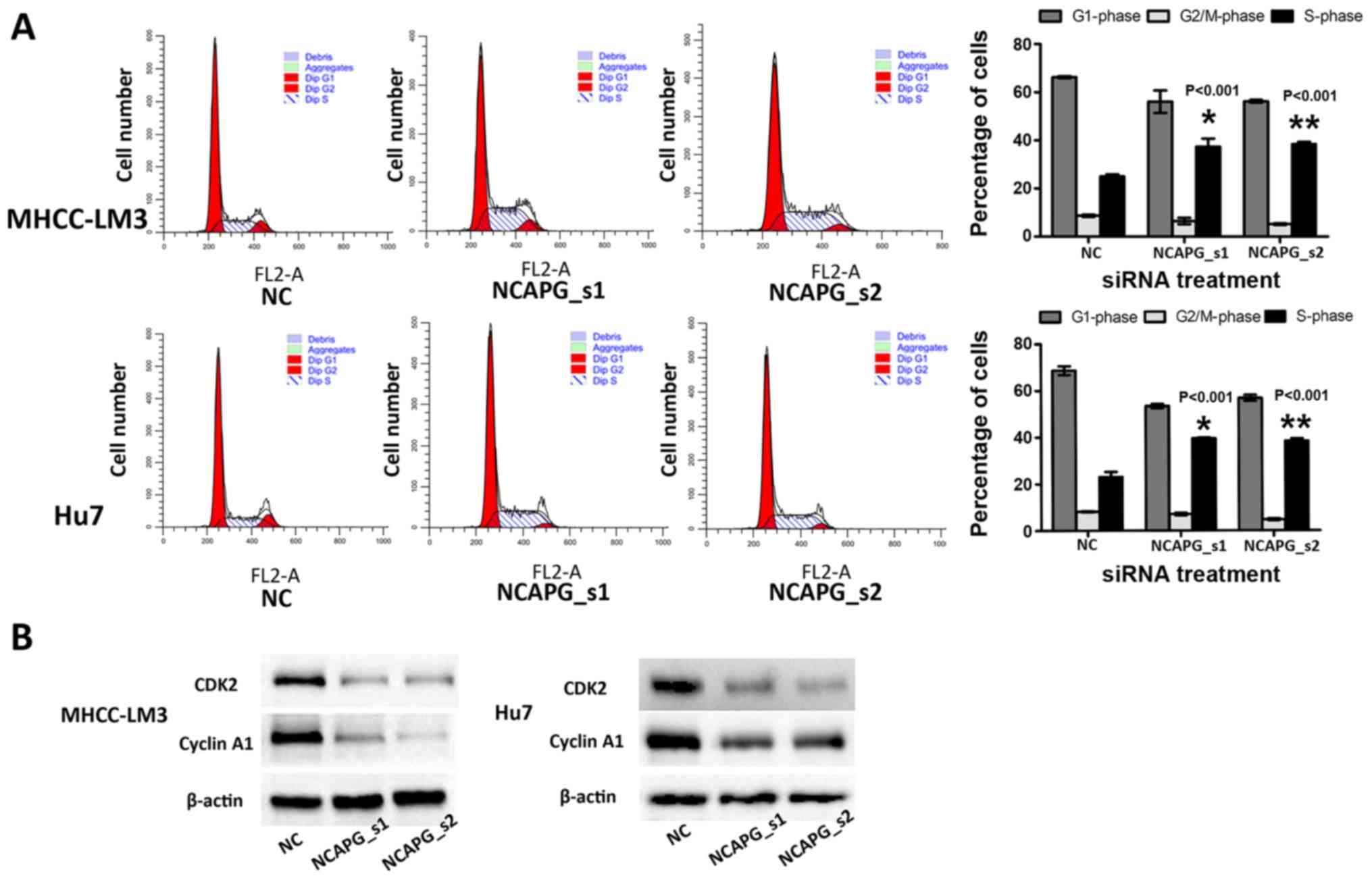
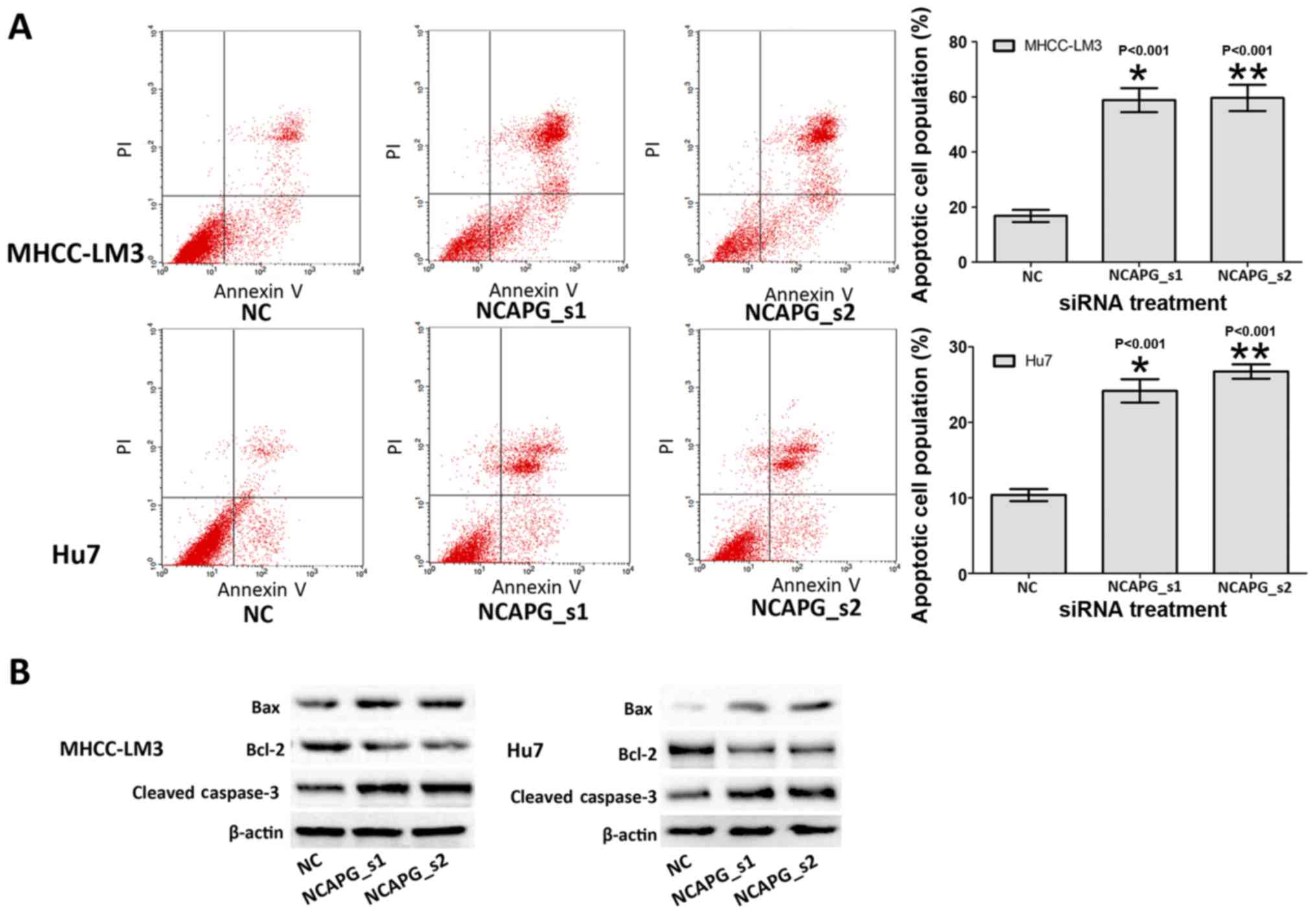
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Giordano S and Columbano A: Met as a
therapeutic target in HCC: Facts and hopes. J Hepatol. 60:442–452.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hirano T, Kobayashi R and Hirano M:
Condensins, chromosome condensation protein complexes containing
XCAP-C, XCAP-E and a Xenopus homolog of the Drosophila Barren
protein. Cell. 89:511–521. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gerlich D, Hirota T, Koch B, Peters JM,
Ellenberg J and Condensin I: Condensin I stabilizes chromosomes
mechanically through a dynamic interaction in live cells. Curr
Biol. 16:333–344. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kimura K, Cuvier O and Hirano T:
Chromosome condensation by a human condensin complex in Xenopus egg
extracts. J Biol Chem. 276:5417–5420. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Herzog S, Nagarkar Jaiswal S, Urban E,
Riemer A, Fischer S and Heidmann SK: Functional dissection of the
Drosophila melanogaster condensin subunit Cap-G reveals its
exclusive association with condensin I. PLoS Genet. 9:e10034632013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Seipold S, Priller FC, Goldsmith P, Harris
WA, Baier H and Abdelilah-Seyfried S: Non-SMC condensin I complex
proteins control chromosome segregation and survival of
proliferating cells in the zebrafish neural retina. BMC Dev Biol.
9:402009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hirano T: At the heart of the chromosome:
SMC proteins in action. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:311–322. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hirano T: Condensins: Organizing and
segregating the genome. Curr Biol. 15:R265–R275. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Eberlein A, Takasuga A, Setoguchi K, Pfuhl
R, Flisikowski K, Fries R, Klopp N, Fürbass R, Weikard R and Kühn
C: Dissection of genetic factors modulating fetal growth in cattle
indicates a substantial role of the non-SMC condensin I complex,
subunit G (NCAPG) gene. Genetics. 183:951–964. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jäger D, Stockert E, Jäger E, Güre AO,
Scanlan MJ, Knuth A, Old LJ and Chen YT: Serological cloning of a
melanocyte rab guanosine 5′-triphosphate-binding protein and a
chromosome condensation protein from a melanoma complementary DNA
library. Cancer Res. 60:3584–3591. 2000.
|
|
12
|
Lam WW, Peterson EA, Yeung M and Lavoie
BD: Condensin is required for chromosome arm cohesion during
mitosis. Genes Dev. 20:2973–2984. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Satow R, Shitashige M, Kanai Y, Takeshita
F, Ojima H, Jigami T, Honda K, Kosuge T, Ochiya T, Hirohashi S, et
al: Combined functional genome survey of therapeutic targets for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2518–2528. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wheeler LW, Lents NH and Baldassare JJ:
Cyclin A-CDK activity during G1 phase impairs MCM chromatin loading
and inhibits DNA synthesis in mammalian cells. Cell Cycle.
7:2179–2188. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fotedar A, Cannella D, Fitzgerald P,
Rousselle T, Gupta S, Dorée M and Fotedar R: Role for cyclin
A-dependent kinase in DNA replication in human S phase cell
extracts. J Biol Chem. 271:31627–31637. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ogryzko VV, Wong P and Howard BH: WAF1
retards S-phase progression primarily by inhibition of
cyclin-dependent kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 17:4877–4882. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ishimi Y, Komamura-Kohno Y, You Z, Omori A
and Kitagawa M: Inhibition of Mcm4,6,7 helicase activity by
phosphorylation with cyclin A/Cdk2. J Biol Chem. 275:16235–16241.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Song X, Li L, Shi Q, Lehmler HJ, Fu J, Su
C, Xia X, Song E and Song Y: Polychlorinated biphenyl quinone
metabolite promotes p53-dependent DNA damage checkpoint activation,
S Phase cycle arrest and extrinsic apoptosis in human liver
hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Chem Res Toxicol.
28:2160–2169. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sever-Chroneos Z, Angus SP, Fribourg AF,
Wan H, Todorov I, Knudsen KE and Knudsen ES: Retinoblastoma tumor
suppressor protein signals through inhibition of cyclin-dependent
kinase 2 activity to disrupt PCNA function in S phase. Mol Cell
Biol. 21:4032–4045. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nguyen DX, Chiang AC, Zhang XH, Kim JY,
Kris MG, Ladanyi M, Gerald WL and Massagué J: WNT/TCF signaling
through LEF1 and HOXB9 mediates lung adenocarcinoma metastasis.
Cell. 138:51–62. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hayashida T, Takahashi F, Chiba N,
Brachtel E, Takahashi M, Godin-Heymann N, Gross KW, Vivanco M,
Wijendran V, Shioda T, et al: HOXB9, a gene overexpressed in breast
cancer, promotes tumorigenicity and lung metastasis. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 107:1100–1105. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yuan R, Wang K, Hu J, Yan C, Li M, Yu X,
Liu X, Lei J, Guo W, Wu L, et al: Ubiquitin-like protein FAT10
promotes the invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by
modifying β-catenin degradation. Cancer Res. 74:5287–5300. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chiba N, Comaills V, Shiotani B, Takahashi
F, Shimada T, Tajima K, Winokur D, Hayashida T, Willers H, Brachtel
E, et al: Homeobox B9 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition-associated radioresistance by accelerating DNA damage
responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:2760–2765. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Sha L, Dong L, Lv L, Bai L and Ji X: HOXB9
promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via transforming
growth factor-β1 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Clin
Exp Med. 15:55–64. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|